Water has been showing up in all sorts of unexpected places in our Solar System, such as the Moon, Mercury and Jupiter’s moon Ganymede. Add one more place to the list: Asteroid 16 Psyche. This metal-rich asteroid may have traces of water molecules on its surface that shouldn’t be there, researchers say.
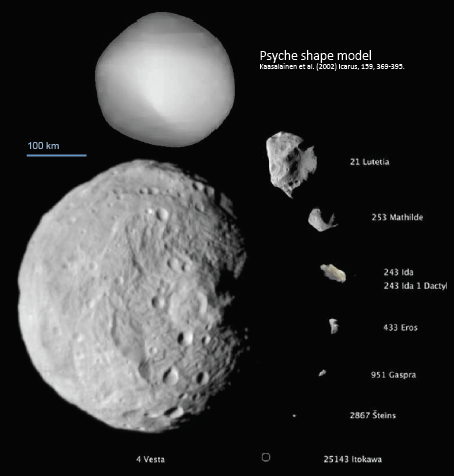
Psyche is thought to be the largest metallic asteroid in the Solar System, at 300 km (186 miles) across and likely consists of almost pure nickel-iron metal. Scientists had thought Psyche was made up of the leftover core of a protoplanet that was mostly destroyed by impacts billions of years ago, but they may now be rethinking that.
“The detection of a 3 micron hydration absorption band on Psyche suggests that this asteroid may not be metallic core, or it could be a metallic core that has been impacted by carbonaceous material over the past 4.5 Gyr,” the team said in their paper.
While previous observations of Psyche had shown no evidence for water on its surface, new observations with the NASA Infrared Telescope Facility found evidence for volatiles such as water or hydroxyl on the asteroid’s surface. Hydroxyl is a free radical consisting of one hydrogen atom bound to one oxygen atom.
“We did not expect a metallic asteroid like Psyche to be covered by water and/or hydroxyl,” said Vishnu Reddy, from the University of Arizona’s Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, a co-author of the new paper about Psyche. “Metal-rich asteroids like Psyche are thought to have formed under dry conditions without the presence of water or hydroxyl, so we were puzzled by our observations at first.”
Asteroids usually fall into two categories: those rich in silicates, and those rich in carbon and volatiles. Metallic asteroids like Psyche are extremely rare, making it a laboratory to study how planets formed.

For now, the source of the water on Psyche remains a mystery. But Redddy and his colleagues propose a few different explanations. One is, again, Psyche may not be as metallic as previously thought. Another option is that the water or hydroxyl could be the product of solar wind interacting with silicate minerals on Psyche’s surface, such as what is occurring on the Moon.
The most likely explanation, however is that the water seen on Psyche might have been delivered by carbonaceous asteroids that impacted Psyche in the distant past, as is thought to have occurred on early Earth.
“Our discovery of carbon and water on an asteroid that isn’t supposed to have those compounds supports the notion that these building blocks of life could have been delivered to our Earth early in the history of our solar system,” said Reddy.
If we’re lucky, we won’t have to wait too long to find out more about Psyche. A mission to Psyche is on the short list of mission proposals being considered by NASA, with a potential launch as early as 2020. Reddy and team said an orbiting spacecraft could explore this unique asteroid and determine if whether there is water or hydroxyl on the surface.
Sources: Europlanet, University of Arizona, paper: Detection of Water and/or Hydroxyl on Asteroid (16) Psyche.