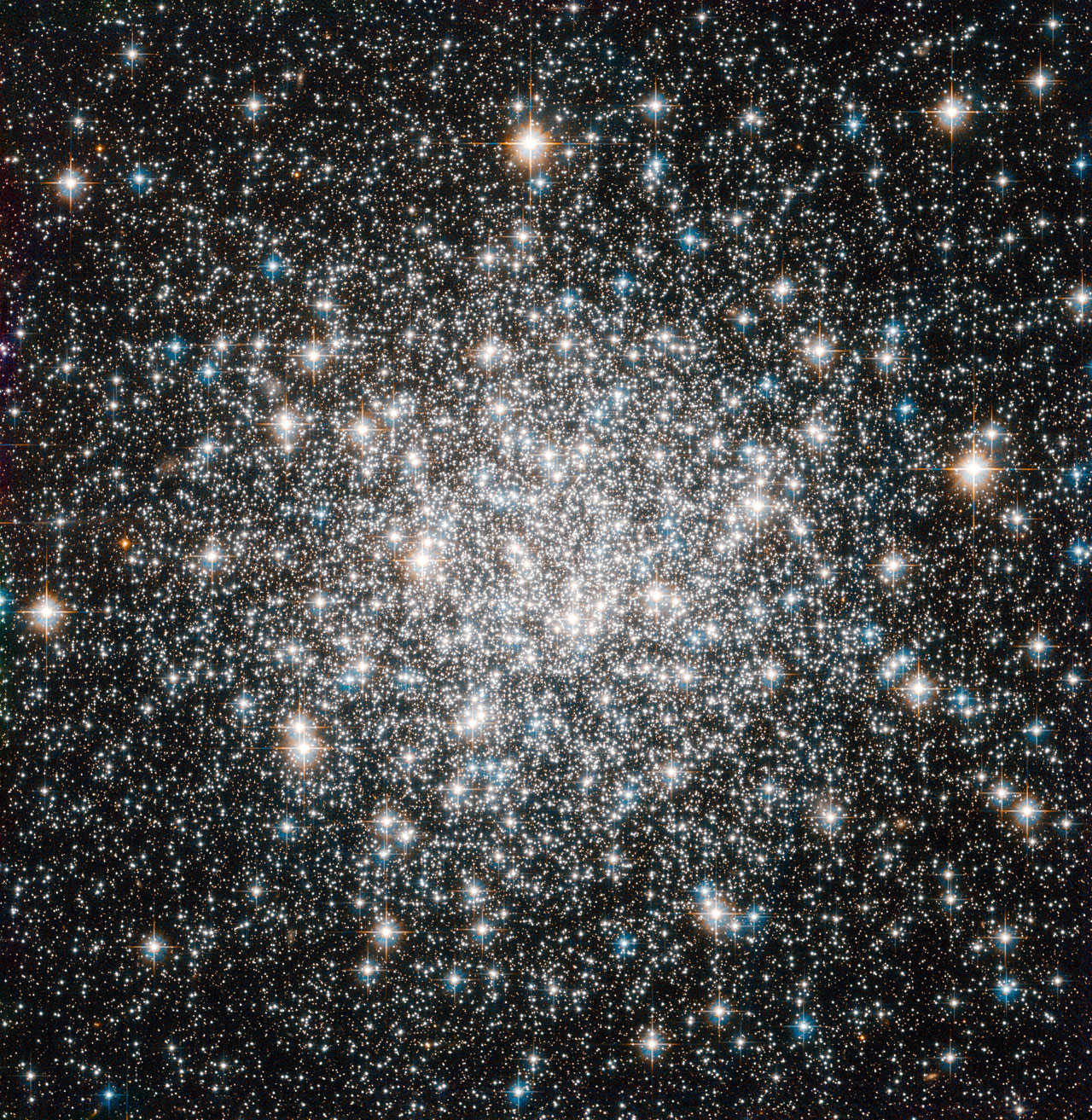
It’s relatively easy for galaxies to make stars. Start out with a bunch of random blobs of gas and dust. Typically those blobs will be pretty warm. To turn them into stars, you have to cool them off. By dumping all their heat in the form of radiation, they can compress. Dump more heat, compress more. Repeat for a million years or so.
Eventually pieces of the gas cloud shrink and shrink, compressing themselves into a tight little knots. If the densities inside those knots get high enough, they trigger nuclear fusion and voila: stars are born.
Continue reading “New Research Reveals How Galaxies Stay Hot and Bothered”




![This illustration shows the percentage of marine animals that went extinct during Earth's worst extinction at the end of the Permian era by latitude, from the model (black line) and from the fossil record (blue dots).A greater percentage of marine animals survived in the tropics than at the poles. The color of the water shows the temperature change, with red being most severe warming and yellow less warming. At the top is the supercontinent Pangaea, with massive volcanic eruptions emitting carbon dioxide. The images below the line represent some of the 96 percent of marine species that died during the event. [Includes fossil drawings by Ernst Haeckel/Wikimedia; Blue crab photo by Wendy Kaveney/Flickr; Atlantic cod photo by Hans-Petter Fjeld/Wikimedia; Chambered nautilus photo by John White/CalPhotos.]Justin Penn and Curtis Deutsch/University of Washington](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/Penn_sumfig_final.jpg)