Subsurface oceans of liquid water are a common feature of the moon’s of Jupiter and Saturn. Researchers are exploring whether the icy moons of Uranus and Neptune might have them as well. Their new paper suggests future missions to the outer Solar System could measure the rotation of the moons and detect any wobbles pointing to liquid oceans. Less wobble means the moons is mostly solid but large wobbles can indicate ice floating on an ocean of liquid.
Continue reading “Uranus’s Wobbling Moons Could Point to Oceans Under the Ice”The Search for Exomoons is On

Moons are the norm in our Solar System. The International Astronomical Union recognizes 288 planetary moons, and more keep being discovered. Saturn has a whopping 146 moons. Every planet except Mercury and Venus has moons, and their lack of moons is attributed to their small size and proximity to the Sun.
It seems reasonable that there are moons around exoplanets in other Solar Systems, and now we’re going to start looking for them with the James Webb Space Telescope.
Continue reading “The Search for Exomoons is On”A Stellar Flyby Jumbled Up the Outer Solar System

An ancient passerby may have visited the Sun and inadvertently helped shape the Solar System into what it is today. It happened billions of years ago when a stellar drifter came to within 110 astronomical units (AU) of our Sun. The effects were long-lasting and we can see evidence of the visitor’s fleeting encounter throughout the Solar System.
Continue reading “A Stellar Flyby Jumbled Up the Outer Solar System”Comparing Two Proposed NASA Missions to Jupiter’s Moon Io

Thanks to NASA’s Juno mission to the Jupiter system, we’re getting our best looks ever at the gas giant’s volcanic moon Io. Even as Juno provides our best views of the moon, it also deepens our existing questions. Only a dedicated mission to Io can answer those questions, and there are two proposed missions.
Continue reading “Comparing Two Proposed NASA Missions to Jupiter’s Moon Io”If We Want To Find Life-Supporting Worlds, We Should Focus on Small Planets With Large Moons

There’s no perfect way of doing anything, including searching for exoplanets. Every planet-hunting method has some type of bias. We’ve found most exoplanets using the transit method, which is biased toward larger planets. Larger planets closer to their stars block more light, meaning we detect large planets transiting in front of their stars more readily than we detect small ones.
That’s a problem because some research says that life-supporting planets are more likely to be small, like Earth. It’s all because of moons and streaming instability.
Continue reading “If We Want To Find Life-Supporting Worlds, We Should Focus on Small Planets With Large Moons”How Mars’ Moon Phobos Captures Our Imaginations

For a small, lumpy chunk of rock that barely reflects any light, Mars’ Moon Phobos draws a lot of attention. Maybe because it’s one of only two moons to orbit the planet, and its origins are unclear. But some of the attention is probably because we have such great images of it.
Continue reading “How Mars’ Moon Phobos Captures Our Imaginations”Are Titan's Dunes Made of Comet Dust?
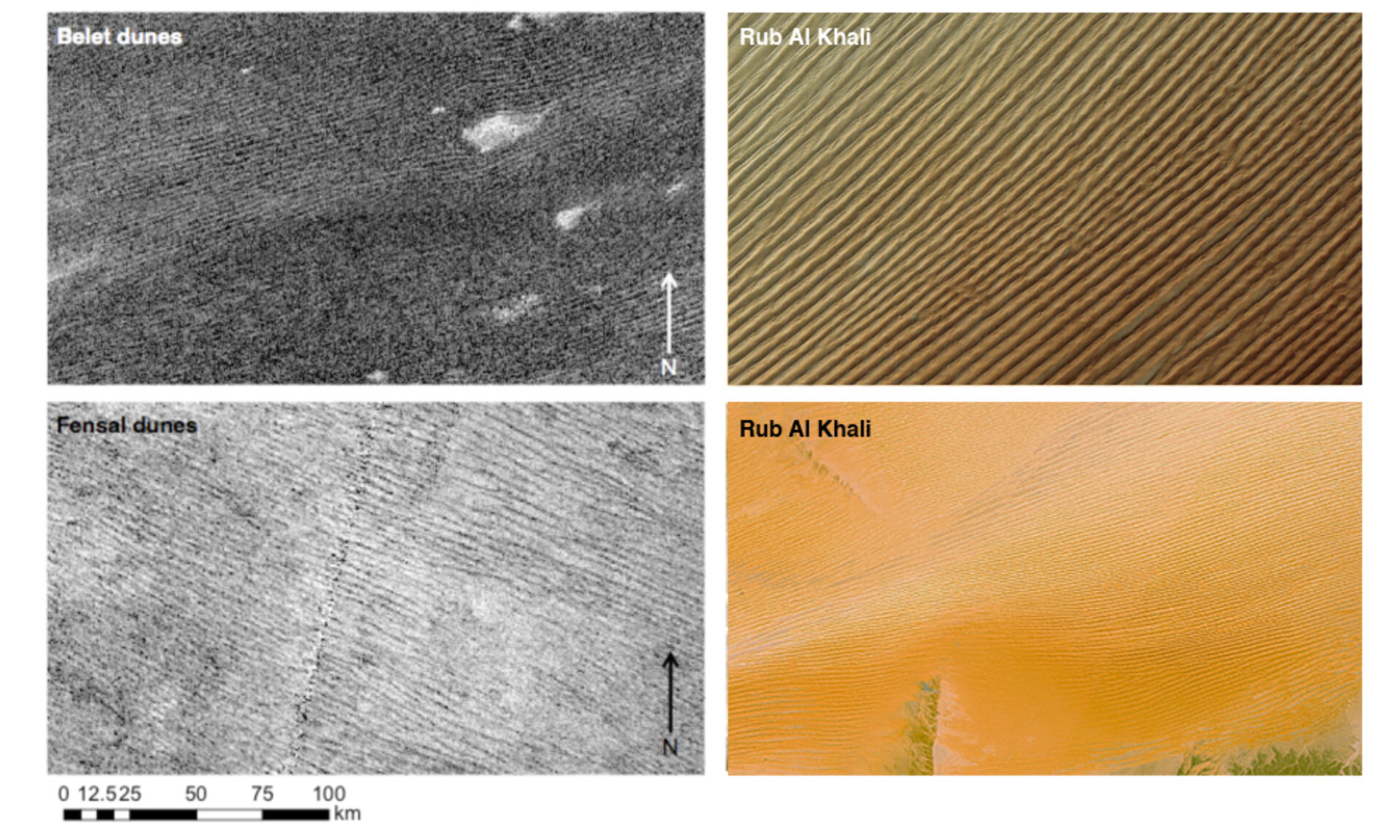
A new theory suggests that Titan’s majestic dune fields may have come from outer space. Researchers had always assumed that the sand making up Titan’s dunes was locally made, through erosion or condensed from atmospheric hydrocarbons. But researchers from the University of Colorado want to know: Could it have come from comets?
Continue reading “Are Titan's Dunes Made of Comet Dust?”Did An Ancient Icy Impactor Create the Martian Moons?

The Martian moons Phobos and Deimos are oddballs. While other Solar System moons are round, Mars’ moons are misshapen and lumpy like potatoes. They’re more like asteroids or other small bodies than moons.
Because of their odd shapes and unusual compositions, scientists are still puzzling over their origins.
Continue reading “Did An Ancient Icy Impactor Create the Martian Moons?”A Single Grain of Ice Could Hold Evidence of Life on Europa and Enceladus
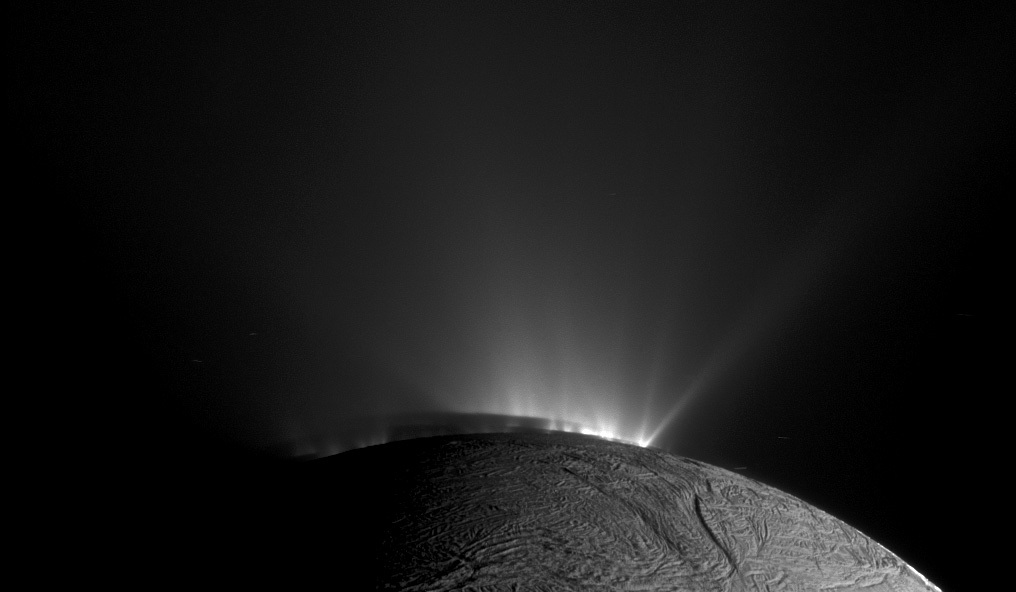

The Solar System’s icy ocean moons are primary targets in our search for life. Missions to Europa and Enceladus will explore these moons from orbit, improving our understanding of them and their potential to support life. Both worlds emit plumes of water from their internal oceans, and the spacecraft sent to both worlds will examine those plumes and even sample them.
New research suggests that evidence of life in the moons’ oceans could be present in just a single grain of ice, and our spacecraft can detect it.
Continue reading “A Single Grain of Ice Could Hold Evidence of Life on Europa and Enceladus”Europe Has Big Plans for Saturn’s Moon Enceladus
Saturn’s moon, Enceladus, is a gleaming beacon that captivates our intellectual curiosity. Its clean, icy surface makes it one of the most reflective objects in the entire Solar System. But it’s what’s below that ice that really gets scientists excited.
Under its icy shell is an ocean of warm, salty water, and the ESA says investigating the moon should be a top priority.
Continue reading “Europe Has Big Plans for Saturn’s Moon Enceladus”

