[/caption]
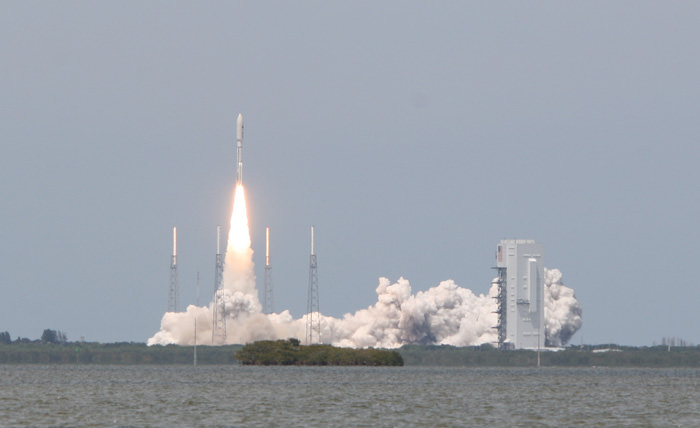
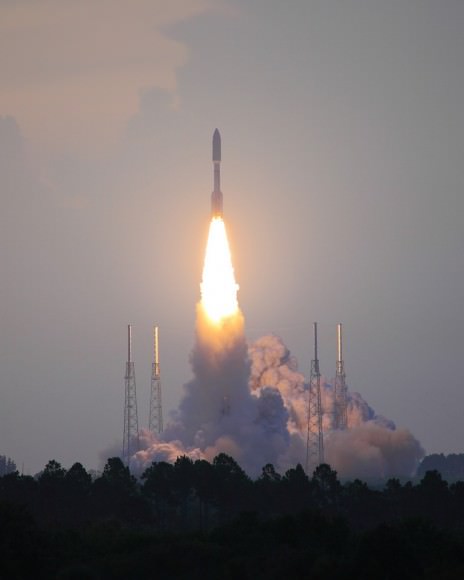
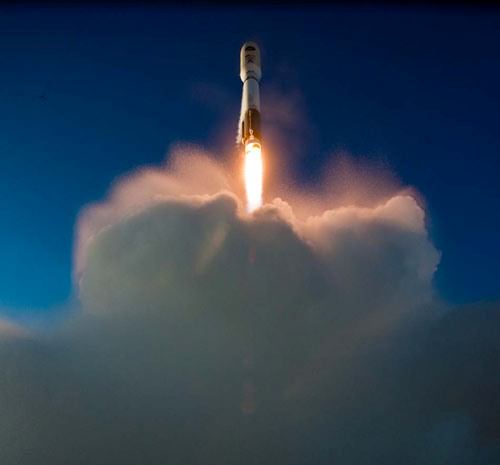
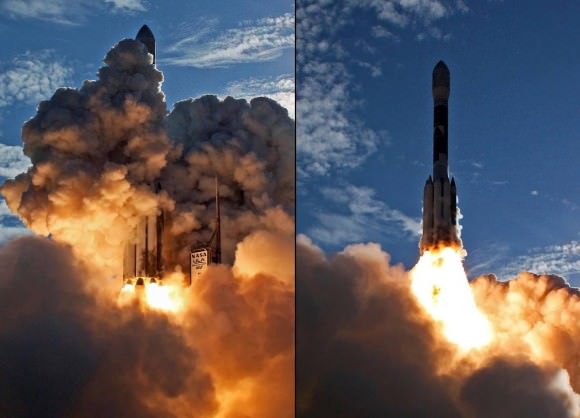
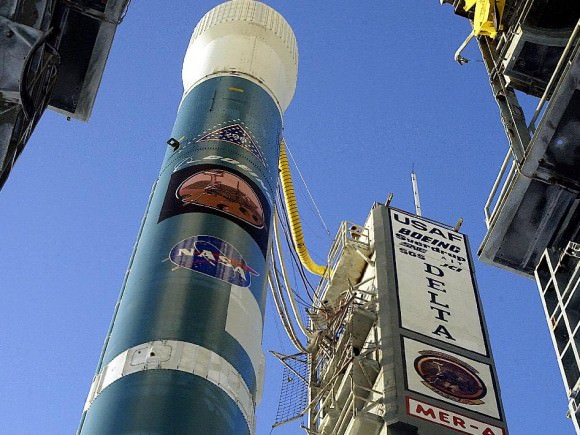
The second satellite in the new constellation of next generation military communications satellites for the US Air Force was successfully launched to orbit today (May 4) atop a powerful Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at Space Launch Complex- 41 in Florida. It will provide worldwide highly secure communications between the President and the Armed Forces.
Blastoff of the expensive and highly capable $1.7 Billion satellite – dubbed Advanced Extremely High Frequency-2 (AEHF-2) – at the precisely appointed time of 2:42 p.m. EDT (1842 GMT) came after a suspect helium valve and spurious signals forced a scrub of the first launch attempt yesterday, May 3, causing a 24 hour postponement of the launch.
“The AEHF satellites will provide the backbone of protection for US strategic satellite communications,” Capt John Francis, of the Space & Missile Systems Center SATCOM Division, told Universe Today in an interview at the Florida launch site.
“I’m thrilled with today’s launch !” Francis told me after witnessing the liftoff.
The United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster stands 197 feet tall. The liquid fueled first stage is powered by a Russian designed RD-180 engine augmented with three Aerojet solid rocket motors strapped on to the side of the first stage. The solids are jettisoned during ascent.
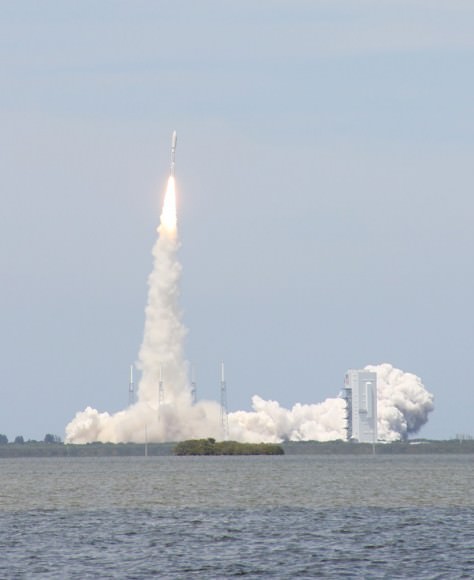

The extremely reliable Atlas V rockets boosted NASA’s Curiosity Mars Science Laboratory and Juno Jupiter Orbiter to their interplanetary destinations in 2011.
AEHF-2 weighs approximately 13,600 pounds and was built by Lockheed Martin.
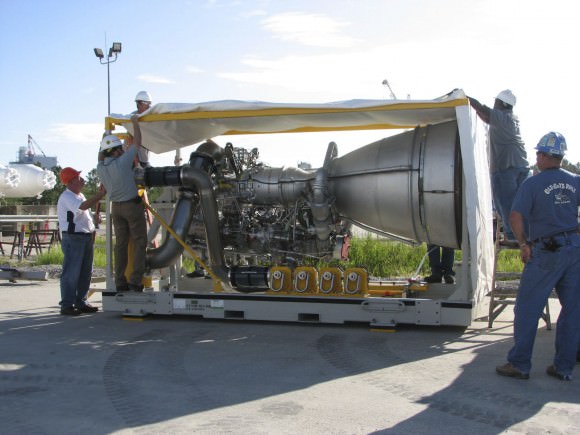
The spacecraft was successfully separated from the Centaur upper stage about 51 minutes after liftoff as planned and placed into a preliminary transfer orbit. The Centaur was powered by a single Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne RL10A engine.
On board thrusters and the Hall current thruster electric propulsion system will maneuver the spacecraft over about the next three months to its final orbit about 22,300 miles above the equator.
The AEHF satellite family is a vastly improved and upgraded version of the Lockheed Martin-built Milstar constellation currently on-orbit.
“The AEHF constellation has 10 times more throughput compared to Milstar”, Capt. Francis explained.
“They will provide 24 hour near whole world coverage and have a 14 year lifetime.”
“AEHF-2 can maneuver in orbit. It will take about 100 days to reach its parking orbit and can move to theatre hot spots as needed to assist the local troops such as in Afghanistan”, said Francis.

It will operate 24/7 and provide vastly improved global, survivable, highly secure, protected communications for warfighters operating on ground, sea and air platforms. AEHF will also serve America’s international partners including Canada, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom.
AEHF-2 is the second satellite in a planned constellation of at least four satellites – and perhaps as many as six satellites – that the military says will eventually replace the aging Milstar system.
“The remaining AEHF satellites will be launched over the next 2 years”, Capt. Francis stated.
A single AEHF satellite provides greater total capacity than the entire five-satellite Milstar constellation. Individual user data rates will be increased five-fold, permitting transmission of tactical military communications, such as real-time video, battlefield maps and targeting data. In addition to its tactical mission, AEHF also provides the critical survivable, protected, and endurable communications links to national leaders including presidential conferencing in all levels of conflict.
The satellite system is used by all levels of the US Government from soldiers in the field in Afghanistan to President Obama in the White House.