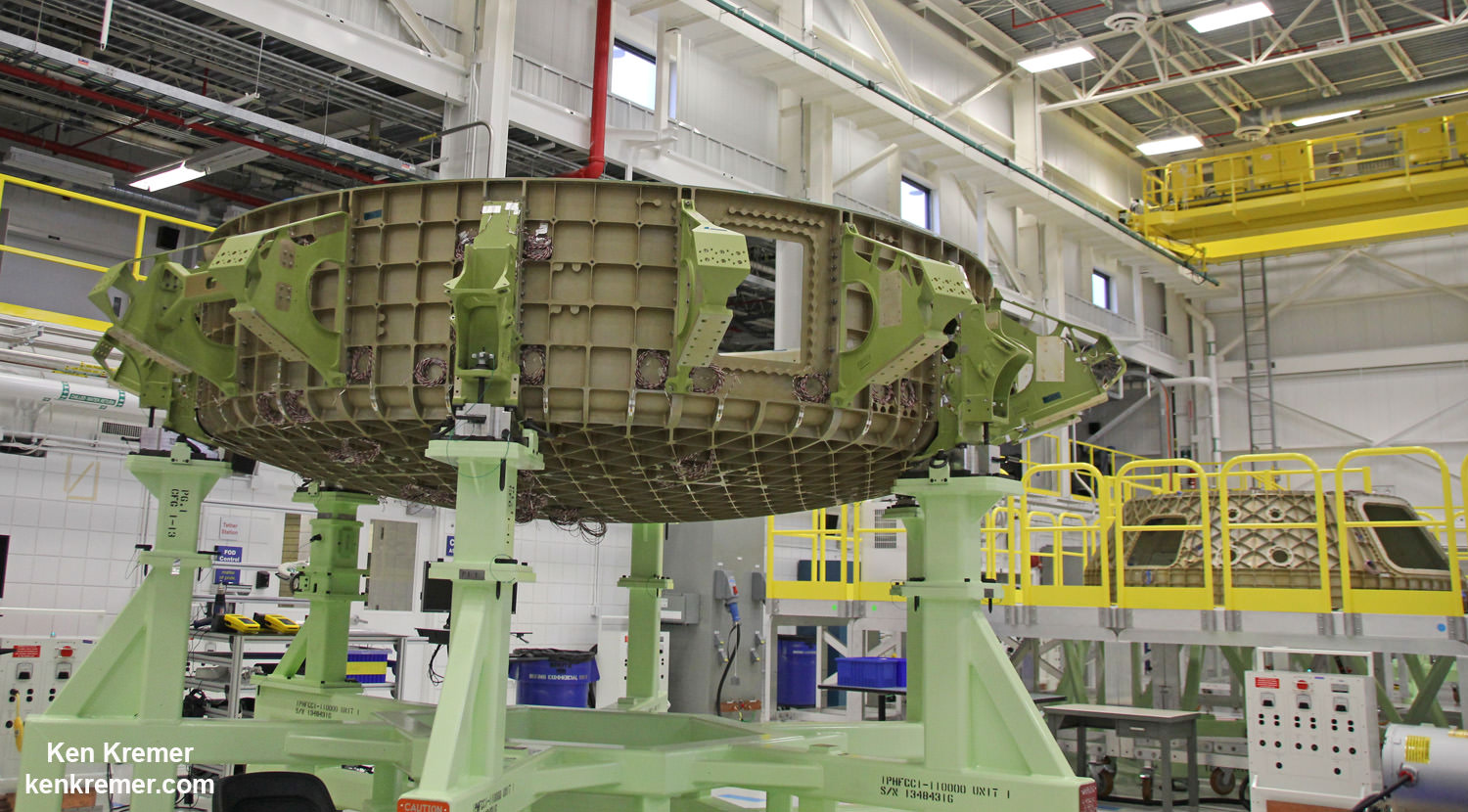
NASA GODDARD SPACE FLIGHT CENTER, MD – Rigorous testing has begun on the advanced robotic arm and boulder extraction mechanisms that are key components of the unmanned probe at the heart of NASA’s Asteroid Redirect Robotic Mission (ARRM) now under development to pluck a multi-ton boulder off a near-Earth asteroid so that astronauts visiting later in an Orion crew capsule can harvest a large quantity of samples for high powered scientific analysis back on Earth. Universe Today inspected the robotic arm hardware utilizing “leveraged robotic technology” during an up close visit and exclusive interview with the engineering development team at NASA Goddard.
“The teams are making great progress on the capture mechanism that has been delivered to the robotics team at Goddard from Langley,” NASA Associate Administrator Robert Lightfoot told Universe Today.
“NASA is developing these common technologies for a suite of missions like satellite servicing and refueling in low Earth orbit as well as autonomously capturing an asteroid about 100 million miles away,” said Ben Reed, NASA Satellite Servicing Capabilities Office (SSCO) Deputy Project Manager, during an exclusive interview and hardware tour with Universe Today at NASA Goddard in Greenbelt, Maryland, regarding concepts and goals for the overall Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM) initiative.
NASA is leveraging technology originally developed for satellite servicing such as with the Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) currently on board the International Space Station (ISS) and repurposing them for the asteroid retrieval mission.
“Those are our two near term mission objectives that we are developing these technologies for,” Reed explained.
ARRM combines both robotic and human missions to advance the new technologies required for NASA’s agency wide ‘Journey to Mars’ objective of sending a human mission to the Martian system in the 2030s.
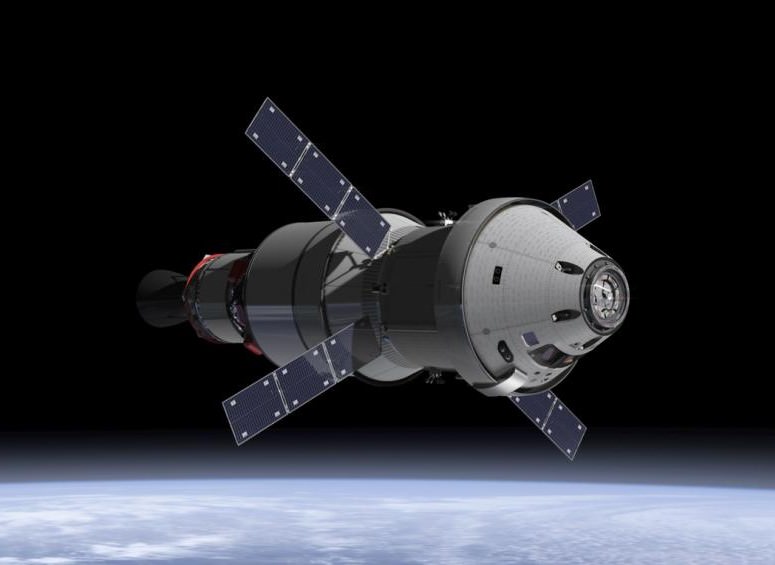
The unmanned Asteroid Redirect Robotic Mission (ARRM) to grab a boulder is the essential first step towards carrying out the follow on sample retrieval with the manned Orion Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM) by the mid-2020s.
ARRM will use a pair of highly capable robotic arms to autonomously grapple a multi-ton (> 20 ton) boulder off the surface of a large near-Earth asteroid and transport it to a stable, astronaut accessible orbit around the Moon in cislunar space.
“Things are moving well. The teams have made really tremendous progress on the robotic arm and capture mechanism,” Bill Gerstenmaier, NASA Associate Administrator for Human Exploration and Operations, told Universe Today.
Then an Orion crew capsule can fly to it and the astronauts will collect a large quantity of rock samples and gather additional scientific measurements.
“We are working on a system to rendezvous, capture and service different [target] clients using the same technologies. That is what we are working on in a nut shell,” Reed said.
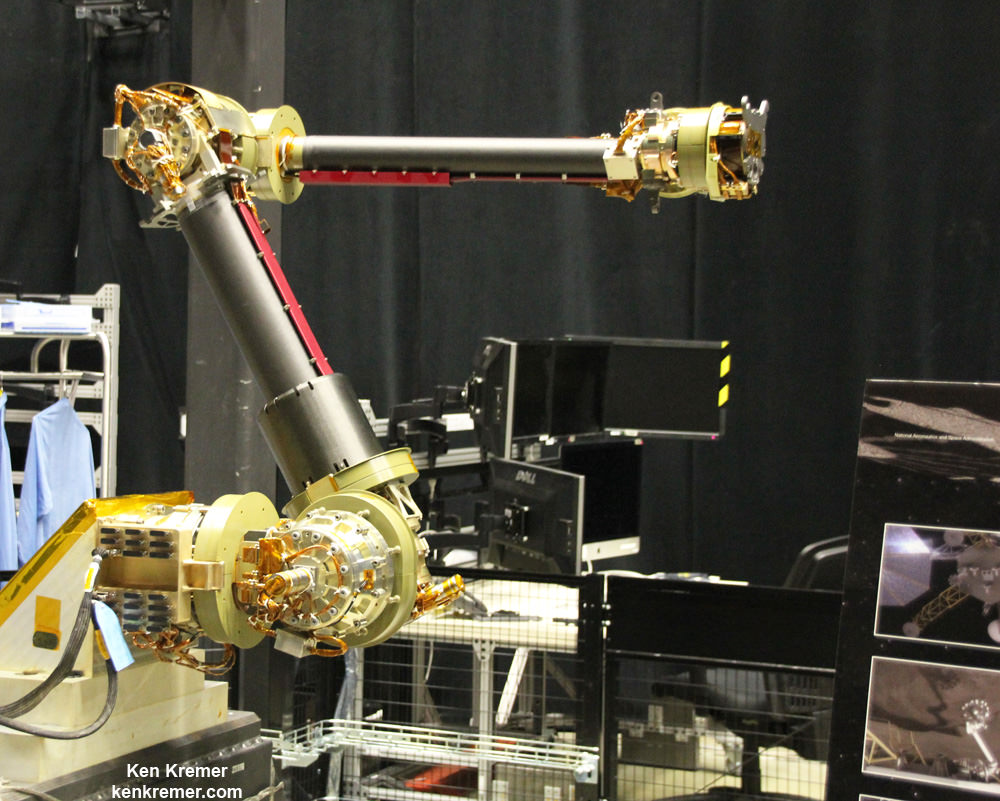
“Right now the plan is to launch ARRM by about December 2020,” Reed told me. But a huge amount of preparatory work across the US is required to turn NASA’s plan into reality.
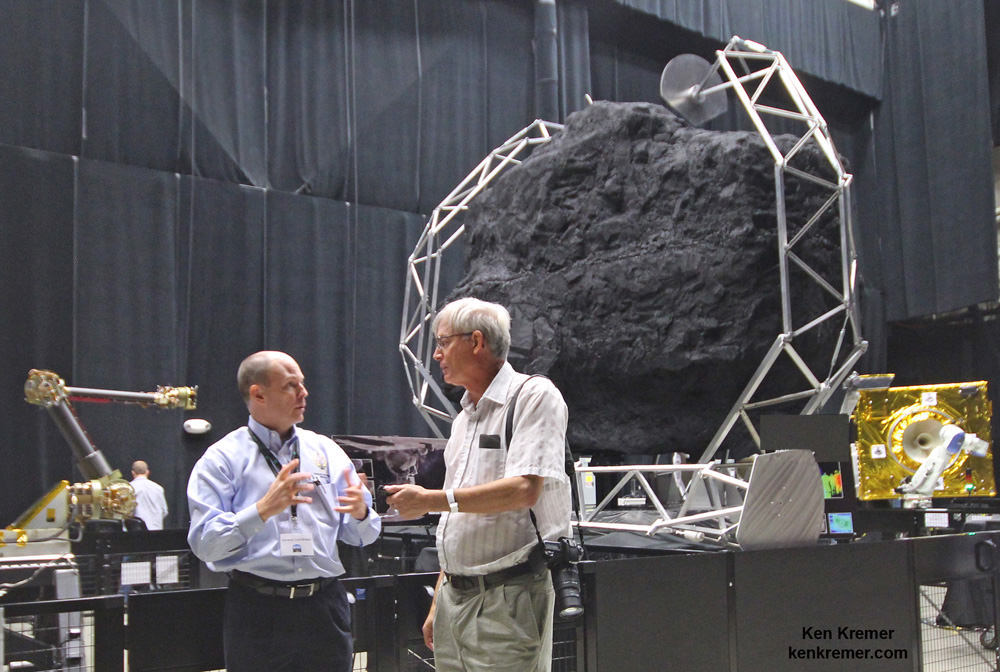
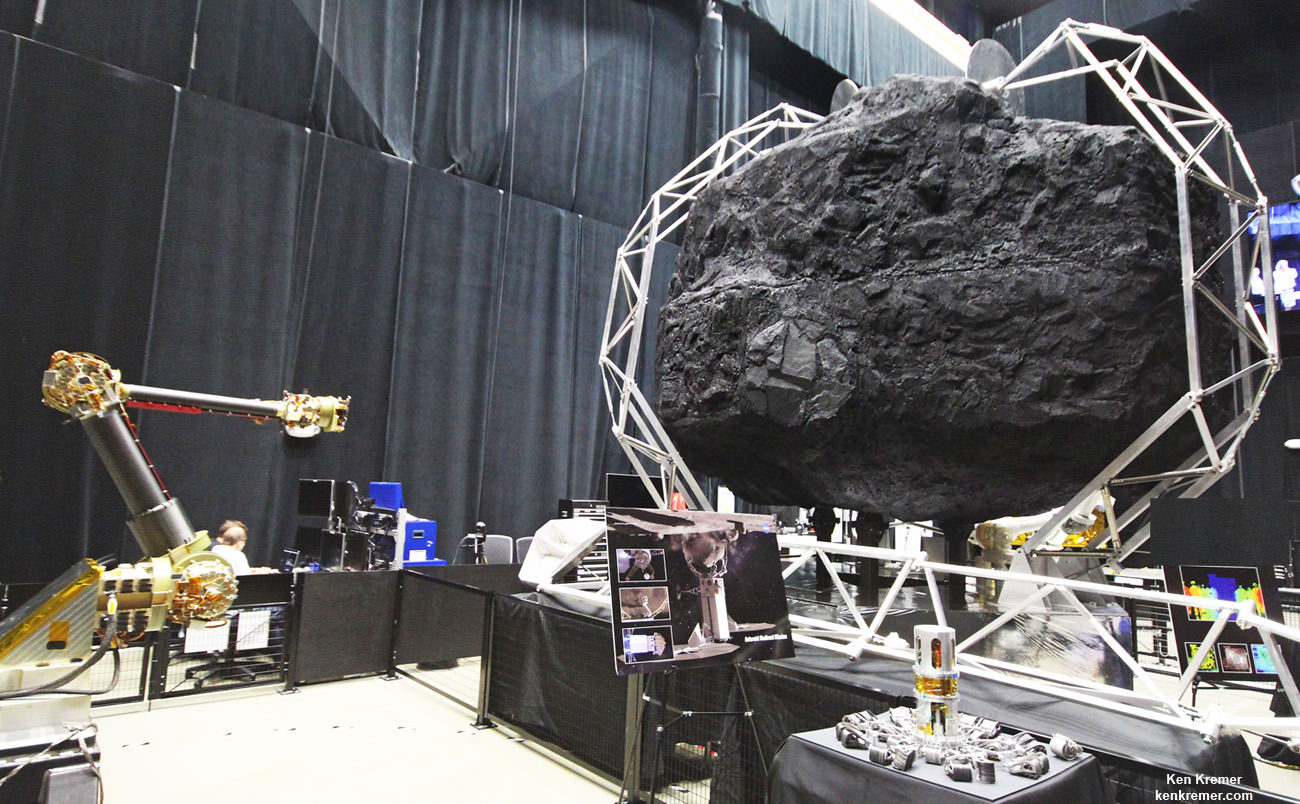
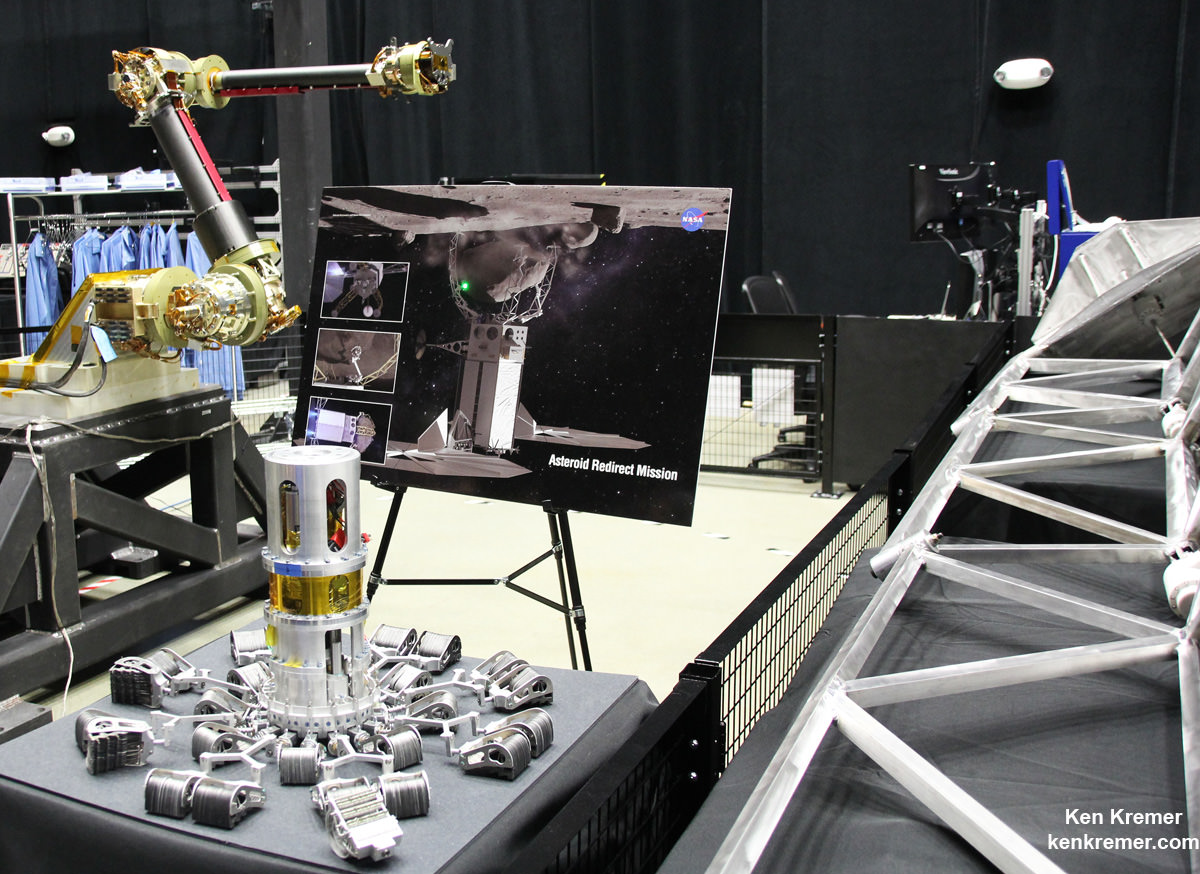
Key mission enabling technologies are being tested right now with a new full scale engineering model of the ‘Robotic Servicing Arm’ and a full scale mockup of the boulder snatching ARRM Capture Module at NASA Goddard, in a new facility known as “The Cauldron.”

“The robotic arm we have here now is an engineering development unit. The 2.2 meter-long arms can be used for assembling large telescopes, repairing a failed satellite, removing orbital debris and capturing an asteroid,” said Reed.
“There are two little arms and three big capture legs.”
“So, we are leveraging one technology development program into multiple NASA objectives.”
“We are working on common technologies that can service a legacy orbiting satellite, not designed to be serviced, and use those same technologies with some tweaking that we can go out with 100 million miles and capture an asteroid and bring it back to the vicinity of the Moon.”
“Currently the [capture module] system can handle a boulder that’s up to about 3 x 4 x 5 meters in diameter.”

The Cauldron is a brand new Goddard facility for testing technologies and operations for multiple exploration and science missions, including satellite servicing and ARRM that just opened in June 2015 for the centers Satellite Servicing Capabilities Office.
Overall project lead for ARRM is the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) with numerous contributions from other NASA centers and industrial partners.
“This is an immersive development lab where we bring systems together and can do lifetime testing to simulate what’s in space. This is our robotic equivalent to the astronauts NBL, or neutral buoyancy lab,” Reed elaborated.
“So with this same robotic arm that can cut wires and thermal blankets and refuel an Earth sensing satellite, we can now have that same arm go out on a different mission and be able to travel out and pick up a multi-ton boulder and bring it back for astronauts to harvest samples from.”
“So that’s quite a technical feat!”
The Robotic Servicing Arm is a multi-jointed powerhouse designed to function like a “human arm” as much as possible. It builds on extensive prior research and development investment efforts conducted for NASA’s current Red Planet rovers and a flight-qualified robotic arm developed for the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA).
“The arm is capable of seven-degrees-of-freedom to mimic the full functionally of a human arm. It has heritage from the arm on Mars right now on Curiosity as well as ground based programs from DARPA,” Reed told me.
“It has three degrees of freedom at our shoulder, two at our elbow and two more at the wrist. So I can hold the hand still and move the elbow.”
The arm will also be equipped with a variety of interchangeable “hands” that are basically tools to carry out different tasks with the asteroid such as grappling, drilling, sample gathering, imaging and spectrometric analysis, etc.

The ARRM spacecraft will carefully study, characterize and photograph the asteroid in great detail for about a month before attempting the boulder capture.
Why does the arm need all this human-like capability?
“When we arrive at an asteroid that’s 100 million miles away, we are not going to know the fine local geometry until we arrive,” Reed explained to Universe Today.
“Therefore we need a flexible enough arm that can accommodate local geometries at the multi-foot scale. And then a gripper tool that can handle those geometry facets at a much smaller scale.”
“Therefore we chose seven-degrees-of-freedom to mimic humans very much by design. We also need seven-degrees-of-freedom to conduct collision avoidance maneuvers. You can’t do that with a six-degree-of-freedom arm. It has to be seven to be a general purpose arm.”
How will the ARRM capture module work to snatch the boulder off the asteroid?
“So the idea is you come to the mother asteroid and touch down and make contact on the surface. Then you hold that position and the two arms reach out and grab the boulder.”
“Once its grabbed the boulder, then the legs straighten and pull the boulder off the surface.”
“Then the arms nestle the asteroid onto a cradle. And the legs then change from a contact system to become a restraint system. So the legs wrap around the boulder to restrain it for the 100 million mile journey back home.
“After that the little arms can let go – because the legs have wrapped around and are holding the asteroid.”
“So now the arm can also let go of the gripper system and pick up a different tool to do other things. For example they can collect a sample with another tool. And maybe assist an astronaut after the crew arrives.”
“During the 100 million mile journey back to lunar orbit they can be also be preparing the surface and cutting into it for later sample collection by the astronauts.”
Be sure to watch this video animation:
Since the actual asteroid encounter will occur very far away, the boulder grappling will have to be done fully autonomously since there will be no possibility for real time communications.
“The return time for communications is like about 30 minutes. So ‘human in the loop’ control is out of the question.
“Once we get into hover position over the landing site we hit the GO button. Then it will be very much like at Mars and the seven minutes of terror. It will take awhile to find out if it worked.”
Therefore the team at Goddard has already spent years of effort and practice sessions just to get ready for working with the early engineering version of the arm to maximize the probability of a successful capture.
“In this facility we put systems together to try and practice and rehearse and simulate as much of the mission as is realistically possible.”
“It took a lot of effort to get to this point, in the neighborhood of four years to get the simulation to behave correctly in real time with contact dynamics and the robotic systems. So the arm has to touch the boulder with force torque sensors and feed that into a computer to measure that and move the actuators to respond accordingly.”
“So the capture of the boulder is autonomous. The rest is teleoperated from the ground, but not the capture itself.”
How realistic are the rehearsals?
“We are practicing here by reaching out with the arm to grasp the client target using autonomous capture [procedures]. In space the client [target] is floating and maybe tumbling. So when we reach out with the arm to practice autonomous capture we make the client tumble and move – with the inertial properties of the target we are practicing on.”
“Now for known objects like satellites we know the mass precisely. And we can program all that inertial property data in very accurately to give us much more realistic simulations.”
“We learned from all our astronaut servicing experiences in orbit is that the more we know for the simulations, the easier and better the results are for the astronauts during an actual mission because you simulated all the properties.”
“But with this robotic mission to an asteroid there is no backup like astronauts. So we want to practice here at Goddard and simulate the space environment.”
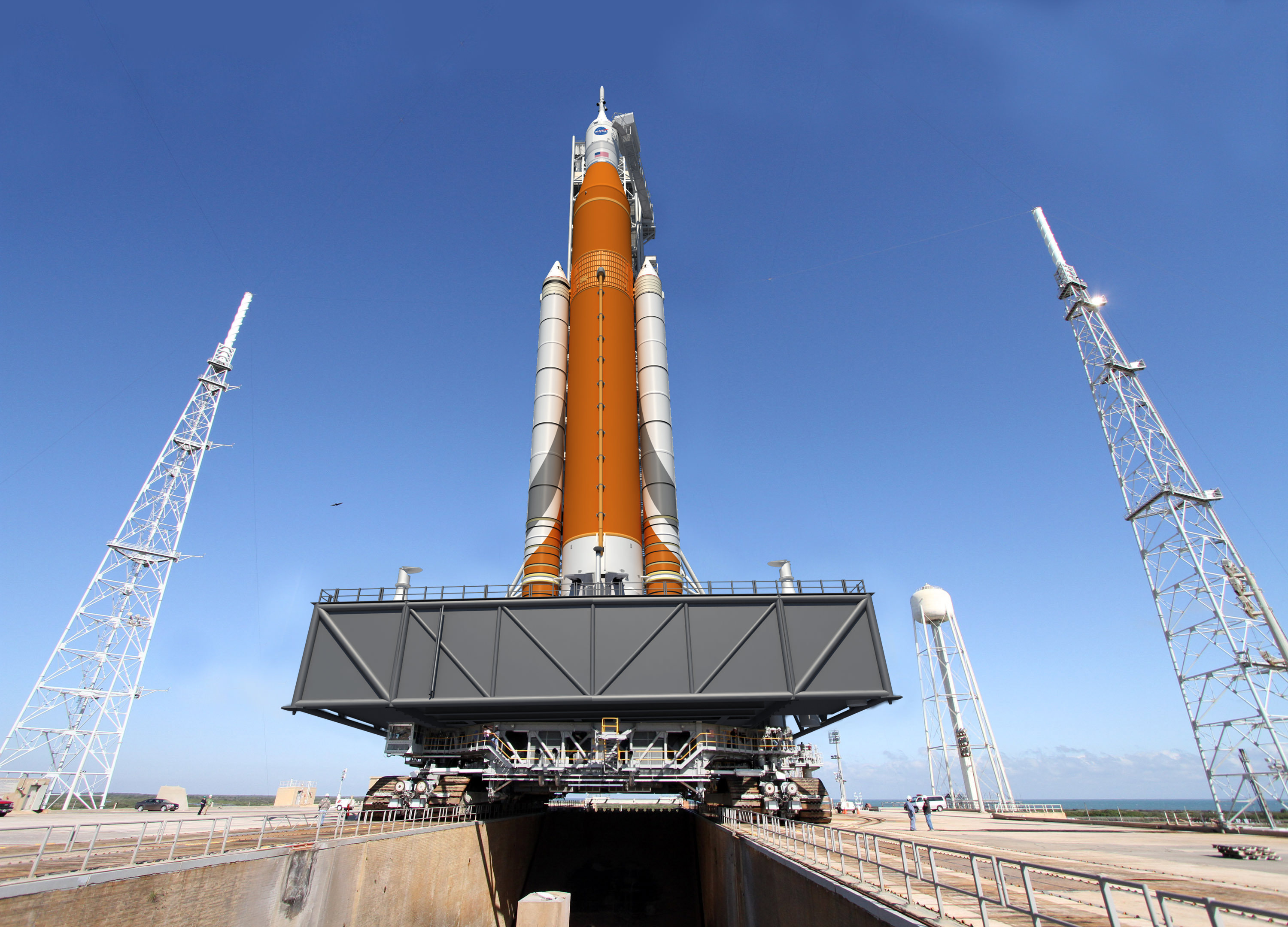
ARRM will launch by the end of 2020 on either an SLS, Delta IV Heavy or a Falcon Heavy. NASA has not yet chosen the launch vehicle.
Several candidate asteroids have already been discovered and NASA has an extensive ongoing program to find more.

Again, this robotic technology was selected for development for ARRM because it has a lot in common with other objectives like fixing communications satellites, refueling satellites and building large telescopes in the future.
NASA is also developing other critical enabling technologies for the entire ARM project like solar electric propulsion that will be the subject of another article.
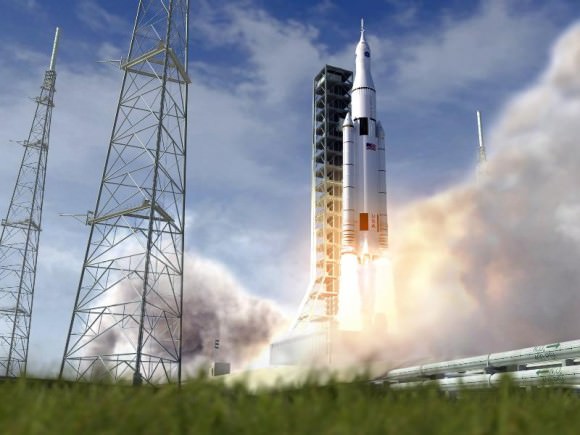
Therefore NASA is leveraging one technology development program into multiple spaceflight objectives that will greatly assist its plans to send ‘Humans to Mars’ in the 2030s with the Orion crew module launched by the monster Space Launch System (SLS) rocket.
The maiden uncrewed launch of the Orion/SLS stack is slated for November 2018.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.