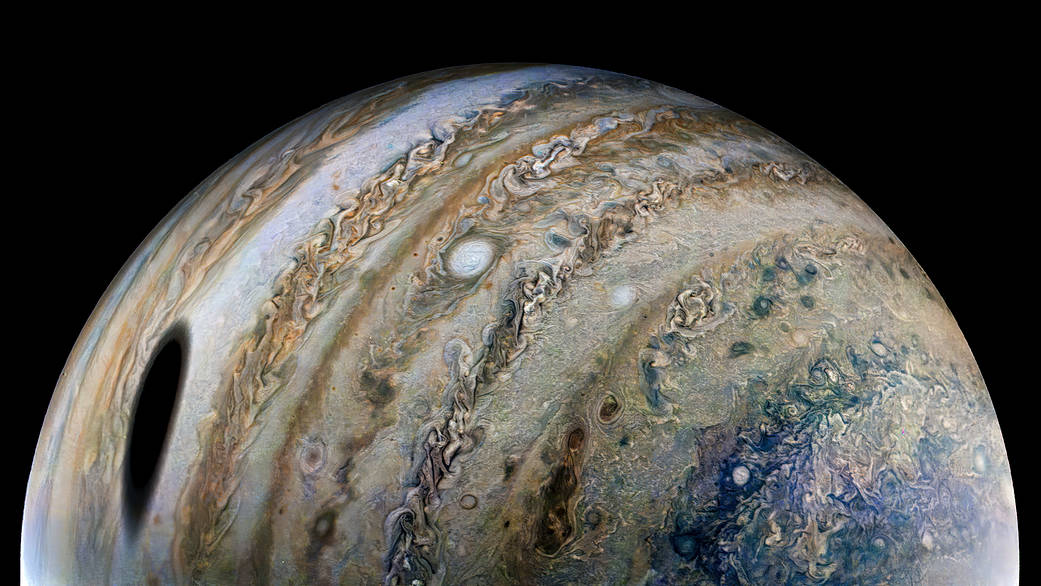
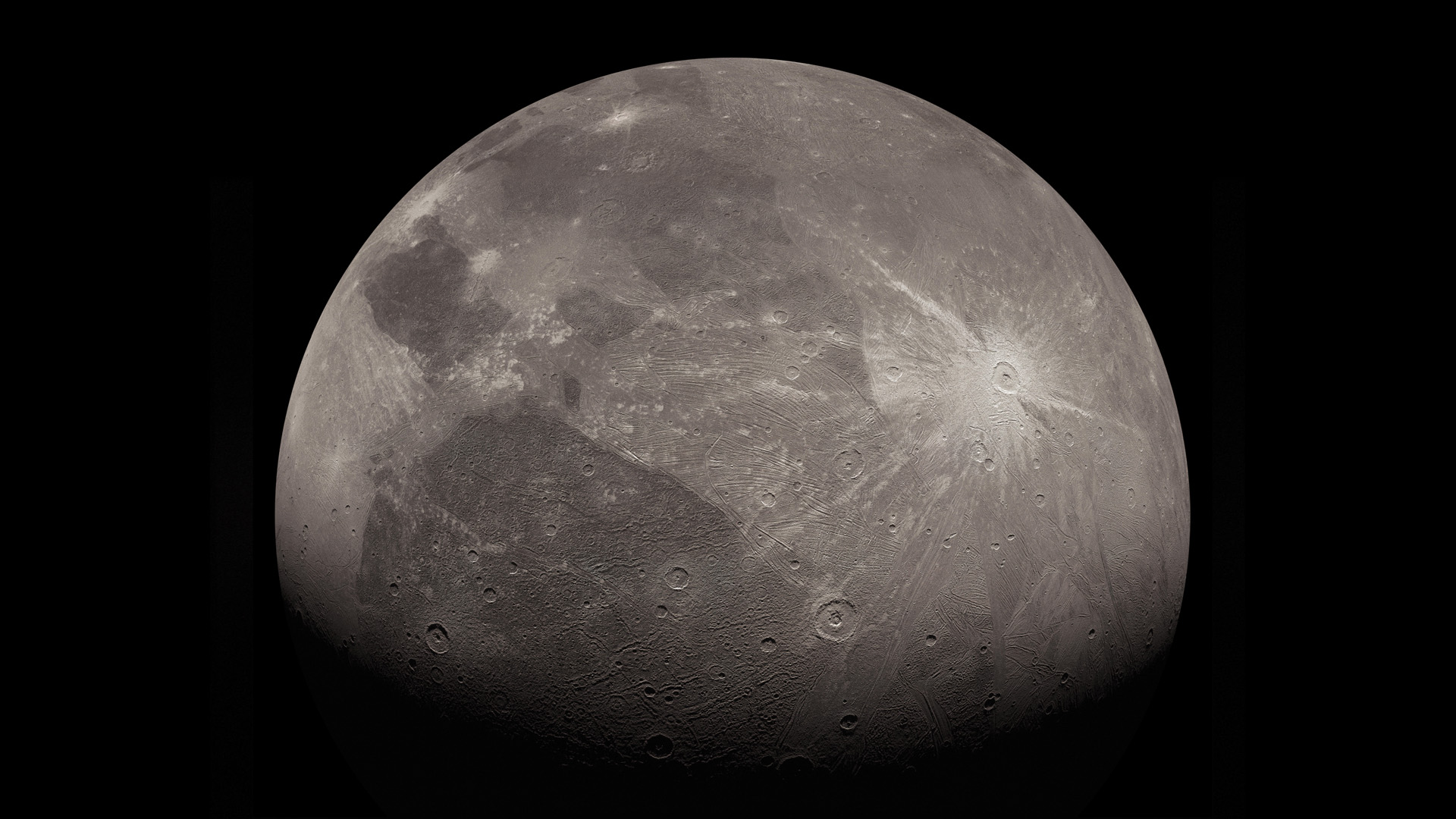
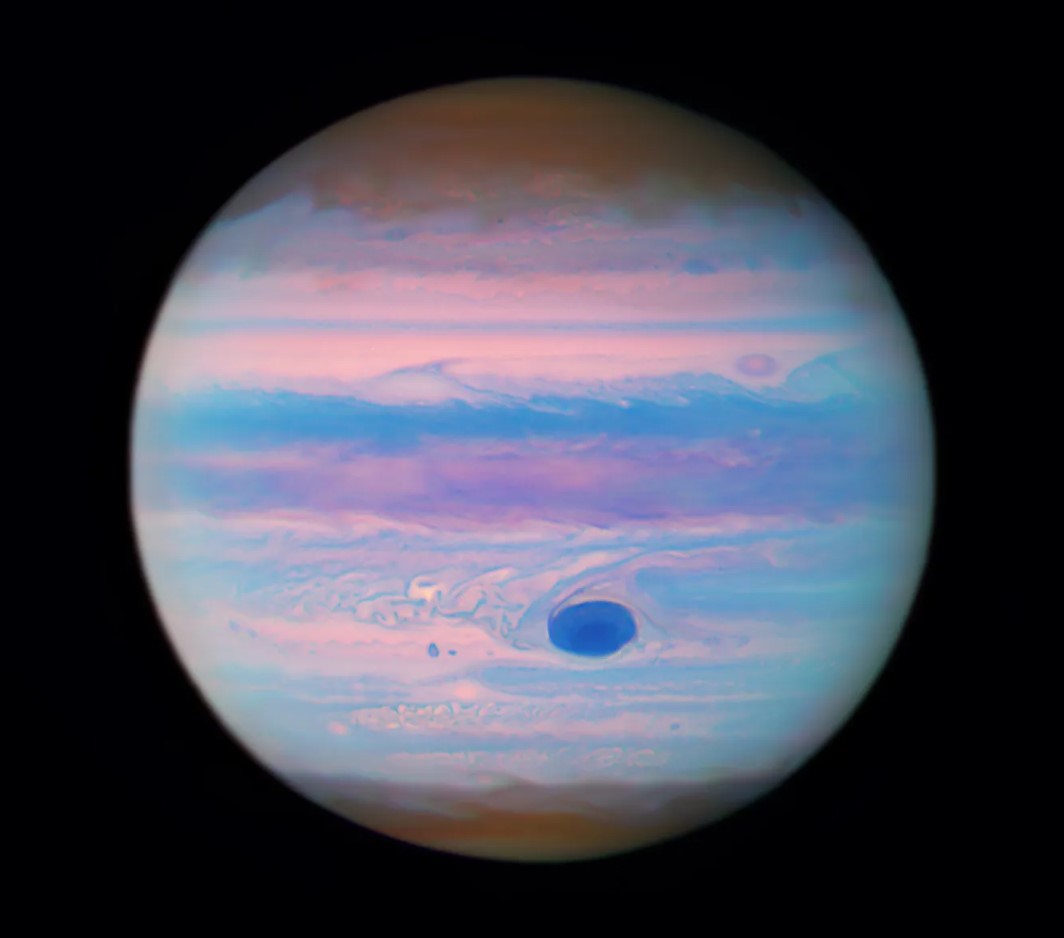
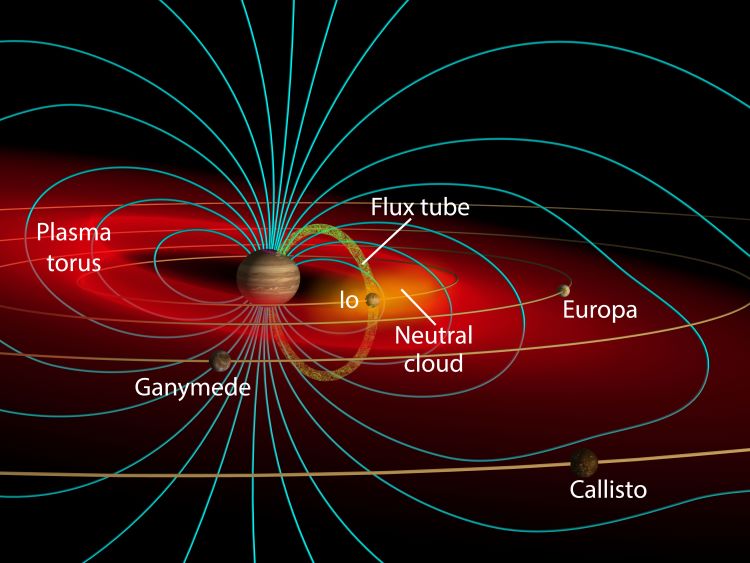
The Juno spacecraft has revealed some fascinating things about Jupiter since it began exploring the system on July 4th, 2016. Not only is it the first robotic mission to study Jupiter up close while orbiting it since the Galileo spacecraft, which studied the gas giant and its satellites from 1995 to 2003. Juno is also the first robotic explorer to look below Jupiter’s dense clouds to investigate the planet’s magnetic field, composition, and structure. The data this has produced is helping scientists address questions about how Jupiter formed and the origins of the Solar System.
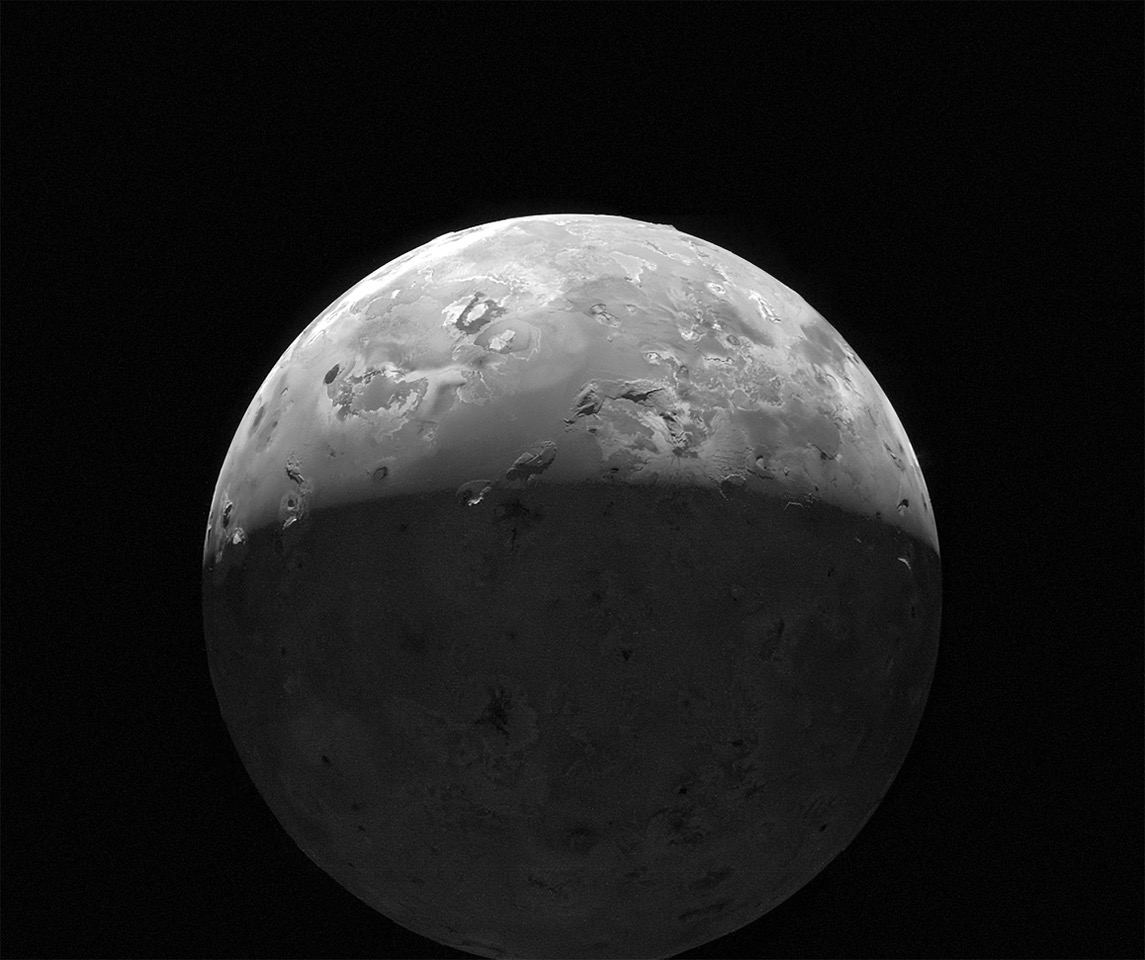
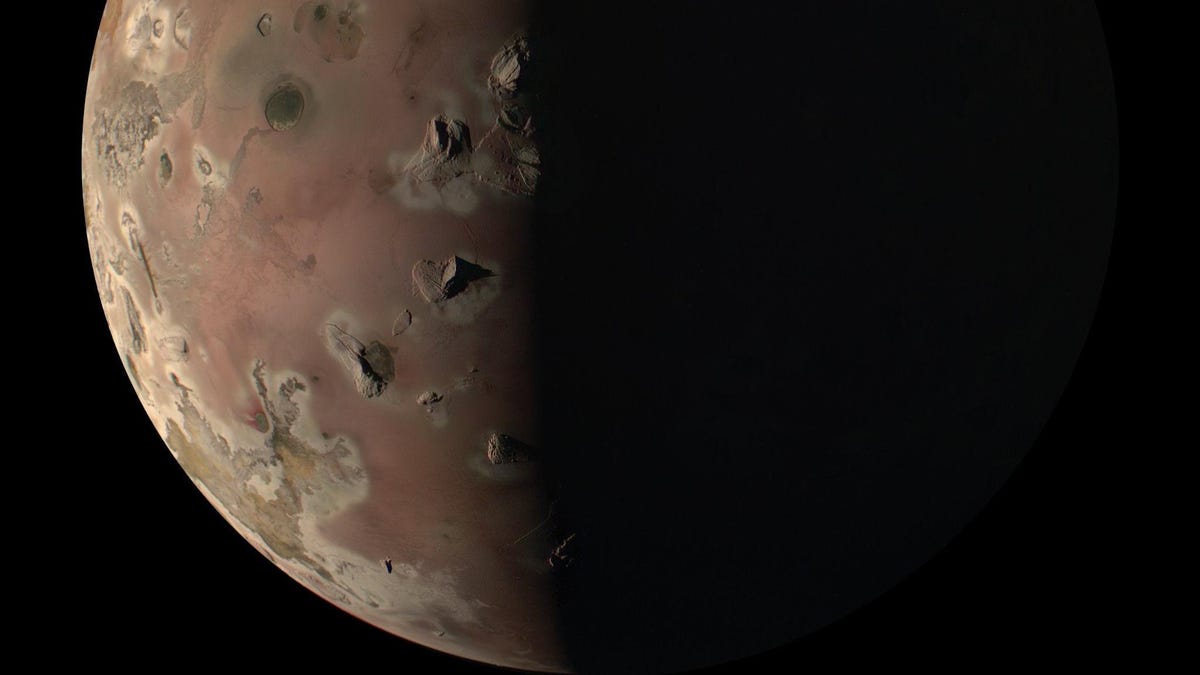
Since 2021, the probe has been in an extended mission phase, where it has been making flybys of some of Jupiter’s largest moons, including Ganymede, Europa, and Io. As it passes these satellites, Juno has captured some incredible images with its main imaging instrument, the JunoCam. On Saturday, February 3rd, 2024, the Juno spacecraft made another flyby of Io and took more captivating photos of the volcanic moon and its pockmarked surface. This was the second part of a twin flyby designed to provide new insight into Io’s volcanic nature and the interior structure of the satellite.
Continue reading “NASA’s Juno Probe Makes Another Close Flyby of Io”