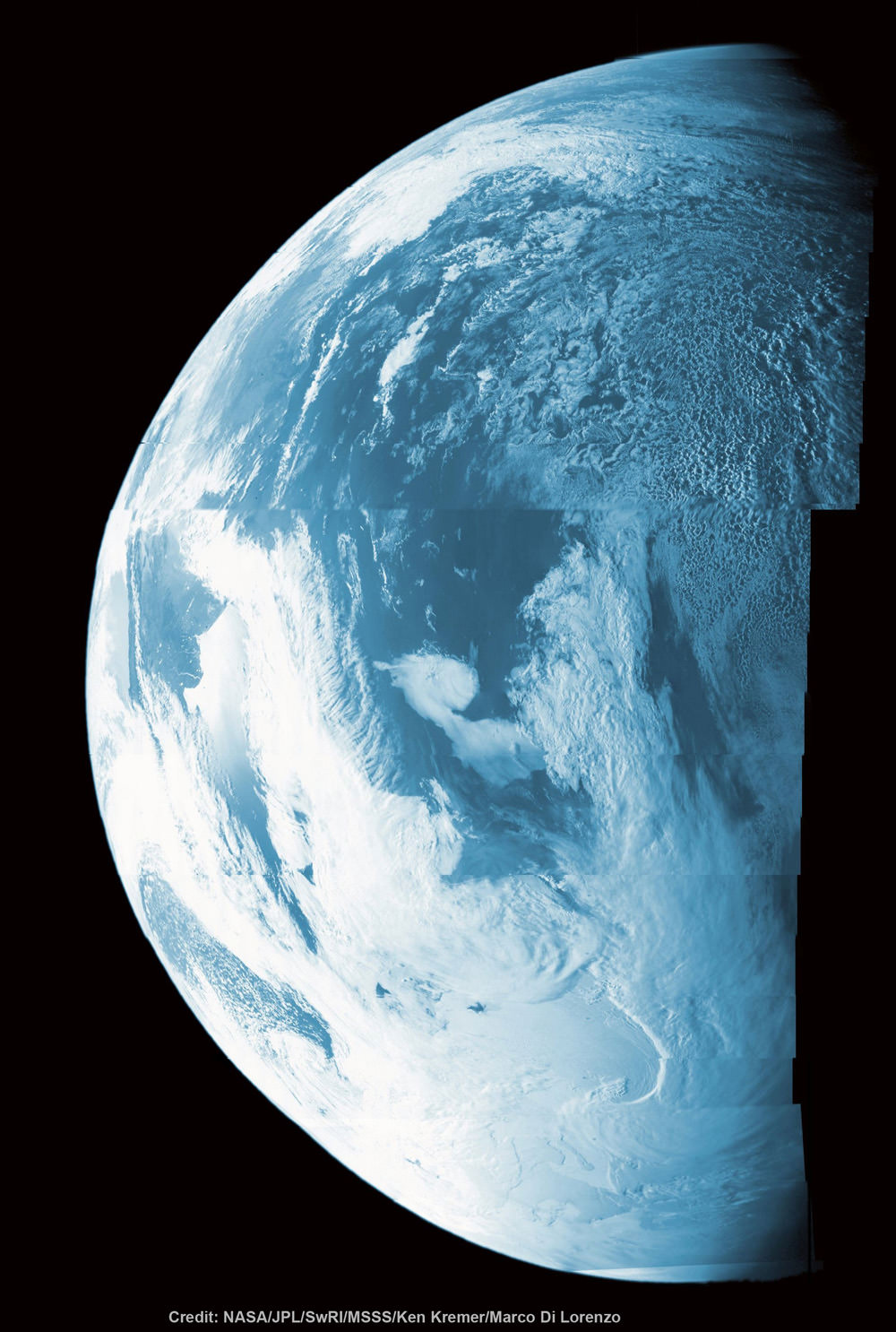
Opportunity by Solander Point peak – 2nd Mars Decade Starts here!
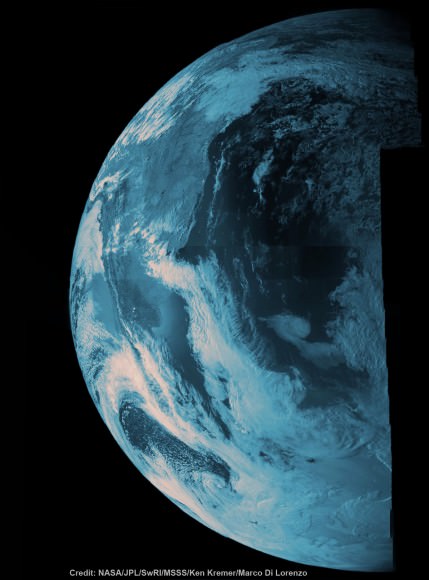
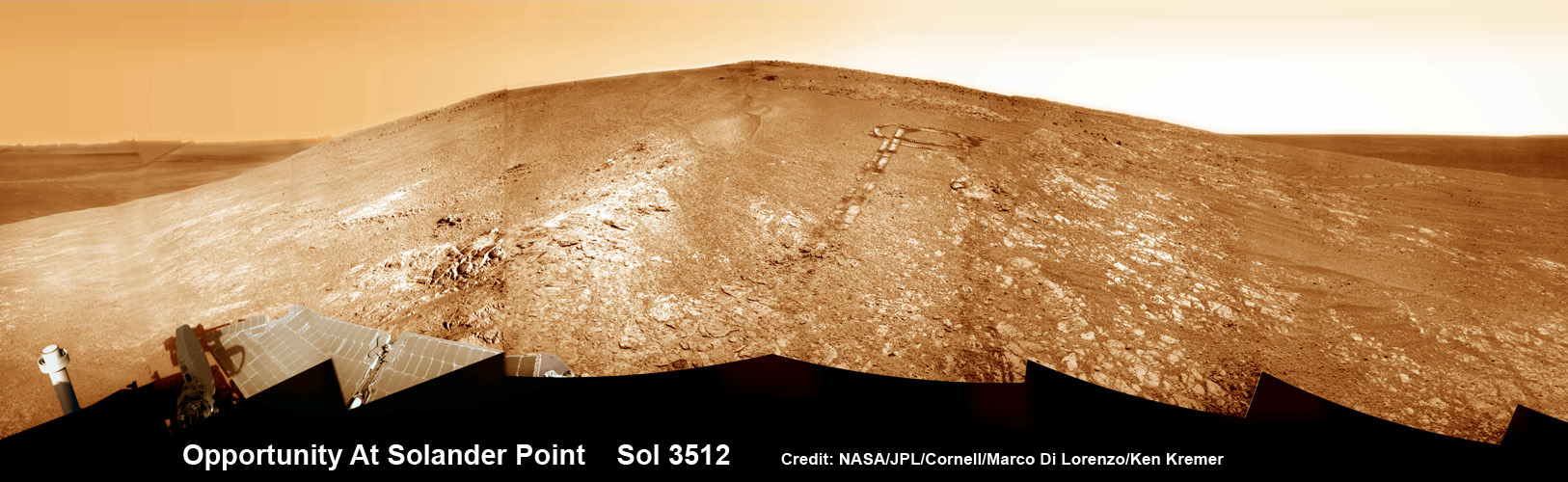
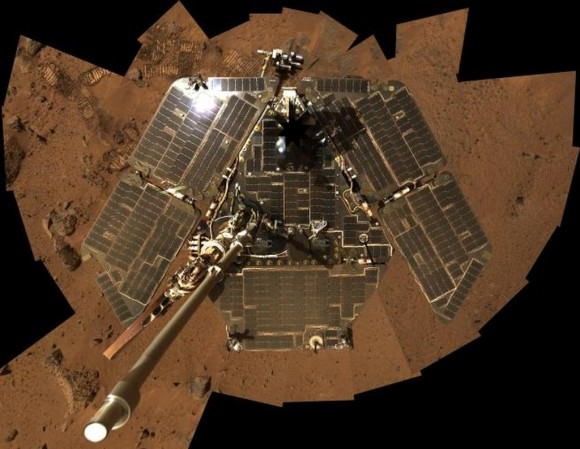
NASA’s Opportunity rover captured this panoramic mosaic on Dec. 10, 2013 (Sol 3512) near the summit of “Solander Point” on the western rim of Endeavour Crater where she starts Decade 2 on the Red Planet. She is currently investigating outcrops of potential clay minerals formed in liquid water on her 1st mountain climbing adventure. Assembled from Sol 3512 navcam raw images. Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer-kenkremer.com
See full mosaic with Dust Devil and 10 Year Route Map – below
Story updated[/caption]
NASA’s long-lived Opportunity Mars rover has accomplished what absolutely no one expected.
Opportunity is about to embark on her 2nd decade exploring the Red Planet since her nail biting touchdown in 2004.
And to top that off she is marking that miraculous milestone at a spectacular outlook by the summit of the first mountain she has ever scaled!
See our Solander Point summit mosaic showing the robots current panoramic view – in essence this is what her eyes see today; above and below.
And that mountaintop is riven with outcrops of minerals that likely formed in flowing liquid neutral water conducive to life – potentially a scientific goldmine.
“We expect we will reach some of the oldest rocks we have seen with this rover — a glimpse back into the ancient past of Mars,” says the rover principal investigator, Steve Squyres of Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y.
“It’s like starting a whole new mission.”

Opportunity is nearly at the peak of Solander Point, an eroded segment on the western flank of vast Endeavour Crater, that spans some 22 kilometers (14 miles) in diameter.
The six wheeled rover reached the top section of Solander on Sol 3512, just before Christmas in December 2013. It’s situated nearly 40 meters (130 feet) above the crater plains.
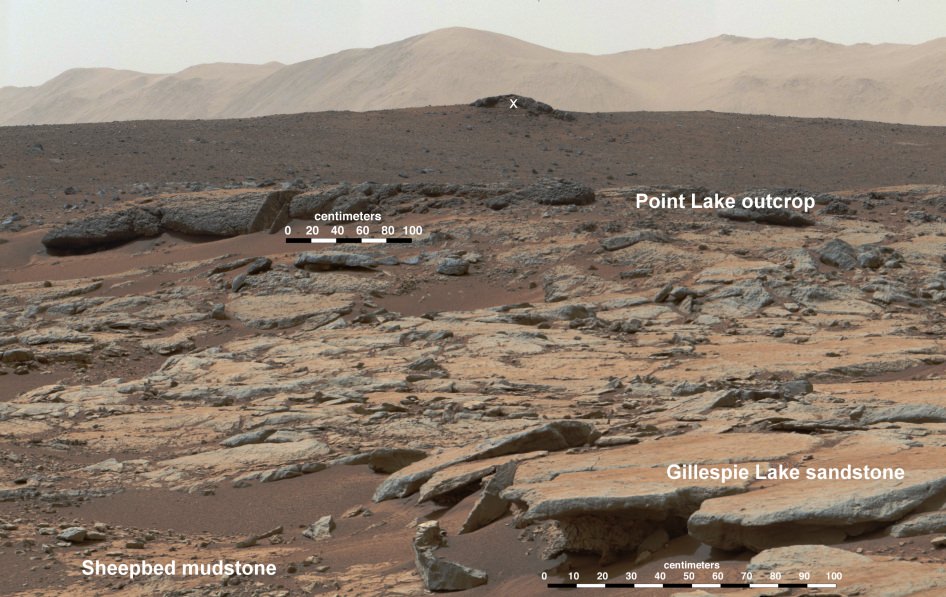
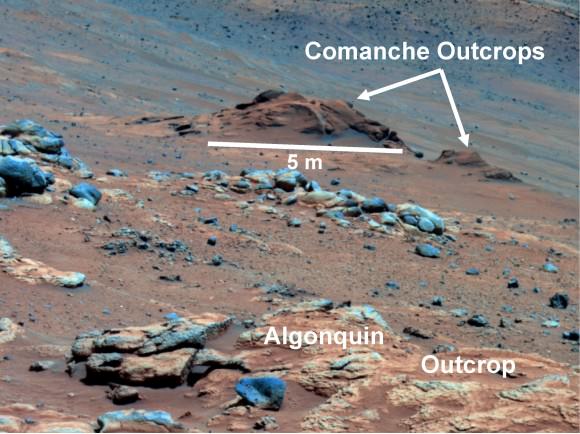
There she began inspecting and analyzing an area of exposed outcrops called ‘Cape Darby’ that scientists believe holds caches of clay minerals which form in drinkable water and would constitute a habitable zone.

NASA’s Opportunity rover captured this panoramic mosaic on Dec. 10, 2013 (Sol 3512) near the summit of “Solander Point” on the western rim of vast Endeavour Crater where she starts Decade 2 on the Red Planet. She is currently investigating summit outcrops of potential clay minerals formed in liquid water on her 1st mountain climbing adventure. See wheel tracks at center and dust devil at right. Assembled from Sol 3512 navcam raw images.
Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer-kenkremer.com
The science team directed Opportunity to ‘Cape Darby’ based on predictions from spectral observations collected from the CRISM spectrometer aboard one of NASA’s spacecraft circling overhead the Red Planet – the powerful Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
Opportunity is using all its cameras and instruments as well as those on the robotic arm to inspect the outcrop area, including the rock abrasion tool, spectrometers and microscopic imager.
As reported earlier this week, the rover is also investigating a mysterious rock that suddenly appeared in images nearby the robot. ‘Pinnacle Island’ rock may have been flung up by the wheels. No one knows for sure – yet.

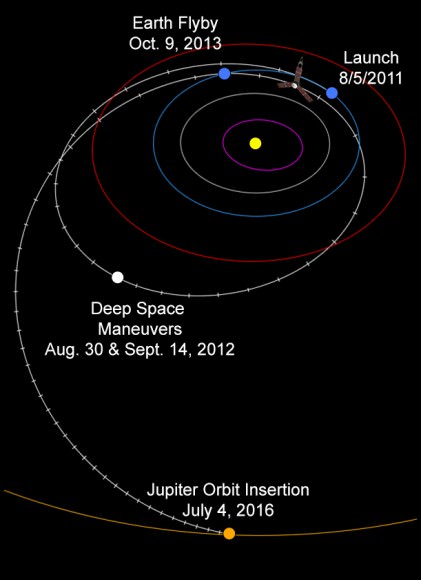
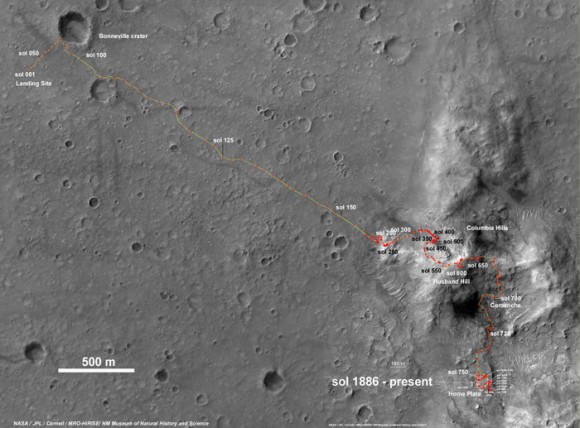
Solander Point is the first mountain she has ever climbed along her epic 10 year journey across the plains of Meridiani. Heretofore she toured a string of Martian craters. See 10 Years Route map below.
In mid-2013, the scientists used similar orbital observations to find a rock called “Esperance’ – which was loaded with clay minerals and located along another Endeavour crater rim segment called Cape York.
Squyres ranked “Esperance” as one of the “Top 5 discoveries of the mission.”
The team hopes for similar mineralogical discoveries at Solander.
The northward-facing slopes at Solander also afford another major benefit to Opportunity. They will tilt the rover’s solar panels toward the sun in the southern-hemisphere winter sky thereby providing an important energy boost.
The power boost will enable continued mobile operations through the upcoming frigidly harsh winter- her 6th since landing 10 years ago.

So Opportunity will be moving from outcrop to outcrop around the summit during the Martian winter. Daily sunshine reaches a minimum in February 2014.
As of Wednesday, Jan. 15, 2014, or Sol 3547, the solar array energy production on the rover is 353 watt-hours, compared to 900 watt-hours after landing. But that is sufficient to keep moving and actively conduct research throughout the winter at the mountaintop.
Opportunity’s long and winding road on the Red Planet began when she safely settled upon the alien world on 24 January 2004, following a harrowing plummet through the thin Martian atmosphere and an airbag assisted, bouncing ball landing.
She arrived barely 3 weeks after her twin sister, Spirit on 3 January 2004.
Today marks Opportunity’s 3551st Sol or Martian Day roving Mars – for what was expected to be only a 90 Sol mission.
So far she has snapped over 188,100 amazing images on the first overland expedition across the Red Planet.
Her total odometry stands at over 24.07 miles (38.73 kilometers) since touchdown on Jan. 24, 2004 at Meridiani Planum.
Read more about sister Spirit – here and here.
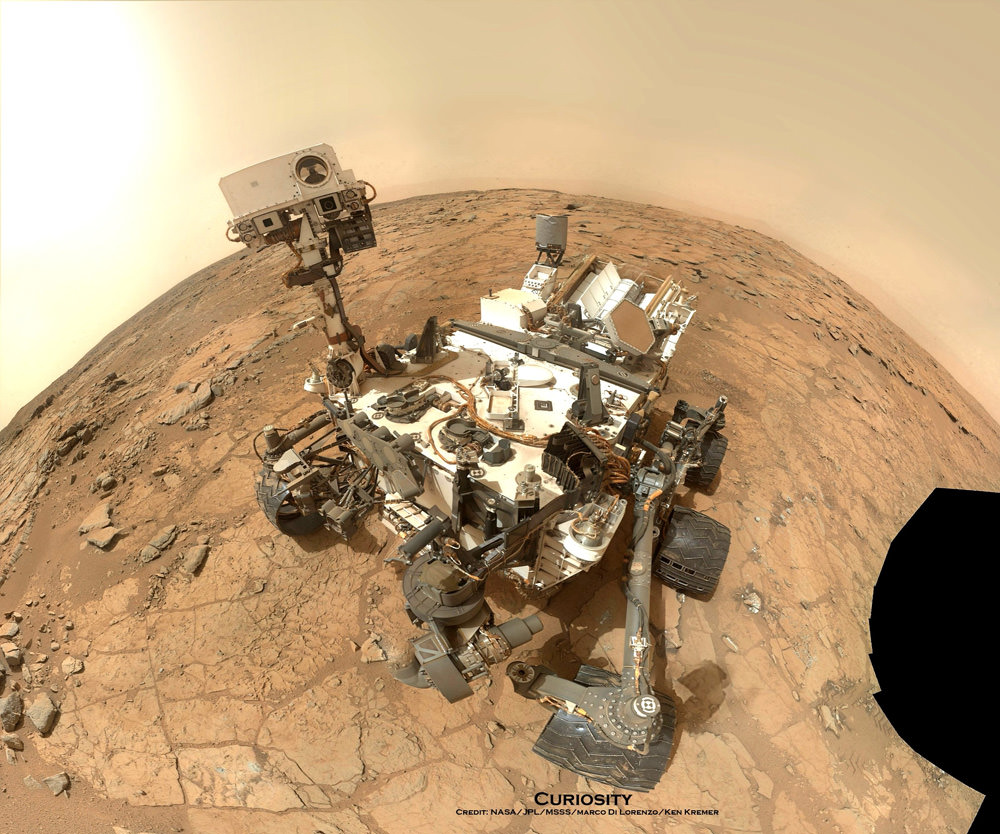
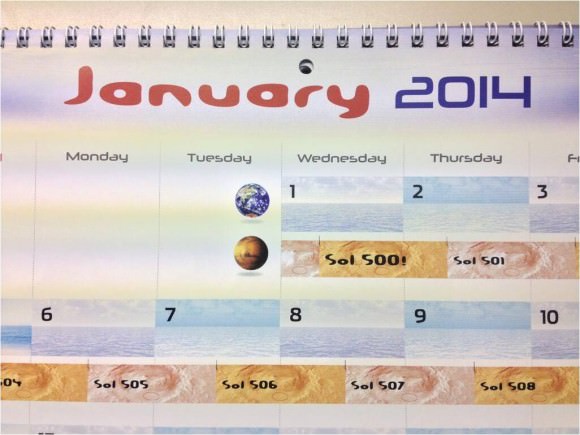
Meanwhile on the opposite side of Mars, Opportunity’s younger sister rover Curiosity is trekking towards gigantic Mount Sharp. She celebrated 500 Sols on Mars on New Years Day 2014.
And a pair of new orbiters are streaking to the Red Planet to fortify the Terran fleet- NASA’s MAVEN and India’s MOM.
Finally, China’s Yutu rover is trundling across pitted moonscapes.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Opportunity, Curiosity, Chang’e-3, LADEE, MAVEN, Mars rover and MOM news.

See the tilted terrain and rover tracks in this look-back mosaic view from Solander Point peering across the vast expanse of huge Endeavour Crater. Moasic assembled from navcam raw images taken on Sol 3431 (Sept.18, 2013). Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer – kenkremer.com
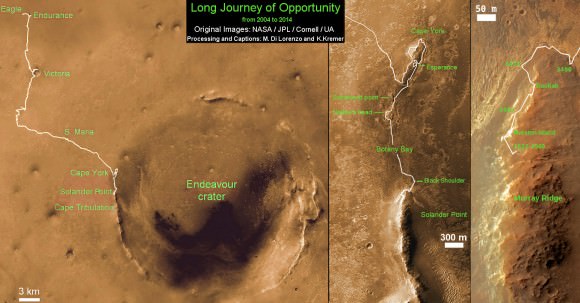
This map shows the entire path the rover has driven during a decade on Mars and over 3552 Sols, or Martian days, since landing inside Eagle Crater on Jan 24, 2004 to current location by f Solander Point summit at the western rim of Endeavour Crater. Rover will spnd 6th winter here atop Solander. Opportunity discovered clay minerals at Esperance – indicative of a habitable zone. Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/ASU/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer













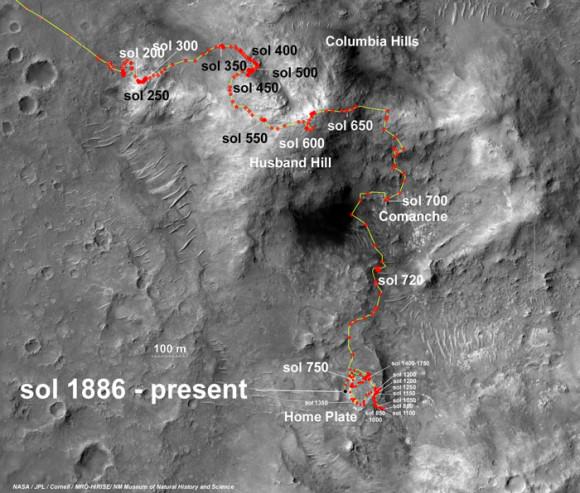
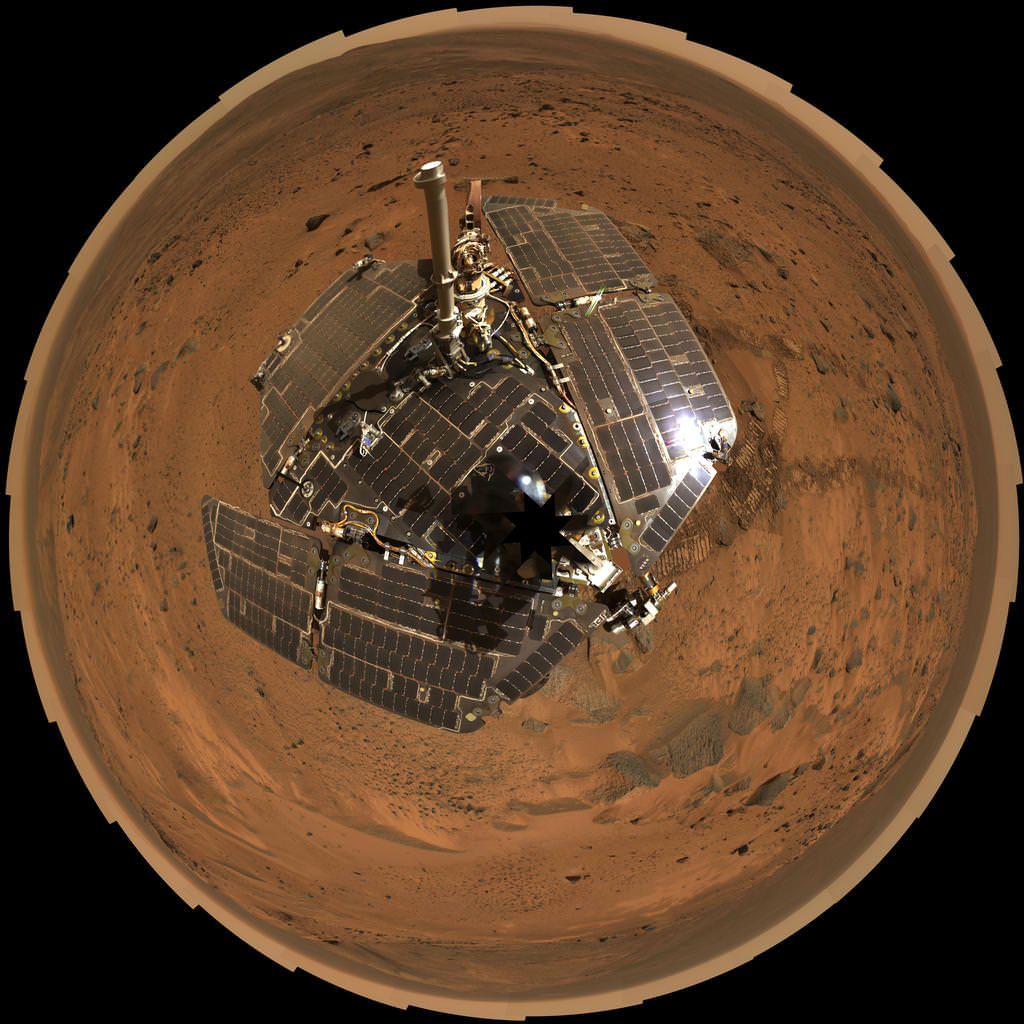




![MER10-SpiritAndOpportunity_ByTheNumbers[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/MER10-SpiritAndOpportunity_ByTheNumbers1-580x423.jpg)