Do exoplanets have exomoons? It would be extraordinary if they didn’t, but as with all things, we don’t know until we know. Astronomers thought they may have found exomoons several years ago around two exoplanets: Kepler-1625b and Kepler-1708b. Did they?
Continue reading “Did We Find Exomoons or Not? The Question Lingers.”Another Explanation for K2-18b? A Gas-Rich Mini-Neptune with No Habitable Surface
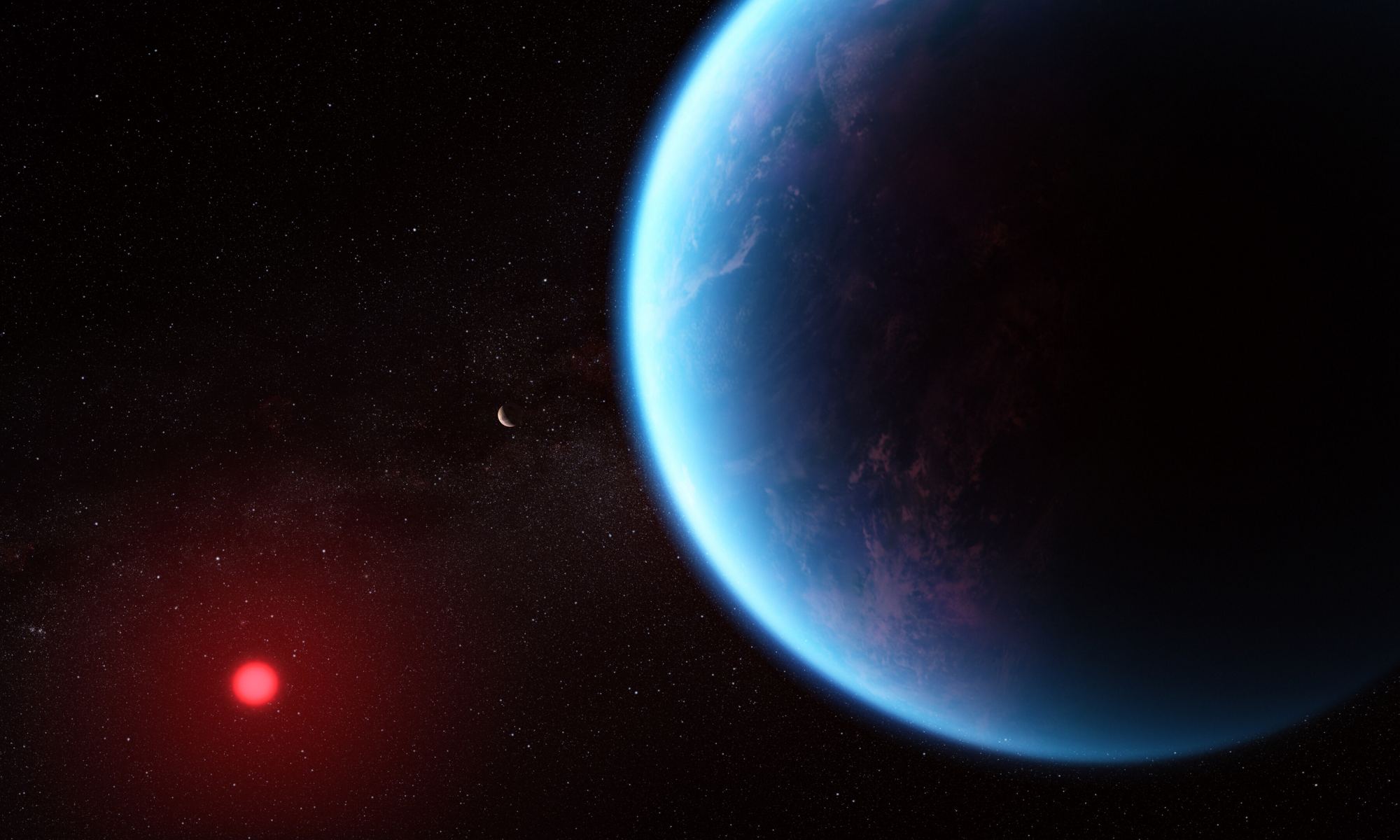

Exoplanet K2-18b is garnering a lot of attention. James Webb Space Telescope spectroscopy shows it has carbon and methane in its atmosphere. Those results, along with other observations, suggest the planet could be a long-hypothesized ‘Hycean World.’ But new research counters that.
Instead, the planet could be a gaseous mini-Neptune.
Continue reading “Another Explanation for K2-18b? A Gas-Rich Mini-Neptune with No Habitable Surface”Exoplanets: Why study them? What are the challenges? What can they teach us about finding life beyond Earth?
Universe Today has explored the importance of studying impact craters and planetary surfaces and what these scientific disciplines can teach us about finding life beyond Earth. We learned that impact craters are caused by massive rocks that can either create or destroy life, and planetary surfaces can help us better understand the geologic processes on other worlds, including the conditions necessary for life. Here, we will venture far beyond the confines of our solar system to the many stars that populate our Milky Way Galaxy and the worlds they orbit them, also known as exoplanets. We will discuss why astronomers study exoplanets, challenges of studying exoplanets, what exoplanets can teach us about finding life beyond Earth, and how upcoming students can pursue studying exoplanets, as well. So, why is it so important to study exoplanets?
Continue reading “Exoplanets: Why study them? What are the challenges? What can they teach us about finding life beyond Earth?”What Could the Extremely Large Telescope See at Proxima Centauri's Planet?
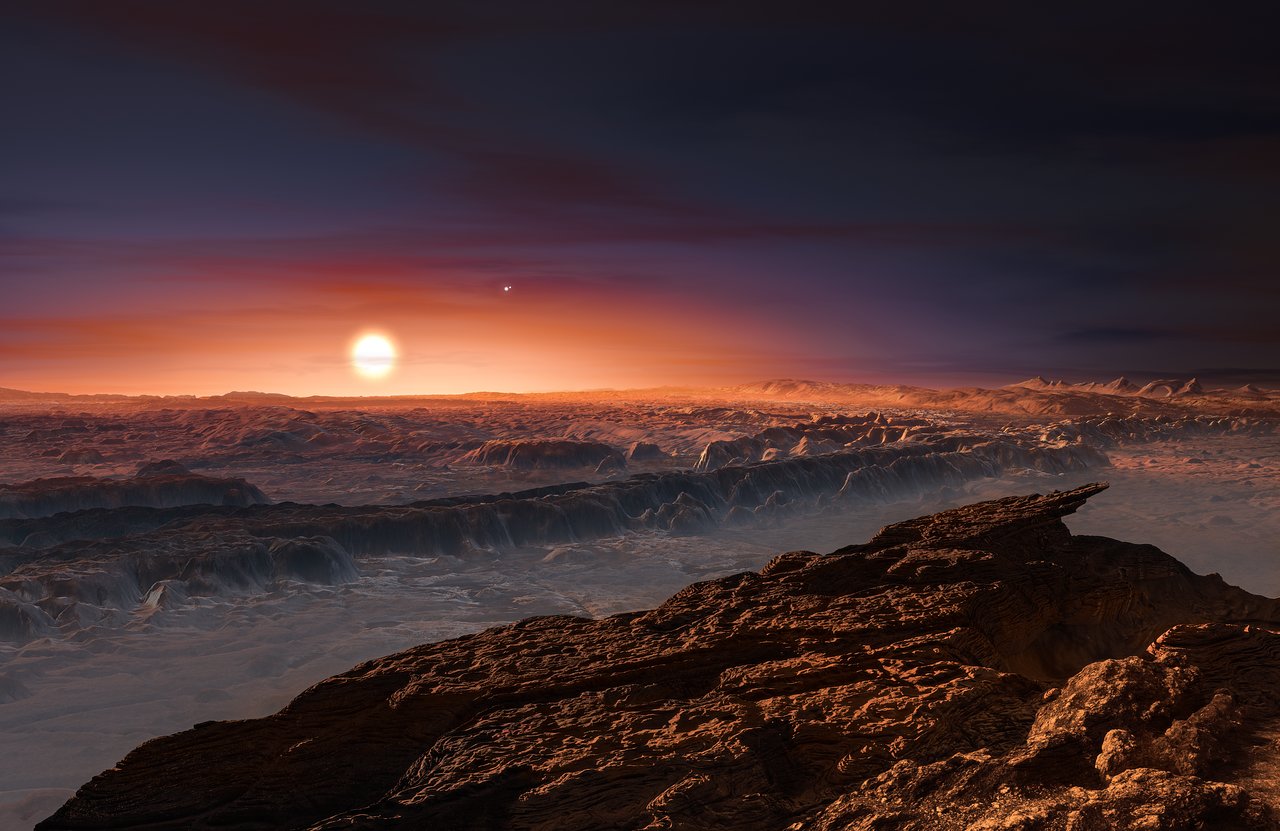

Proxima Centauri B is the closest exoplanet to Earth. It is an Earth-mass world right in the habitable zone of a red dwarf star just 4 light-years from Earth. It receives about 65% of the energy Earth gets from the Sun, and depending on its evolutionary history could have oceans of water and an atmosphere rich with oxygen. Our closest neighbor could harbor life, or it could be a dry rock, but is an excellent target in the search for alien life. There’s just one catch. Our usual methods for detecting biosignatures won’t work with Proxima Centauri B.
Continue reading “What Could the Extremely Large Telescope See at Proxima Centauri's Planet?”Is K2-18b Covered in Oceans of Water or Oceans of Lava?
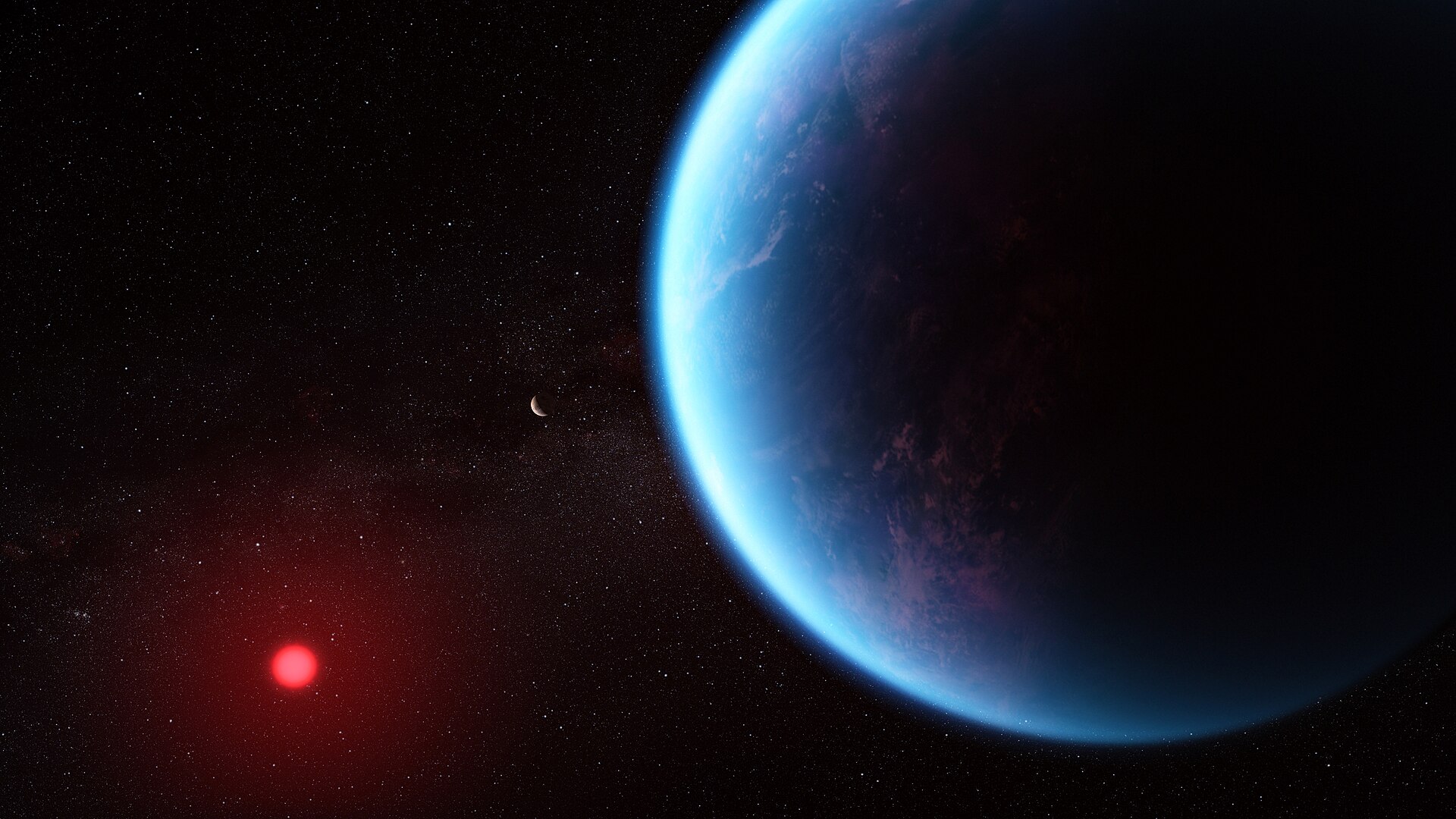

In the search for potentially life-supporting exoplanets, liquid water is the key indicator. Life on Earth requires liquid water, and scientists strongly believe the same is true elsewhere. But from a great distance, it’s difficult to tell what worlds have oceans of water. Some of them can have lava oceans instead, and getting the two confused is a barrier to understanding exoplanets, water, and habitability more clearly.
Continue reading “Is K2-18b Covered in Oceans of Water or Oceans of Lava?”A Hot Jupiter With a Comet-Like Tail
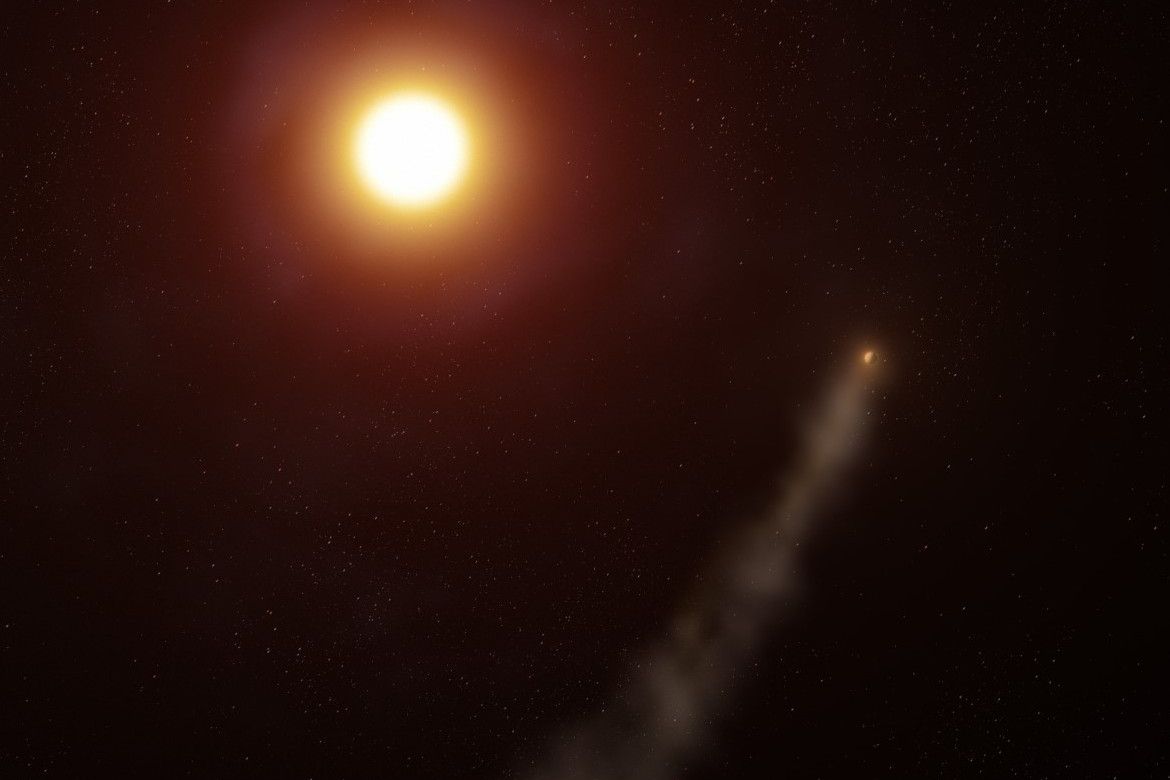

About 164 light-years away, a Hot Jupiter orbits its star so closely that it takes fewer than four days to complete an orbit. The planet is named WASP-69b, and it’s losing mass into space, stripped away by the star’s powerful energy. The planet’s lost atmosphere forms a trail that extends about 560,000 km (350,000 miles) into space.
Continue reading “A Hot Jupiter With a Comet-Like Tail”Big Planets Don’t Necessarily Mean Big Moons
Does the size of an exomoon help determine if life could form on an exoplanet it’s orbiting? This is something a February 2022 study published in Nature Communications hopes to address as a team of researchers investigated the potential for large exomoons to form around large exoplanets (Earth-sized and larger) like how our Moon was formed around the Earth. Despite this study being published almost two years ago, its findings still hold strong regarding the search for exomoons, as astronomers have yet to confirm the existence of any exomoons anywhere in the cosmos. But why is it so important to better understand the potential for large exomoons orbiting large exoplanets?
Continue reading “Big Planets Don’t Necessarily Mean Big Moons”Half of this Exoplanet is Covered in Lava
Astronomers working with TESS (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite) have discovered a planet that’s been left out in the Sun too long. Or at least half of it has. The newly discovered planet is tidally locked to its star, and one side is completely molten.
Continue reading “Half of this Exoplanet is Covered in Lava”Hubble Watches an Exoplanet Atmosphere Change Over Three Years

If you want to know more about an exoplanet atmosphere, watch how it changes over time. That’s the mantra of a group of astronomers who just reported on conditions at Tylos, otherwise known as WASP-121 b.
Continue reading “Hubble Watches an Exoplanet Atmosphere Change Over Three Years”GJ 367b is Another Dead World Orbiting a Red Dwarf
Red dwarf exoplanet habitability is a hot topic in space science. These small dim stars host lots of exoplanets, including small rocky ones the size of Earth. But the little stars emit extremely powerful flares that can damage and strip away atmospheres.
If we’re ever going to understand red dwarf habitability, we need to understand the atmospheres of the exoplanets that orbit them.
Continue reading “GJ 367b is Another Dead World Orbiting a Red Dwarf”


