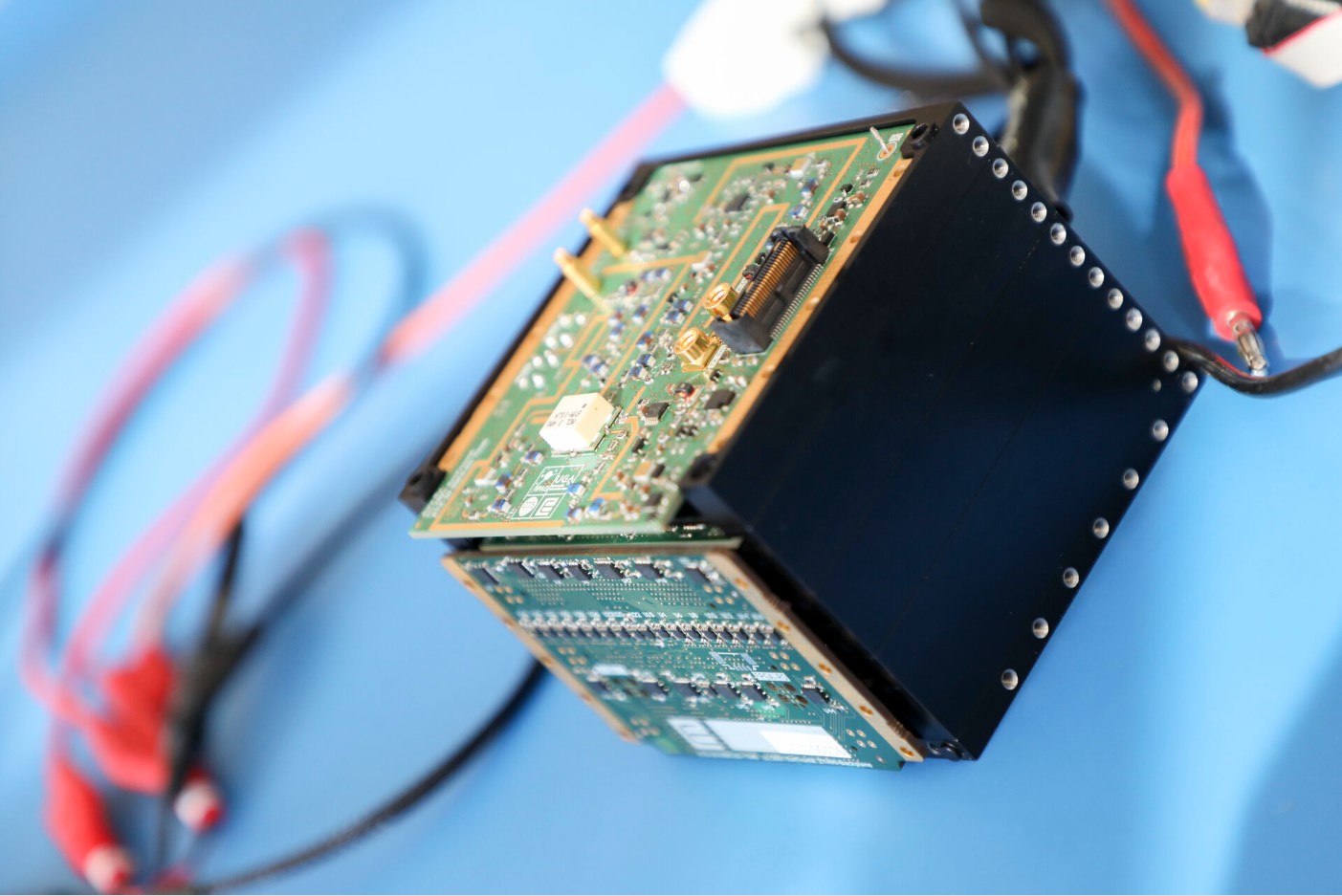
Are miniature probes the future of deep space exploration?
Continue reading “The Smallest Radar Ever Sent to Space Will Probe the Interior of Dimorphos After its Impact From DART”Planets Make it Harder to Figure out a Star’s age
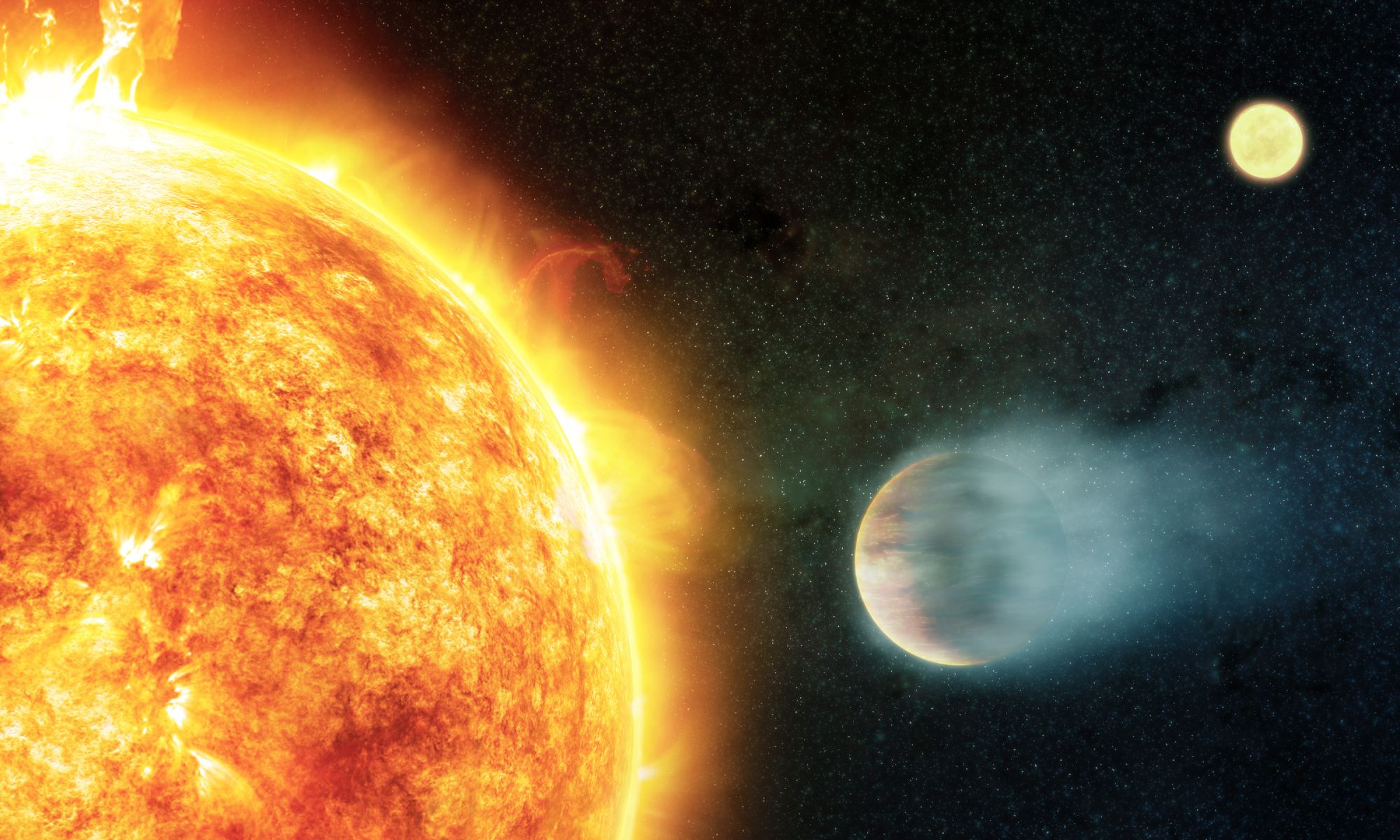

Estimating stellar age has always been a challenge for astronomers. Now, a certain class of exoplanets is making the process even more complicated. Hot Jupiters – gas giants with orbital periods smaller than that of Mercury – appear to have an anti-aging effect on their stars, according to a new study. These enormous planets inflict both magnetic and tidal interference on their host star, speeding up the star’s rotation and causing them to emit X-rays more energetically, both of which are hallmarks of stellar youth. The result calls into question some of what we previously believed about stellar age, and offers a glimpse at the ongoing interconnectivity between a star and its planets long after their formation.
Continue reading “Planets Make it Harder to Figure out a Star’s age”Satellites can now Measure the Thickness of Ice Sheets all Year Long
Artificial intelligence can do more than paint planets as bowls of soup. It’s now helping researchers acquire better climate change data by teaching Earth observation satellites how to measure ice thickness in the Arctic year-round.
Continue reading “Satellites can now Measure the Thickness of Ice Sheets all Year Long”We Still Have no Idea if it's Safe to be Pregnant in Space
Can humans reproduce in space? The short answer is that we don’t know. The long answer is maybe, but there are significant barriers to overcome to make zero-gravity pregnancy safe, and research into the subject is only just beginning.
Continue reading “We Still Have no Idea if it's Safe to be Pregnant in Space”A New Map Shows how Solar Winds Rain Down Everywhere on Mars
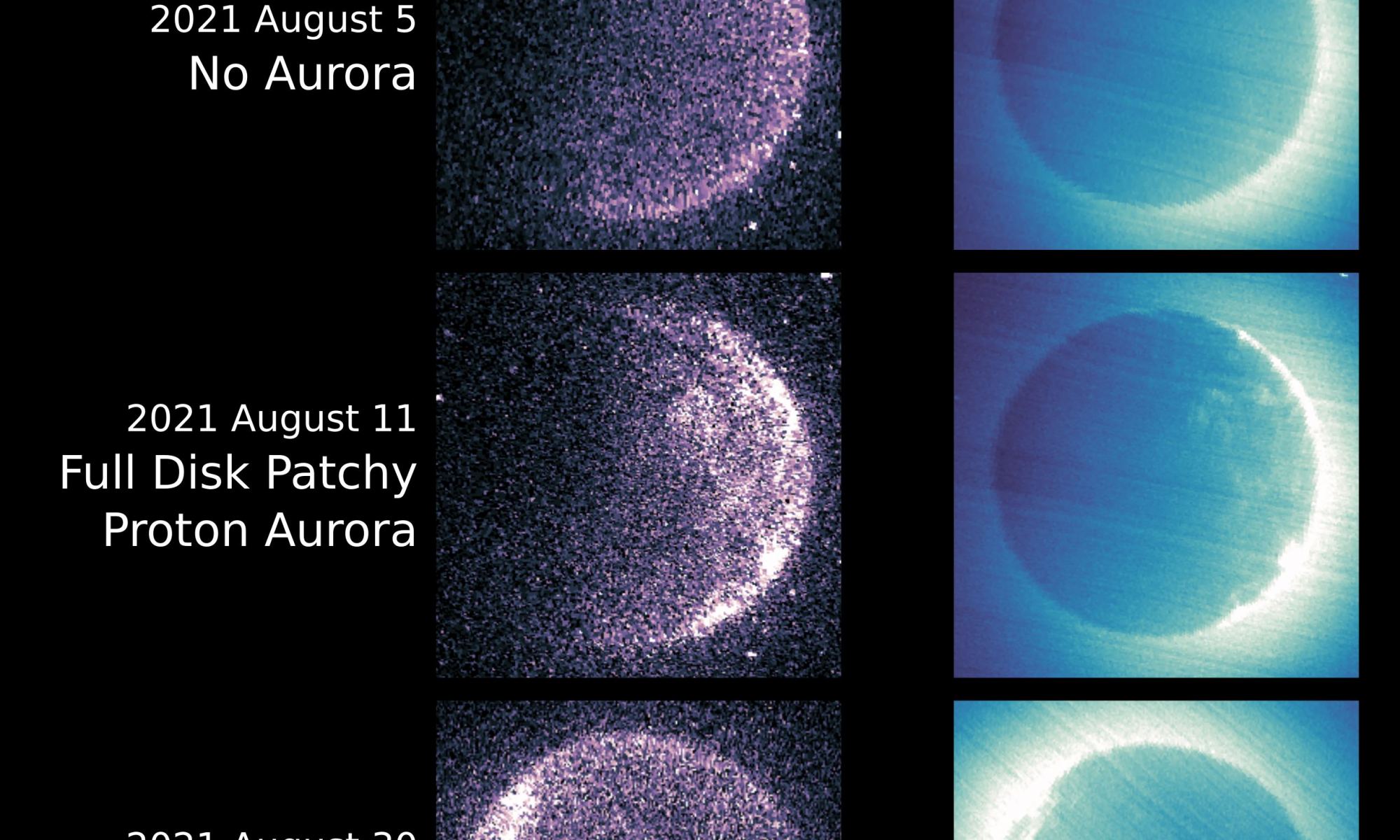
In a joint effort between NASA’s MAVEN spacecraft and the United Arab Emirates’ Emirates Mars mission (EMM), scientists have observed an uncommonly chaotic interaction between the solar wind and Mars’ upper atmosphere, creating a unique ultraviolet aurora. The phenomenon represents an unusual occurrence in Martian space weather, and scientists are excited to take advantage of future collaborations between spacecraft to keep an eye out for repeat events.
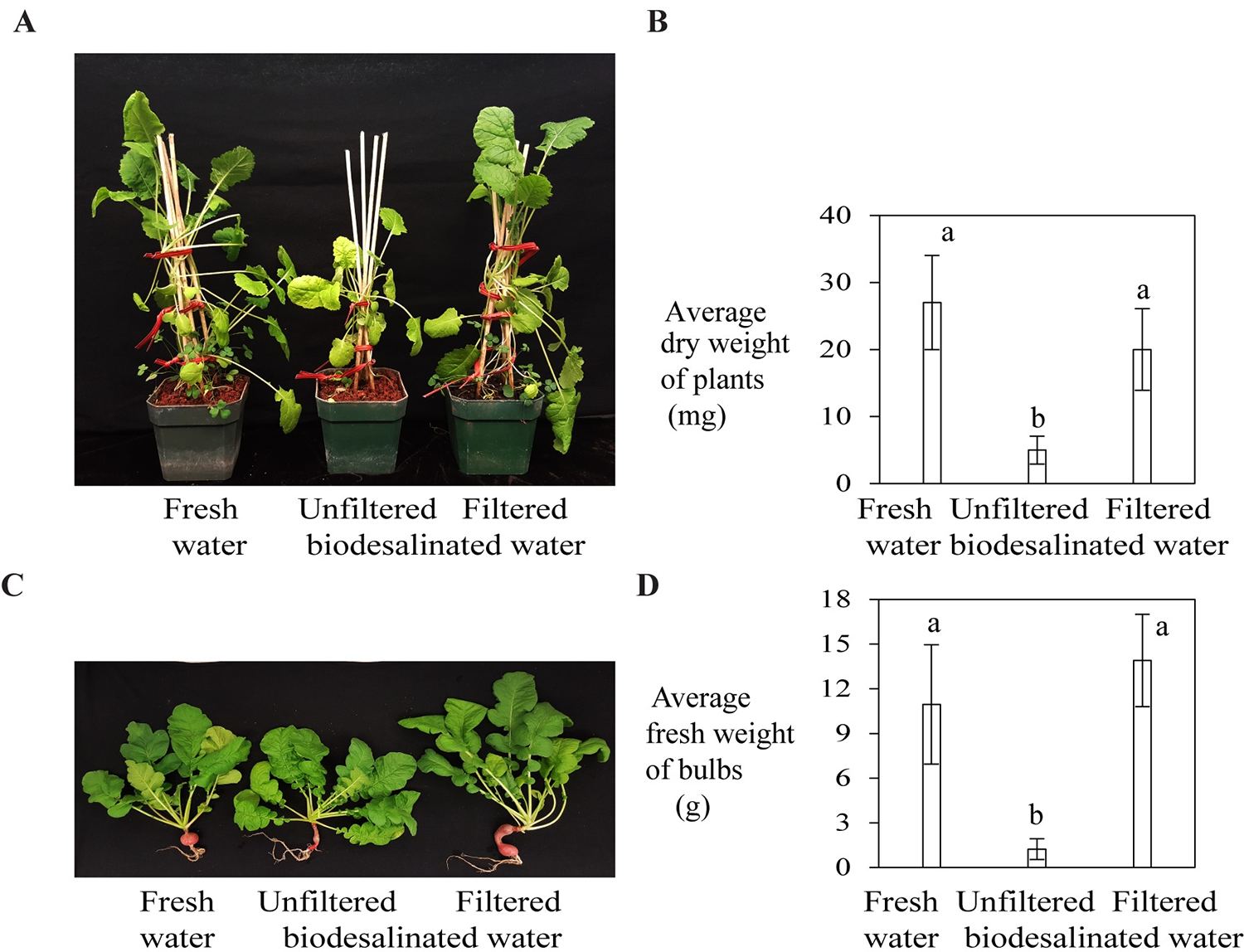
Continue reading “A New Map Shows how Solar Winds Rain Down Everywhere on Mars”The First Crops on Mars Should be Alfalfa and Cyanobacteria. Then Comes Tastier Plants
Mark Watney can keep his potatoes. Real astronauts should grow alfalfa.
Continue reading “The First Crops on Mars Should be Alfalfa and Cyanobacteria. Then Comes Tastier Plants”Lunar Rocks Have Earth's Noble Gases Trapped Inside. More Evidence That the Moon Came From the Earth
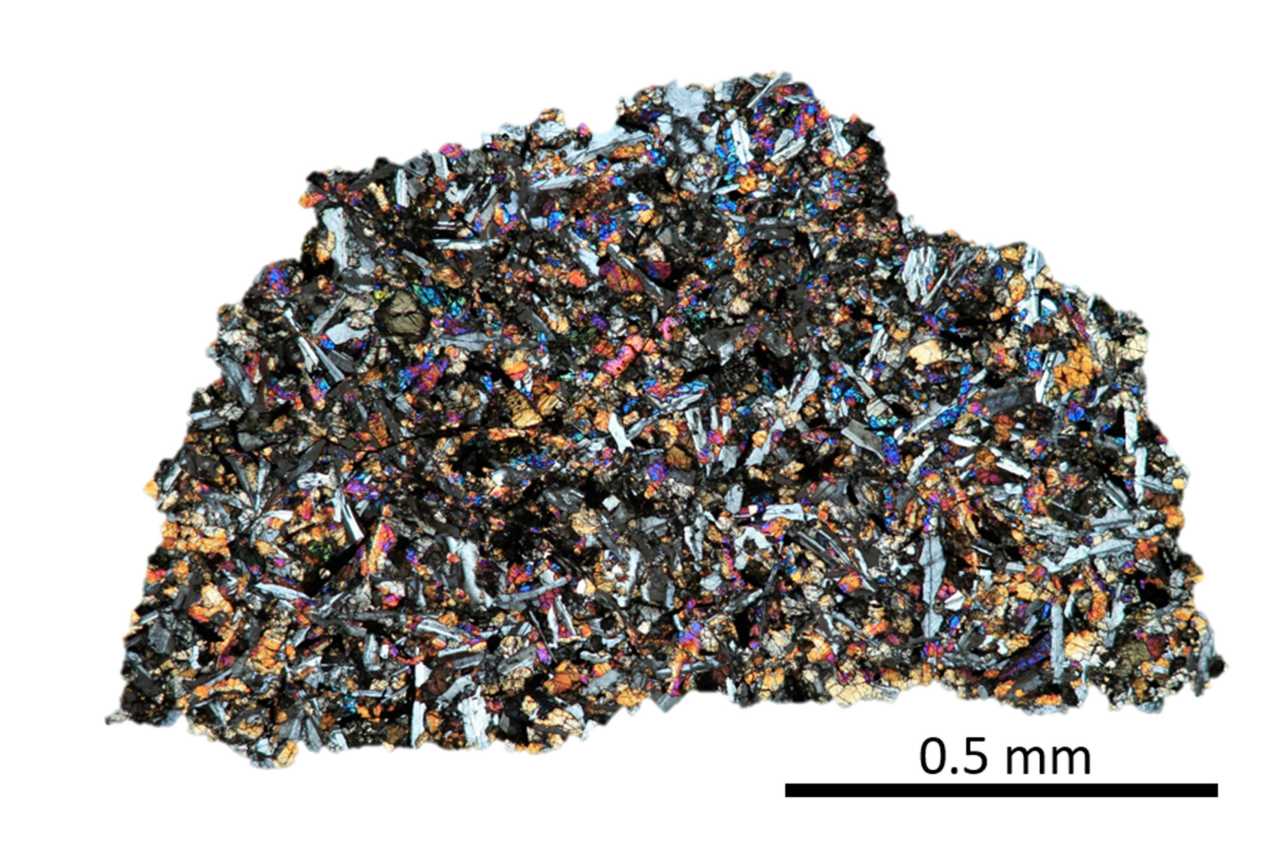
Piecing together the history of the Solar System from the traces left behind isn’t easy. Bit by bit, however, we’re working it out. This month, new research examining the composition of lunar meteorites offers compelling evidence that the Moon and the Earth were formed from the same material, perhaps in the aftermath of a cataclysmic collision some 4.5 billion years ago.
Continue reading “Lunar Rocks Have Earth's Noble Gases Trapped Inside. More Evidence That the Moon Came From the Earth”An Interstellar Meteor Struck the Earth in 2014, and now Scientists Want to Search for it at the Bottom of the Ocean
Back in 2014, an object crashed into the ocean just off the coast of Papua New Guinea. Data collected at the time indicated that the meteorite just might be an interstellar object, and if that’s true, then it’s only the third such object known (after Oumuamua and Borisov), and the first known to exist on Earth. Launching an undersea expedition to find it would be a long shot, but the scientific payoff could be enormous.
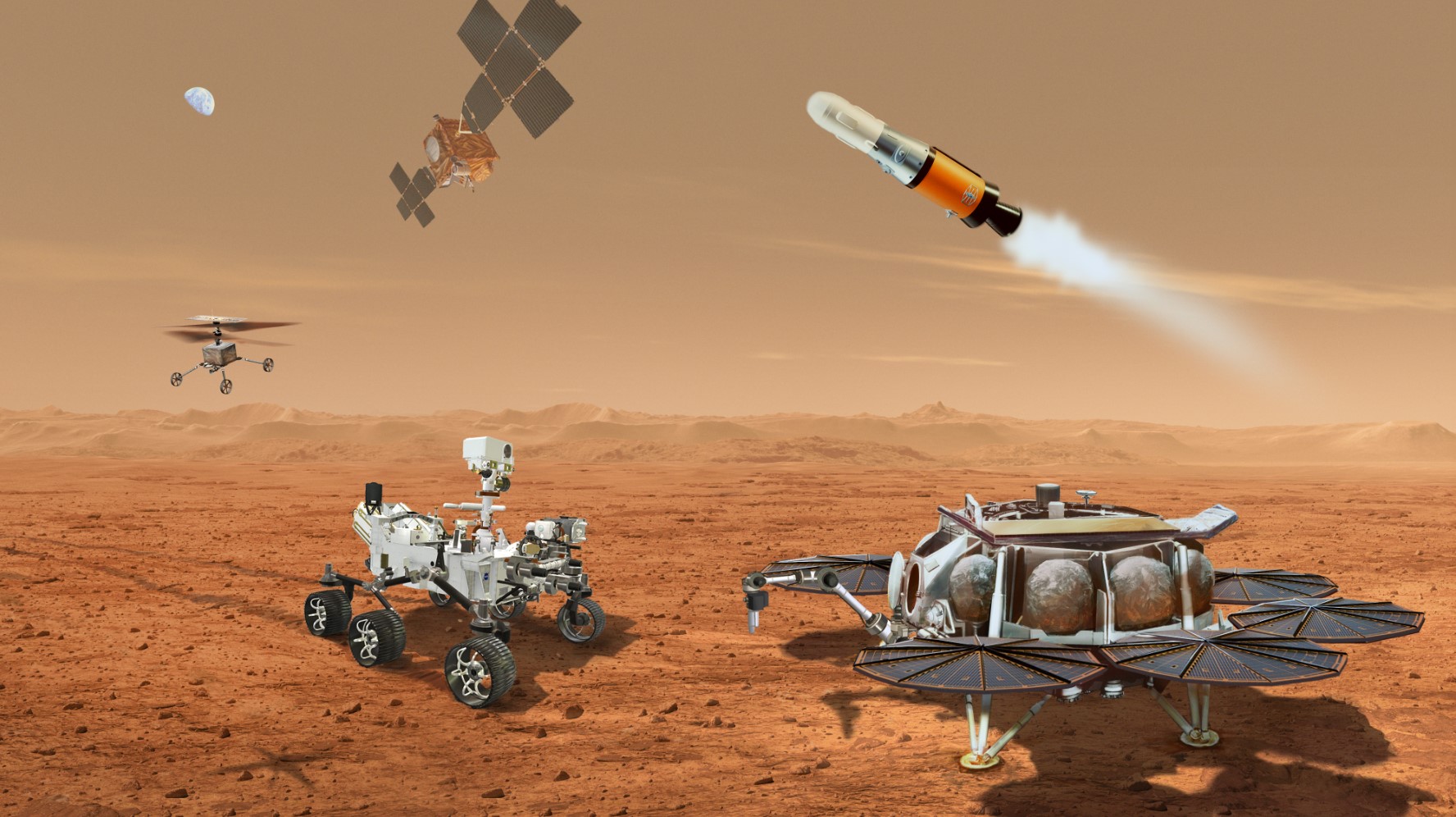
Continue reading “An Interstellar Meteor Struck the Earth in 2014, and now Scientists Want to Search for it at the Bottom of the Ocean”The Mars Sample Return Mission Will Take Two Helicopters to the Red Planet to Help Retrieve Samples
NASA’s upcoming Mars Sample Return mission plan just received a glow-up: it will now carry a pair of twin helicopters, each capable of retrieving samples and delivering them to the ascent vehicle for return to Earth.
Continue reading “The Mars Sample Return Mission Will Take Two Helicopters to the Red Planet to Help Retrieve Samples”Betelgeuse and Antares Have Been Observed for Over 2,000 Years. Astronomers can use This to Figure out how old They are
Stars don’t usually evolve fast enough for humans to notice them change within one lifetime. Even a hundred lifetimes won’t do – astronomical processes are just too slow. But not always. There are some phases of stellar evolution that happen quickly, and when they do, they can be tracked. A new paper posted to ArXiv last week uses astronomical observations found in ancient Roman texts, medieval astronomical logs, and manuscripts from China’s Han Dynasty to trace the recent evolution of several bright stars, including red supergiant Antares, and Betelgeuse: one of the most dynamic stars in our sky. With observations from across the historical record, the paper suggests that Betelgeuse may have just recently passed through the ‘Hertzsprung gap,’ the transitional phase between a main sequence star and its current classification as a red supergiant.
Continue reading “Betelgeuse and Antares Have Been Observed for Over 2,000 Years. Astronomers can use This to Figure out how old They are”