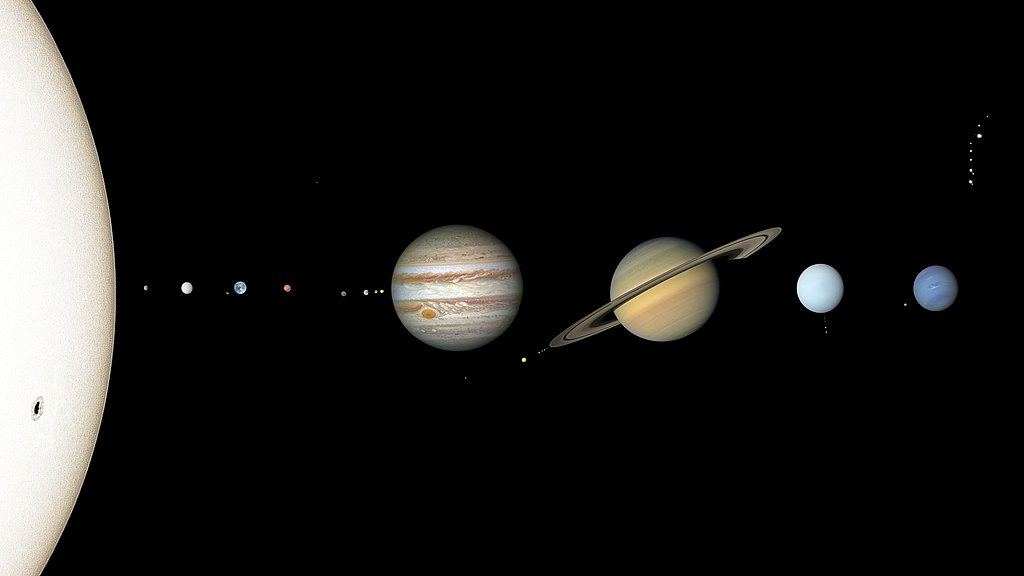
It’s nice to have a feel-good story every once in a while, so here’s one to hold off the existential dread: the Earth isn’t likely to get flung off into deep space for at least 100,000 years. In fact, all of the Solar System’s planets are safe for that time frame, so there is good news all around, for you and your favorite planetary body.
Continue reading “The Solar System is Stable for at Least the Next 100,000 Years”Remember That Rocket That was Going to Crash Into the Moon? Scientists Think They've Found the Crater
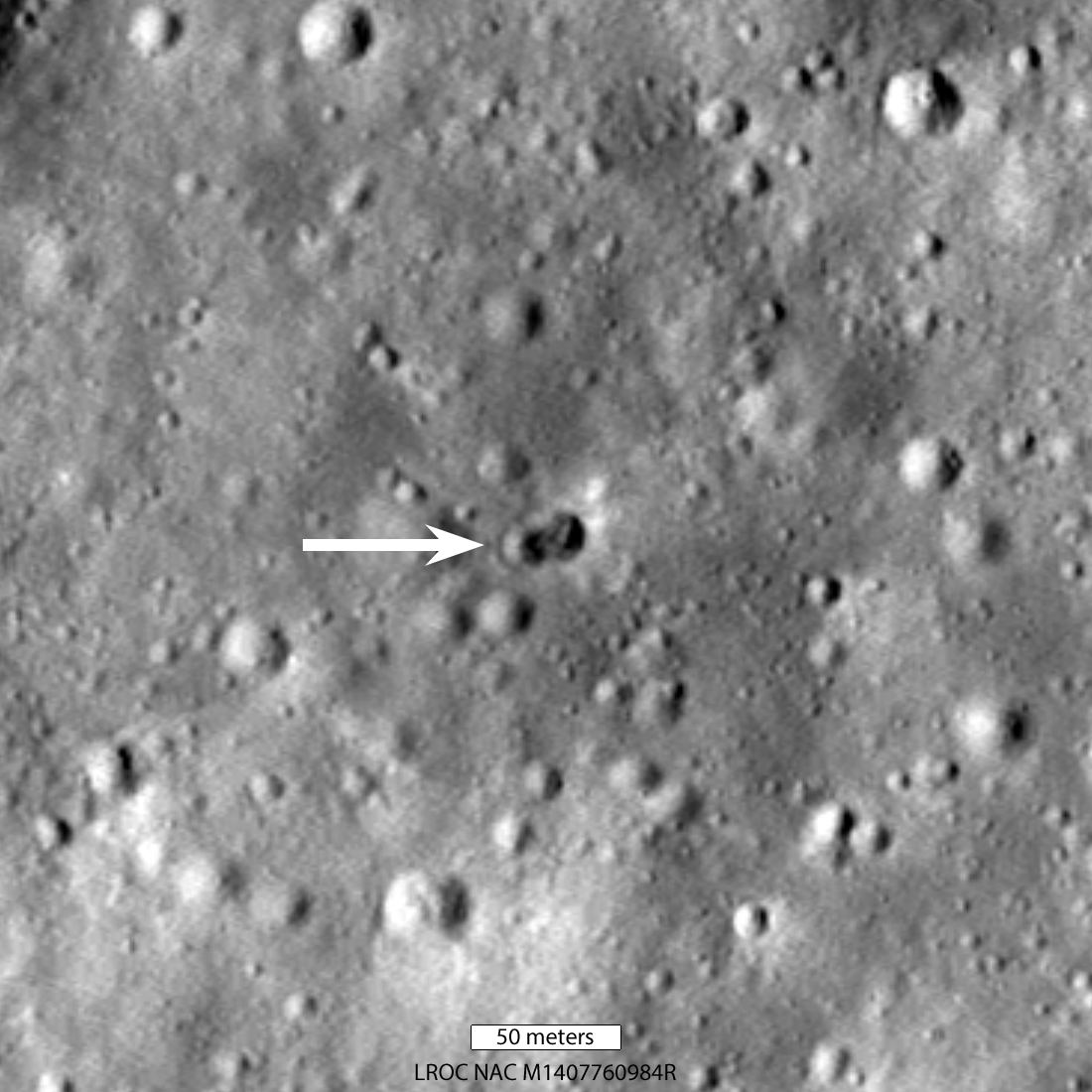
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) – NASA’s eye-in-the-sky in orbit around the Moon – has found the crash site of the mystery rocket booster that slammed into the far side of the Moon back on March 4th, 2022. The LRO images, taken May 25th, revealed not just a single crater, but a double crater formed by the rocket’s impact, posing a new mystery for astronomers to unravel.
Continue reading “Remember That Rocket That was Going to Crash Into the Moon? Scientists Think They've Found the Crater”Once Again, Galaxies Look Surprisingly Mature Shortly After the Beginning of the Universe
A young galaxy with the catchy, roll-off-the-tongue name A1689-zD1 has experts in galactic formation talking. Recent observations show that this galaxy, seen as it would have looked just 700 million years after the Big Bang, is larger than initially believed, with significant outflows of hot gas from its core, and a halo of cold gas emanating from its outer rim. A1689-zD1 is considered representative of young ‘normal’ galaxies (as opposed to ‘massive’ galaxies), and the new observations suggest that the adolescence of normal galaxies may be more rambunctious than previous models suggest.
Continue reading “Once Again, Galaxies Look Surprisingly Mature Shortly After the Beginning of the Universe”Spacesuits are Leaking Water and NASA is Holding off any Spacewalks Until They can Solve the Problem
NASA’s spacesuits are getting old. The extra-vehicular mobility units – EMUs for short – were designed and built for spacewalks outside NASA’s space shuttles, which flew for the last time in 2011. Nowadays, the EMUs are an integral part of maintaining and upgrading the International Space Station (ISS) exterior, providing the crew with the ability to live and work in the vacuum of space for extended periods of time (spacewalks regularly last from 6 to 8 hours). However, at the end of the most recent spacewalk on March 23, NASA astronaut Kayla Barron discovered water in the helmet of German astronaut Matthias Maurer while she helped him remove the suit.
Continue reading “Spacesuits are Leaking Water and NASA is Holding off any Spacewalks Until They can Solve the Problem”Cosmic Rays can Help Keep the World's Clocks in Sync
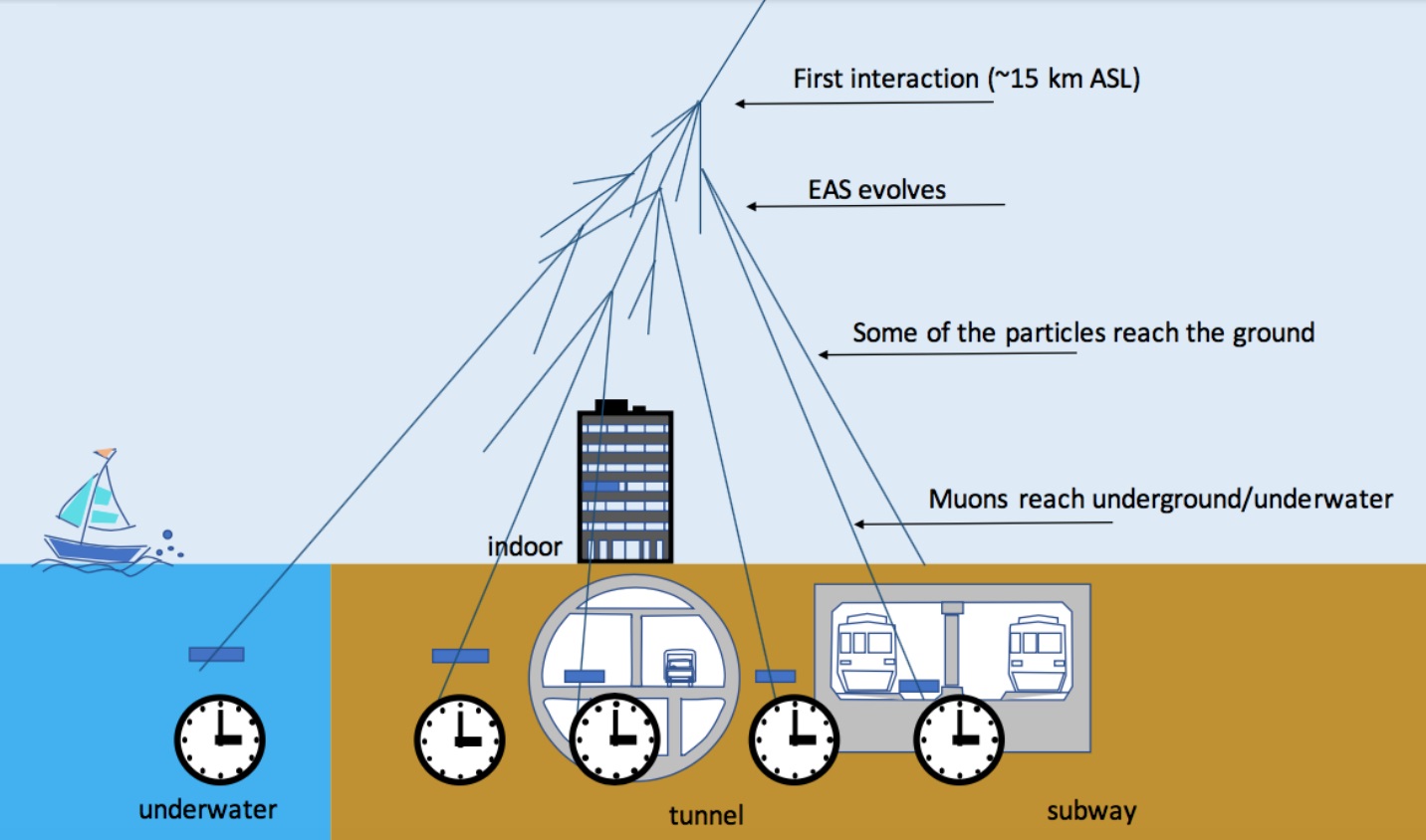
The world has a robust, accurate timekeeping system that regulates our clocks. Humanity uses it for everything we do, from our financial systems to satellite navigation, computer and phone networks, and GPS. But the current system is not perfect, and has vulnerabilities to cyber-attack and disruption. Given the importance of accurate timekeeping to our society (as a fundamental underpinning of life in the 21st century), experts are always looking for ways to improve the system and add redundancy. Researchers at the University of Tokyo have taken a big step in this direction, developing a new method of time synchronization that takes advantage of cosmic rays to calibrate the world’s clocks.
Continue reading “Cosmic Rays can Help Keep the World's Clocks in Sync”‘The Clocks are Telling Lies:’ A New Book from Universe Today Writer Scott Alan Johnston
Scott Alan Johnston (that’s me!) joined the Universe Today team just over a year ago. Since then, I’ve written over 50 space news stories for the website – time flies when you’re having fun! But when I’m not writing articles here on Universe Today, I’m a historian of science, and I recently released a new book about the history of timekeeping.
Have you ever wondered why we tell time the way we do? Well, history buffs, come along for a journey:
Continue reading “‘The Clocks are Telling Lies:’ A New Book from Universe Today Writer Scott Alan Johnston”Even Stars Doomed to Die as Supernovae can Have Planets
90 percent of all exoplanets discovered to date (there are now more than 5000 of them) orbit around stars the same size or smaller than our sun. Giant stars seem to lack planetary companions, and this fact has serious implications for how we understand solar system formation. But is the dearth of planets around large stars a true reflection of nature, or is there some bias inherent in how we look for exoplanets that is causing us to miss them? The recent discovery of two gas giants orbiting a giant star called µ2 Scorpii suggests it might be the latter.
Continue reading “Even Stars Doomed to Die as Supernovae can Have Planets”China is Building an Asteroid Deflection Mission of its own, due for Launch in 2025
There’s an old joke that the dinosaurs are only extinct because they didn’t develop a space agency. The implication, of course, is that unlike our reptilian ancestors, we humans might be able to save ourselves from an impending asteroid strike on Earth, given our six-and-a-half decades of spaceflight experience. But the fact is that while we have achieved amazing things since Sputnik kicked off the space age in 1957, very little effort thus far has gone into developing asteroid deflection technologies. We are woefully inexperienced in this arena, and aside from our Hollywood dramatizations of it, we’ve never yet put our capabilities to the test. But that’s about to change.
Continue reading “China is Building an Asteroid Deflection Mission of its own, due for Launch in 2025”NASA is Ready to try and fix Lucy’s Unlatched Solar Panel
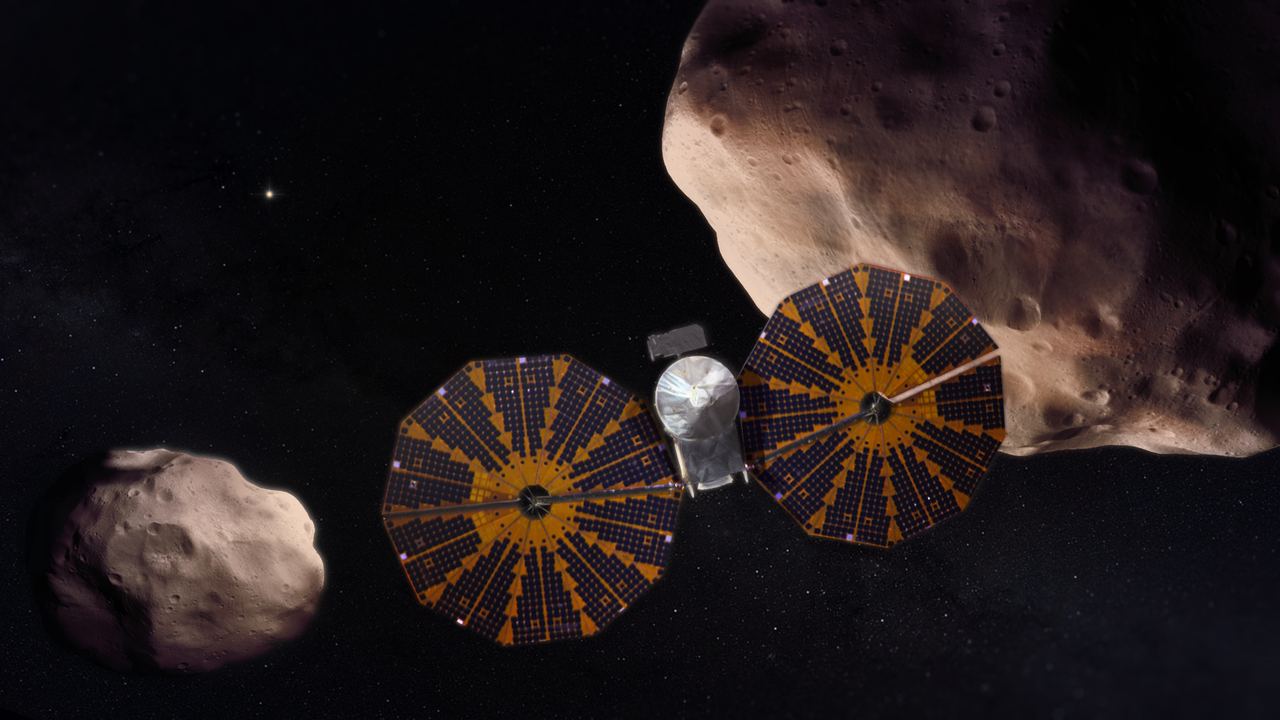
NASA’s Lucy spacecraft, currently on its way to the outer Solar System to study Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids, has a solar panel problem. Shortly after its launch last October, engineers determined that one of Lucy’s two solar panels failed to open completely. While the spacecraft has enough power to function, the team is concerned about how the unlatched panel might hinder Lucy’s performance going forward. In an attempt to fix the problem, the team will carry out a new procedure next month that is designed to unfurl the solar panel the rest of the way, and latch it firmly in place.
Continue reading “NASA is Ready to try and fix Lucy’s Unlatched Solar Panel”Life Might Have Gotten Started Just 300 Million Years After the Earth Formed
On an outcrop of exposed volcanic and sedimentary rock on the eastern shores of Hudson Bay in northern Quebec, researchers have discovered what may be the earliest fossilized lifeforms ever discovered. These microbial ancestors lived between 3.75 and 4.28 billion years ago, only 300 million years after the Earth itself formed – a blink of an eye in geologic timescales. If life developed this rapidly on Earth, it suggests that abiogenesis – the process by which non-living matter becomes a living organism – is potentially ‘easy’ to achieve, and life in the Universe may be more common than we thought.
Continue reading “Life Might Have Gotten Started Just 300 Million Years After the Earth Formed”