The Cassini spacecraft is nearing the end of its lifespan. This September, after spending the past twenty years in space – twelve and a half of which were dedicated to studying Saturn and its system of moons – the probe will be crash into Saturn’s atmosphere. But between now and then, the probe will be making its “Grand Finale” – the final phase of its mission where it will dive between the planet and its rings 22 times.
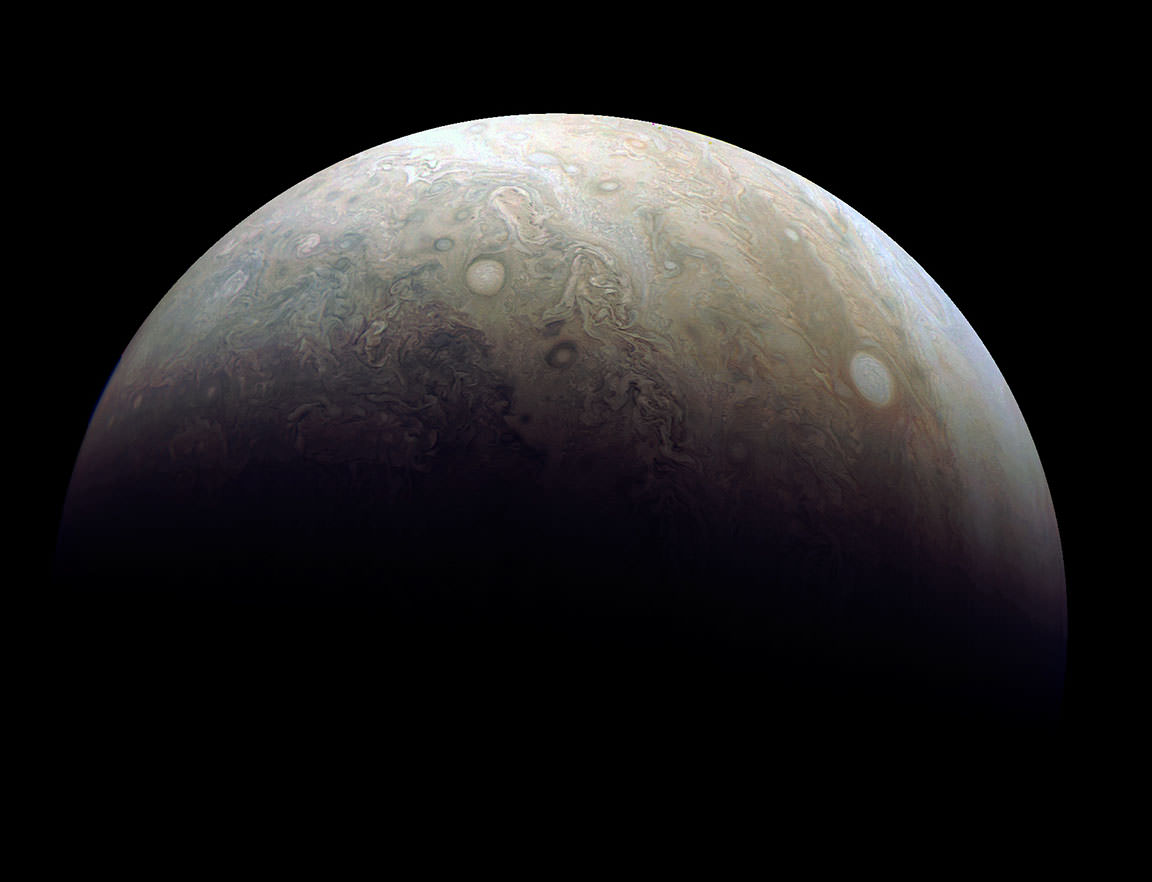
In addition to exploring this region of Saturn (something no other mission has done), the probe will also be using this opportunity to study Saturn’s hexagonal polar jet stream in greater detail. This persistent storm, which rages around Saturn’s northern polar region, has been a subject of interest for decades. And now that it enjoys full sunlight, Cassini will be able to directly image it with every pass it makes over Saturn’s north pole.
This persistent storm was first noticed in images sent back by the Voyager 1 and 2 missions, which flew by Saturn in 1980 and 1981, respectively. As storms go, it is extremely massive, with each side measuring about 13,800 km (8,600 mi) in length – longer than the diameter of the Earth. It also rotates with a period of 10 hours 39 minutes and 24 seconds, which is assumed to be equal to the rotation of Saturn’s interior.
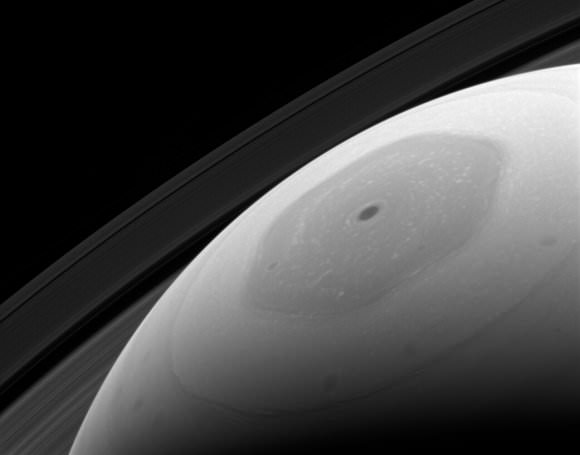

When the Cassini spacecraft arrived around Saturn in 2004 to conduct the first part of its mission, this region was in shadow. This was due to the fact that the northern hemisphere was still coming out of winter, and was hence tilted away from the Sun. However, since Saturn began its summer solstice in May of 2017, the northern polar region is now fully illuminated – at least by Saturn’s standards.
In truth, between its distance from the Sun (an average of 9.5549 AU) and its axial tilt (26.73°), the northern polar region only gets about 1% as much sunlight as Earth does. And from the perspective of the north pole, the Sun is very low in the sky. Nevertheless, the sunlight falling on the north pole at this point is enough to allow the Cassini mission to directly image the region by capturing its reflected light.
Images of the hexagonal jet stream (like the one above) will be taken by Cassini’s wide-angle camera, which uses special filters that admit wavelengths of near-infrared light. Already, Cassini has captured some impressive imagery during its first plunge between Saturn and its rings (which took place on April 26th, 2017). The rapid-fire images acquired by one of Cassini’s cameras were then stitched together to create a movie (posted below).
As you can see, the movie begins with a view of the vortex at the center of the hexagon, then heads past the outer boundary of the jet stream and continues further southward. Toward the end of the movie, the spacecraft reorients itself to direct its saucer-shaped antenna in the direction of the spacecraft’s motion, which is apparent from the way the camera frame rotates.
The images that make up this movie were captured as the Cassini spacecraft dropped in altitude from 72,400 to 6,700 km (45,000 to 4,200 miles) above Saturn’s cloud tops. As this happened, the features which the camera could resolve changed drastically – going from 8.7 km (5.4 mi) per pixel to 810 meters (0.5 mi) per pixel.
The movie was produced by Kunio Sayanagi and John Blalock – an associate of the Cassini imaging team and a graduate research assistant (respectively) at Hampton University in Virginia – who collaborated with the Cassini imaging team. And thanks to this video, new insights are already being made into the hexagonal jet stream and the mechanisms that power it.
For example, as Sayanagi indicated in a NASA press release, the video captured the boundary regions of the jet stream rather nicely, which allowed him to note an interesting fact about them. “I was surprised to see so many sharp edges along the hexagon’s outer boundary,” he said. “Something must be keeping different latitudes from mixing to maintain those edges.”
Andrew Ingersoll, a member of the Cassini imaging team based at Caltech, expressed how similar movies will result from future plunges taken as part of the Grand Finale. “The images from the first pass were great, but we were conservative with the camera settings,” he said. “We plan to make updates to our observations for a similar opportunity on June 29th that we think will result in even better views.”
Between now and the end of the mission, who knows what we might learn about this mysterious storm? The next plunge – aka. Grand Finale Dive No. 4 – will take place on Sunday, May 15th at 4:42 p.m. UTC (12:42 p.m EDT; 9:42 a.m. PDT). A total of 22 dives will be made on a weekly basis before the probe takes the final plunge – the one that will cause it to breakup in Saturn’s atmosphere – on Friday, September 15th, 2017.
For more information, consult Cassini’s Grand Finale Orbit Guide. And be sure to enjoy this video of the final phase of the probe’s mission, courtesy of NASA: