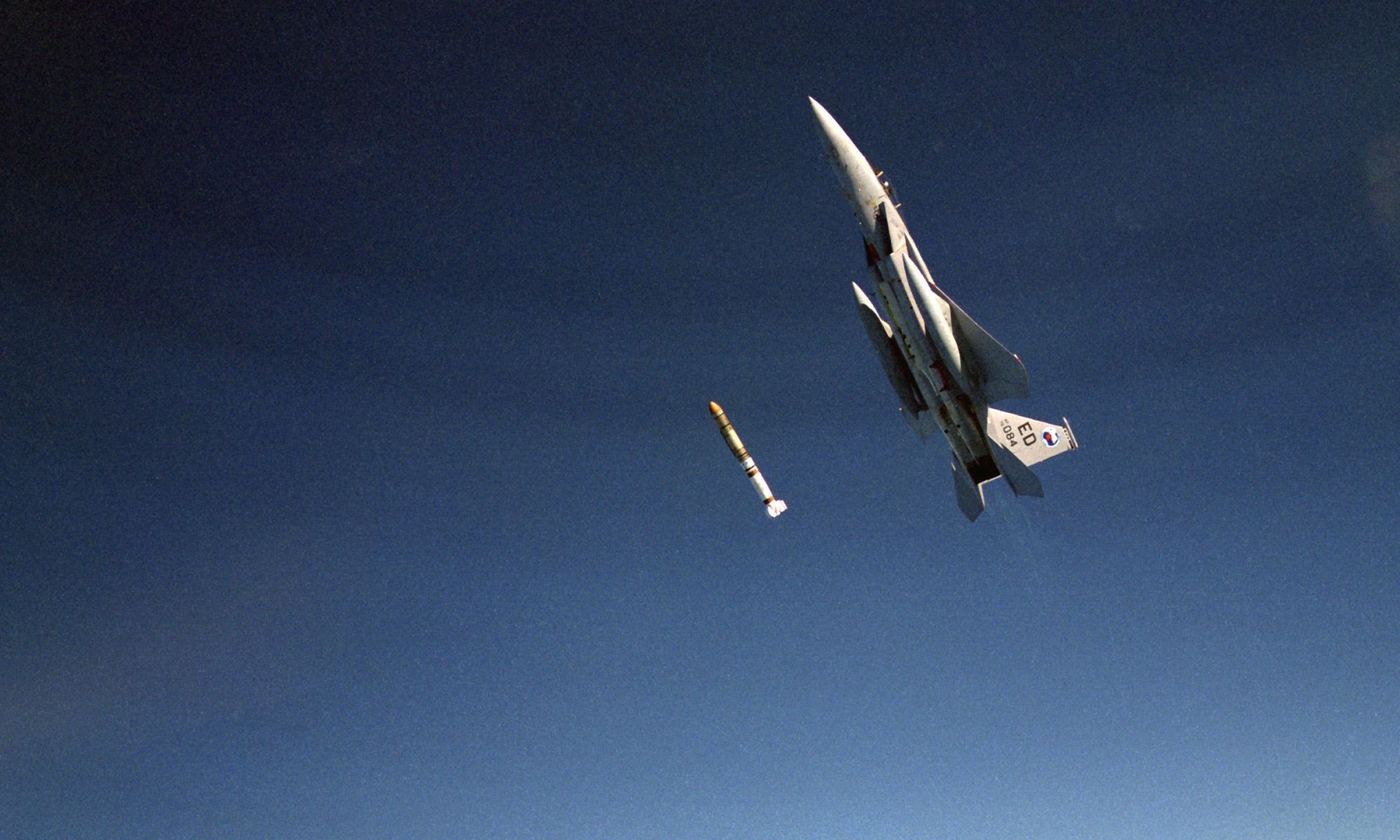
As long as human beings have been sending satellites into space, they have been contemplating ways to destroy them. In recent years, the technology behind anti-satellite (ASAT) weapons has progressed considerably. What’s more, the ability to launch and destroy them extends beyond the two traditional superpowers (the US and Russia) to include newcomers like India, China, and others.
For this reason, Sandia National Laboratories – a federal research center headquartered in New Mexico – has launched a seven-year campaign to develop autonomous satellite protection systems. Known as the Science and Technology Advancing Resilience for Contested Space (