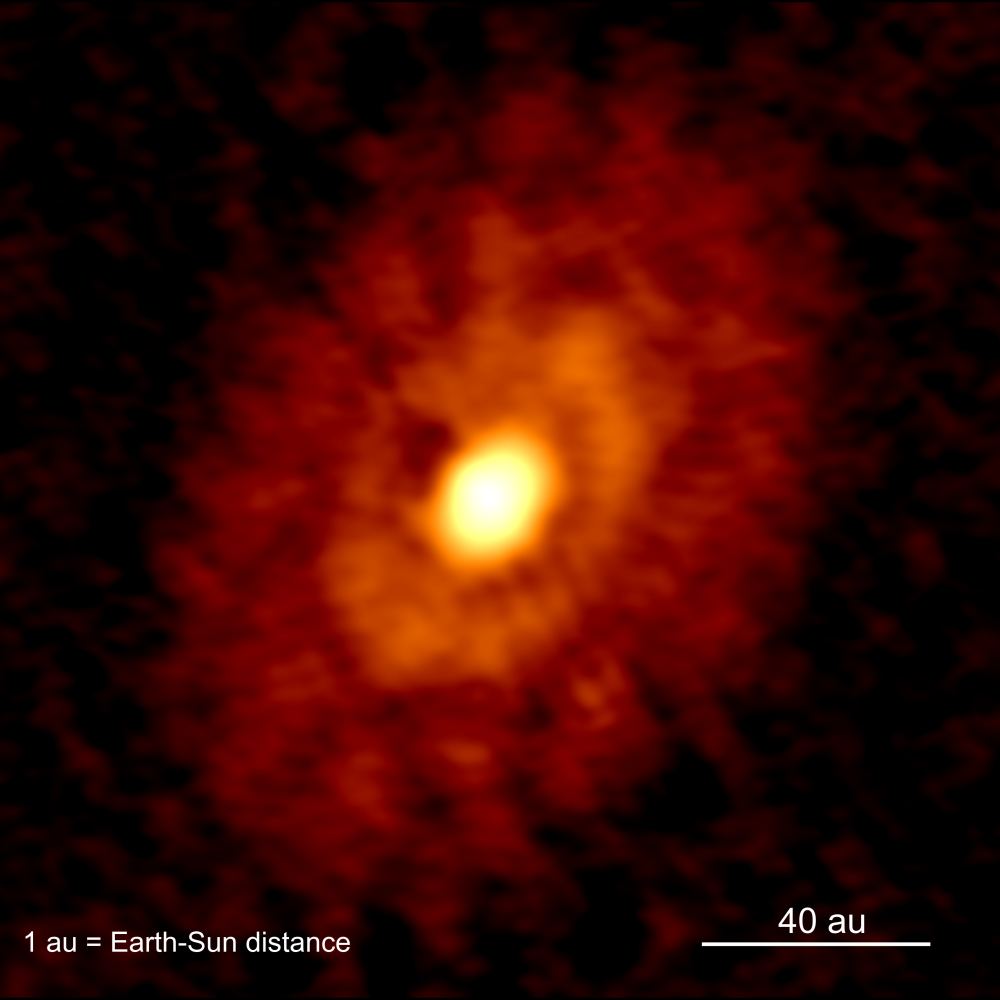
It looks like we may have to update our theories on how stars and planets form in new solar systems. A team of astronomers has discovered young planets forming in a solar system that’s only about 500,000 years old. Prior to this discovery, astronomers thought that stars are well into their adult life of fusion before planets formed from left over material in the circumstellar disk.
Now, according to a new study, it looks like planets and stars can form and grow up together.
Continue reading “Planets Don’t Wait for Their Star to Form First”