Our nearest star has exhibited some schizophrenic behavior thus far for 2013.
By all rights, we should be in the throes of a solar maximum, an 11-year peak where the Sun is at its most active and dappled with sunspots.
Thus far though, Solar Cycle #24 has been off to a sputtering start, and researchers that attended the meeting of the American Astronomical Society’s Solar Physics Division earlier this month are divided as to why.“Not only is this the smallest cycle we’ve seen in the space age, it’s the smallest cycle in 100 years,” NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center research scientist David Hathaway said during a recent press teleconference conducted by the Marshall Space Flight Center.
Cycle #23 gave way to a profound minimum that saw a spotless Sol on 260 out of 365 days (71%!) in 2009. Then, #Cycle 24 got off to a late start, about a full year overdue — we should have seen a solar maximum in 2012, and now that’s on track for the late 2013 to early 2014 time frame. For solar observers, both amateur, professional and automated, it seems as if the Sun exhibits a “split-personality” this year, displaying its active Cycle #24-self one week, only to sink back into a blank despondency the next.
This new cycle has also been asymmetrical as well. One hallmark heralding the start of a new cycle is the appearance of sunspots at higher solar latitudes on the disk of the Sun. These move progressively toward the Sun’s equatorial regions as the cycle progresses, and can be mapped out in what’s known as a Spörer’s Law.

But the northern hemisphere of the Sun has been much more active since 2006, with the southern hemisphere experiencing a lag in activity. “Usually this asymmetry lasts a year or so, and then the hemispheres synchronize,” said Giuliana de Toma of the High Altitude Observatory.
So far, several theories have been put forth as to why our tempestuous star seems to be straying from its usual self. Along with the standard 11-year cycle, it’s thought that there may be a longer, 100 year trend of activity and subsidence known as the Gleissberg Cycle.
The Sun is a giant ball of gas, rotating faster (25 days) at the equator than at the poles, which rotate once every 34.5 days. This dissonance sets up a massive amount of torsion, causing the magnetic field lines to stretch and snap, releasing massive amounts of energy. The Sun also changes polarity with every sunspot cycle, another indication that a new cycle is underway.
But predictions have run the gamut for Cycle #24. Recently, solar scientists have projected a twin peaked solar maximum for later this year, and thus far, Sol seems to be following this modified trend. Initial predictions by scientists at the start of Cycle #24 was for the sunspot number to have reached 90 by August 2013; but here it is the end of July, and we’re sitting at 68, and it seems that we’ll round out the northern hemisphere Summer at a sunspot number of 70 or so.
Some researchers predict that the following sunspot Cycle #25 may even be absent all together.
“If this trend continues, there will be almost no spots in Cycle 25,” Noted Matthew Penn of the National Solar Observatory, hinting that we may be on the edge of another Maunder Minimum.
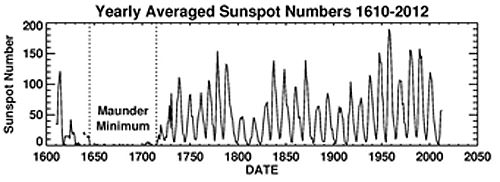
The Maunder Minimum was a period from 1645 to 1715 where almost no sunspots were seen. This span of time corresponded to a medieval period known as the Little Ice Age. During this era, the Thames River in London froze, making Christmas “Frost Fairs” possible on the ice covered river. Several villages in the Swiss Alps were also consumed by encroaching glaciers, and the Viking colony established in Greenland perished. The name for the period comes from Edward Maunder, who first noted the minimum in papers published in the 1890s. The term came into modern vogue after John Eddy published a paper on the subject in the journal of Science in 1976. Keep in mind, the data from the period covered by the Maunder Minimum is far from complete— Galileo had only started sketching sunspots via projection only a few decades prior to the start of the Maunder Minimum. But tellingly, there was a span of time in the early 18th century when many researchers supposed that sunspots were a myth! They were really THAT infrequent…
Just what role a pause in the solar cycle might play in the climate change debate remains to be seen. Perhaps, humanity is getting a brief (and lucky) reprieve, a chance to get serious about controlling our own destiny and doing something about anthropogenic climate-forcing. On a more ominous note, however, an extended cooling phase may give us reason to stall on preparing for the inevitable while giving ammunition to deniers, who like to cite natural trends exclusively.
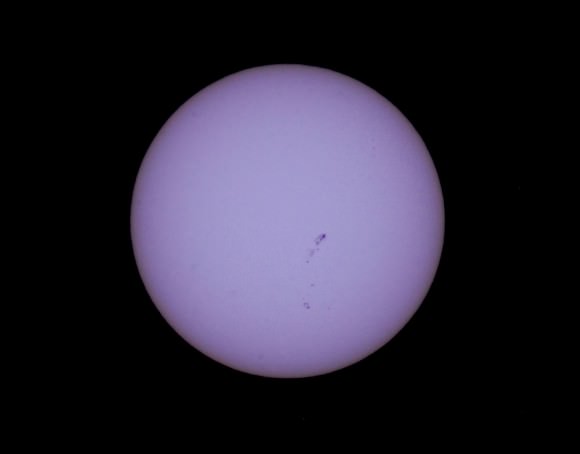

Whatever occurs, we now have an unprecedented fleet of solar monitoring spacecraft on hand to watch the solar drama unfold. STEREO A & B afford us a 360 degree view of the Sun. SOHO has now monitored the Sun for the equivalent of more than one solar cycle, and NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory has joined it in its scrutiny. NASA’s Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS) just launched earlier this year, and has already begun returning views of the solar atmosphere in unprecedented detail. Even spacecraft such as MESSENGER orbiting Mercury can give us vital data from other vantage points in the solar system.
Cycle #24 may be a lackluster performer, but I’ll bet the Sun has a few surprises in store. You can always get a freak cloud burst, even in the middle of a drought. Plus, we’re headed towards northern hemisphere Fall, a time when aurora activity traditionally picks up.
Be sure to keep a (safely filtered) eye on ol’ Sol— it may be the case over these next few years that “no news is big news!”