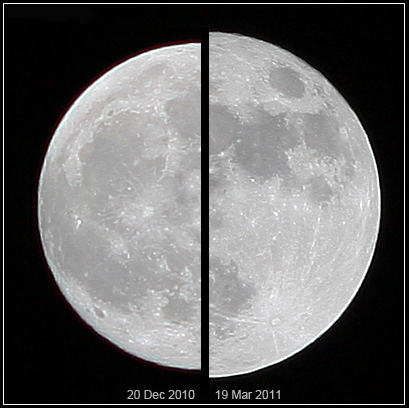
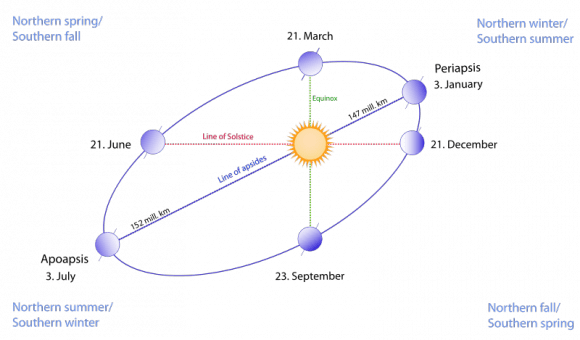
This 4th of July weekend brings us one more reason to celebrate. On July 5th at approximately 11:00 AM EDT/15:00 UT, our fair planet Earth reaches aphelion, or its farthest point from the Sun at 1.0167 Astronomical Units (A.U.s) or 152,096,000 kilometres distant.
Though it may not seem it to northern hemisphere residents sizzling in the summer heat, we’re currently 3.3% farther from the Sun than our 147,098,290 kilometre (0.9833 A.U.) approach made in early January.
We thought it would be a fun project to capture this change. A common cry heard from denier circles as to scientific facts is “yeah, but have you ever SEEN it?” and in the case of the variation in distance between the Sun and the Earth from aphelion to perihelion, we can report that we have!
We typically observe the Sun in white light and hydrogen alpha using a standard rig and a Coronado Personal Solar Telescope on every clear day. We have two filtered rigs for white light- a glass Orion filter for our 8-inch Schmidt-Cassegrain, and a homemade Baader solar filter for our DSLR. We prefer the DSLR rig for ease of deployment. We’ve described in a previous post how to make a safe and effective solar observing rig using Baader solar film.
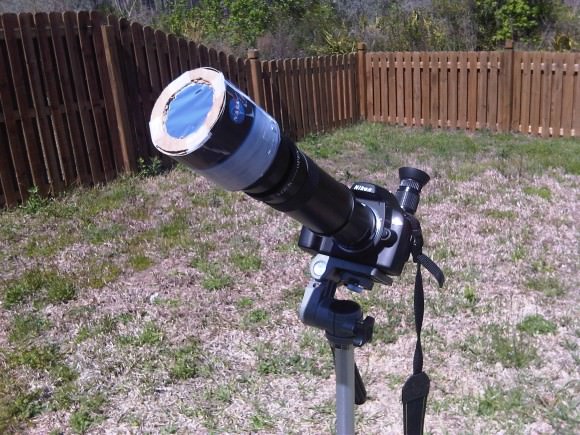

We’ve been imaging the Sun daily for a few years as part of our effort to make a home-brewed “solar rotation and activity movie” of the entire solar cycle. We recently realized that we’ve imaged Sol very near aphelion and perihelion on previous years with this same fixed rig, and decided to check and see if we caught the apparent size variation of our nearest star. And sure enough, comparing the sizes of the two disks revealed a tiny but consistent variation.
It’s a common misconception that the seasons are due to our distance from the Sun. The insolation due to the 23.4° tilt of the rotational axis of the Earth is the dominant driving factor behind the seasons. (Don’t they still teach this in grade school? You’d be surprised at the things I’ve heard!) In the current epoch, a January perihelion and a July aphelion results in milder climatic summers in the northern hemisphere and more severe summers in the southern. The current difference in solar isolation between hemispheres due to eccentricity of Earth’s orbit is 6.8%.
The orbit of the Earth also currently has one of the lowest eccentricities (how far it deviates for circular) of the planets at 0.0167, or 1.67%. Only Neptune (1%) and Venus (0.68%) are “more circular.”
The orbital eccentricity of the Earth also oscillates over a 413,000 year period between 5.8% (about the same as Saturn) down to 0.5%. We’re currently at the low end of the scale, just below the mean value of 2.8%.
Variation in eccentricity is also coupled with other factors, such as the change in axial obliquity the precession of the line of apsides and the equinoxes to result in what are known as Milankovitch cycles. These variations in extremes play a role in the riddle of climate over hundreds of thousands of years. Climate change deniers like to point out that there are large natural cycles in the records, and they’re right – but in the wrong direction. Note that looking solely at variations in the climate due to Milankovitch cycles, we should be in a cooling trend right now. Against this backdrop, the signal of anthropogenic climate forcing and global dimming of albedo (which also masks warming via cloud cover and reflectivity) becomes even more ominous.
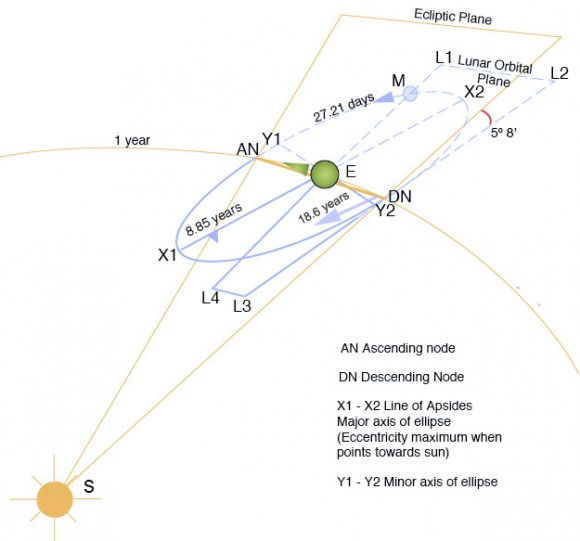
Aphelion can presently fall between July 2nd at 20:00 UT (as it did last in 1960) and July 7th at 00:00 UT as it last did on 2007. The seemingly random variation is due to the position of the Earth with respect to the barycenter of the Earth-Moon system near the time of aphelion. The once every four year reset of the leap year (with the exception of the year 2000!) also plays a lesser role.
I love observing the Sun any time of year, as its face is constantly changing from day-to-day. There’s also no worrying about light pollution in the solar observing world, though we’ve noticed turbulence aloft (in the form of bad seeing) is an issue later in the day, especially in the summertime. The rotational axis of the Sun is also tipped by about 7.25° relative to the ecliptic, and will present its north pole at maximum tilt towards us on September 8th. And yes, it does seem strange to think in terms of “the north pole of the Sun…”
We’re also approaching the solar maximum through the 2013-2014 time frame, another reason to break out those solar scopes. This current Solar Cycle #24 has been off to a sputtering start, with the Sun active one week, and quiet the next. The last 2009 minimum was the quietest in a century, and there’s speculation that Cycle #25 may be missing all together.
And yes, the Moon also varies in its apparent size throughout its orbit as well, as hyped during last month’s perigee or Super Moon. Keep those posts handy- we’ve got one more Super Moon to endure this month on July 22nd. The New Moon on July 8th at 7:15UT/3:15 AM EDT will occur just 30 hours after apogee, and will hence be the “smallest New Moon” of 2013, with a lot less fanfare. Observers worldwide also have a shot at catching the slender crescent Moon on the evening of July 9th. This lunation and the sighting of the crescent Moon also marks the start of the month of Ramadan on the Muslim calendar.
Be sure to observe the aphelion Sun (with proper protection of course!) It would be uber-cool to see a stitched together animation of the Sun “growing & shrinking” from aphelion to perihelion and back. We could also use a hip Internet-ready meme for the perihelion & aphelion Sun- perhaps a “MiniSol?” A recent pun from Dr Marco Langbroek laid claim to the moniker of “#SuperSun;” in time for next January’s perihelion;
Could a new trend be afoot?