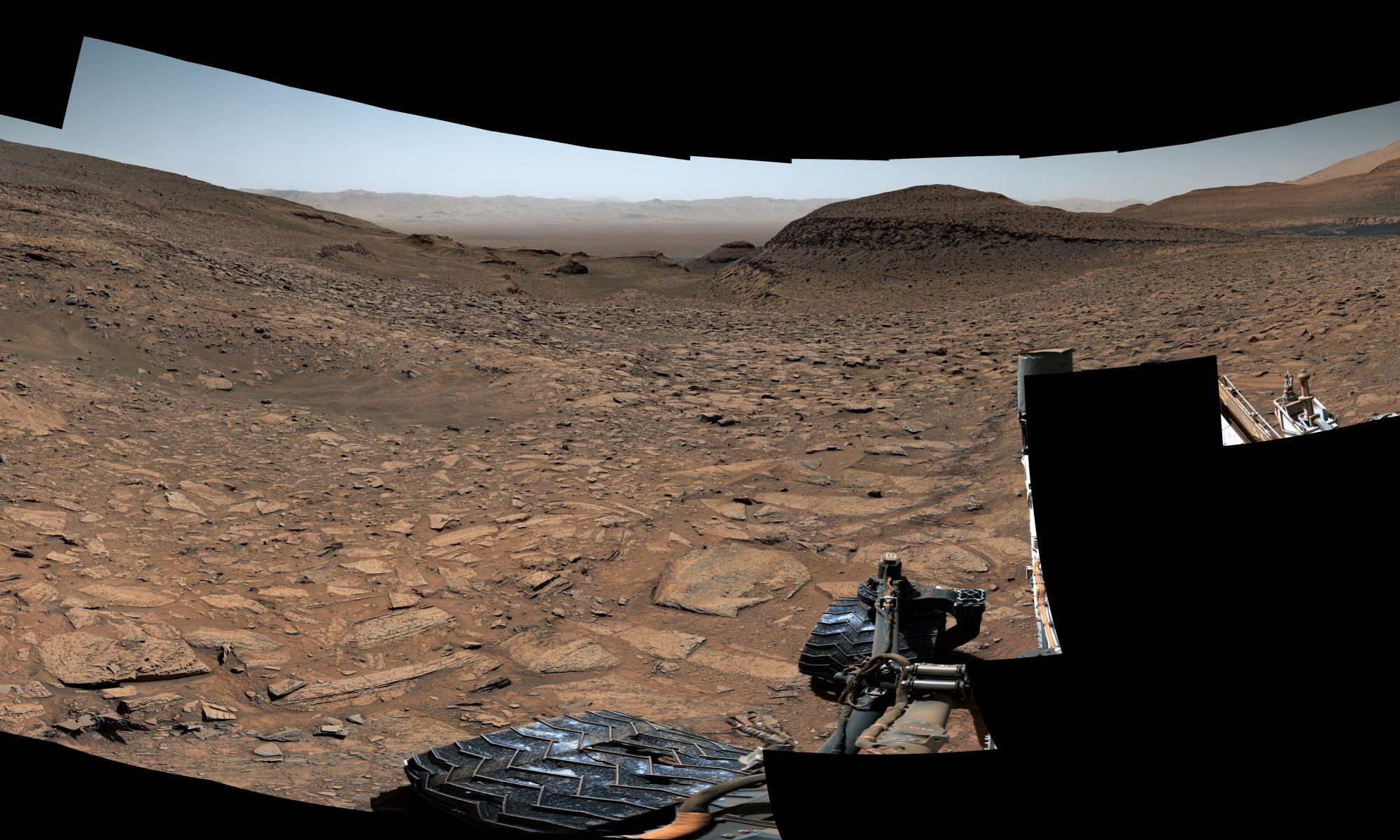
It’s hard to believe, but Mars Curiosity Rover has been on Mars doing its thing for 11 years. And, so what’s it doing to celebrate? Heading up a hill, making one of its toughest climbs ever.
Continue reading “Curiosity Had to Route Around a 23-Degree Slope to Reach a Fascinating Field of Craters”Curiosity Had to Route Around a 23-Degree Slope to Reach a Fascinating Field of Craters