Venus’s atmosphere has drawn a lot of attention lately. In particular, the consistent discovery of phosphine in its clouds points to potential biological sources. That, in turn, has resulted in numerous suggested missions, including floating a balloon into the atmosphere or having a spacecraft scoop down and suck up atmospheric samples. But a team of engineers led by Jeffrey Balcerski, now an adjunct at Kent State University but then part of the Ohio Aerospace Institute, came up with a different idea years ago – use floating sensor platforms shaped like leaves to collect a wide variety of data throughout Venus’ atmosphere.
Continue reading “Floating LEAVES Could Characterize Venus’s Atmosphere”Update your Desktop Wallpaper with 25 New Images from Chandra

It’s not always possible to observe the night sky from the surface of the Earth. The blocking effects of the atmosphere mean we sometimes need to put telescopes out into space. The Chandra X-Ray Observatory is one such telescopes and it has just completed its 25th year of observations. To celebrate, NASA have just released 25 never-before-seen images of various celestial objects in x-rays. The collection includes images showing the region around black holes, giant clouds of hot gas and extreme magnetic fields. Sadly though, NASA is planning on shutting down the mission to save budget so best to enjoy the images while you can.
Continue reading “Update your Desktop Wallpaper with 25 New Images from Chandra”SpaceX Resumes Falcon 9 Rocket Launches After FAA Go-Ahead

SpaceX is flying again after the Federal Aviation Administration ruled that the company can resume Falcon 9 rocket launches while the investigation into a failed July 11 mission continues.
The FAA’s go-ahead came on July 25 after SpaceX reported that the failure was caused by a crack in a sense line for a pressure sensor attached to the upper stage’s liquid-oxygen system. That resulted in an oxygen leak that degraded the performance of the upper-stage engine. As a near-term fix, SpaceX is removing the sense line and the sensors for upcoming Falcon 9 launches.
It didn’t take long for SpaceX to get back to its flight schedule. The company launched a Falcon 9 rocket from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:45 a.m. ET (05:45 GMT) today. Like the July 11 mission, this one sent a batch of SpaceX’s Starlink satellites to low Earth orbit.
The launch appeared to proceed without incident. After stage separation, the first-stage booster descended to a landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic Ocean, while the second stage proceeded to orbit and deployed 23 satellites for the Starlink high-speed internet network.
Continue reading “SpaceX Resumes Falcon 9 Rocket Launches After FAA Go-Ahead”Is This How You Get Hot Jupiters?

When we think of Jupiter-type planets, we usually picture massive cloud-covered worlds orbiting far from their stars. That distance keeps their volatile gases from vaporizing from stellar heat, similar to what we’re familiar with in our Solar System. So, why are so many exoplanets known as “hot Jupiters” orbiting very close to their stars? That’s the question astronomers ask as they study more of these extreme worlds.
Continue reading “Is This How You Get Hot Jupiters?”Now Uranus’ Moon Ariel Might Have an Ocean too

Venus is known for being really quite inhospitable with high surface temperatures and Mars is known for its rusty red horizons. Even the moons of some of the outer planets have fascinating environments with Europa and Enceladus boasting underground oceans. Recent observations from the James Webb Space Telescope show that Ariel, a moon of Uranus, is also a strong candidate for a sub surface ocean. How has this conclusion been reached? Well JWST has detected carbon dioxide ice on the surface on the trailing edge of features trailing away from the orbital direction. The possible cause, an underground ocean!
Continue reading “Now Uranus’ Moon Ariel Might Have an Ocean too”Why is JWST Having So Much Trouble with the TRAPPIST-1 System?

When the James Webb Space Telescope was launched it came with a fanfare expecting amazing things, much like the Hubble Space Telescope. One of JWST’s most anticipated target was TRAPPIST-1. This inconspicuous star is host to seven Earth-sized planets, with at least three in the habitable zone. The two inner planets are airless worlds but so far there has been no word of the third planet, the first in the habitable zone. The question is why and what makes it so tricky to observe?
Continue reading “Why is JWST Having So Much Trouble with the TRAPPIST-1 System?”Planetary Habitability Depends on its Star’s Magnetic Field
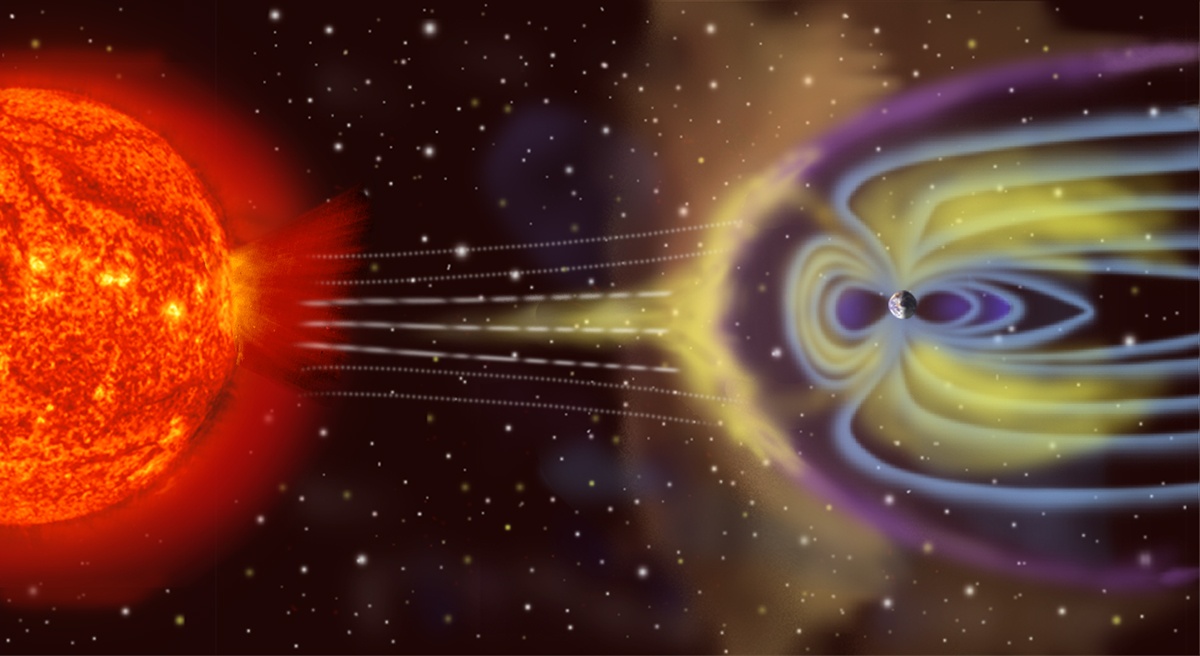
The extrasolar planet census recently passed a major milestone, with 5500 confirmed candidates in 4,243 solar systems. With so many exoplanets available for study, astronomers have learned a great deal about the types of planets that exist in our galaxy and have been rethinking several preconceived notions. These include the notion of “habitability” and whether Earth is the standard by which this should be measured – i.e., could there be “super habitable” exoplanets out there? – and the very concept of the circumsolar habitable zone (CHZ).
Traditionally, astronomers have defined habitable zones based on the type of star and the orbital distance where a planet would be warm enough to maintain liquid water on its surface. But in recent years, other factors have been considered, including the presence of planetary magnetic fields and whether they get enough ultraviolet light. In a recent study, a team from Rice University extended the definition of a CHZ to include a star’s magnetic field. Their findings could have significant implications in the search for life on other planets (aka. astrobiology).
Continue reading “Planetary Habitability Depends on its Star’s Magnetic Field”A Solution to the “Final Parsec Problem?”
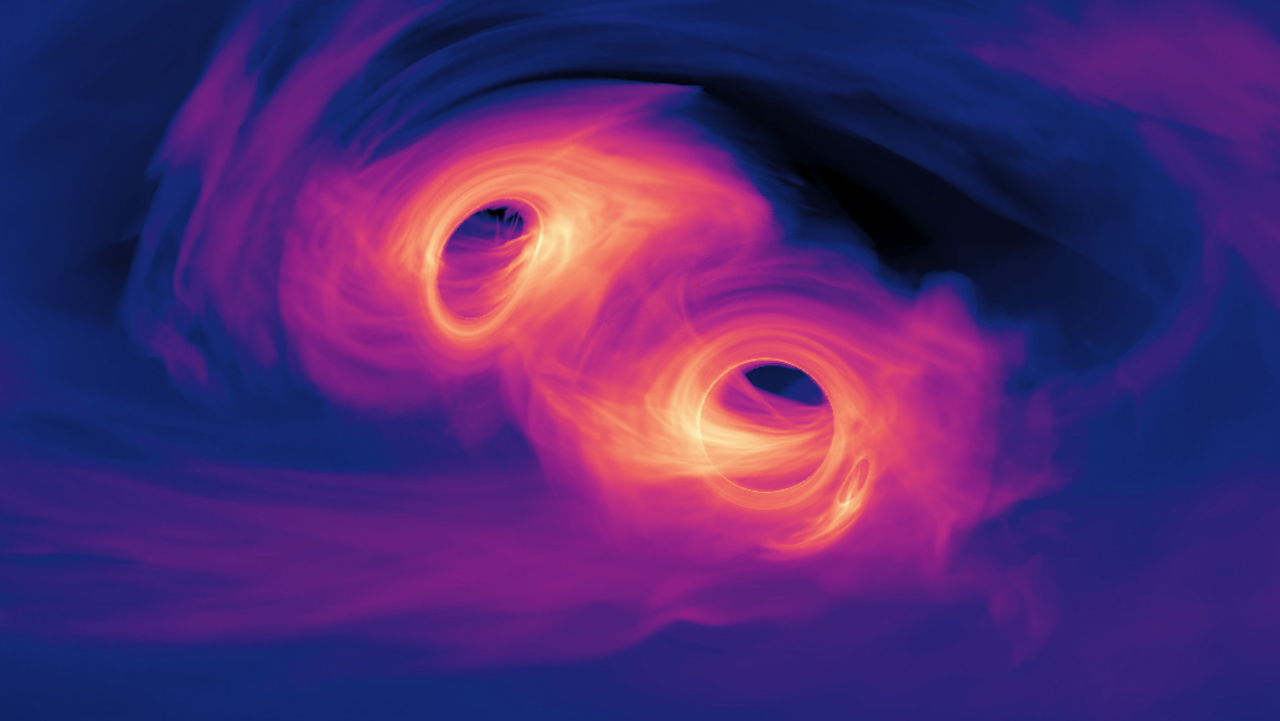
Supermassive Black Holes are Nature’s confounding behemoths. It’s difficult for Earth-bound minds to comprehend their magnitude and power. Astrophysicists have spent decades studying them, and they’ve made progress. But one problem still baffles even them: the Final Parsec Problem.
New research might have solved the problem, and dark matter plays a role in the solution.
Continue reading “A Solution to the “Final Parsec Problem?””Our Carbon Dioxide Emissions Have a Mesmerizing Side
Our CO2 emissions are warming the planet and making life uncomfortable and even unbearable in some regions. In July, the planet set consecutive records for the hottest day.
NASA is mapping our emissions, and while what they show us isn’t uplifting, it is visually appealing in a ghoulish way. Maybe the combination of visual appeal and ghoulishness will build momentum in the fight against climate change.
Continue reading “Our Carbon Dioxide Emissions Have a Mesmerizing Side”Astronauts Can Now Watch 4K Streaming Video on the Station

We take high definition streaming for granted in many parts of the world. Even now, as I type this article, I have the Martian streaming in high definition but until now astronauts on board the Space Station have had to accept low definition streaming. A team of researchers at NASA have developed and used a new system using an aircraft as a relay. A laser terminal was installed on a research aircraft and data was sent to a ground station. The signals were sent around the Earth and beamed to a relay satellite which then sent the signal on to the Space Station. What the astronauts will actually use it for is less likely to be streaming HD movies but will certainly be able to take advantage of the high bandwidth for science data and communications.
Continue reading “Astronauts Can Now Watch 4K Streaming Video on the Station”