Almost everything in the universe spins. Planets rotate on their axis, stars spin around black holes, and galaxies spin in great spiral structures. But what about the universe as a whole?
Structures rotate because of a property known as angular momentum. Angular momentum is a measure of mass and rotation, and it is a conserved physical property. One of its characteristics is that when mass moves closer together, it spins faster to keep angular momentum constant. You see this in figure skaters when they leap into the air and pull their limbs close to their bodies. Galaxies, stars, and planets all formed from great clouds of cosmic gas and dust. As gravity caused these clouds to collapse, even the smallest bit of rotation was amplified. So it is natural that they all spin.
But on a cosmic scale, things are different. It’s generally thought that the universe is homogeneous and isotropic. This means that on average matter should be evenly spread out and that the total angular momentum of the cosmos should be about zero. If that’s true, then the rotation of galaxies should be random. In any region of space you look, about half should be spinning in a clockwise direction, and about half anticlockwise.
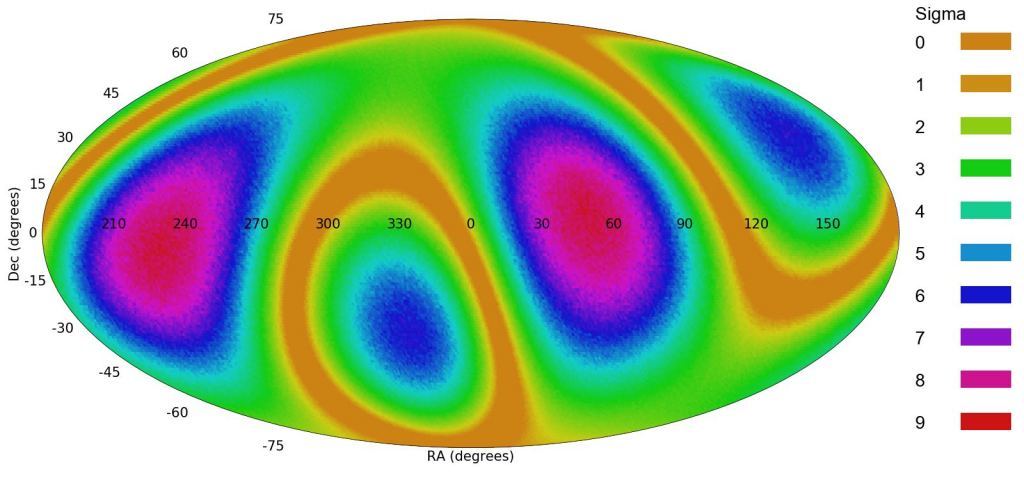
But there is some evidence that galactic rotation isn’t homogeneous. In 2011, a study of 15,000 galaxies found that there was a small bias in rotation. Because of the relatively small sample size, the evidence was somewhat weak. But this week a paper was presented at the 236th American Astronomical Society meeting, which showed an even stronger bias.
It’s important to note that this work has not yet been peer-reviewed, so we should be cautious about the conclusions. The study looked at 200,000 galaxies and their measured rotations. With the larger sample size, it found not only a rotational bias but also some of its cosmological properties. For one, the bias seems to get stronger with greater redshift. At ever-larger scales the bias is harder to ignore.
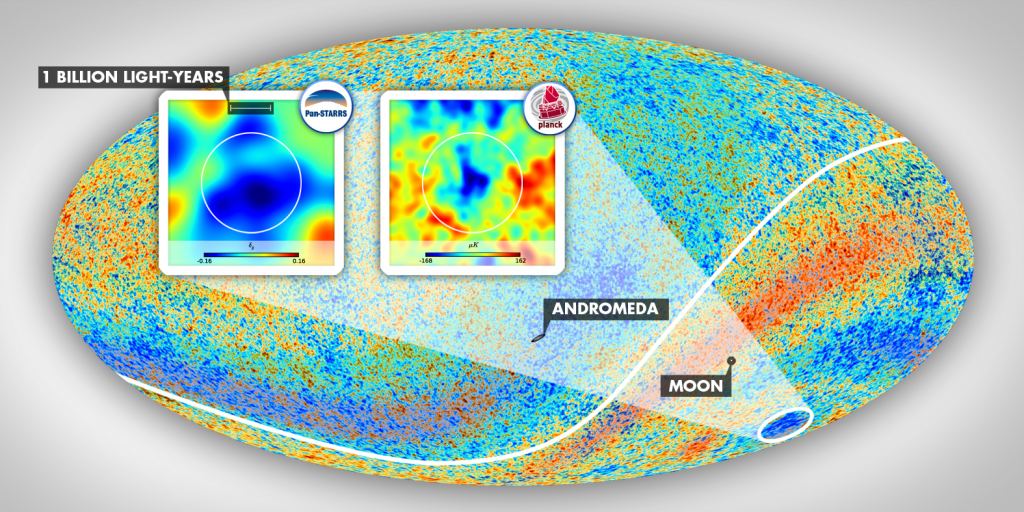
This supports the idea that the universe as a whole has an axis of rotation. Interestingly the cosmic axis seems to align with the so-called cold spot of the cosmic microwave background. While that’s interesting, we probably shouldn’t read too much into it. For one thing, the data doesn’t support a simple, single axis of rotation, such as that of a planet or star. Instead, the bias has a more complicated multipole structure.
All that said, there does seem to be something strange going on. While the universe does seem to be approximately homogeneous and isotropic, studies such as this are hinting that it isn’t exact. While that might not seem like a big deal, it has huge implications for our cosmological models.
Reference: Longo, Michael J. “Detection of a dipole in the handedness of spiral galaxies with redshifts z? 0.04.” Physics Letters B 699.4 (2011): 224-229.
Reference: Shamir, L. “Distribution of galaxy spin directions in Pan-STARRS and SDSS shows large-scale multipoles and redshift dependence.” 236th AAS Meeting (virtual) 336.02, 2020.


Nice, precautionary analysis – thanks!
As noted, this is a conference proceeding and has an arxiv preprint, it has not passed peer review publication.
But in general, the galactic plane obstruct galaxies along the sky map mid line and the typical pattern that show up due to the solar system velocity is a dipole centered where the spin direction map has it. This makes error and contamination suspect. Since the spiral galaxy rotation is measured by small differences in Doppler shift, naively noise could obscure the result in some ways. That could also explain why the asymmetry seems larger at more distant, less spectroscopically identifiable galaxies.
The analogous CMB quadrupole patterns are not statistically significant.
People read in all sorts of axis for the patterns without really defining it, in the Wikipedia article for “the Axis of Evil” it is claimed to be the orbital plane of our system, which is tilted 60 degree in respect to our orbit around the Milky Way disk so not related to any of that.
People also read in all sorts of explanations. In the paper the statistical significance is taken by looking at a cumulative binomial distribution of right/left rotation, not against a cosmological model that aggregates all the data and removes biases such as our system peculiar motion. Those models usually come out with “not statistically significant” as per above.
The current preprint paper show that the data pipeline was tested by hand and by flipping the radial intensity plots. But the filtering – removing 25 % of the sample by requiring 10 spectral peaks showing the same spin direction – is huge and is not analyzed for dust et cetera.
I would like to see a team have go at that, with more people looking into the possible systematic error sources here.
An extraordinary result of asymmetry needs extraordinary, repeated evidence. I don’t yet see that here.
[Links to references removed to not be hold up in moderation. Ask here if you want them.]