In April, when the Hubble Space Telescope looked out towards Jupiter’s orbit and observed what has been billed as the “Comet of the Century” – Comet C/2012 S1 ISON – the space telescope photographed a unique feature in the comet’s coma. Now, a team of ground-based astronomers have performed follow-up observations, imaging Comet ISON as it heads towards the Sun and was just outside the orbit of Mars. They, too, have seen something in the coma and suspect it’s a similar feature to what Hubble imaged. The object is thought to be a jet blasting dust particles off the sunward-facing side of the comet’s nucleus.
These very useful follow-up observations are providing more insight on this highly anticipated comet, as well as helping to predict what might happen when it makes its closest approach to the Sun in November 2013.
“The hype surrounding this comet has been extreme” said Nick Howes from the Remanzacco Observatory, “with some wildly optimistic estimates for magnitude. We’re hoping this measured scientific approach will yield results just as exciting to the science community, even if the comet doesn’t end up meeting everyone’s expectations visually, for whatever reason.”

Some have predicted ISON may briefly become brighter than the full Moon. But right now the comet is far below naked-eye visibility, and larger telescopes are needed to makes observations.
Howes and Ernesto Guido from the Remanzacco Observatory in Italy used a suite of Hubble-sized ground-based telescopes in Australia, Hawaii and the Canary Islands to make their observations. They are collaborating with with Nalin Samarasinha, a Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute (PSI) in an attempt to get high spatial resolution data on Comet ISON.
Howes and Guido have been imaging Comet C/2012 S1 ISON since the day it was discovered and actually played a small role in its discovery. They work on a variety of programs with professional and amateur astronomers around the world, but for this comet, their focus is on the so-called Afrho, a measure of a comet’s dust production. (Learn more about Arfho here.)
Samarasinha, a specialist in comets at the Planetary Science Institute, has been looking at the detailed structure of the near-nucleus coma of comet C/2012 S1 ISON using data, which the Remanzacco team is delivering in to the PSI.
Recently, Samarasinha had looked at image comparisons for the Remanzacco team’s dataset from May 2, 5, and 7 taken with the F10 2-meter Liverpool telescope on La Palma, using an extremely sensitive camera, perfectly suited for detailed comet work.
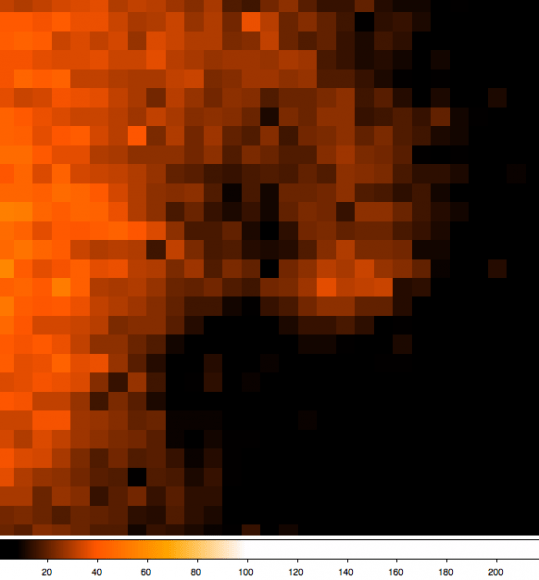
The images shown here are 28×28 pixel crops of the inner region of the comet.
“This comparison shows that the sunward feature Nick’s team suspected from images taken on 02/05/2013 is originating slightly north of west and then the position angle of the feature (measured from north through east) increases as one moves away from the optocenter,” said Nalin.
Nalin’s interpretation is that the curvature of this feature (which the team suspected was not caused by image enhancing initially, but can now categorically state is real) is not due to any rotational effects but is due to radiation pressure pushing dust grains towards the tail. Ultimately, this feature merges in with the tail.
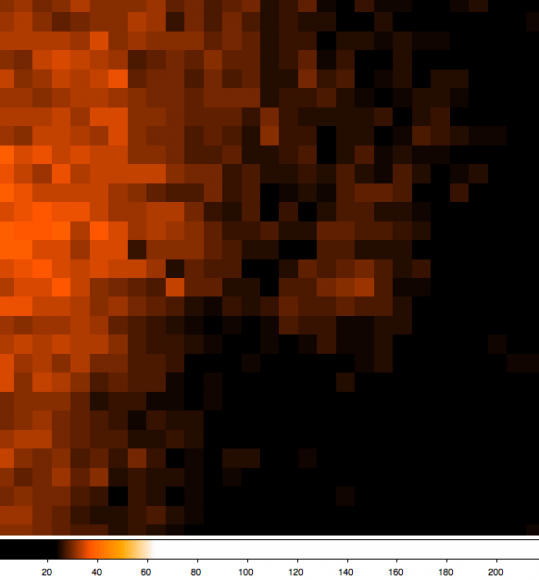
The team says these observations are in close agreement with features detected by the Hubble Space Telescope in April this year. As the comet comes closer to the Earth the spatial resolution will improve, and the team should get more detailed views on the coma structure.
Estimates suggest that the nucleus of ISON is no larger than 4-6 km (3-4 miles) across while the comet’s dusty coma, or head of the comet is approximately 5,000 km (3,100 miles) across, or 1.2 times the width of Australia. A dust tail extends more than 92,000 km (57,000 miles).
Ongoing observations seem to reveal this comet is ‘shedding’ quite a bit of mass, leaving astronomers to wonder if it will have enough body left to survive its perhihelion, the closest approach to the Sun on November 28, 2013.
Excitingly, Comet ISON observations are in the works for when the comet dashes past Mars, and the Curiosity rover is on tap to try imaging it from Mars’ surface with its high resolution Mastcam 100 camera, as well as on-orbit observations with the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
As the comet performs a hairpin turn around the Sun in November, its ices will vaporize in the intense solar heat. Assuming it defies death by evaporation, some predict it could become as bright as the full Moon. If so, that would occur for a brief time around at perihelion when the comet would only be visible in the daytime sky very close to the Sun. When safely viewed, ISON might look like a brilliant, fuzzy star in a blue sky.
As C/2012 S1 ISON is now heading in to the evening twilight glare, Howes and Guido will turn from large aperture instrumentation on this comet for a while, and work on observations with a wider field CCD, more sensitive in the R’ band, and also imaging with the Polarimeter instrument which will allow them to create detailed maps of the inner coma region.
Howes said that these ongoing collaborations with scientists with the amateur community are delivering valuable scientific data on a hugely interesting object.

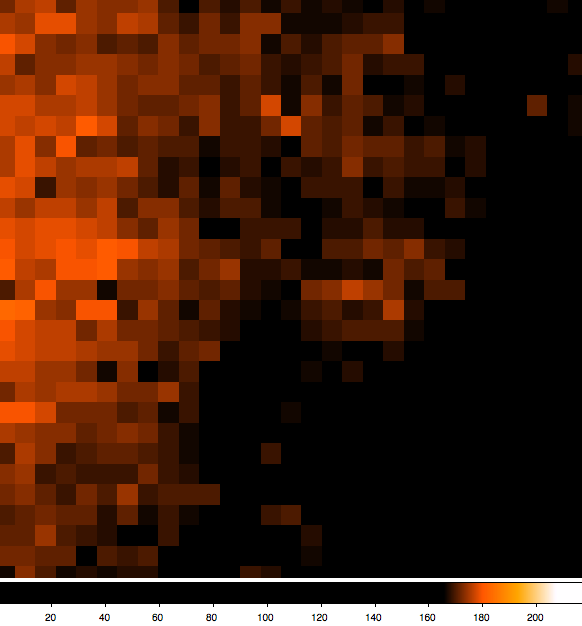
This seems to be quite exciting results for this very distant object. It would be of interest to see the full field, rather than a close up that reminds me of a 100x digital zoom on a camera with no optical zoom! 😉 Seriously, ISON will spur on many public star party events Im sure, bringing all of astronomy to the masses. Maybe some of them will stick with it and become scientists when they grow up.
Samarasinha, a specialist in comets at the Planetary Science
Institute, has been looking at the detailed structure of the
near-nucleus coma of comet C/2012 S1 ISON using data, which the
Remanzacco team is delivering in to the PSI.
Spybubble pro
The full field images are our page at http://www.remanzacco.blogspot.co.uk
May optimistic expectations be realized..
What is a coma – http://youtu.be/T3-dZHRR3eA