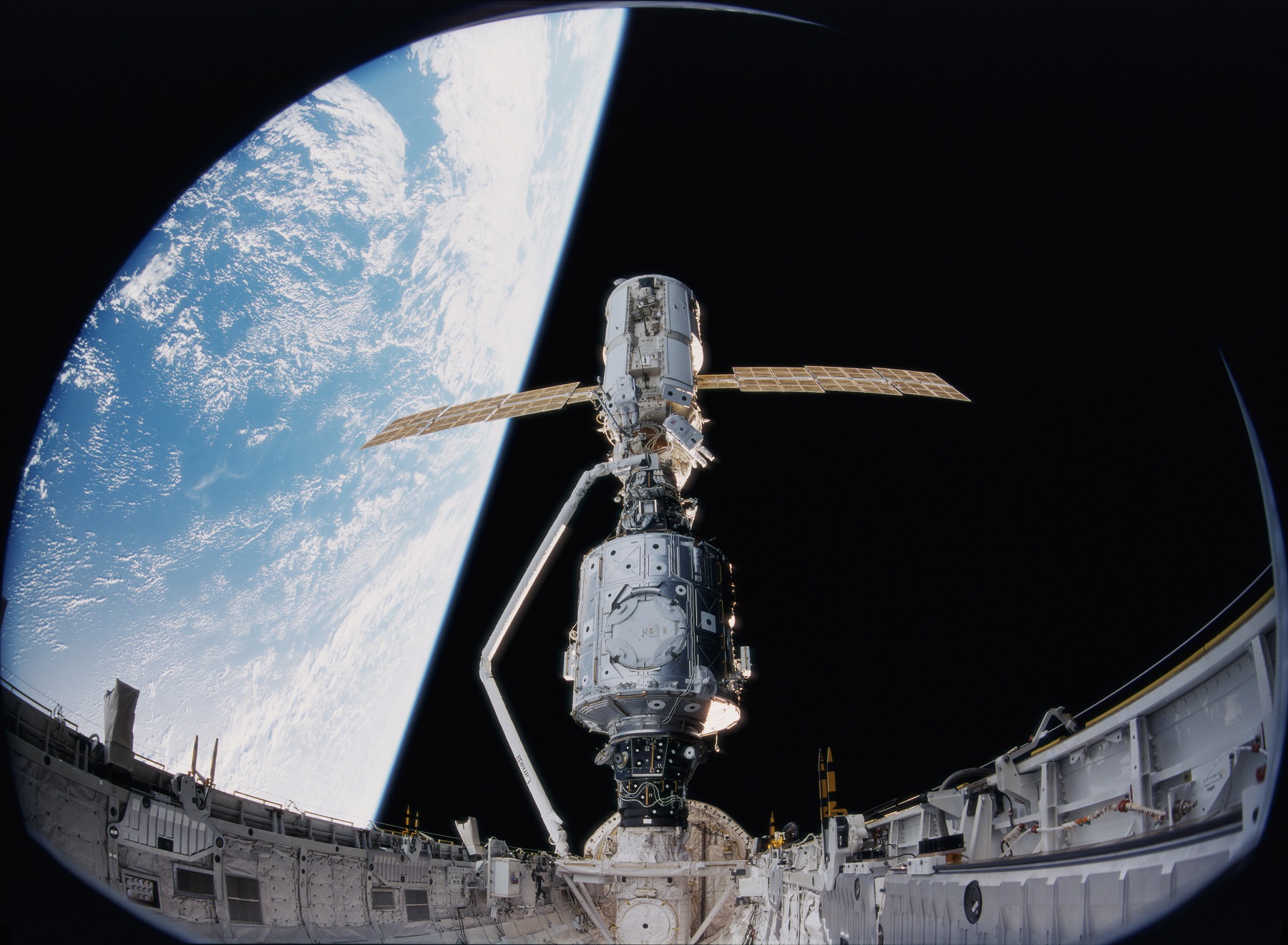
It appears that the International Space Station is showing its age. Or, at least, the older modules that have been in space since 1998 certainly are. According to statements made by a senior Russian space official, cosmonauts aboard the ISS have discovered new cracks in the Functional Cargo Block (FCB) module – aka. Zarya (“Dawn”). These cracks were found in seven of the module’s twenty windows and could eventually threaten the entire station.
Continue reading “Cosmonauts Find Cracks in the Aging Zarya ISS Module”Cosmonauts Find Cracks in the Aging Zarya ISS Module