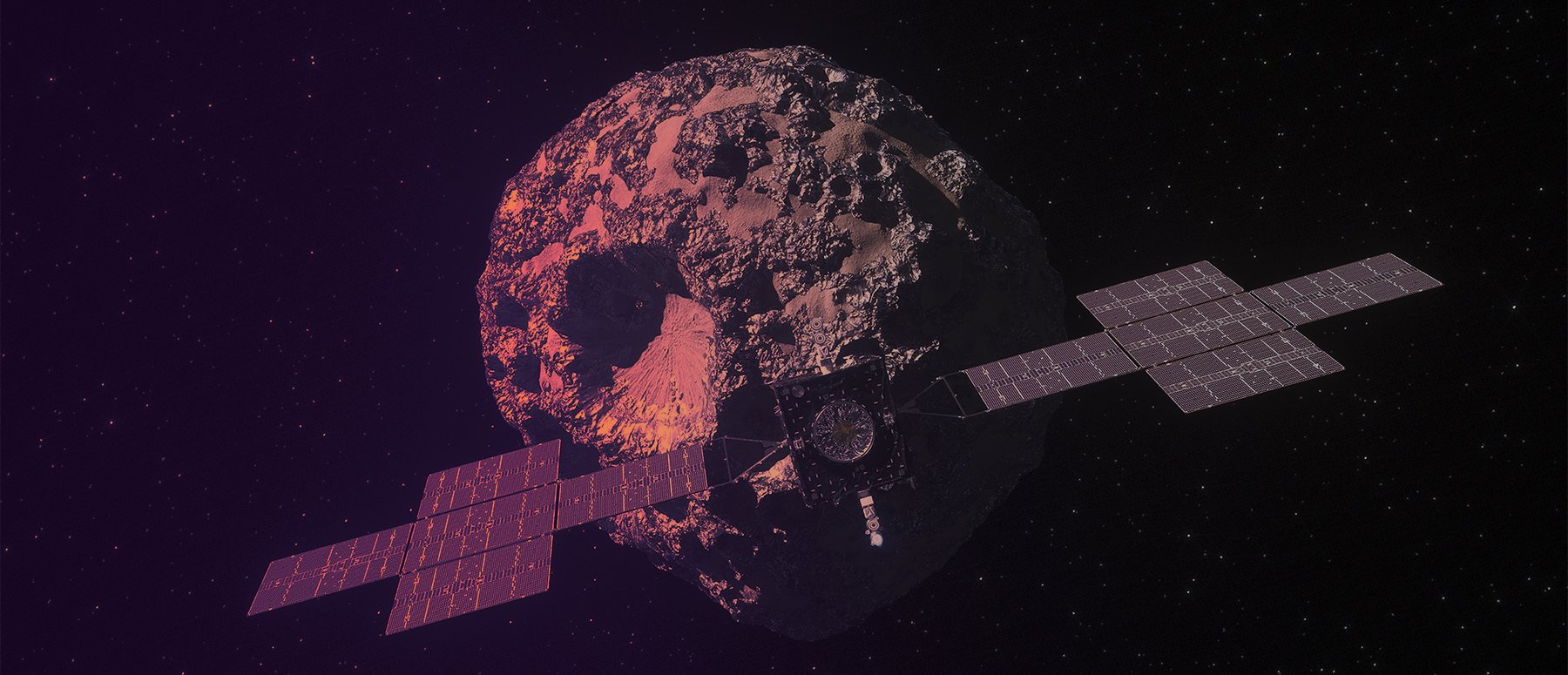
On October 13th, at 10:19 AM Eastern (07:19 AM Pacific), NASA’s Psyche mission successfully launched atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This spacecraft is now on its way to rendezvous with the M-type asteroid of the same name, an object in the Main Asteroid Belt almost entirely composed of metal. This metallic asteroid is thought to be the remnant of a planetoid that lost its outer layers, leaving behind a core of iron-nickel and precious metals. By studying this object, scientists hope to learn more about the formation of rocky planets.
Continue reading “NASA's Psyche Mission is off to Asteroid Psyche”Lucy Has its First Asteroid Target in the Crosshairs
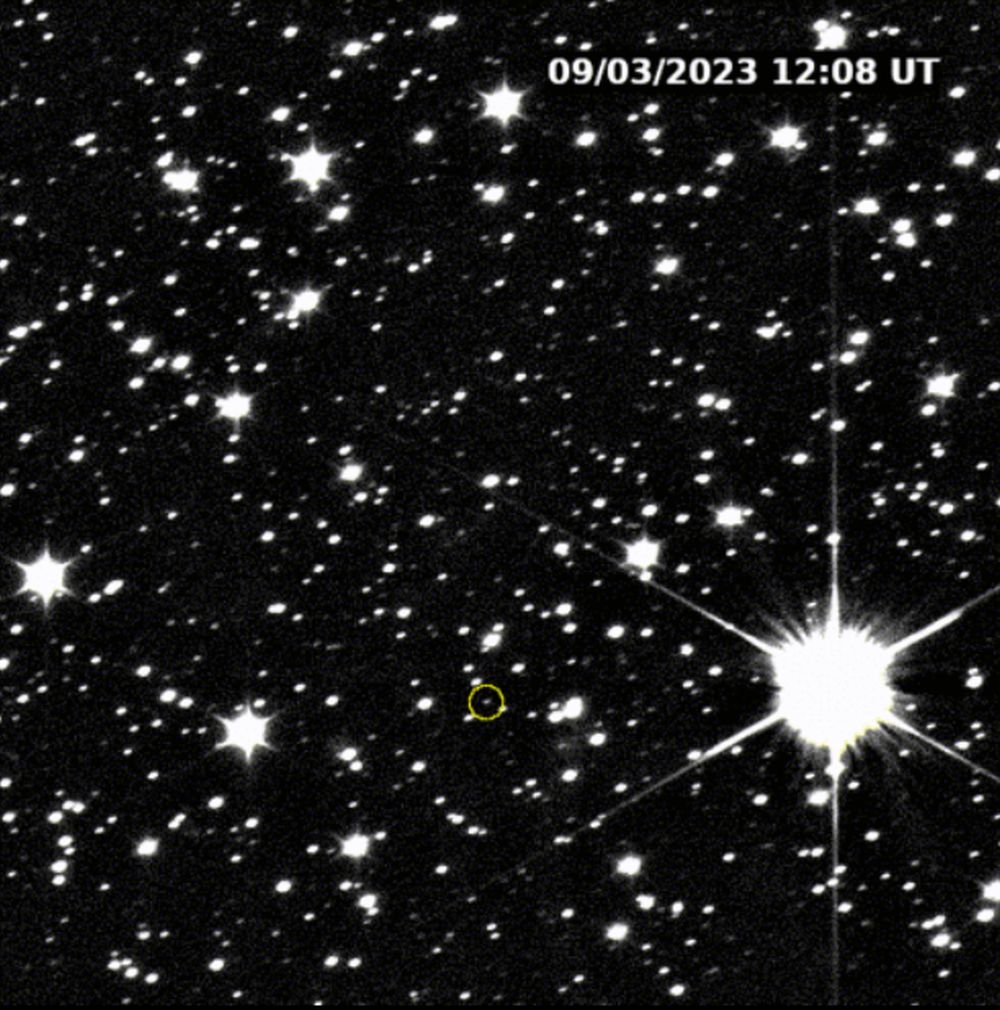
NASA’s Lucy spacecraft launched almost one year ago, in October of 2021. Its journey is an ambitious one, and long. It’ll visit eight different asteroids in its planned 12-year mission. Two of them are main belt asteroids, and the other six are Jupiter Trojans, which share the gas giant’s orbit around the Sun.
Lucy’s first, and smallest, target asteroid is now in the spacecraft’s sights.
Continue reading “Lucy Has its First Asteroid Target in the Crosshairs”JWST Finds a Comet Still Holding Onto Water in the Main Asteroid Belt

Comets are instantly recognizable by their tails of gas and dust. Most comets originate in the far, frozen reaches of our Solar System, and only visit the inner Solar System occasionally. But some are in the Main Asteroid Belt, mixed in with the debris left over after the Solar System formed.
Astronomers just found water vapour coming from one of them.
“With Webb’s observations of Comet Read, we can now demonstrate that water ice from the early Solar System can be preserved in the asteroid belt.”
Michael Kelley, University of Maryland
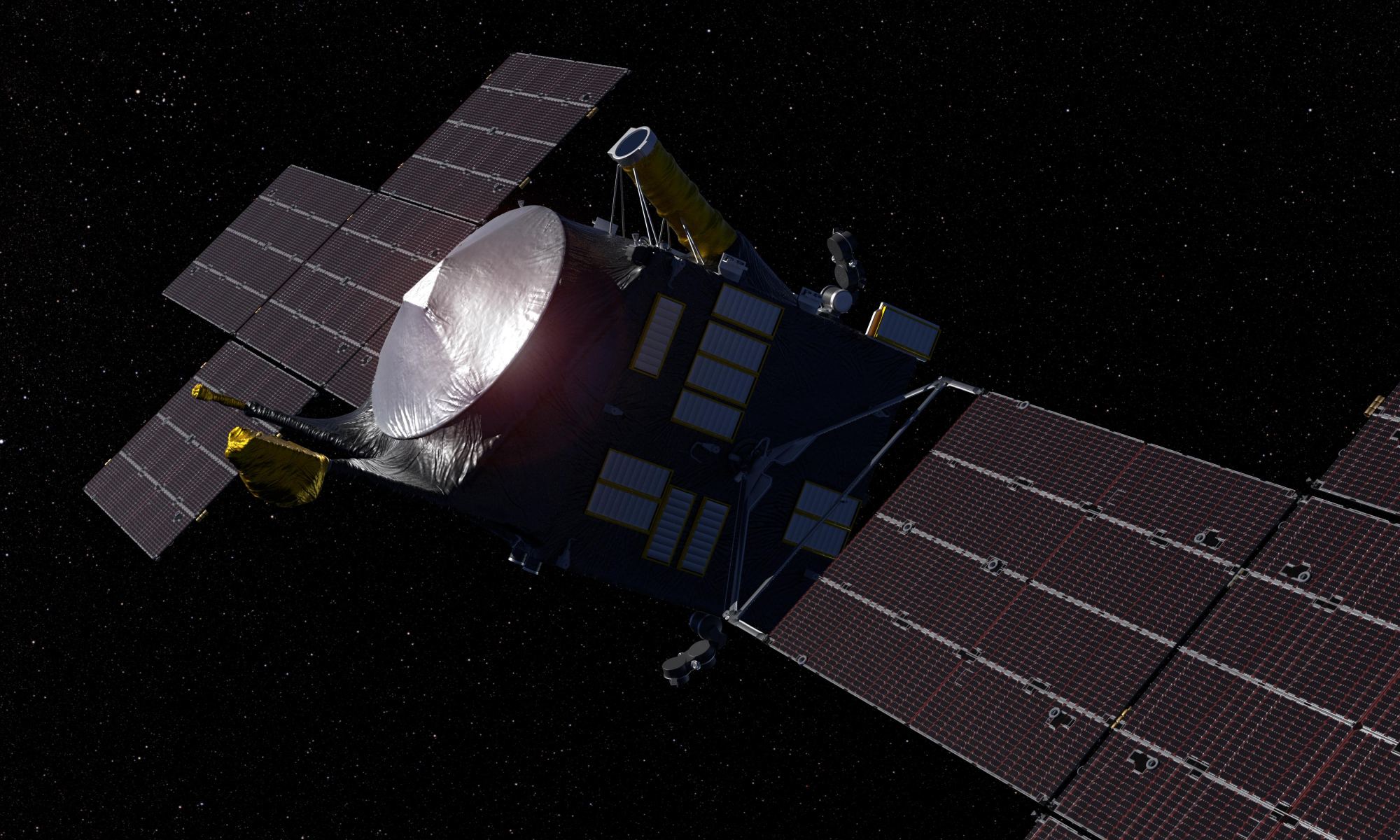
That’s So Metal. NASA’s Psyche Mission is Now Under Construction
In August of 2022, NASA will send a robotic spacecraft to the Main Asteroid Belt to explore a truly unique object: a metal asteroid. This object is known as 16 Psyche, is one of the largest asteroids in the Belt, and is composed almost entirely of iron and nickel. The most widely-accepted theory is that it used to be the core of a protoplanet in the Belt that experienced a massive collision that sent its rocky crust and mantle into space.
The spacecraft, also named Psyche, was submitted as part of a call for proposals for NASA’s Discovery Program in 2015 and was selected as the 14th Discovery mission by 2017. Most recently, the spacecraft passed a crucial milestone by moving from the planning and designing phase to the manufacturing phase, where all of the hardware that will allow it to make the journey is being assembled.
Continue reading “That’s So Metal. NASA’s Psyche Mission is Now Under Construction”New Images of the “Golf Ball” Asteroid Pallas
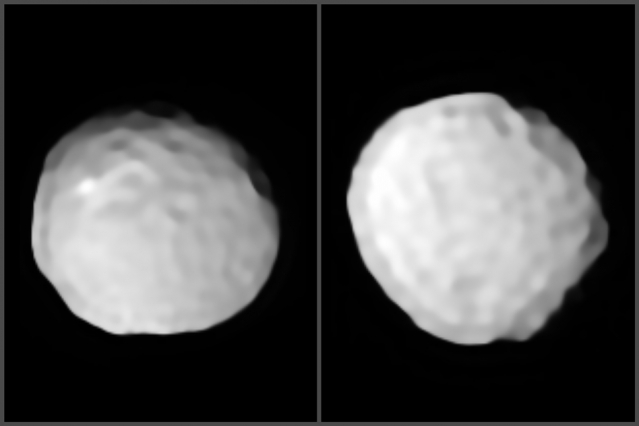
In 1802, German astronomer Heinrich Olbers observed what he thought was a planet within the Main Asteroid Belt. In time, astronomers would come to name this body Pallas, an alternate name for the Greek warrior goddess Athena. The subsequent discovery of many more asteroids in the Main Belt would lead to Pallas being reclassified as a large asteroid, the third-largest in the Belt after Ceres and Vesta.
For centuries, astronomers have sought to get a better look at Pallas to learn more about its size, shape, and composition. As of the turn of the century, astronomers had come to conclude that it was an oblate spheroid (an elongated sphere). Thanks to a new study by an international team, the first detailed images of Pallas have finally been taken, which reveal that its shape is more akin to a “golf ball” – i.e. heavily dimpled.
Continue reading “New Images of the “Golf Ball” Asteroid Pallas”How Do We Settle on Ceres?

Welcome back to our series on Settling the Solar System! Today, we take a look at the largest asteroid/planetoid in the Main Belt – Ceres!
Between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter lies the Solar System’s Main Asteroid Belt. Within this region, it is estimated that there are over 150 million objects that measure 100 meters (330 ft) or more in diameter. The largest of these is the dwarf planet Ceres (aka. 1 Ceres), the only body in the Main Belt that is large enough – 940 km (585 mi) in diameter – to have undergone hydrostatic equilibrium (become spherical).
Because of its important location and the amenities this dwarf planet itself possesses, there are those who have proposed that we establish a colony on Ceres (and even some who’ve explored the idea of terraforming it). This could serve as a base for asteroid mining ventures as well as an outpost of human civilization, one which could facilitate the expansion of humanity farther out into the Solar System.
Continue reading “How Do We Settle on Ceres?”Asteroid Hygiea is Round Enough That it Could Qualify as a Dwarf Planet, the Smallest in the Solar System
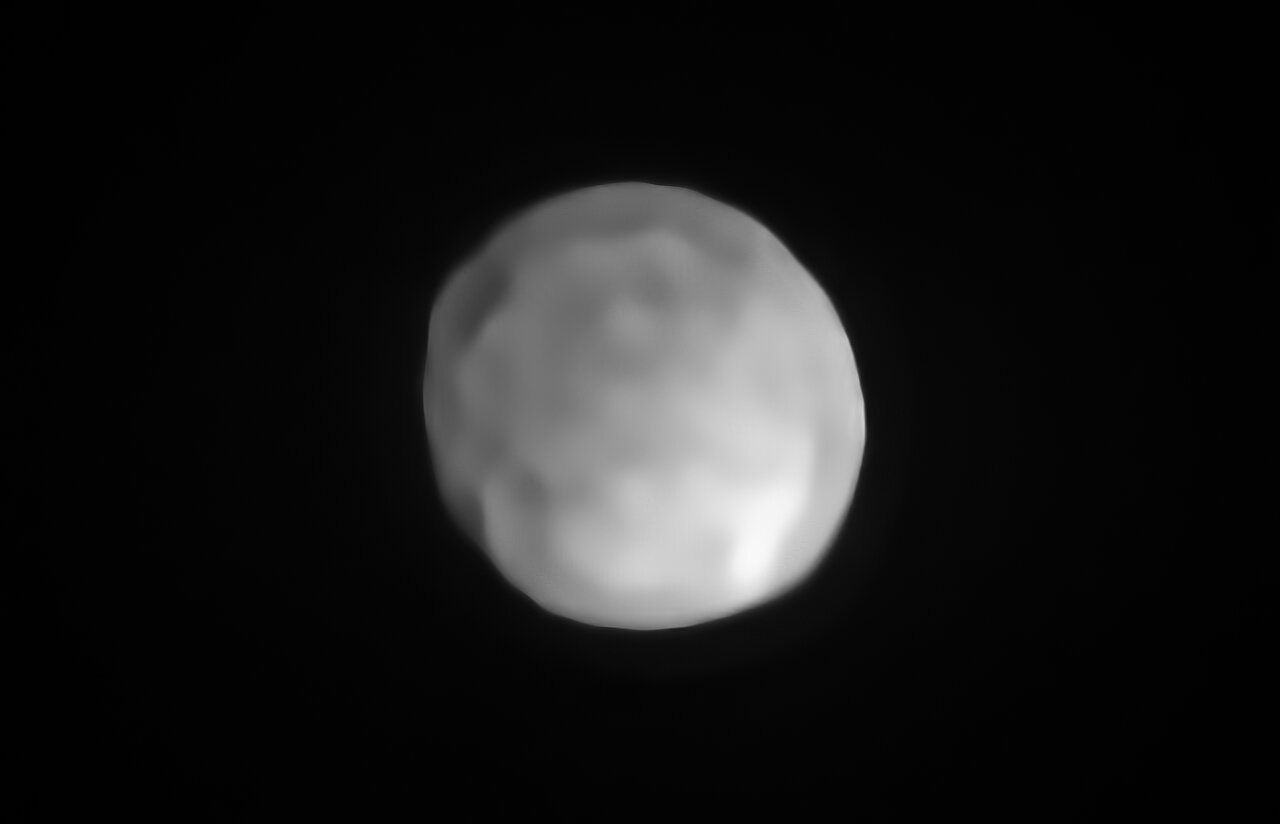

Within the Main Asteroid Belt, there are a number of larger bodies that have defied traditional classification. The largest among them is Ceres, which is followed by Vesta, Pallas, and Hygeia. Until recently, Ceres was thought to be the only object in the Main Belt large enough to undergo hydrostatic equilibrium – where an object is sufficiently massive that its gravity causes it to collapse into a roughly spherical shape.
However, it now seems that there is another body in the Main Belt that has earned the designation of “dwarf planet”. Using data from the Spectro-Polarimetric High-contrast Exoplanet REsearch (SPHERE) instrument at the Very Large Telescope (VLT), an international team of astronomers found compelling evidence that Hygeia is actually round, making it the smallest dwarf planet in the Solar System.
Continue reading “Asteroid Hygiea is Round Enough That it Could Qualify as a Dwarf Planet, the Smallest in the Solar System”Most of the Solar System Should be a Protected Wilderness. One-Eighth Left for Mining and Resource Exploitation
There is no doubt that our world is in the midst of a climate crisis. Between increasing levels of carbon dioxide in our atmosphere, rising temperatures and sea levels, ocean acidification, species extinctions, waste production, diminishing supplies of fresh water, drought, severe weather, and all of the resulting fallout, the “Anthropocene” is not shaping up too well.
It is little wonder then why luminaries like Stephen Hawking, Buzz Aldrin, and Elon Musk believe that we must look off-world to ensure our survival. However, there are those who caution that in so doing, humans will simply shift our burdens onto new locations. Addressing this possibility, two distinguished researchers recently published a paper where they suggest that we should set aside “wilderness” spaces” in our Solar System today.
Continue reading “Most of the Solar System Should be a Protected Wilderness. One-Eighth Left for Mining and Resource Exploitation”Steam-Powered Spacecraft Could Explore the Asteroid Belt Forever, Refueling Itself in Space
The era of renewed space exploration has led to some rather ambitious proposals. While many have been on the books for decades, it has only been in recent years that some of these plans have become technologically feasible. A good example is asteroid mining, where robotic spacecraft would travel to Near-Earth Asteroids and the Main Asteroid Belt to harvest minerals and other resources.
At the moment, one of the main challenges is how these craft would be able to get around and refuel once they are in space. To address this, the New York-based company Honeybee Robotics has teemed up with the University of Central Florida (UFC) to develop a steam-powered robotic spacecraft. The company recently released a demonstration video that shows their prototype World is Not Enough (WINE) “steam hopper” in action.
Continue reading “Steam-Powered Spacecraft Could Explore the Asteroid Belt Forever, Refueling Itself in Space”Ceres Rolled Over at Some Point in the Past
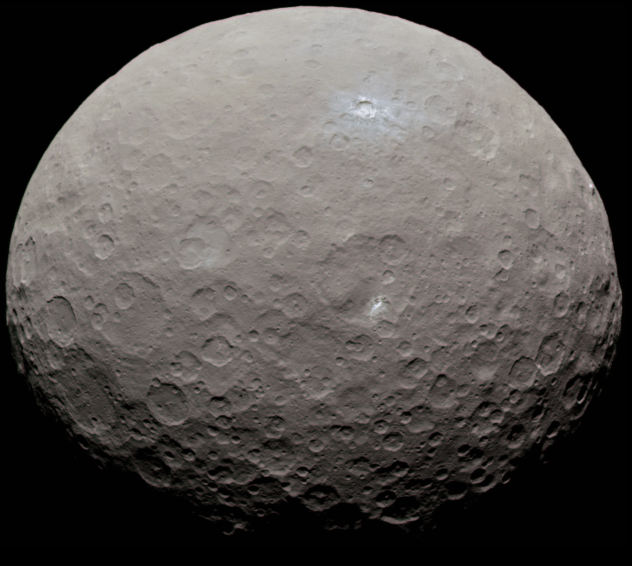

In 2007, the Dawn mission launched from Earth and began making its way towards two historic rendezvous in the Main Asteroid Belt. The purpose of this mission was to learn more about the history of the early Solar System by studying the two largest protoplanets in the Main Belt – Ceres and Vesta – which have remained intact since their formation.
In 2015, the Dawn mission arrived in orbit around Ceres and began sending back data that has shed light on the protoplanet’s surface, composition and interior structure. Based on mission data, Pasquale Tricarico – the senior scientist at the Planetary Science Institute (PSI) – has also determined that the Ceres also experienced an indirect polar reorientation in the past, where its pole rolled approximately 36° off-axis.
Continue reading “Ceres Rolled Over at Some Point in the Past”





