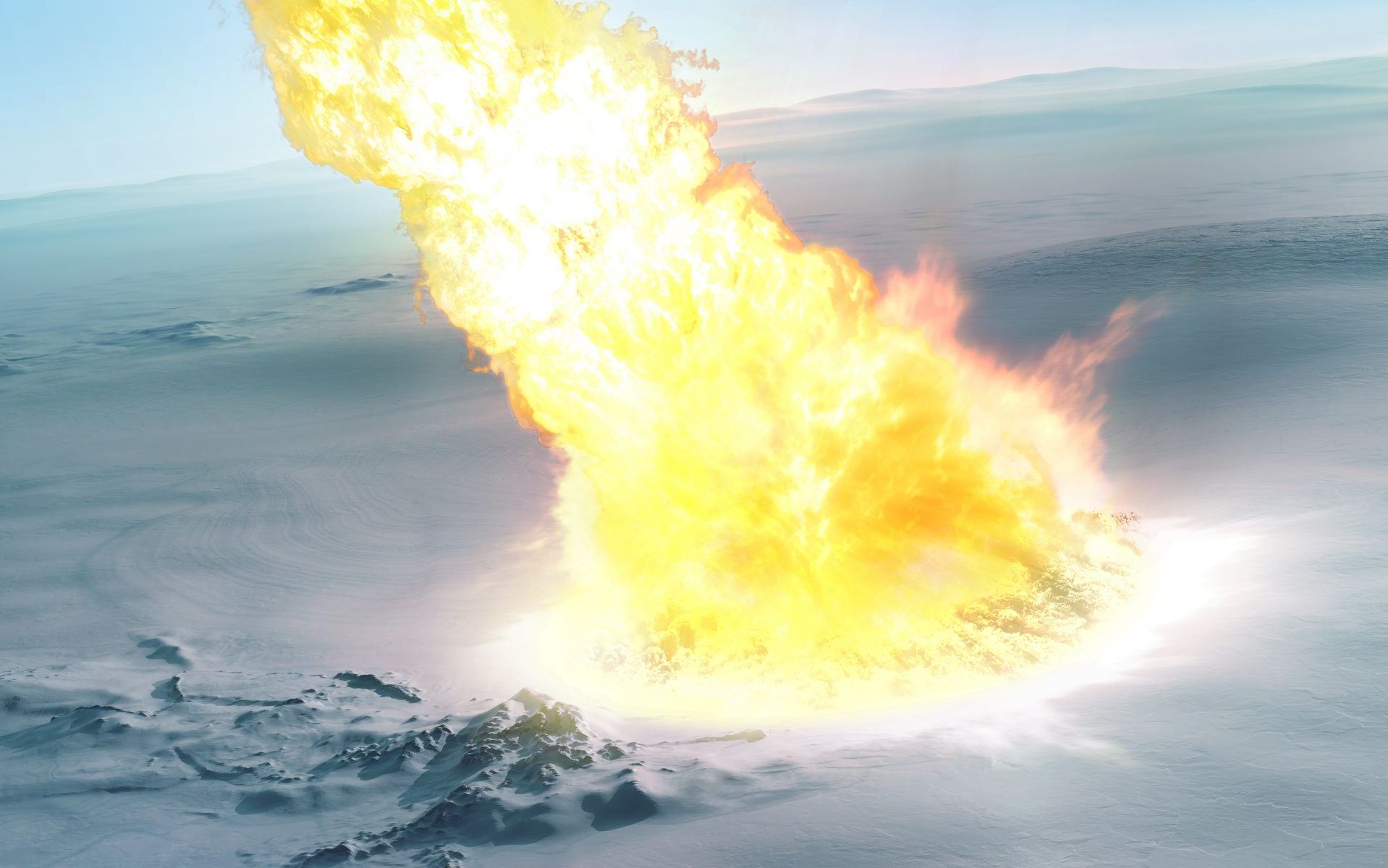
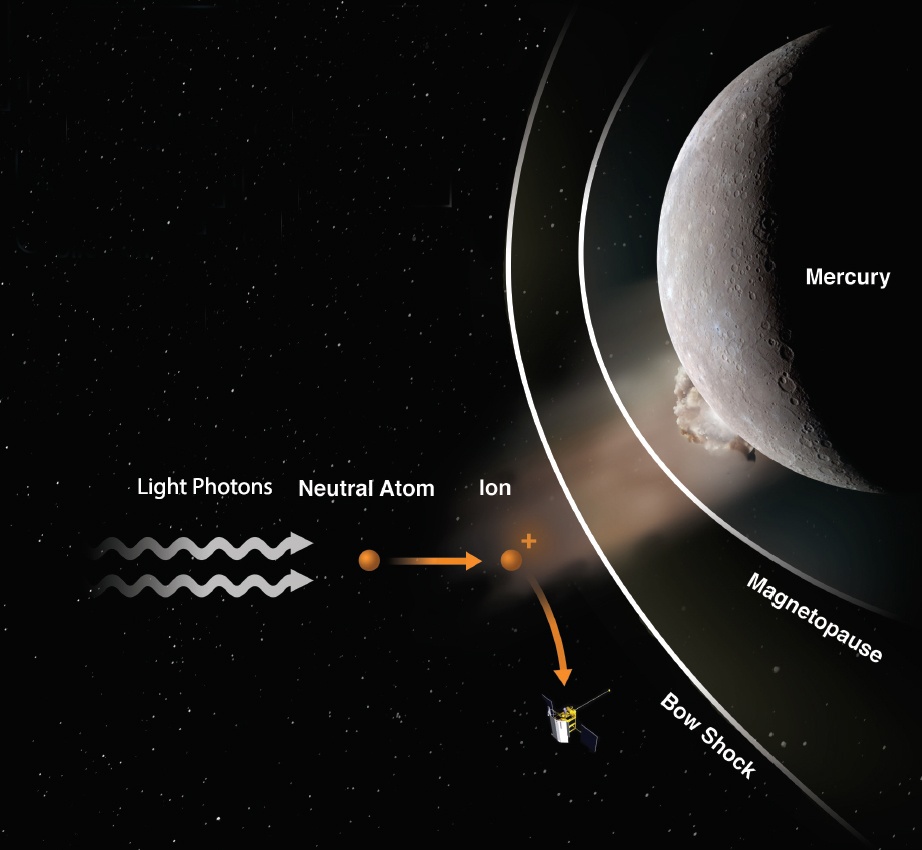
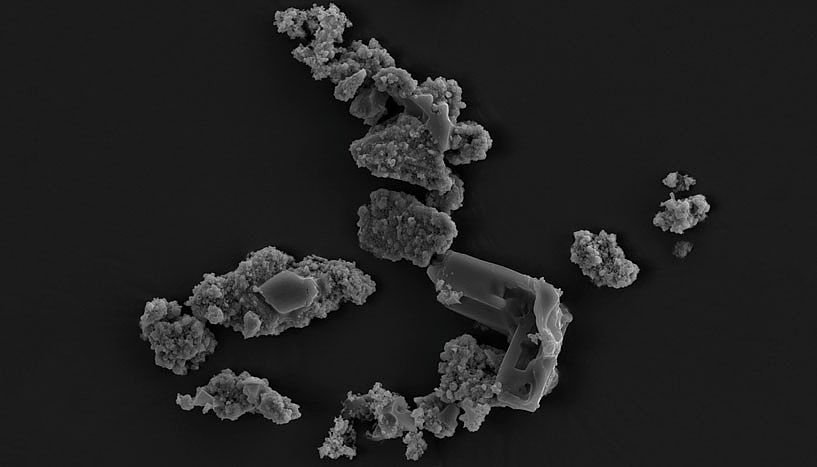
The effects of ancient asteroid impacts on Earth are still evident from the variety of impact craters across our planet. And from the Chelyabinsk event back in 2013, where an asteroid exploded in the air above a Russian town, we know how devastating an “airburst” event can be.
Now, researchers in Antarctica have discovered evidence of a strange intermediate-type event – a combination of an impact and an airburst. The event was so devastating, its effects are still apparent even though it took place 430,000 years ago.
Continue reading “100-meter Asteroid Created a Strange Impact Event in Antarctica 430,000 Years Ago”