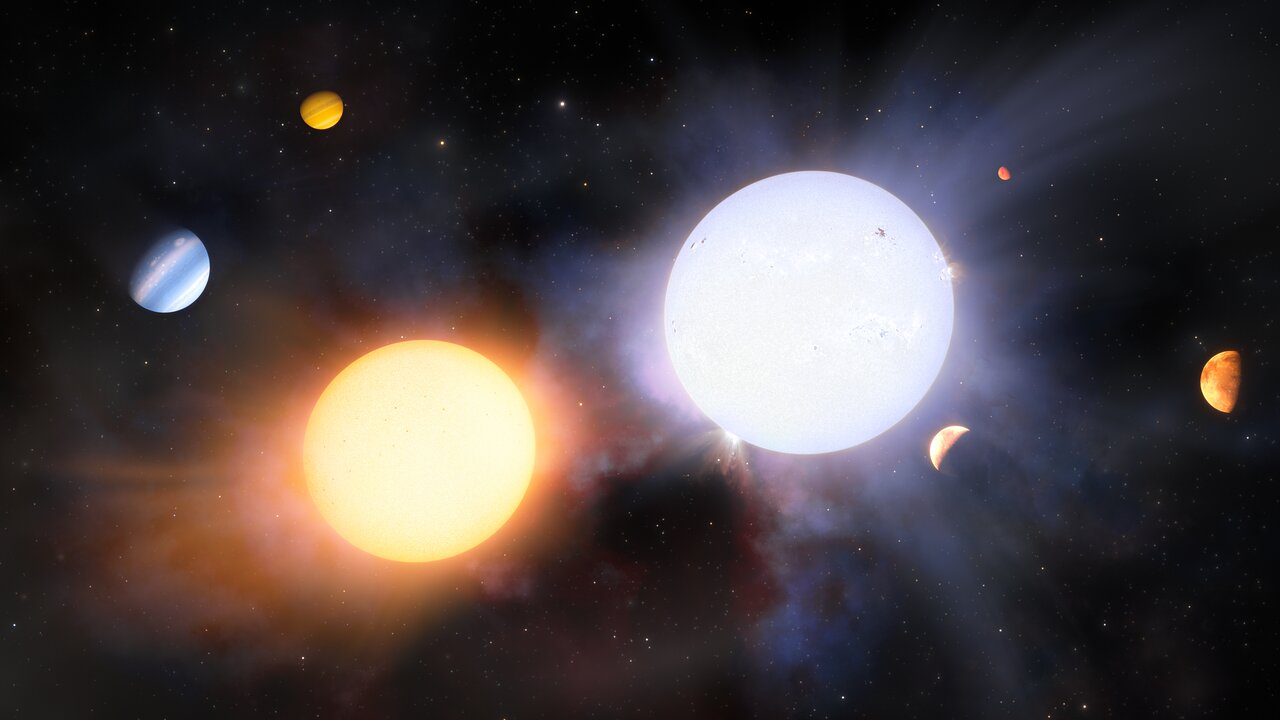
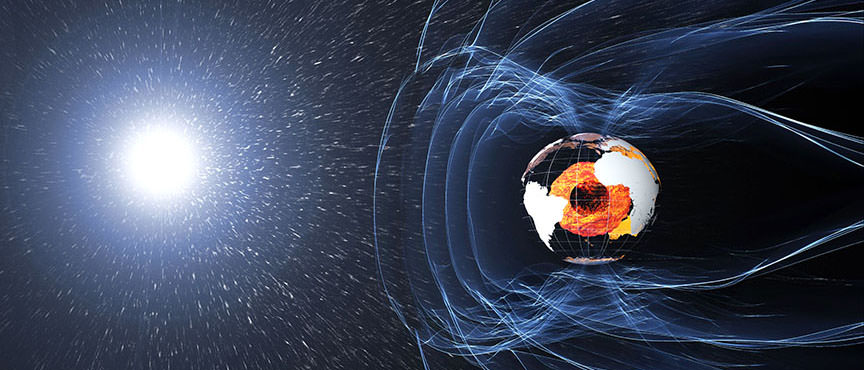
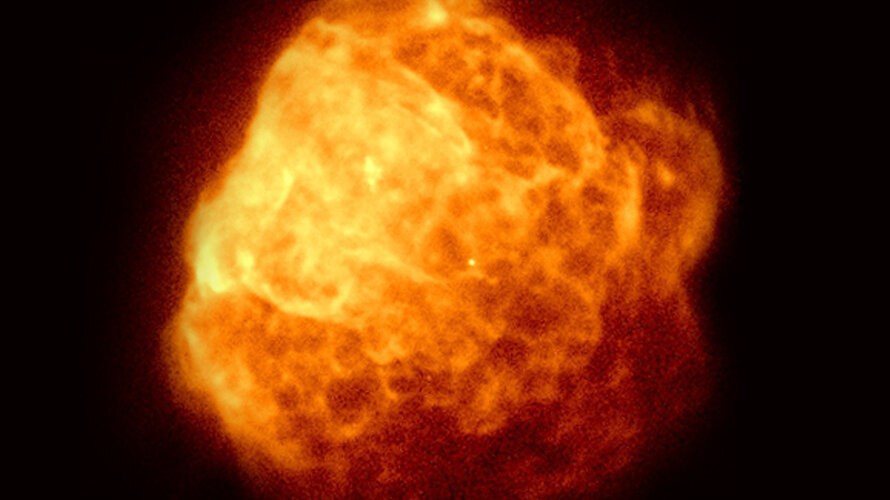
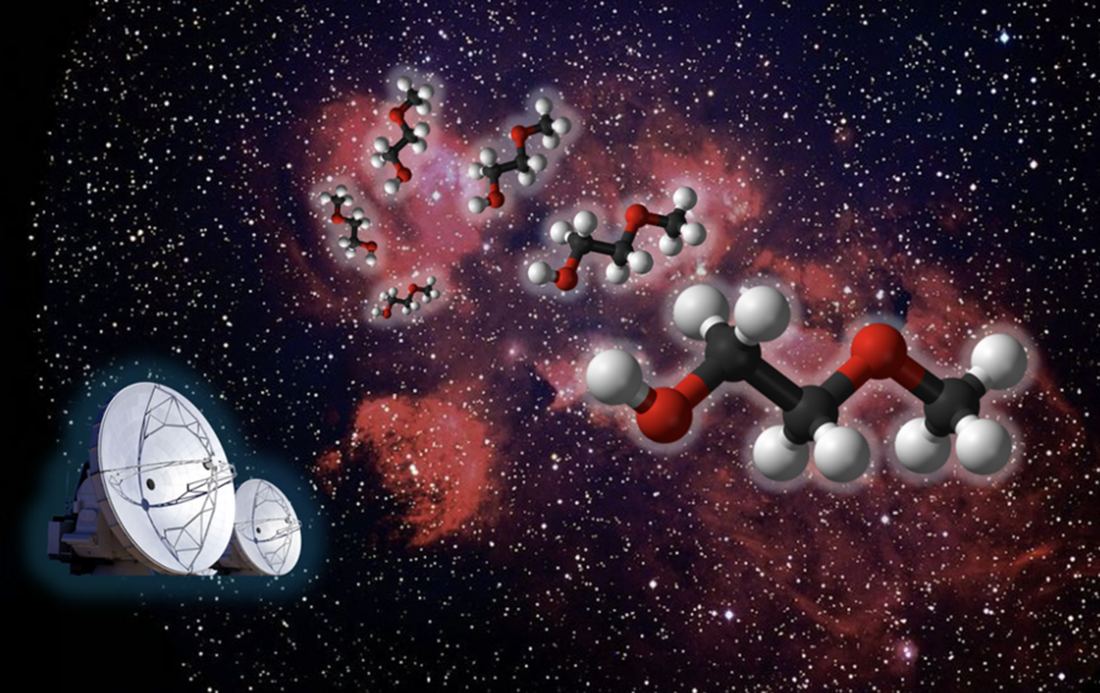
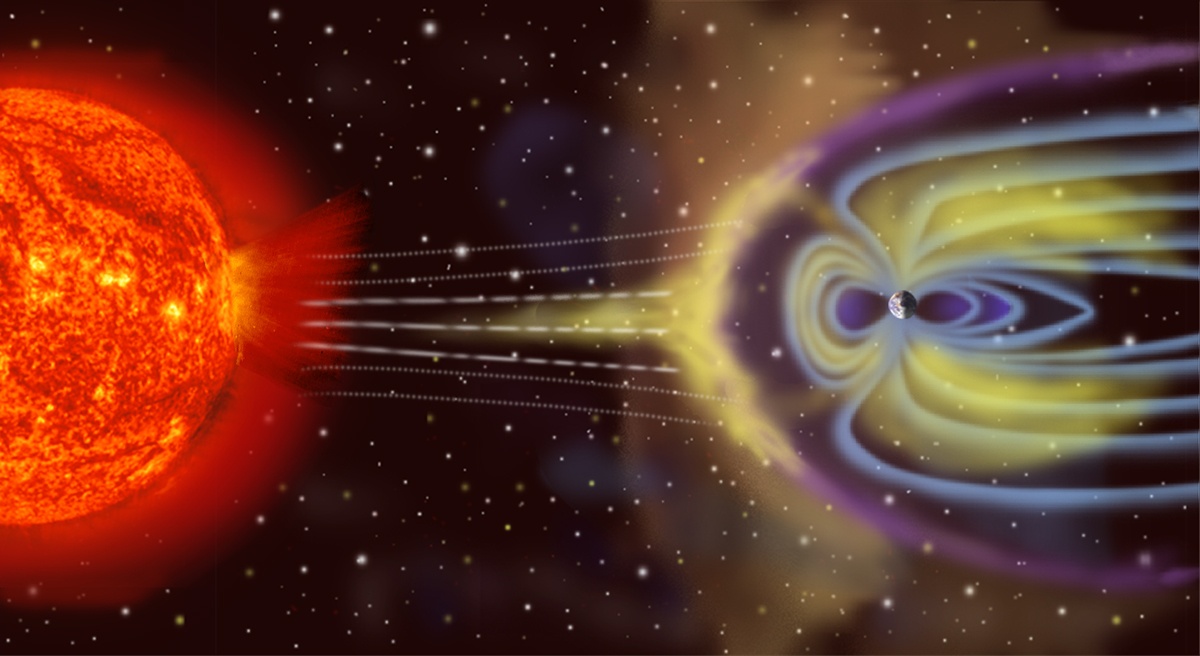
It stands to reason that stars formed from the same cloud of material will have the same metallicity. That fact underpins some avenues of astronomical research, like the search for the Sun’s siblings. But for some binary stars, it’s not always true. Their composition can be different despite forming from the same reservoir of material, and the difference extends to their planetary systems.
New research shows that the differences can be traced back to their earliest stages of formation.
Continue reading “Binary Stars Form in the Same Nebula But Aren’t Identical. Now We Know Why.”