Far away, deep in the dark, near the edge of interstellar space, Voyager 1 and 2 are hurtling near the tenuous edge of the magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun known as the heliosphere and NASA wants you to ride along.
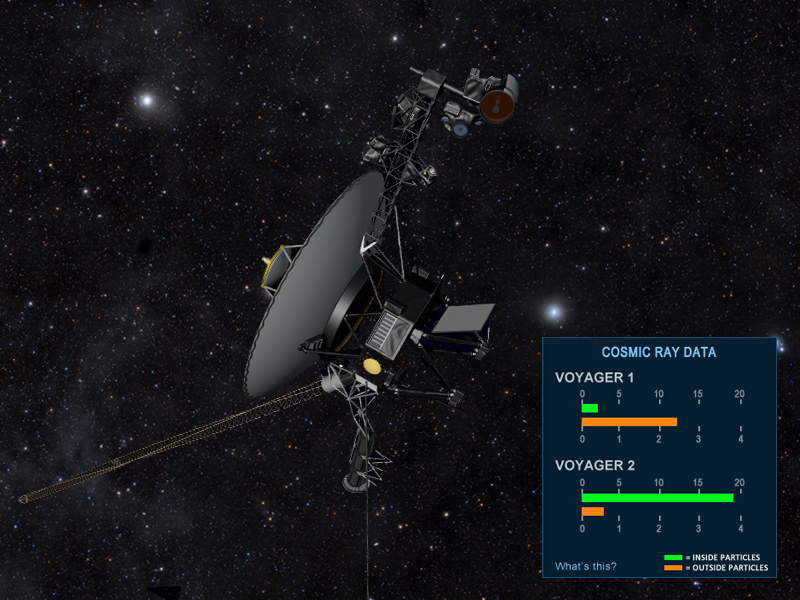
The Voyager website sports a new feature showing cosmic ray data. NASA’s Eyes on the Solar System, a popular Web-based interactive tool, contains a new Voyager module, that not only lets you ride along for the Voyagers’ journeys but also shows important scientific data flowing from the spacecraft.
[Warning:Play with this tool at your own risk. Interacting with this online feature can seriously impact your time; in an educational way, of course!]
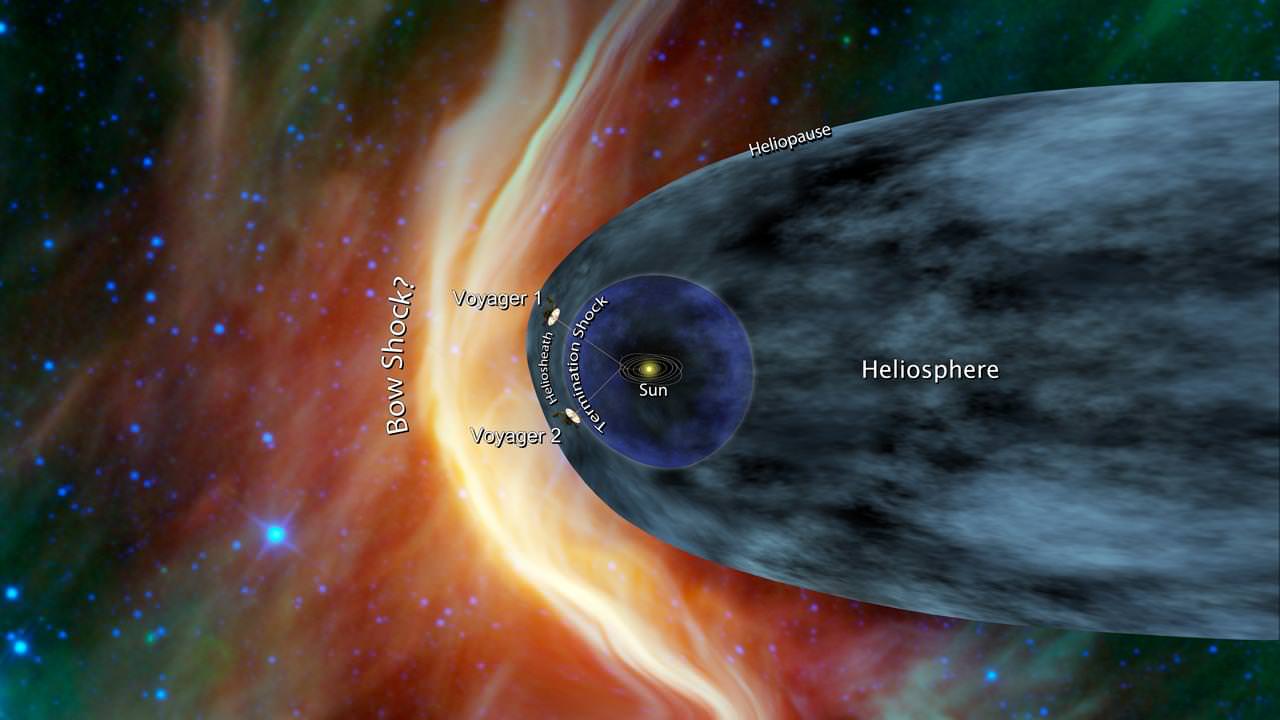
As Voyager 1 explores the outer limits of the heliosphere, where the breath from our Sun is just a whisper, scientists are looking for three key signs that the spacecraft has left our solar system and entered interstellar space, or the space between stars. Voyager 1 began heading for the outer Solar System after zipping through the Saturn system in 1980.
The new module contains three gauges, updated every six hours from real data from Voyager 1 and 2, that indicate the level of fast-moving particles, slower-moving particles and the direction of the magnetic field. Fast-moving charged particles, mainly protons, come from distant stars and originate from outside the heliosphere. Slower-moving particles, also mainly protons, come from within the heliosphere. Scientists are looking for the levels of outside particles to jump dramatically while inside particles dip. If these levels hold steady, it means the Voyager spacecraft no longer feel the wind from our Sun and the gulf between stars awaits.
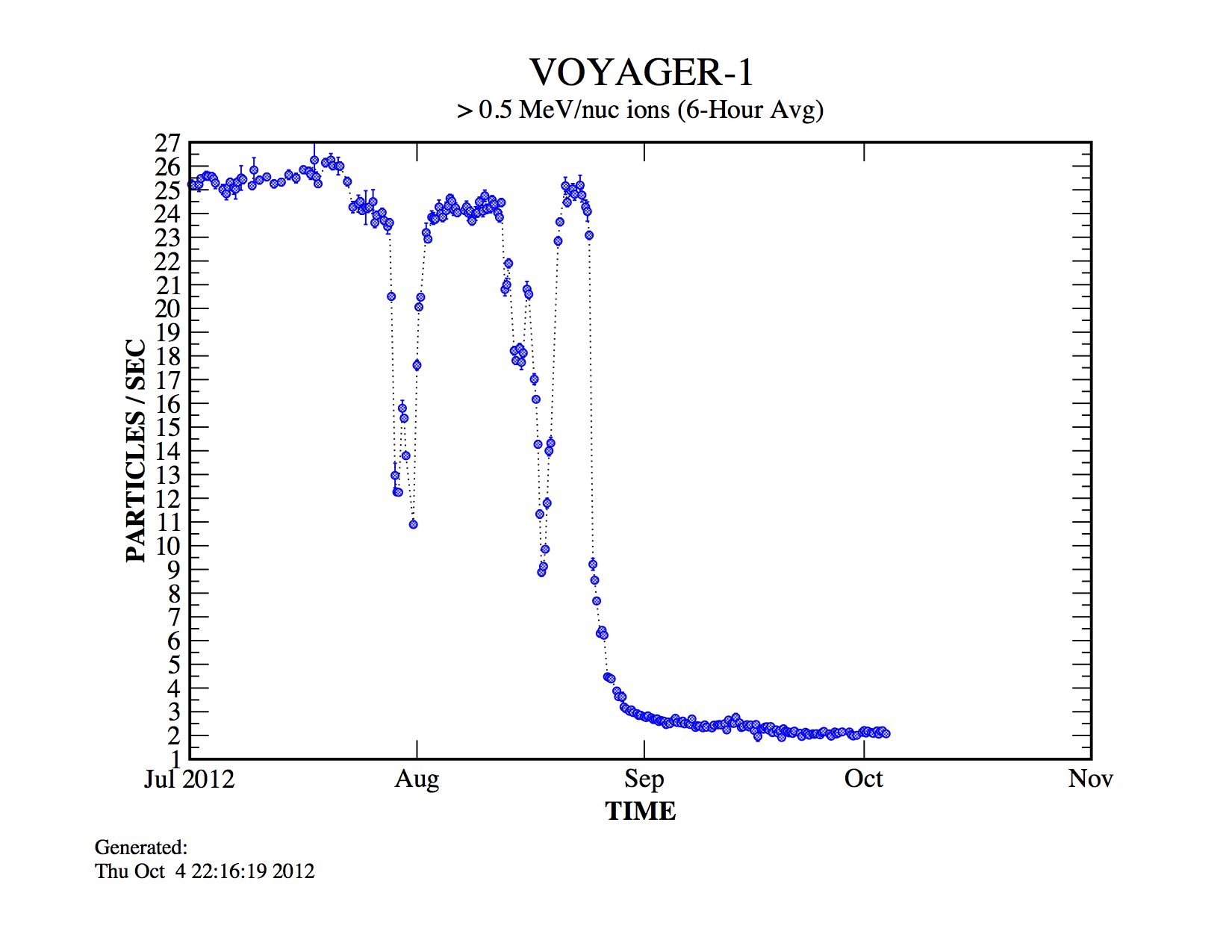
Over the past couple of years, data from Voyager 1, the most distant man-made object, show a steady increase of high-powered cosmic radiation indicating the edge is near, scientists say. Voyager 1 appears to have reached the last region before interstellar space. Scientists dubbed the region the “magnetic highway.” Particles from outside are streaming in while particles from inside are streaming out. Voyager 2’s instruments detect slight drops in inside particles but scientists don’t think the probe has entered the area yet.
Scientists also expect a change in the direction of the magnetic field. While particle data is updated every six hours, analyses of the magnetic field data usually takes a few months to prepare.
Although launched first, Voyager 2 lags behind its twin Voyager 1 by more than 20 times the distance between the Earth and the Sun. Voyager 2 blasted off August 20, 1977 aboard a Titan-Centaur rocket from Cape Canaveral, Florida. The nuclear-powered craft visited Jupiter and Saturn with an additional mission, called the Grand Tour, to study Uranus and Neptune. Voyager 1 launched two weeks later on September 5, 1977. With a faster flight path, Voyager 1 arrived at Jupiter four months before its sister craft. Voyager 1 went on to study Saturn before using the ringed planet’s gravity field to slingshot it up and out of the plane of the solar system toward the constellation Ophiuchus, the Serpent Bearer.
NASA’s Eyes on the Solar System allows viewers to hitch a ride with any of NASA’s spacecraft as they explore the solar system. Time can be slowed for a near approach of a moon or asteroid or sped up to coast between the planets. Watch close at just the right moment and you can witness one of the spacecrafts roll maneuvers. All spacecraft movements are based on actual spacecraft navigation data.
Check out the Voyager module here, and check out the rest of the the Solar System here at Eyes on the Solar System.