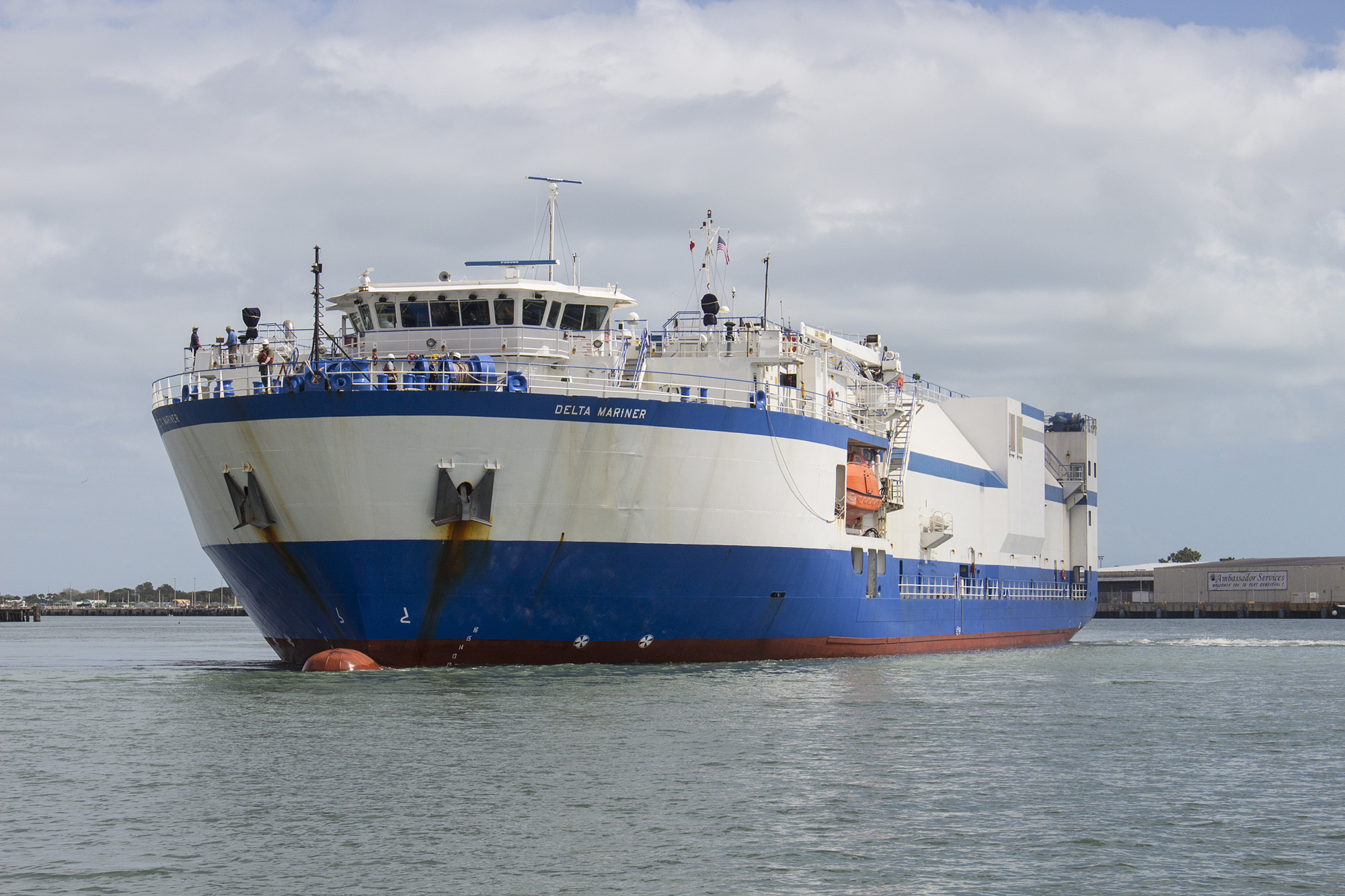
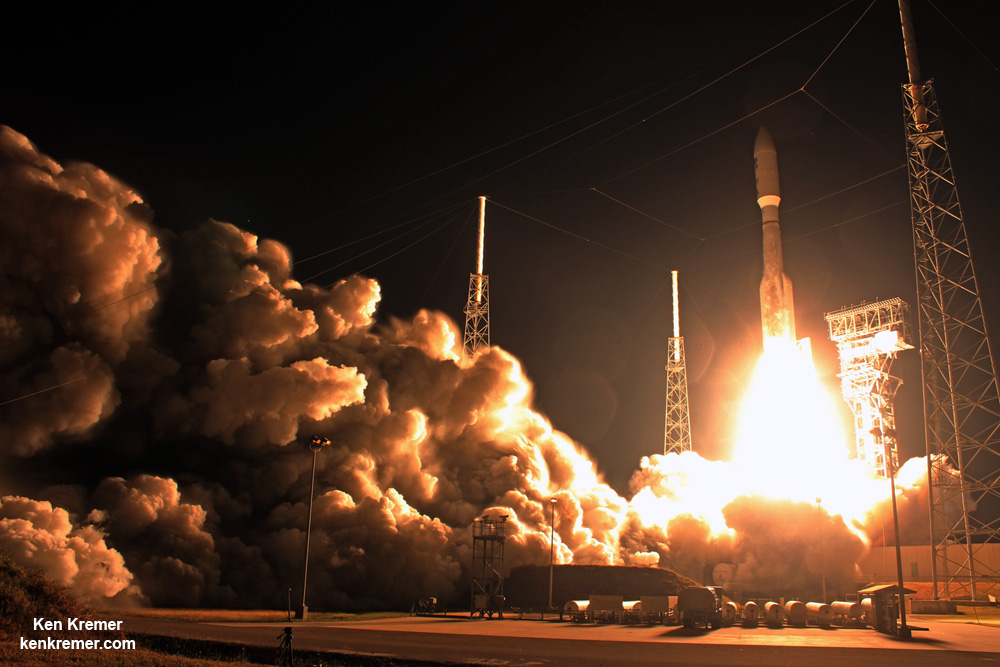
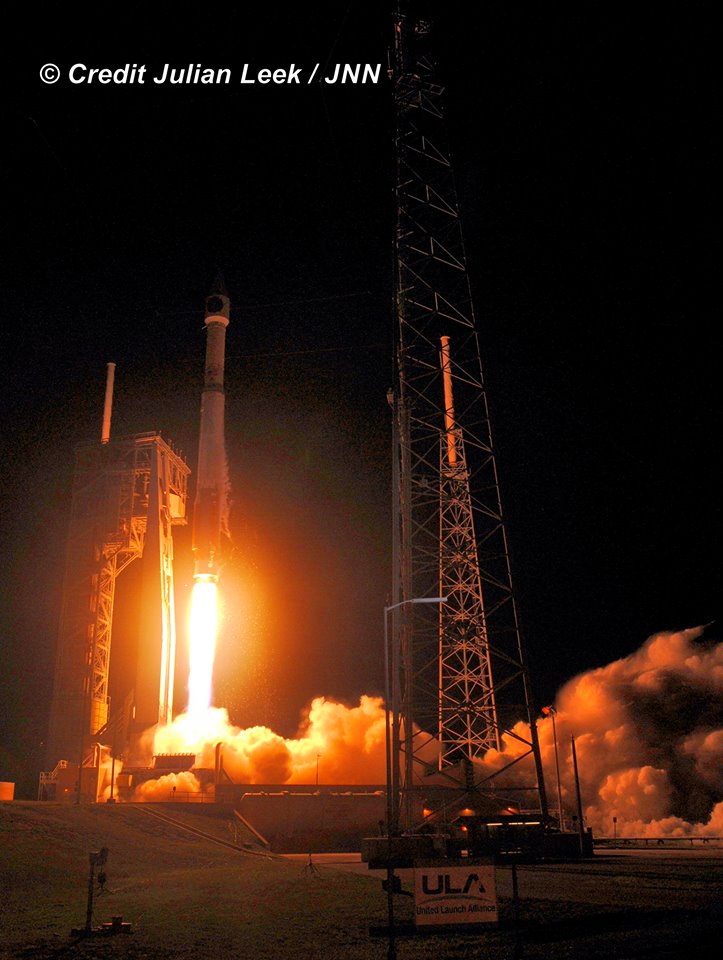
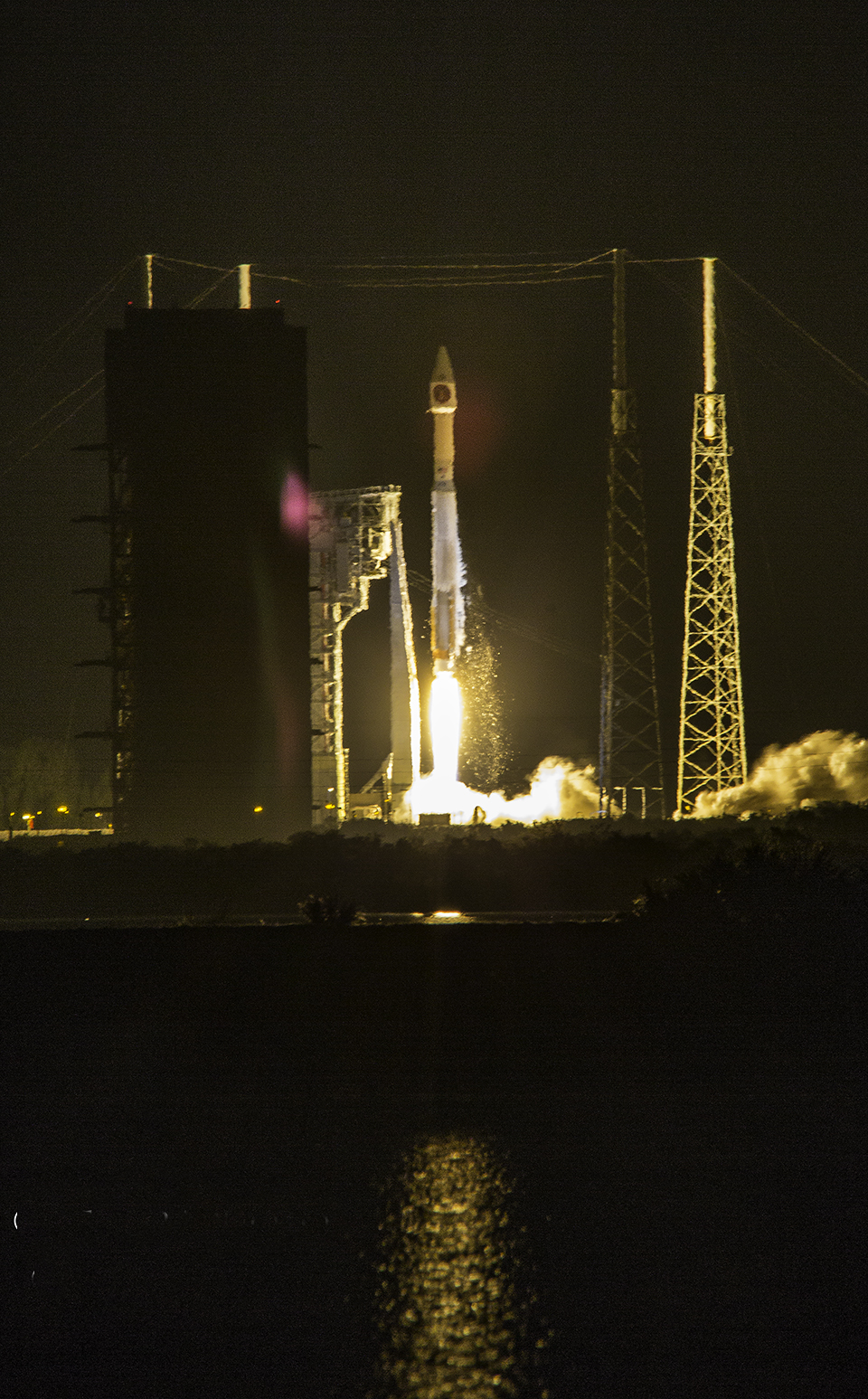
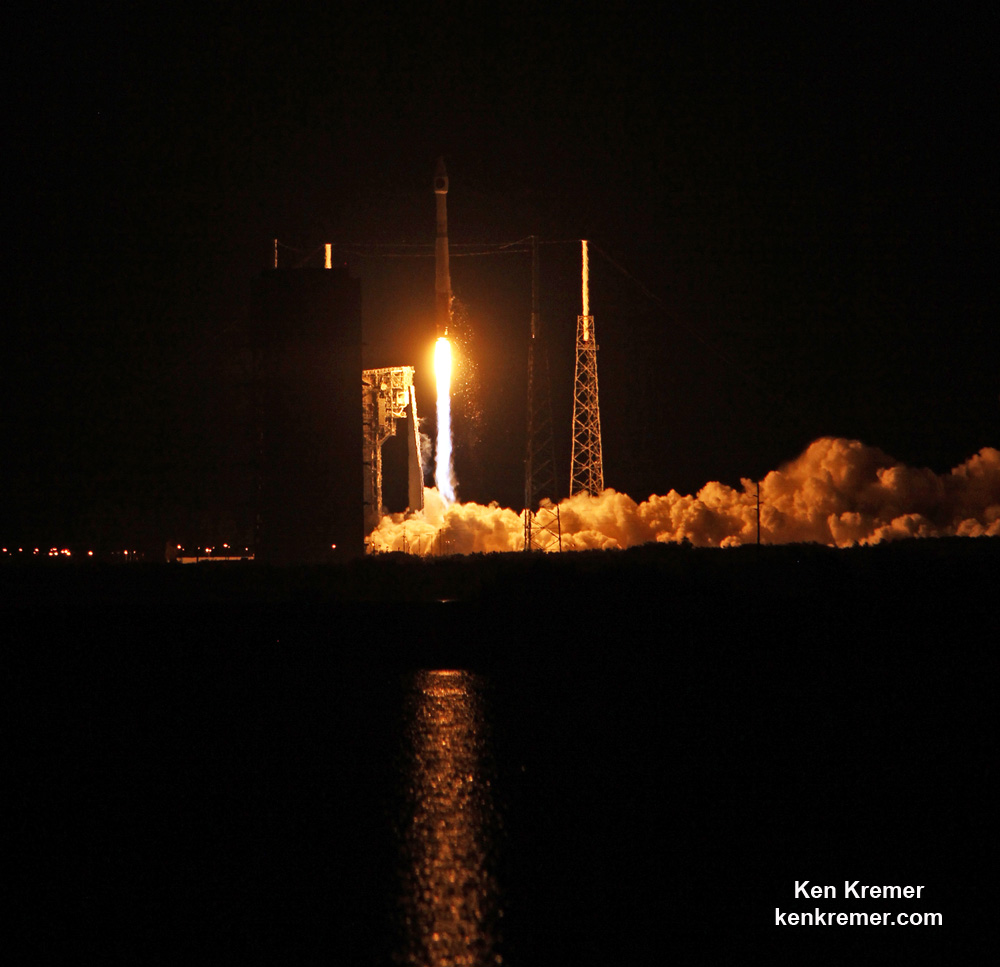
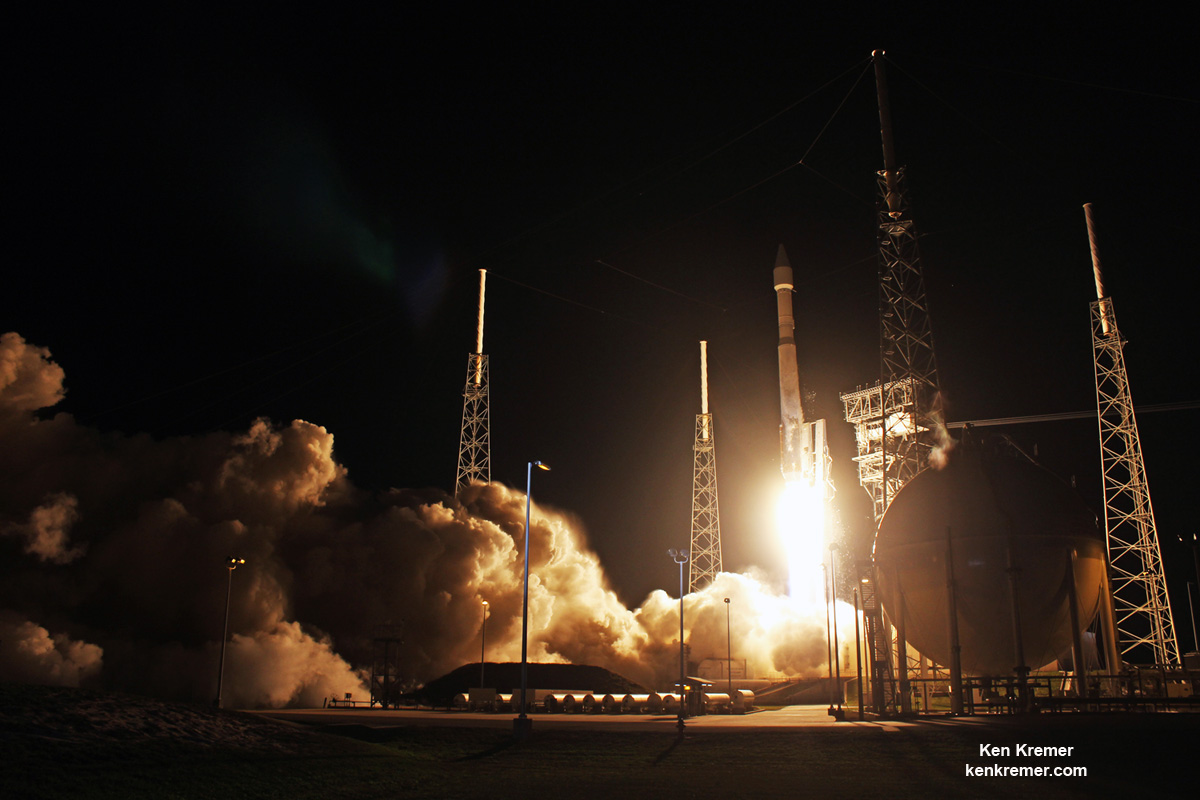
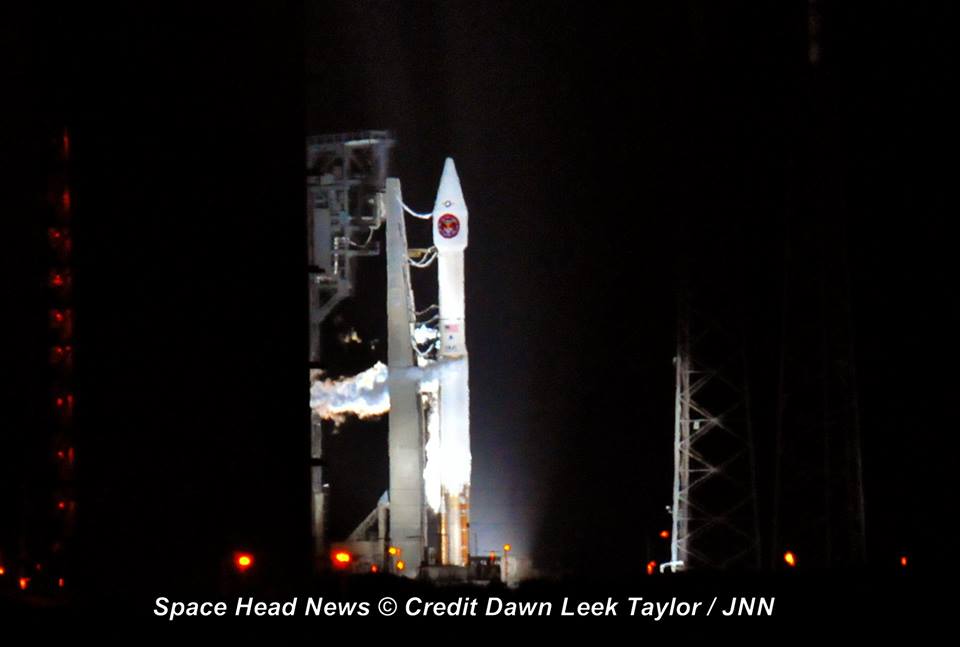
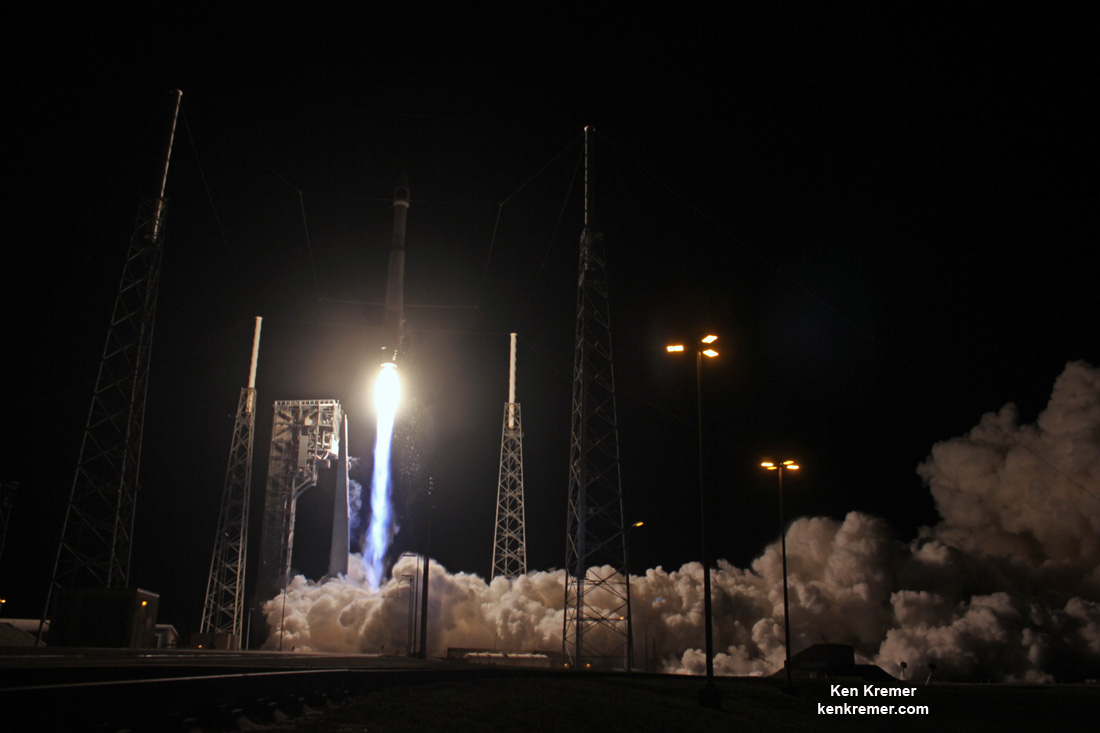
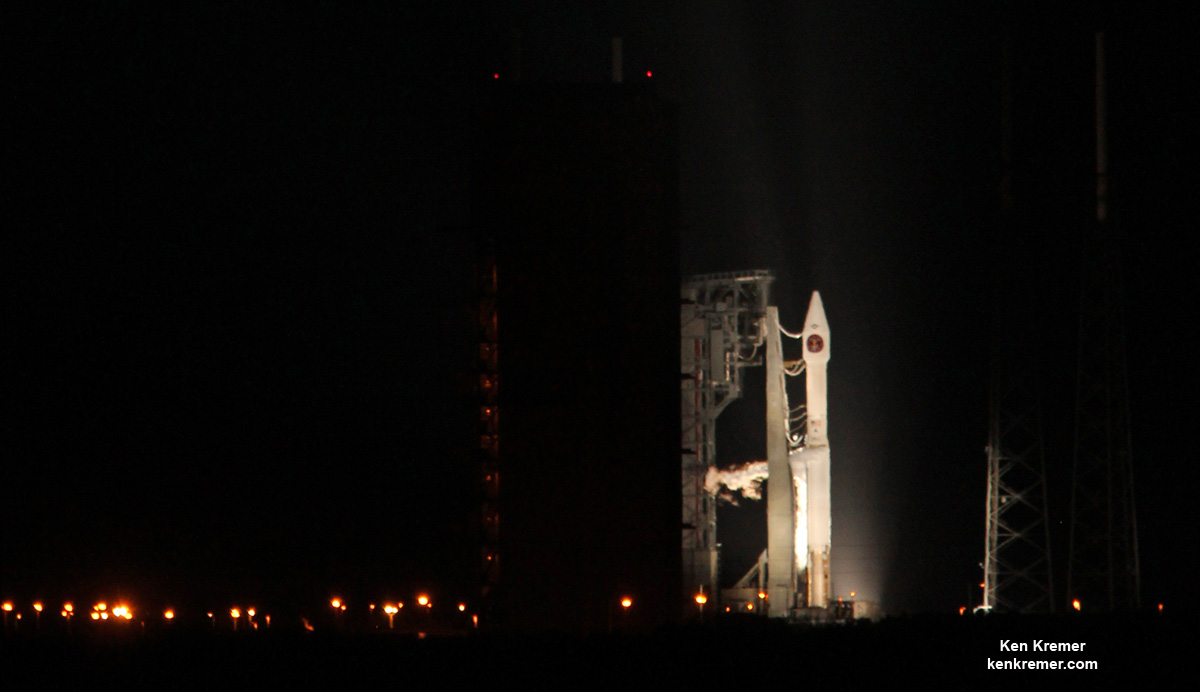
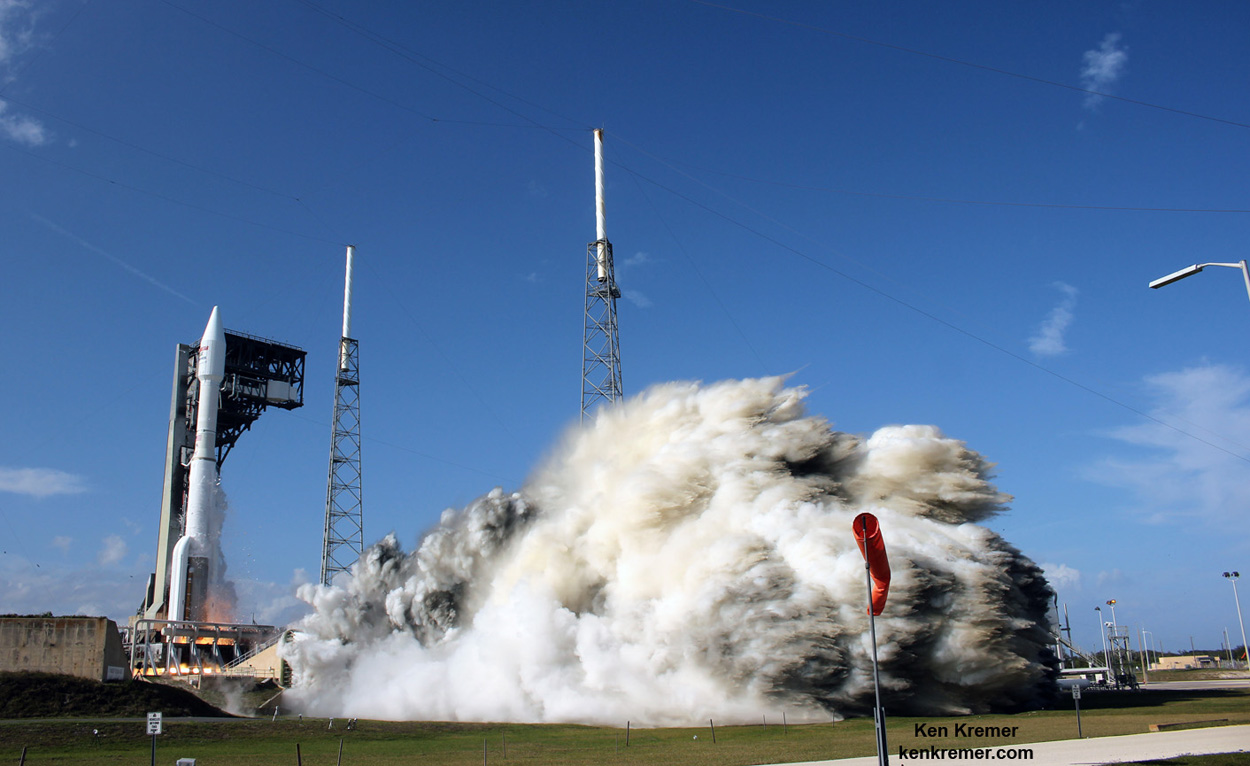
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – It’s March Madness for Space fans worldwide! A triple header of space spectaculars starts overnight with a SpaceX Falcon 9 launching in the wee hours of Tuesday, March 14 from the Florida Space Coast.
Indeed a trio of launches is planned in the next week as launch competitor and arch rival United Launch Alliance (ULA) plans a duo of nighttime blastoffs from their Delta and Atlas rocket families – following closely on the heels of the SpaceX Falcon 9 launching a commercial telecommunications satellite.
Of course it’s all dependent on everything happening like clockwork!
And there is no guarantee of that given the unpredictable nature of the fast changing weather on the Florida Space Coast and unknown encounters with technical gremlins which have already plagued all 3 rockets this month.
Each liftoff has already been postponed by several days this month. And the rocket launch order has swapped positions.
At any rate, SpaceX is now the first on tap after midnight tonight on Tuesday, March 14.
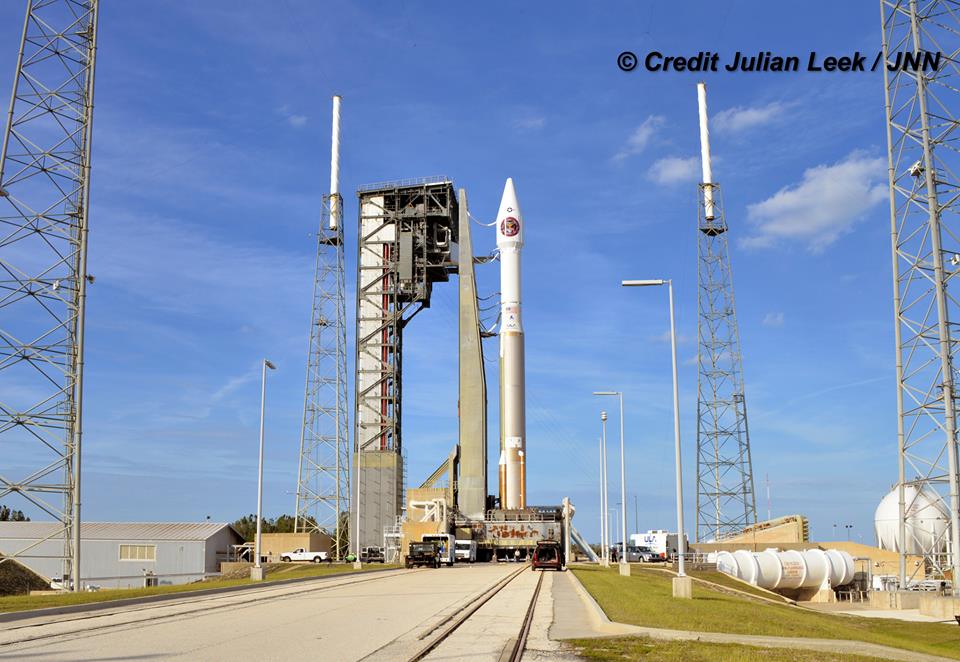
The Delta IV and Atlas V will follow on March 17 and March 21 respectively – if all goes well.
So to paraphrase moon walker Buzz Aldrin;
‘Get Your Ass to the Florida Space Coast – Fast !’
The potential for a grand slam also exists at the very end of the month. But let’s get through at least the first launch of Falcon first.
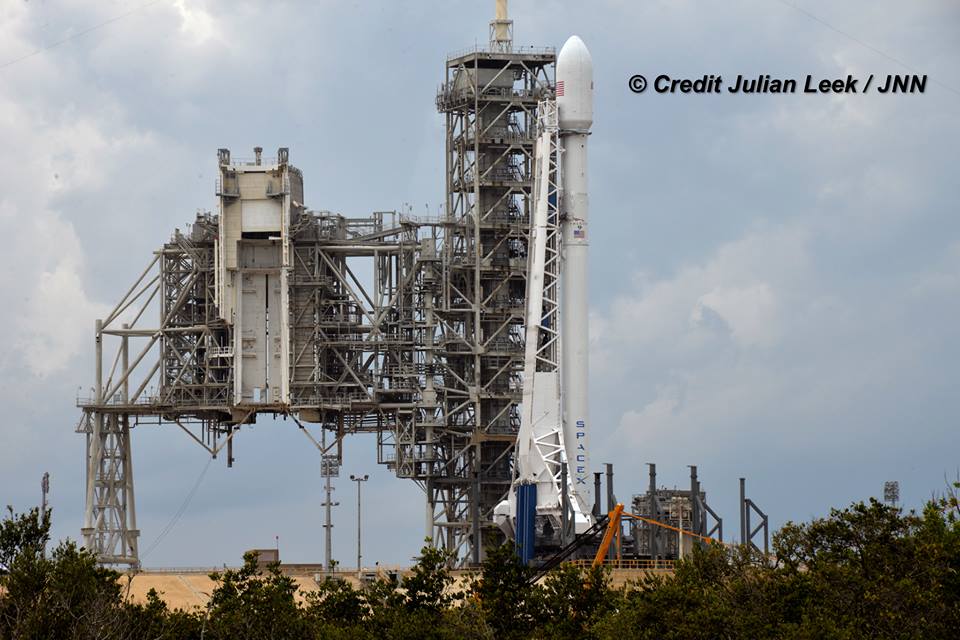

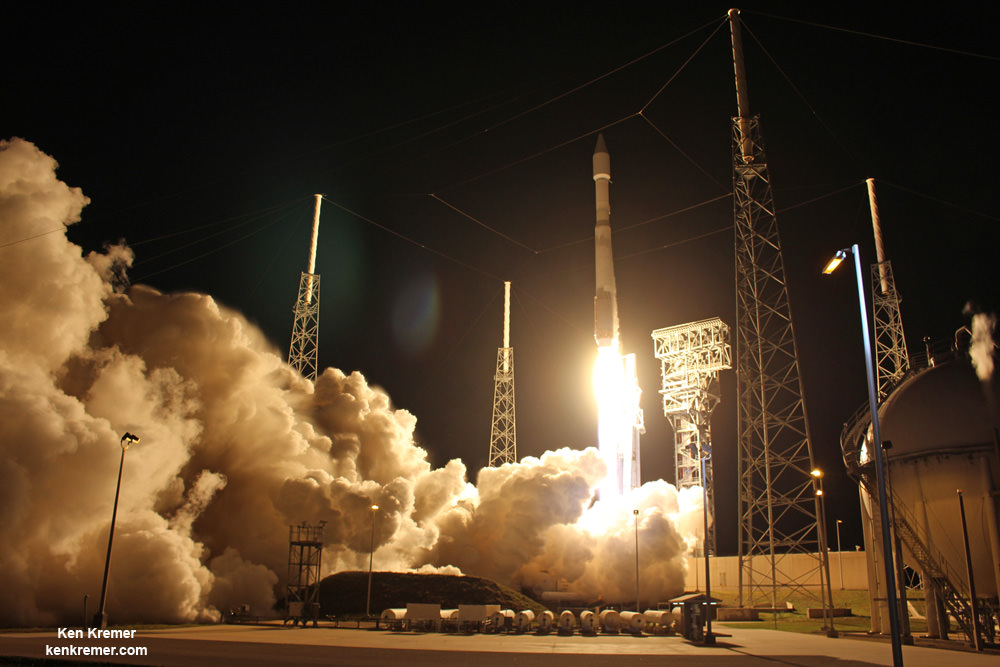
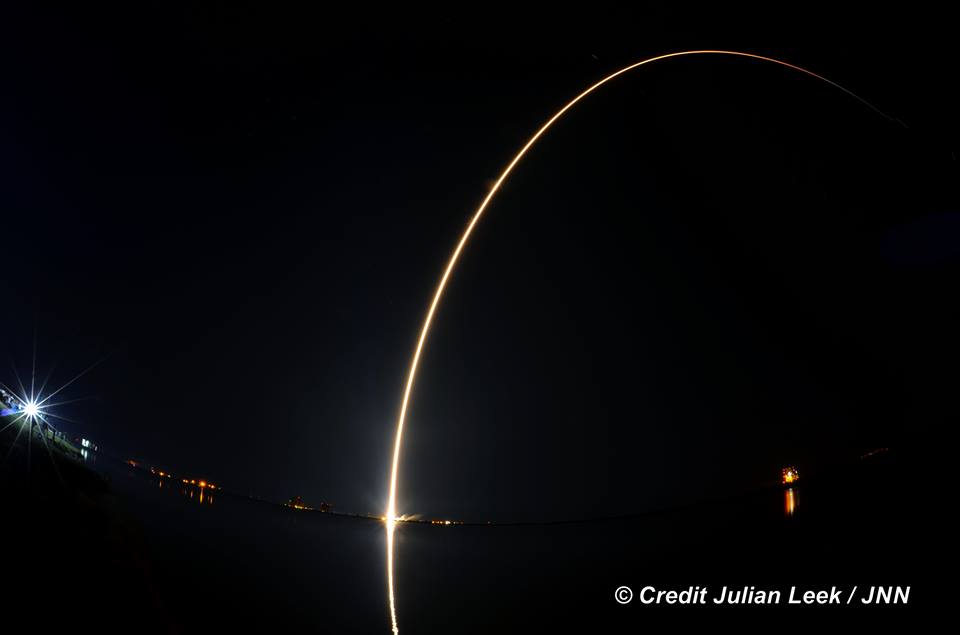
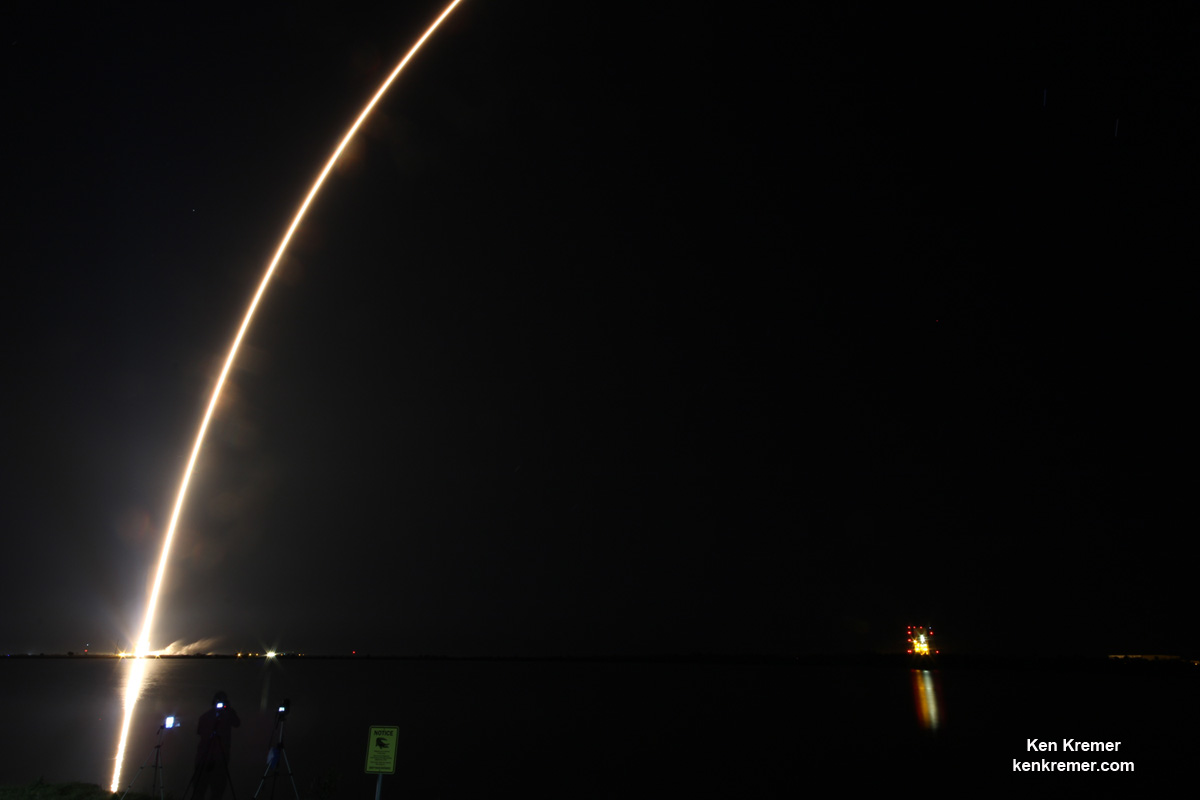
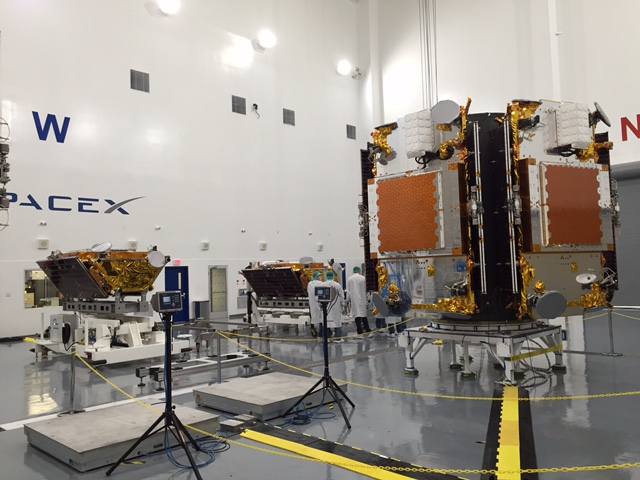
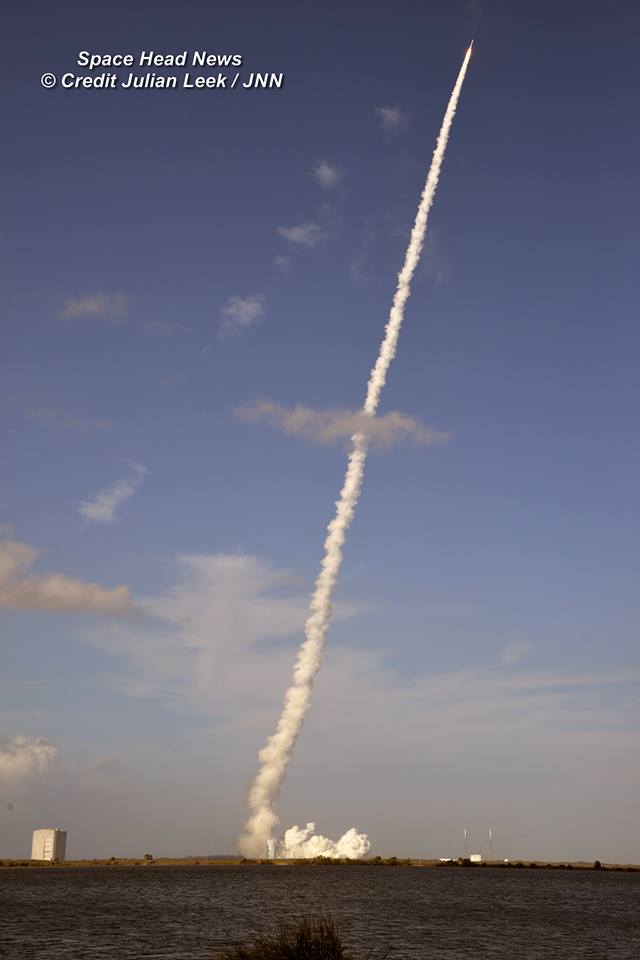
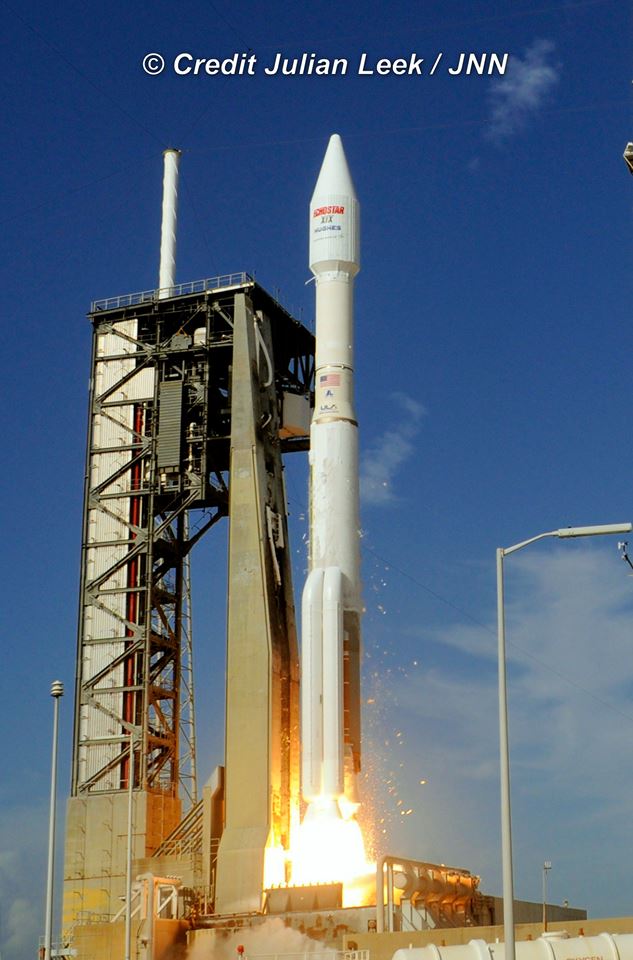
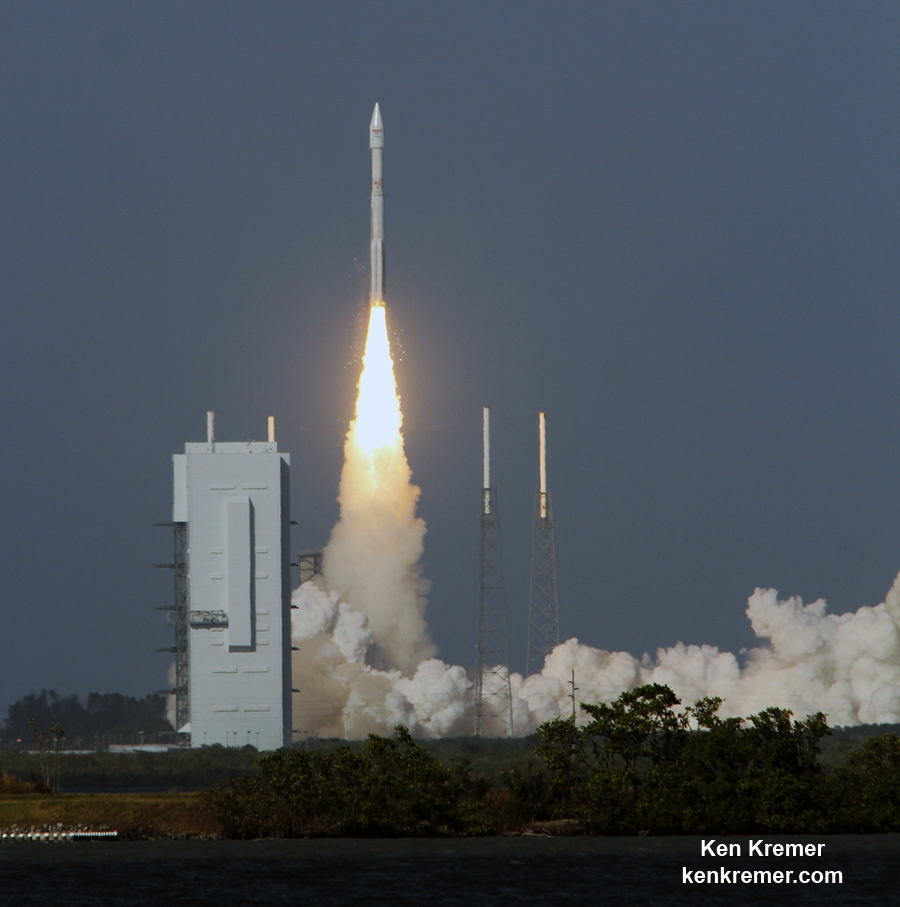
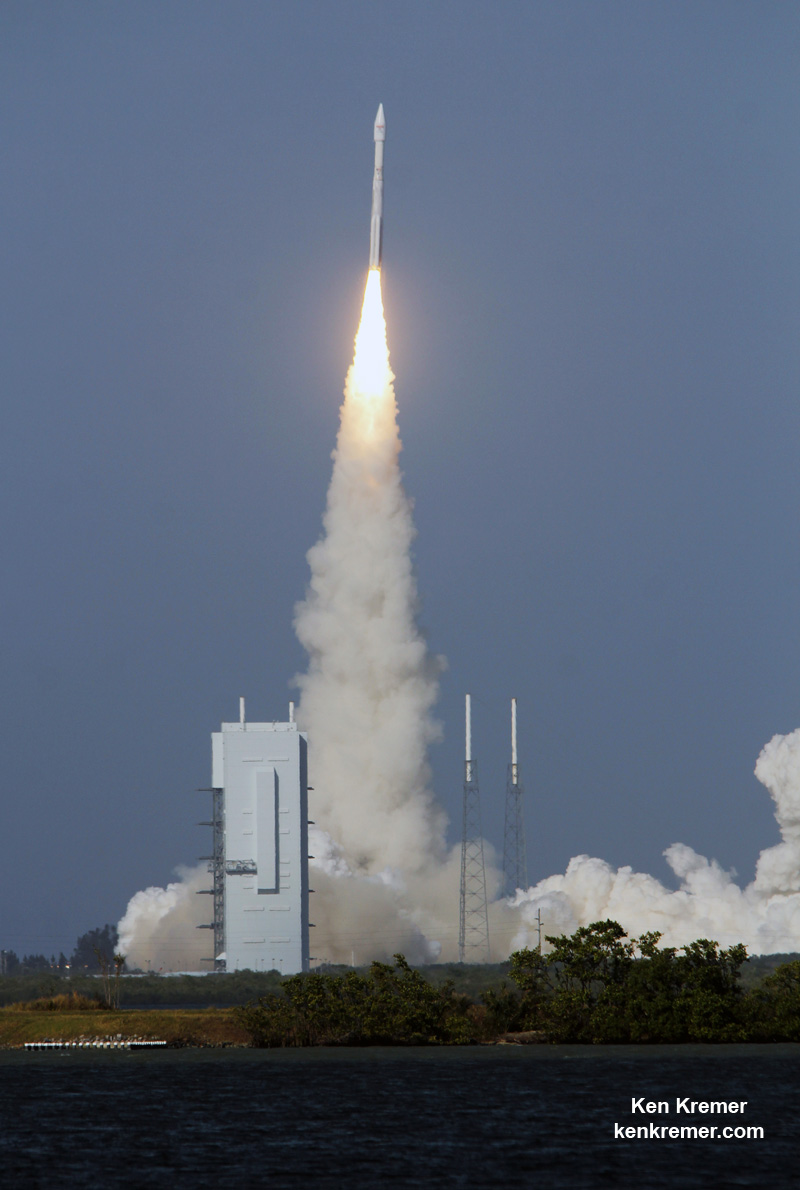
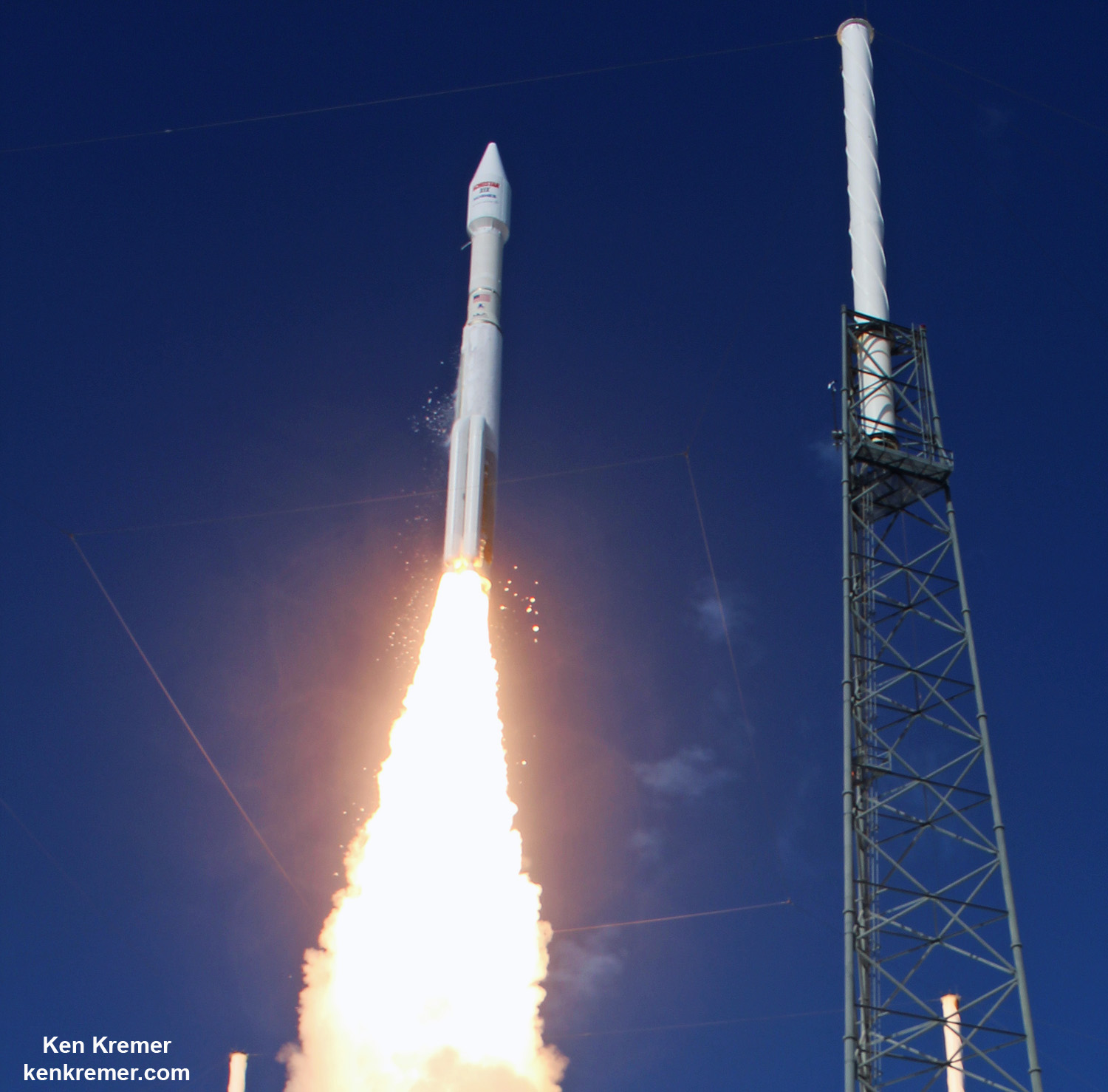
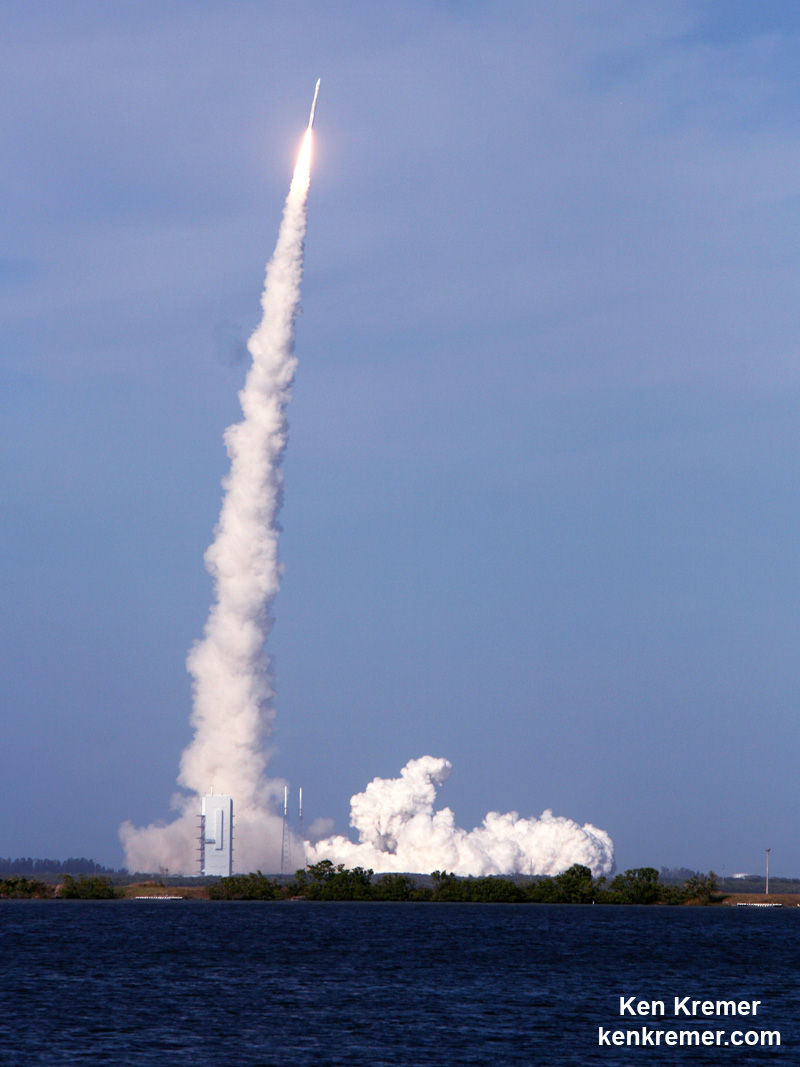
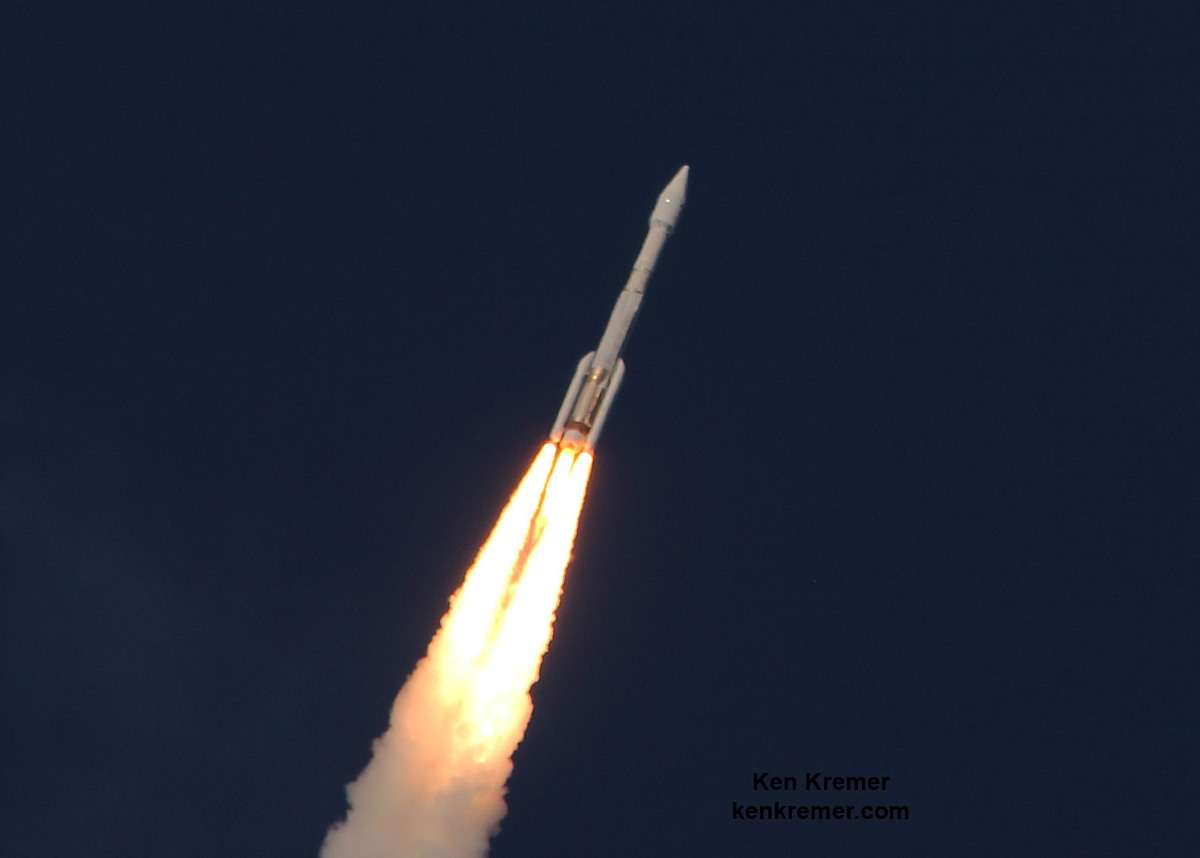
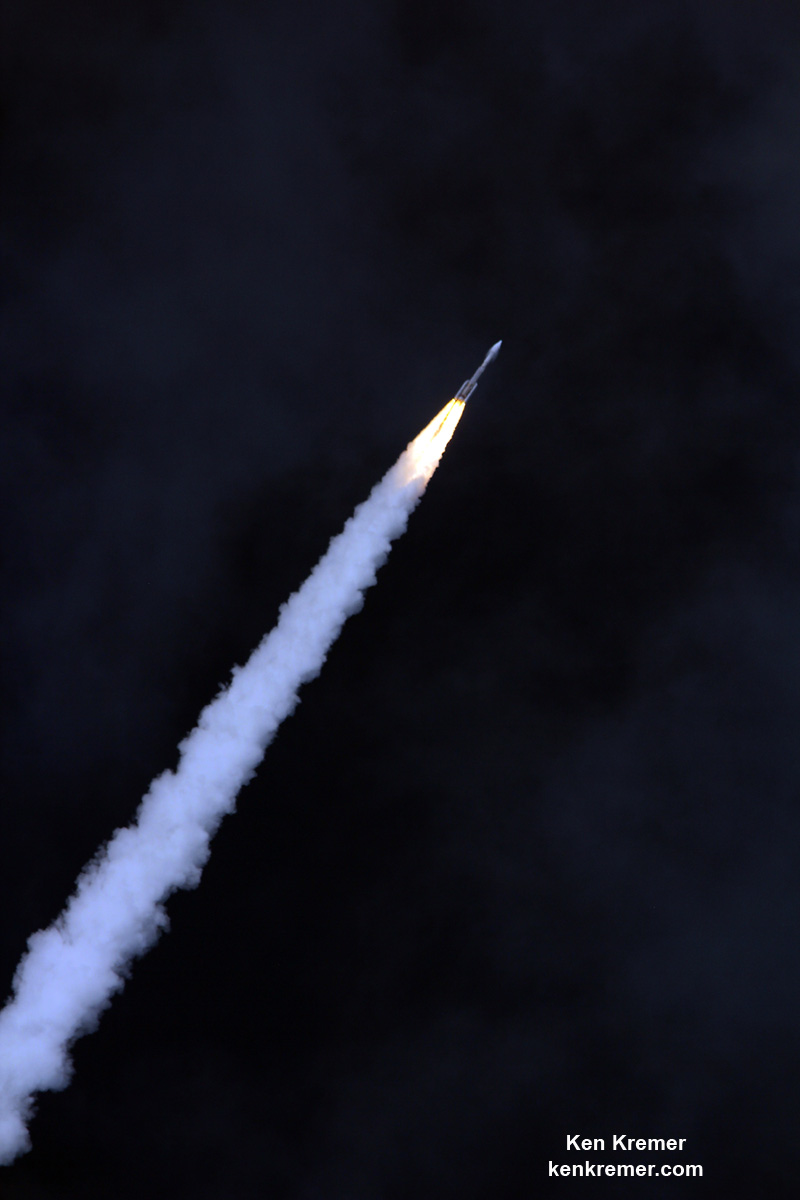
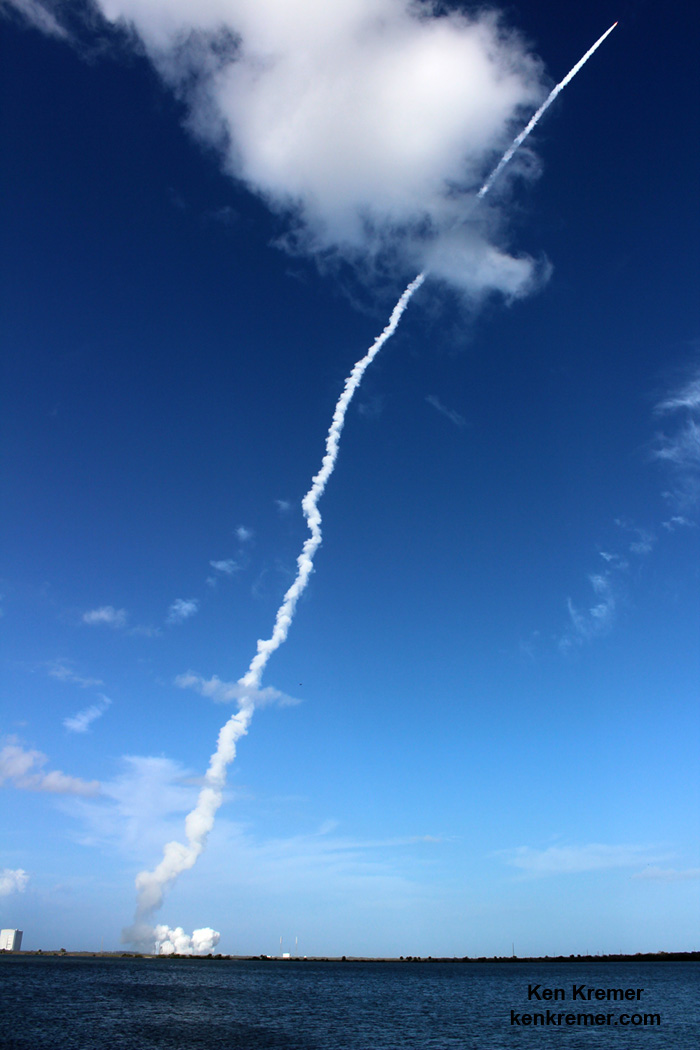
Liftoff of the two stage SpaceX Falcon 9 carrying the EchoStar 23 telecommunications satellite is now slated for a post midnight spectacle next Tuesday, Mar. 14 from launch pad 39A on the Kennedy Space Center at the opening of the launch window at 1:34 a.m. EDT.
The two and a half hour launch window closes at 4:04 a.m. EDT.
You can watch the launch live on a SpaceX dedicated webcast starting about 20 minutes prior to the 1:34 a.m. liftoff time.
The SpaceX webcast will be available starting at about 20 minutes before liftoff, at approximately 1:14 a.m. EDT.
Watch at: SpaceX.com/webcast
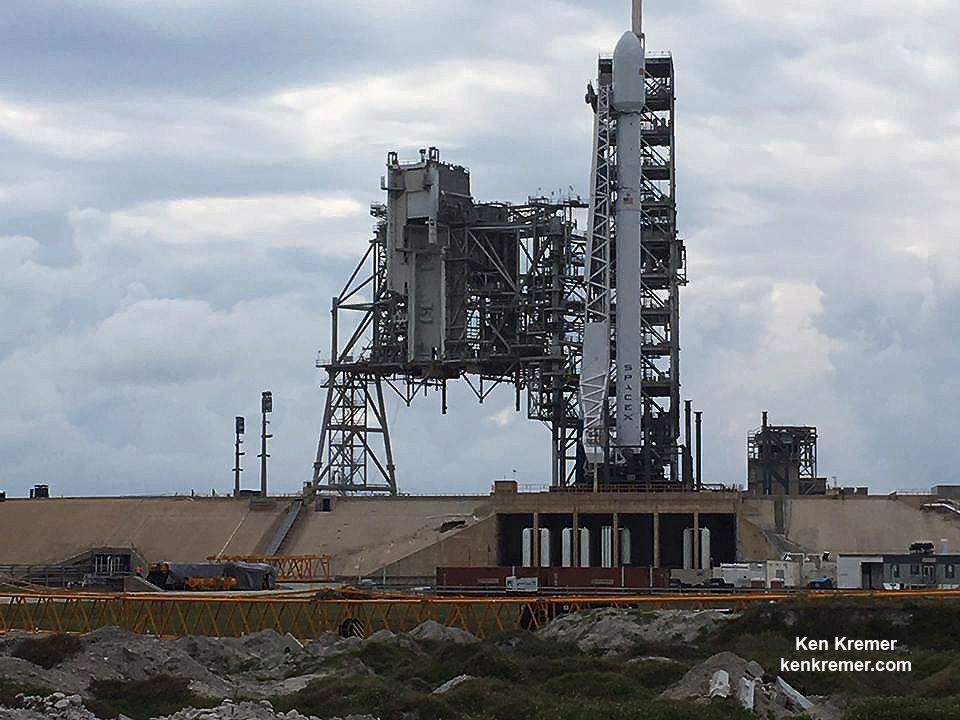

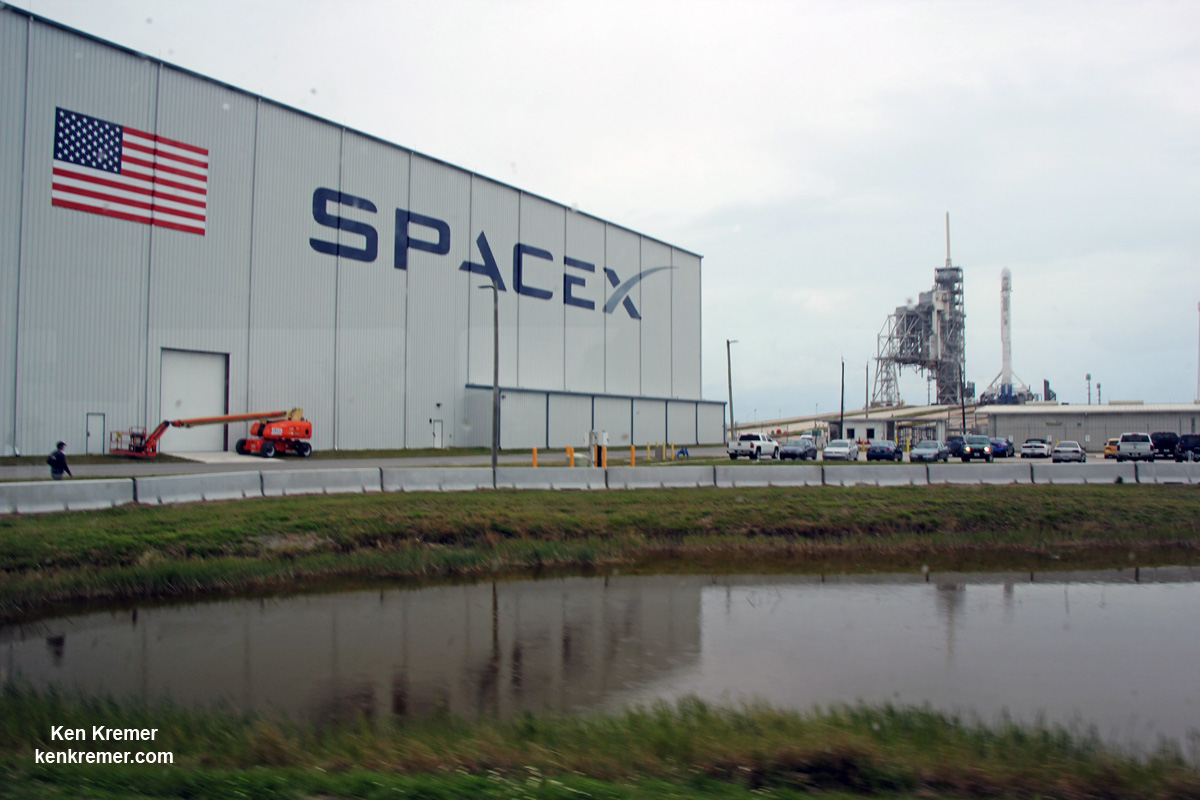
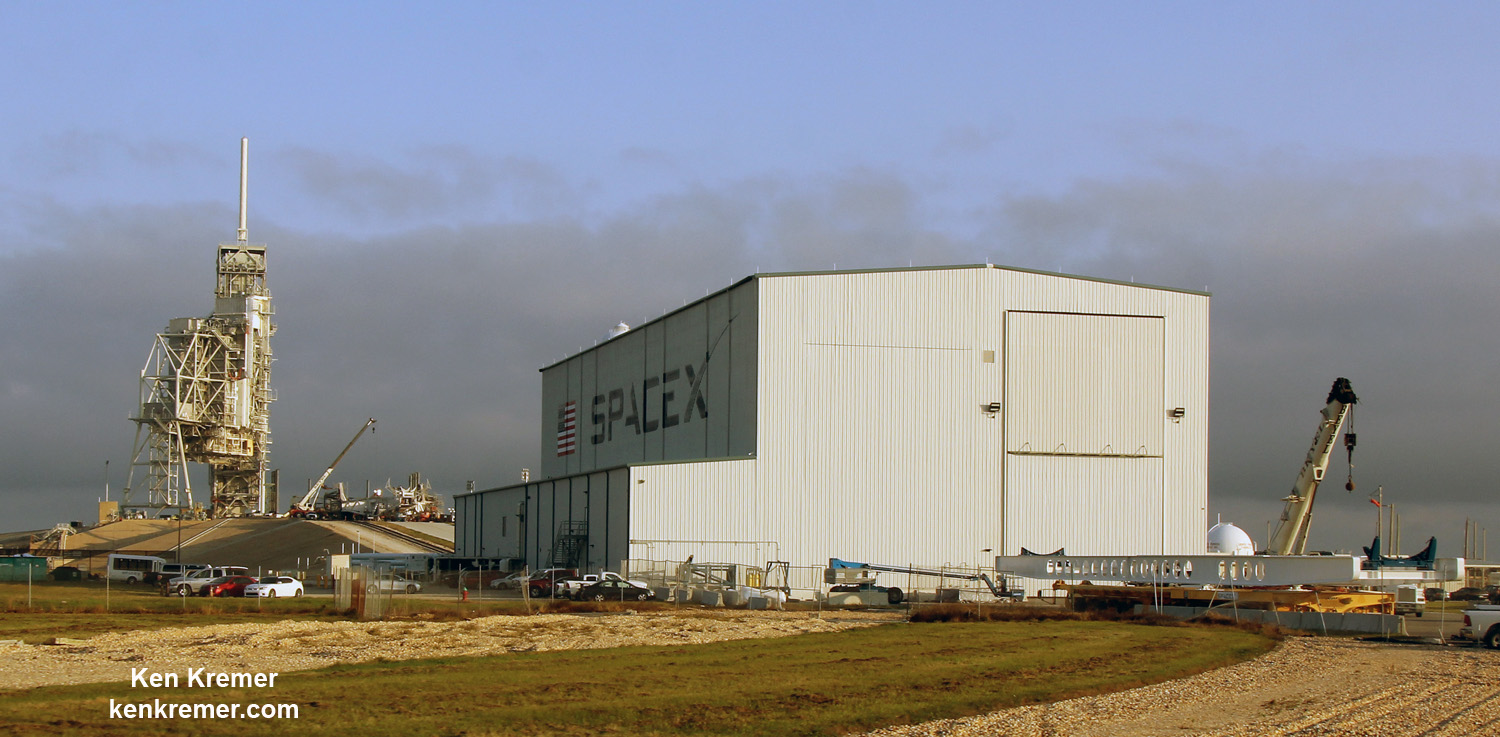
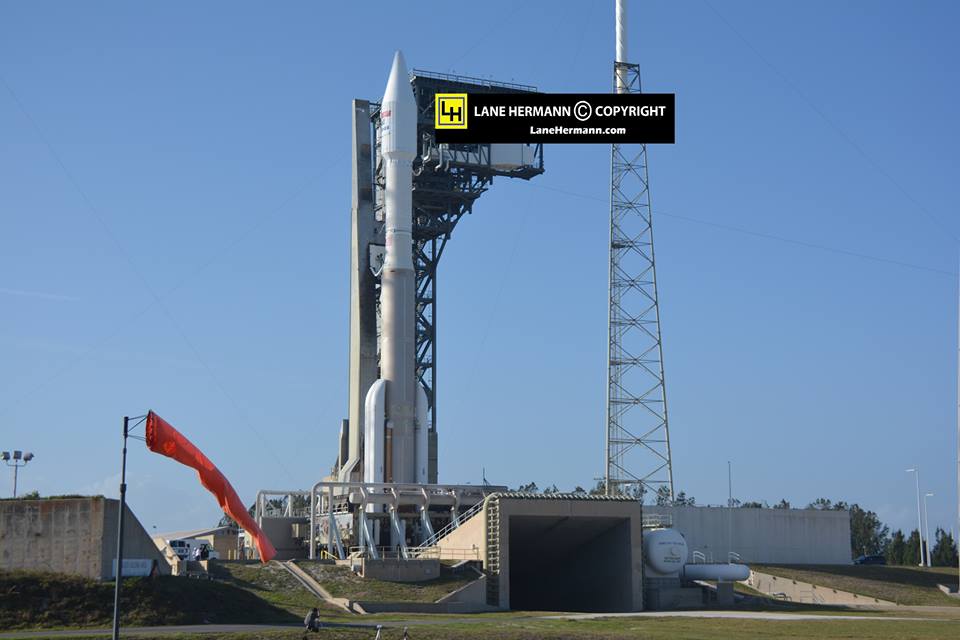
Following a successful static fire test last week on Mar. 9 of the first stage boosters engines, the SpaceX Falcon 9 was integrated with the EchoStar 23 direct to home TV satellite and rolled back out to pad 39A
The Falcon 9 rocket was raised erect into launch position by the time I visited the pad this afternoon, Monday March 13, to set up my cameras.
The weather outlook is not great at this moment, with rain and thick clouds smothering the coastline and central Florida.
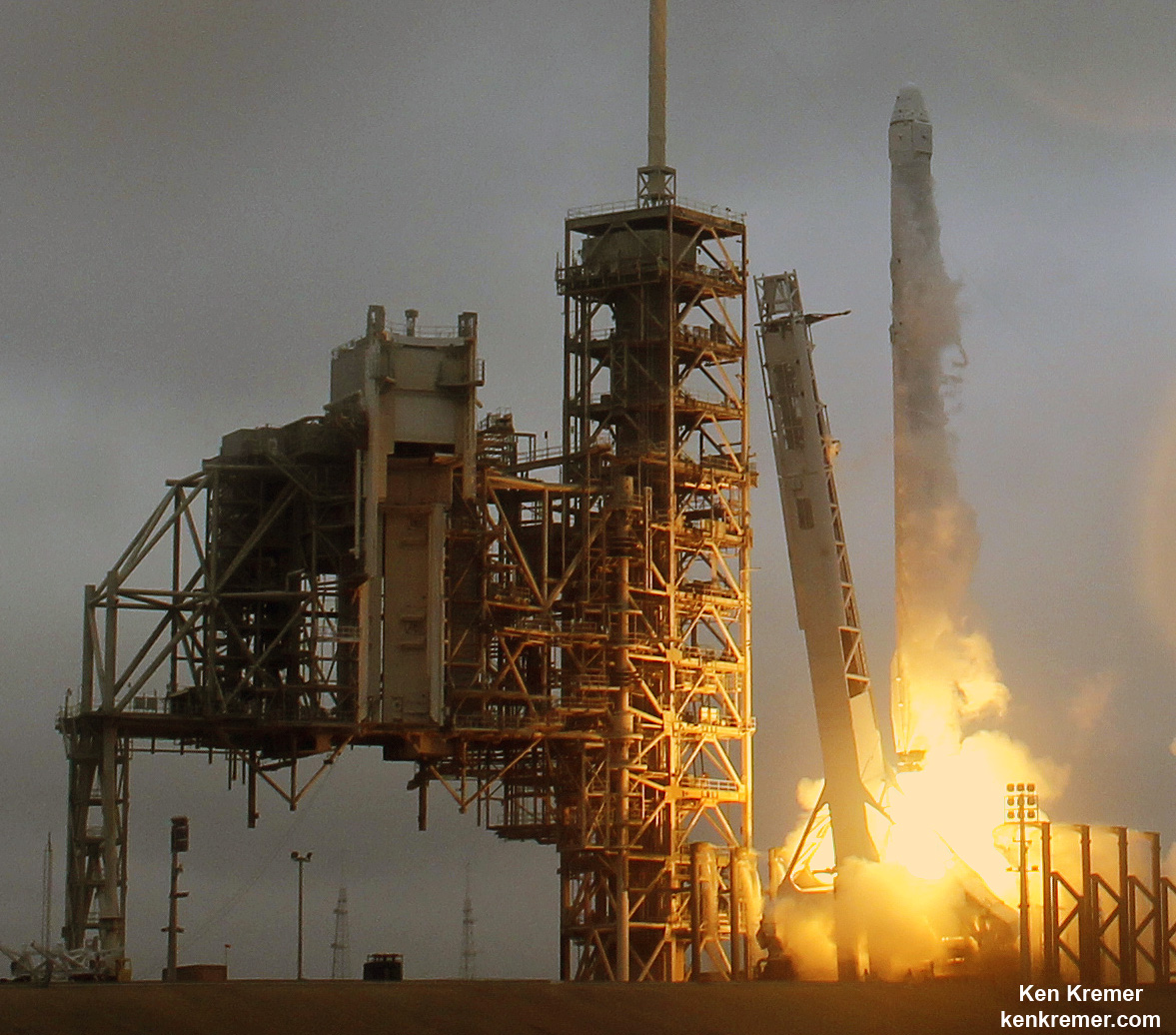
The planned Mar. 14 launch comes barely three weeks after the Falcon’s successful debut on Feb. 19 on the NASA contracted Dragon CRS-10 mission that delivered over 2.5 tons of cargo to the six person crew living and working aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
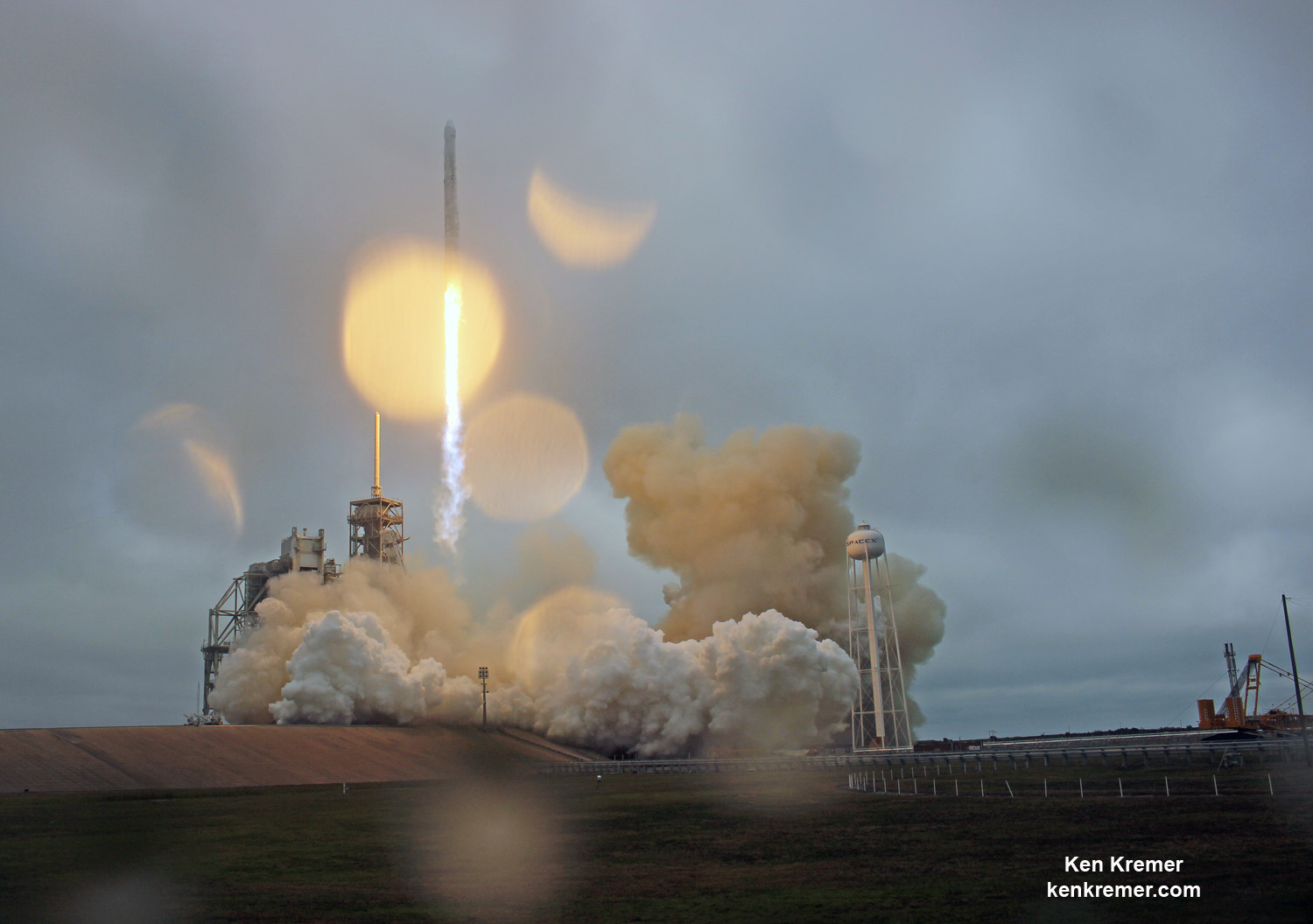

Launch Complex 39A was repurposed by SpaceX from launching Shuttles to Falcons. It had lain dormant for launches for nearly six years since Space Shuttle Atlantis launched on the final shuttle mission STS 135 in July 2011.
SpaceX bilionaire CEO Elon Musk announced last week that he wants to launch a manned Moonshot from pad 39A by the end of next year using his triple barreled Falcon Heavy heavy lift rocket – derived from the Falcon 9.
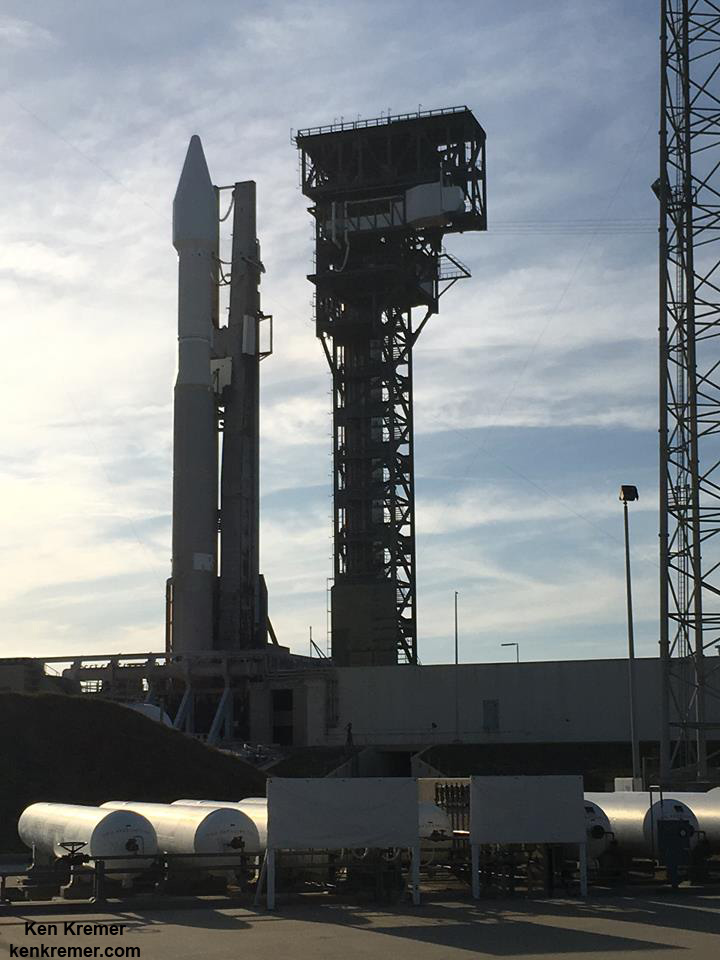
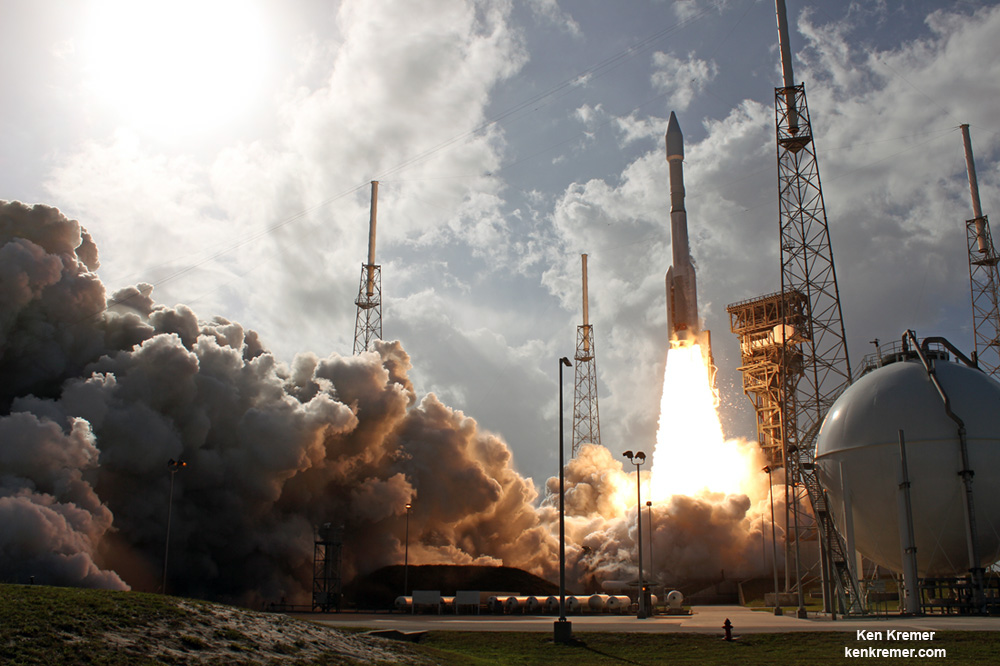
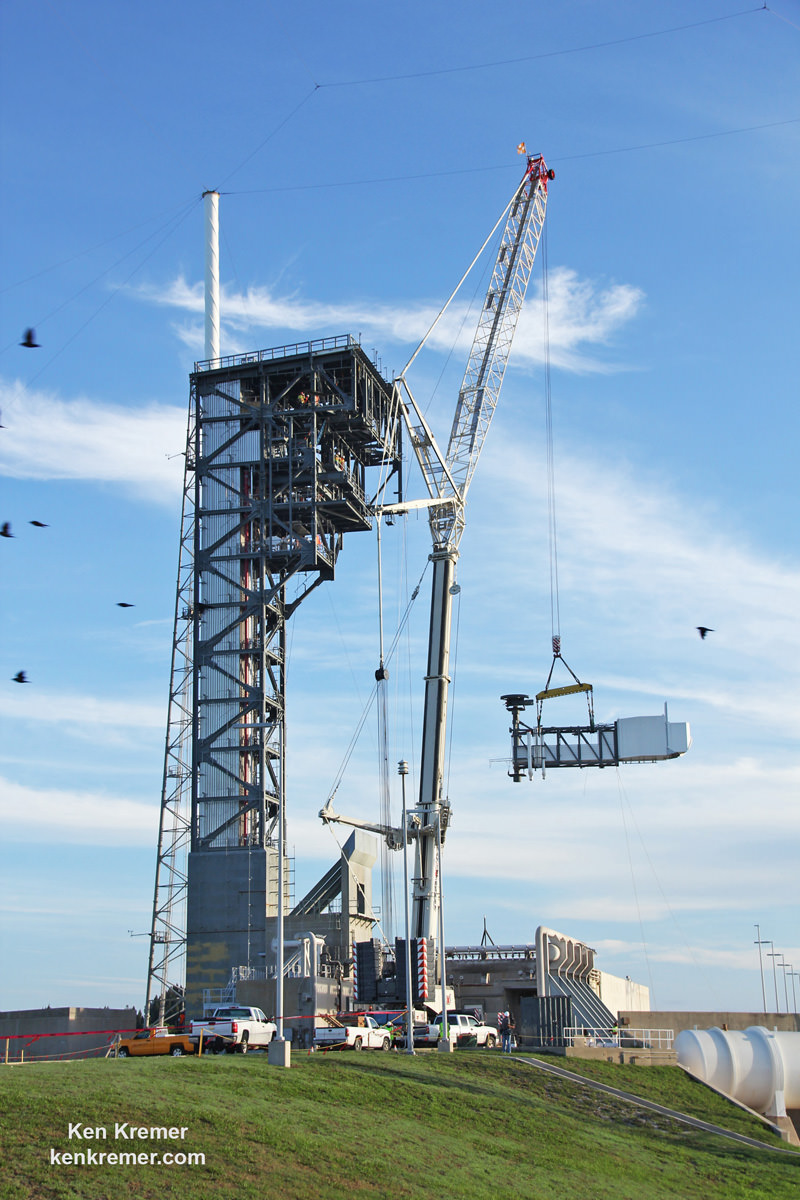
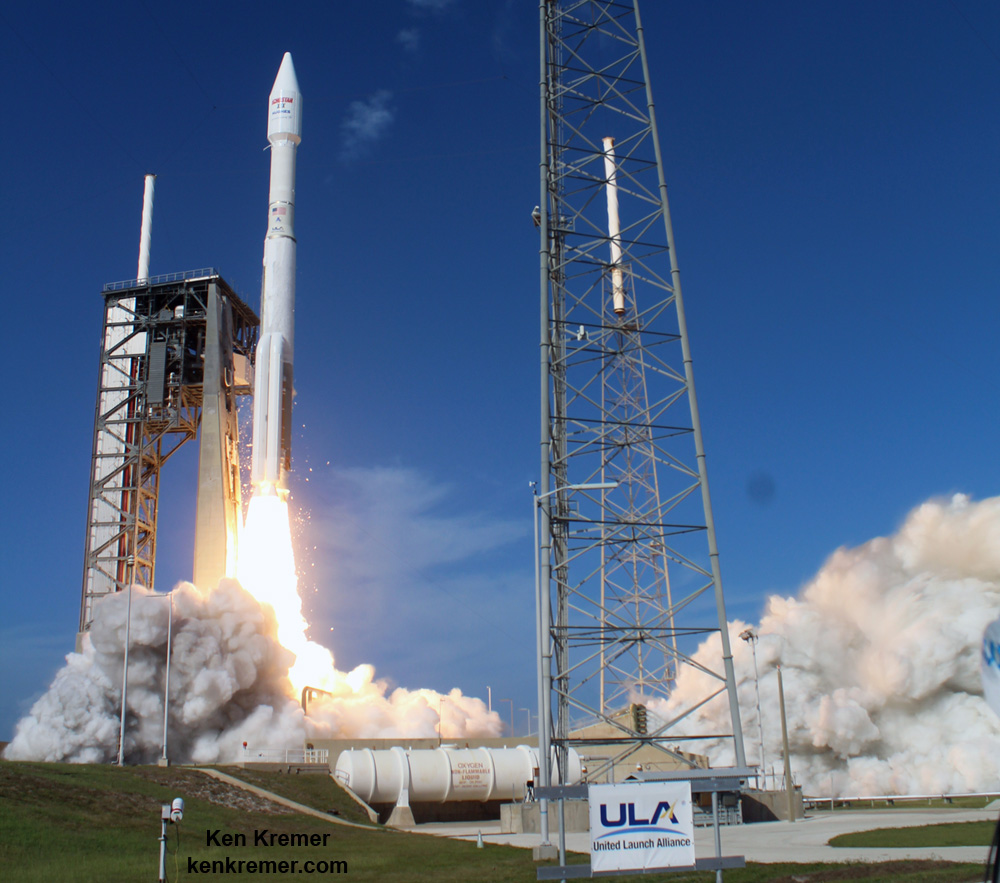
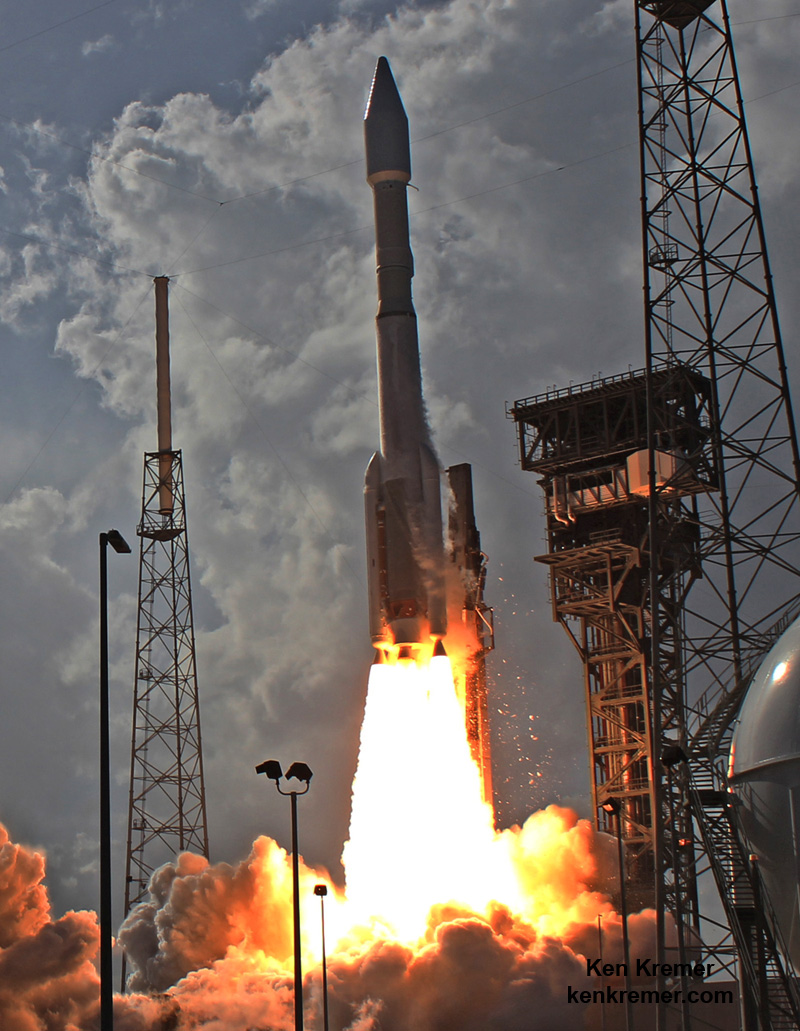
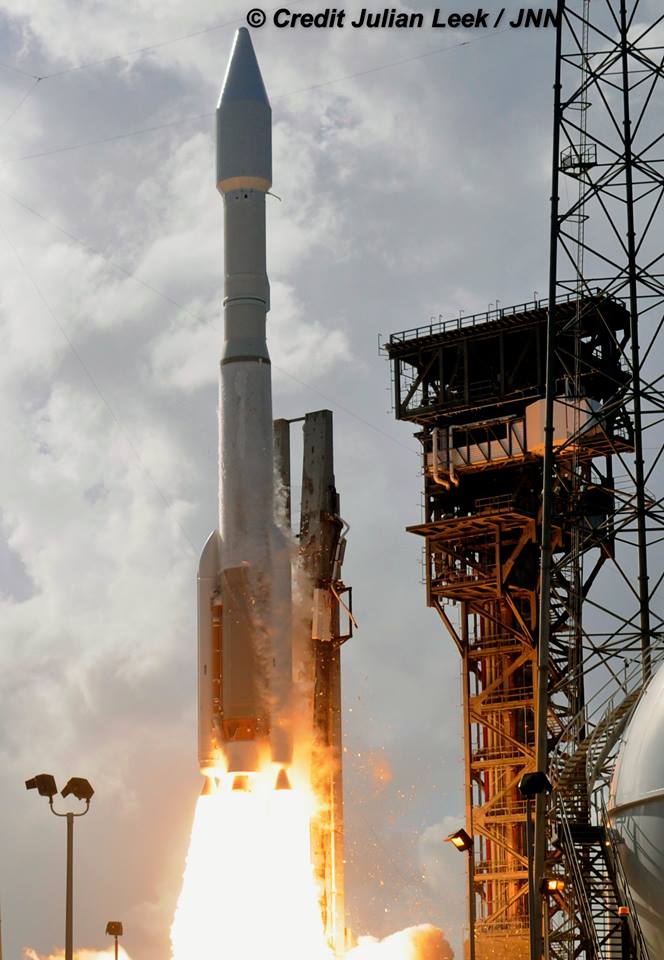
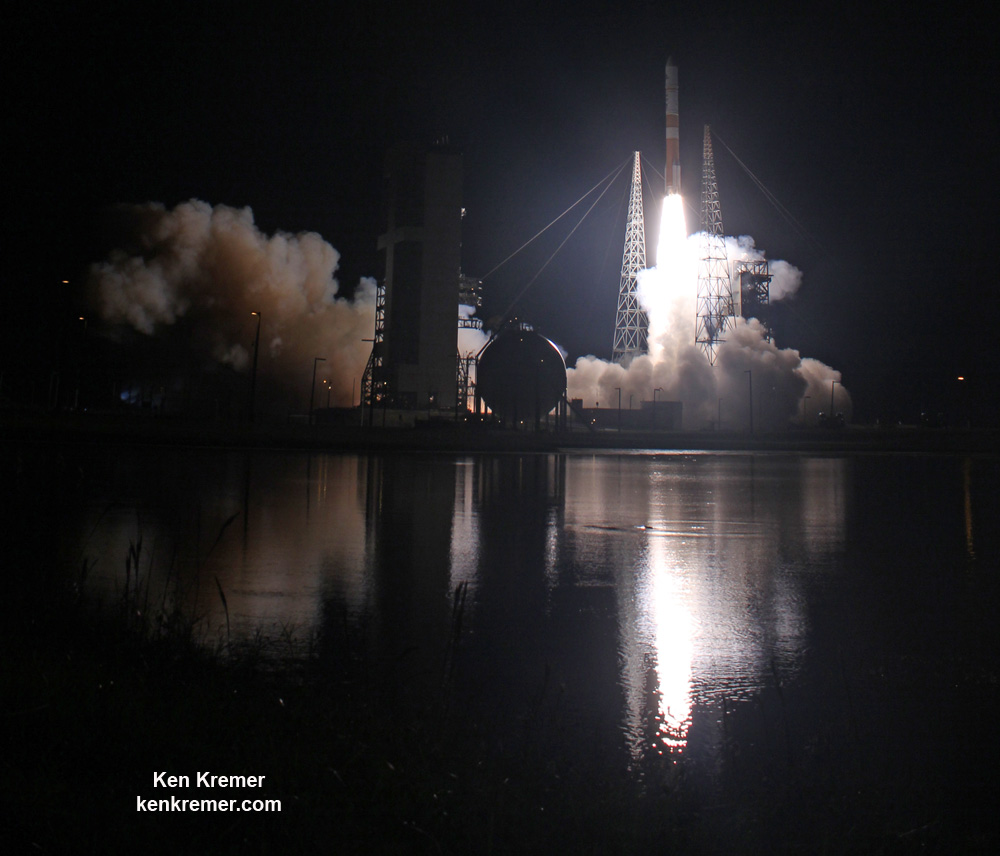
The second launch of the trio on tap is a United Launch Alliance Delta 4 rocket carrying the WGS-9 high speed military communications satellite for the U.S. Air Force.
Liftoff of the ULA Delta is slated for March 17 from Space Launch Complex-37 at 7: 44 p.m. EDT.

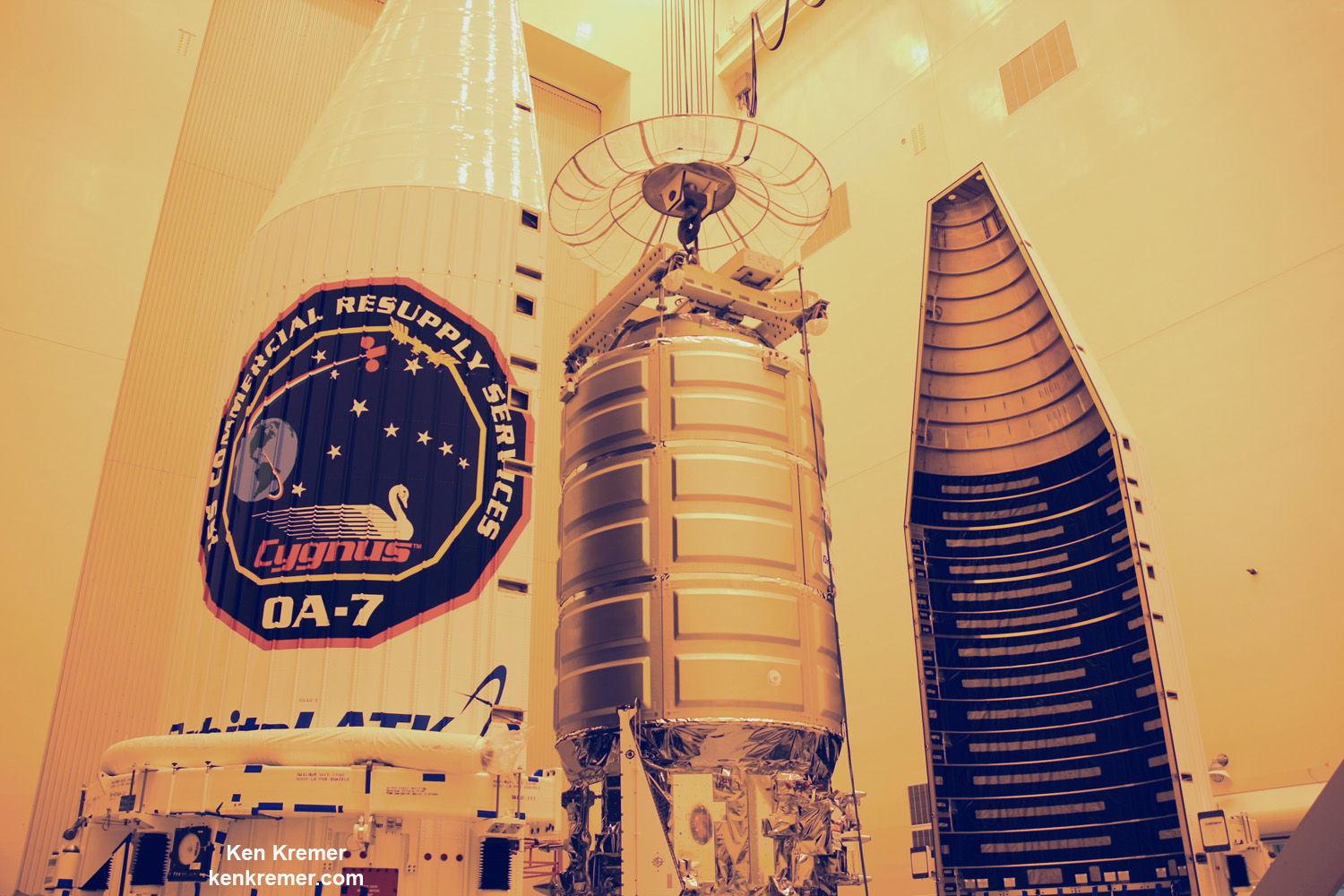
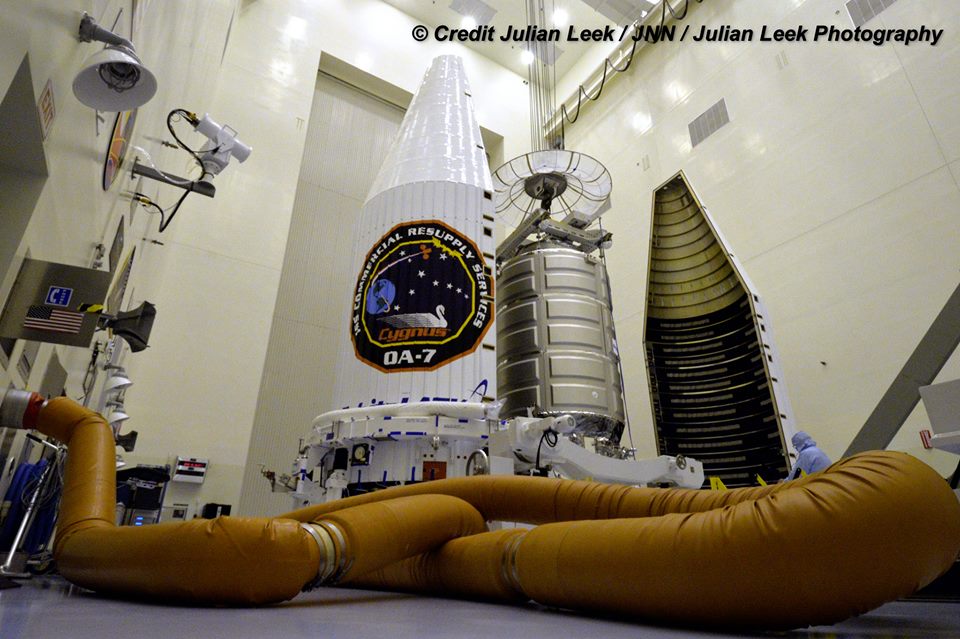
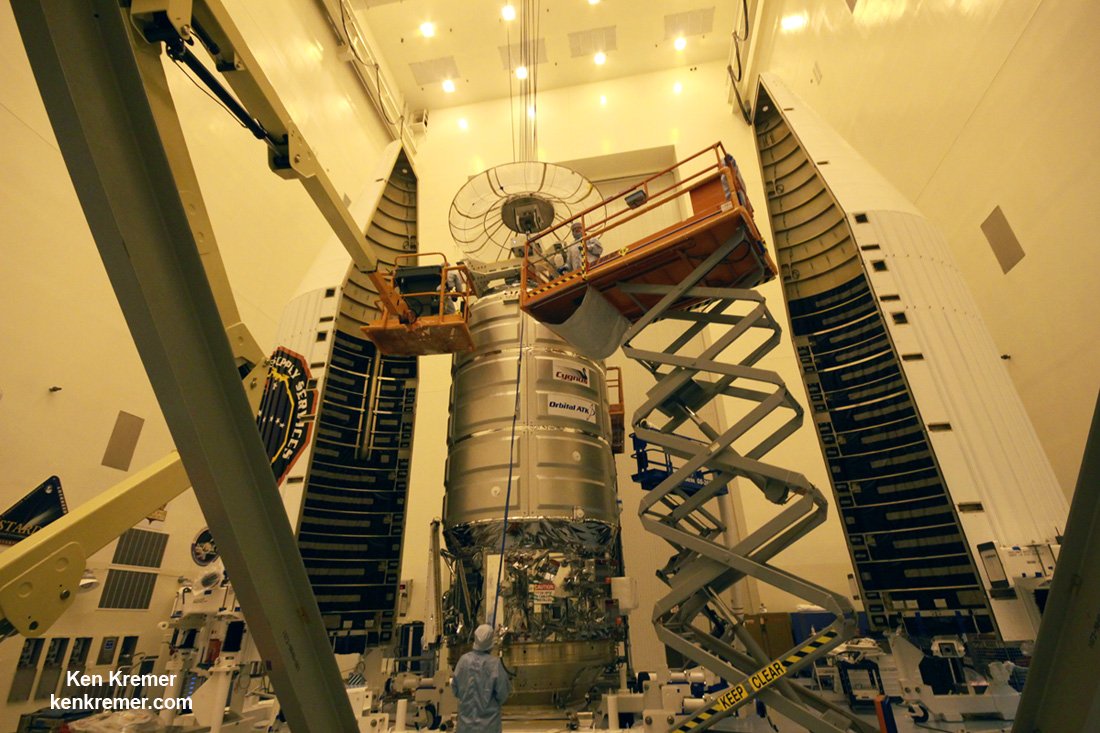
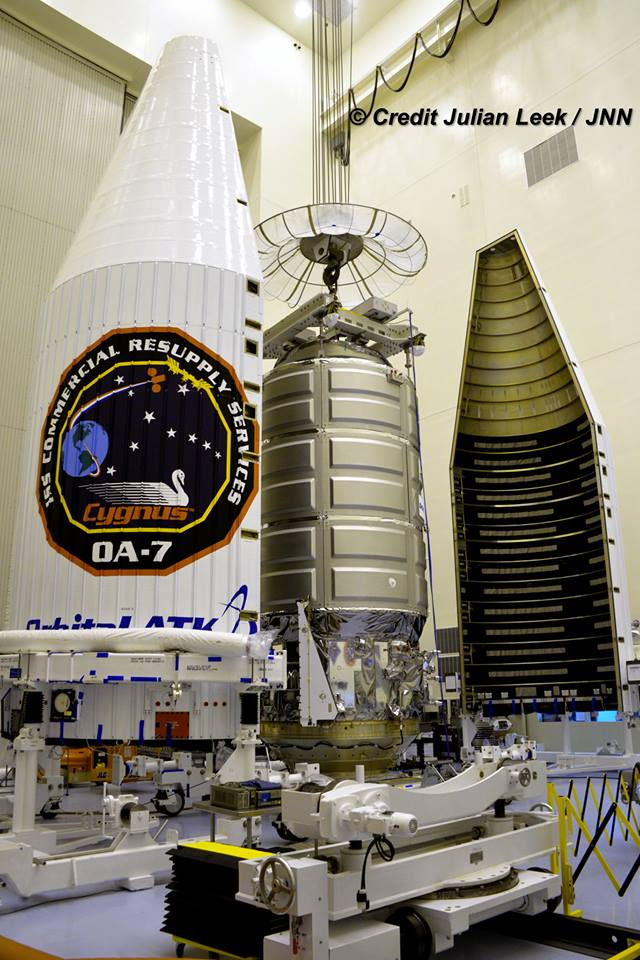
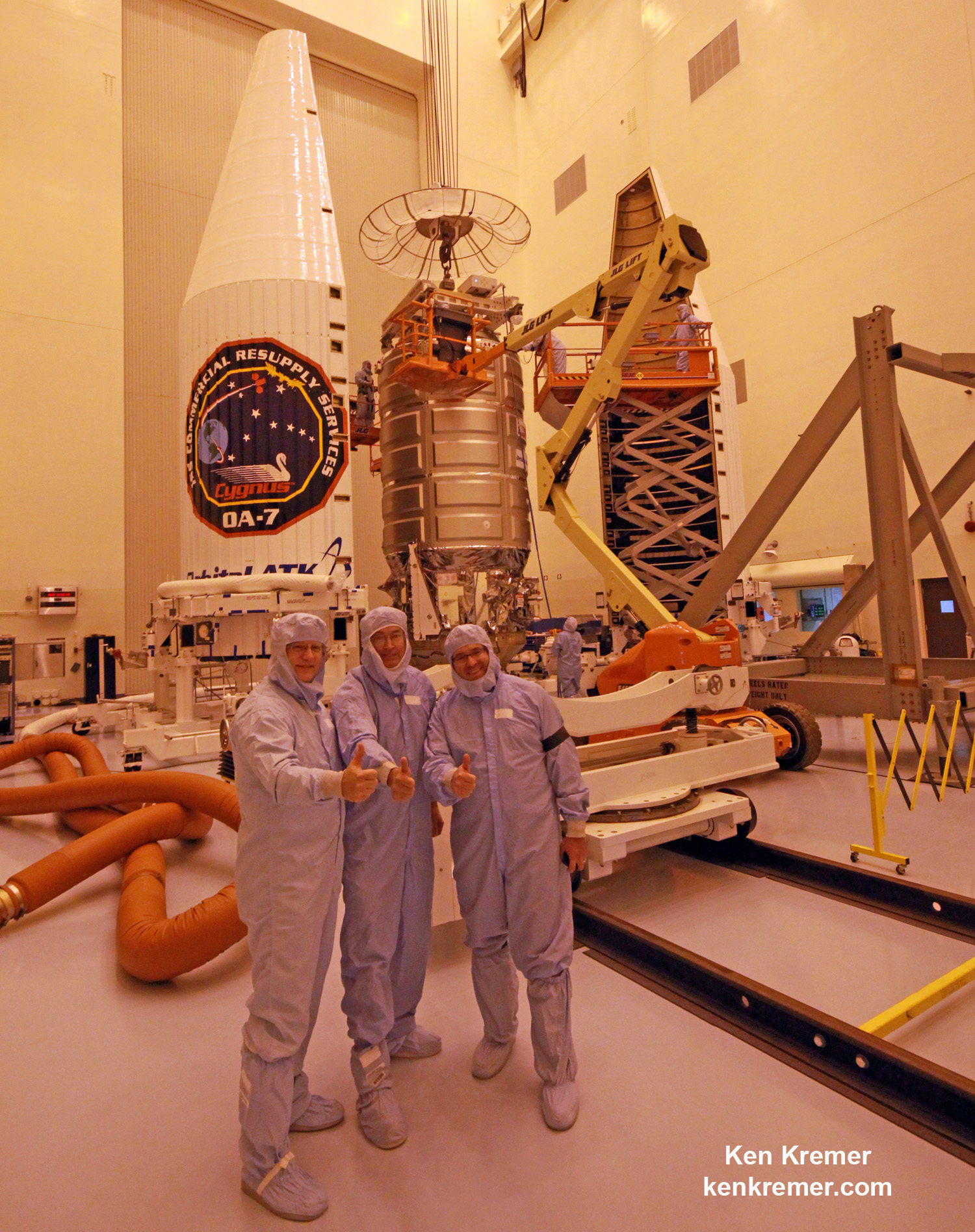
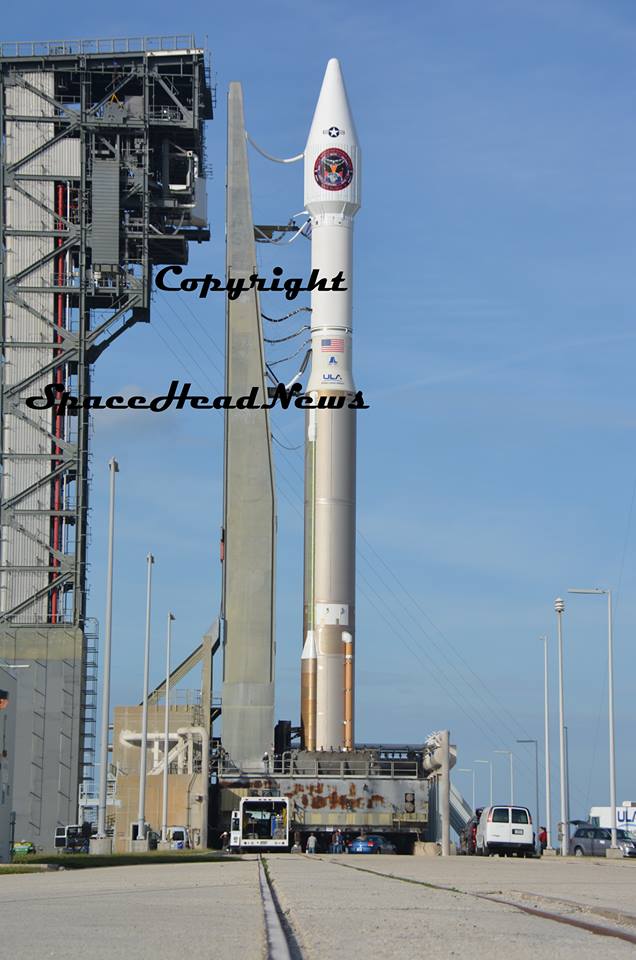
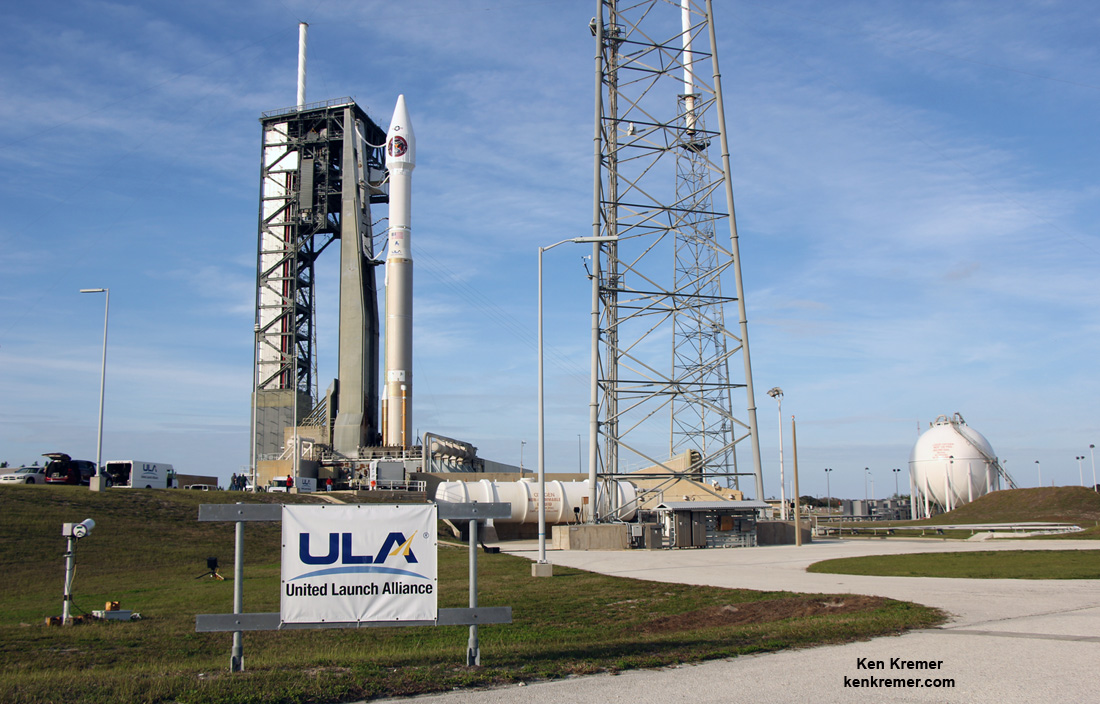
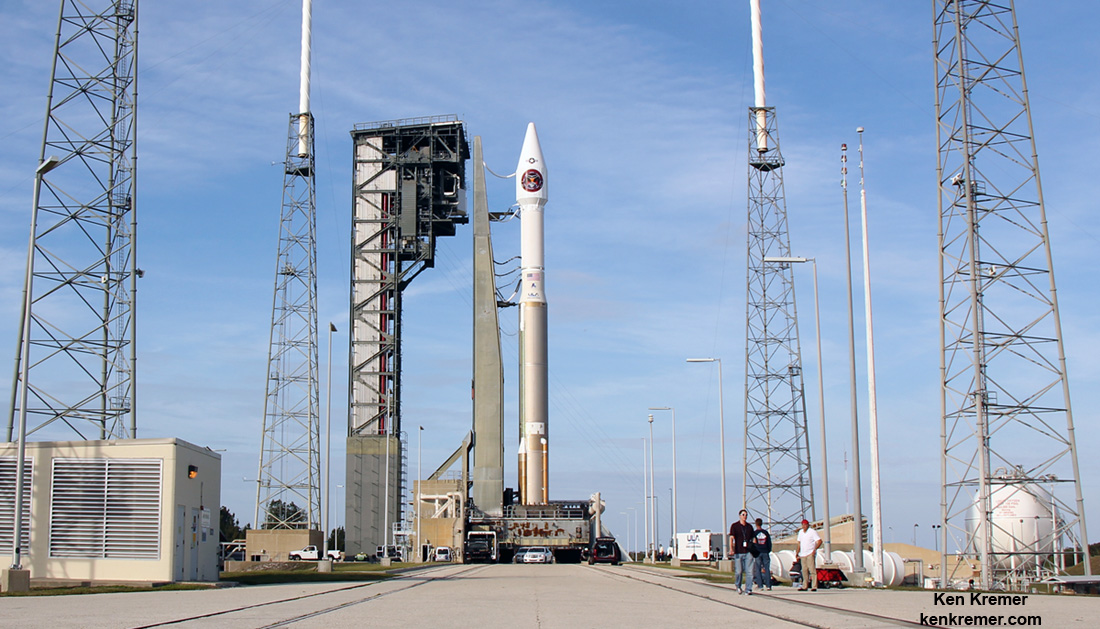
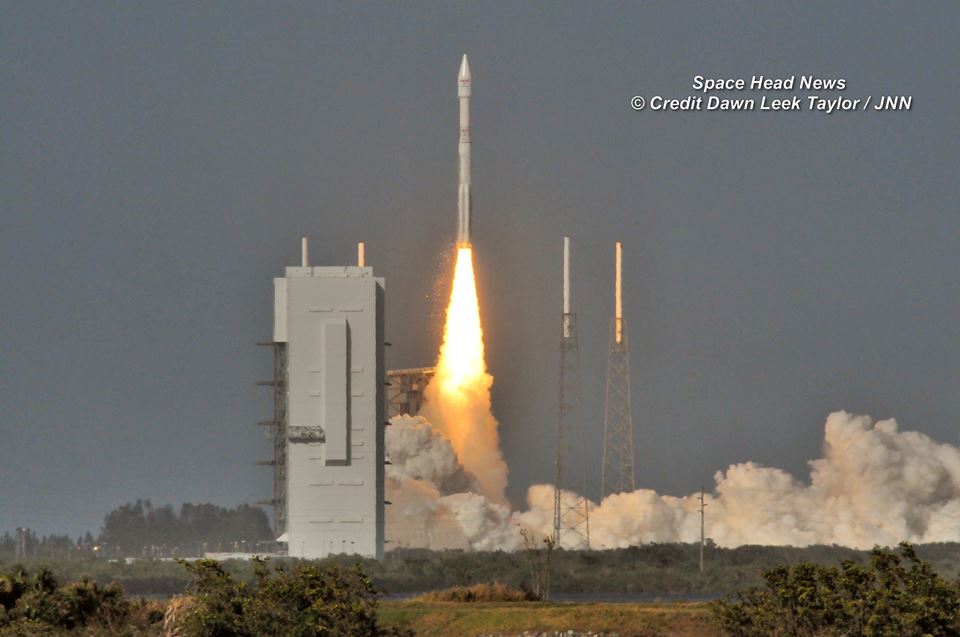
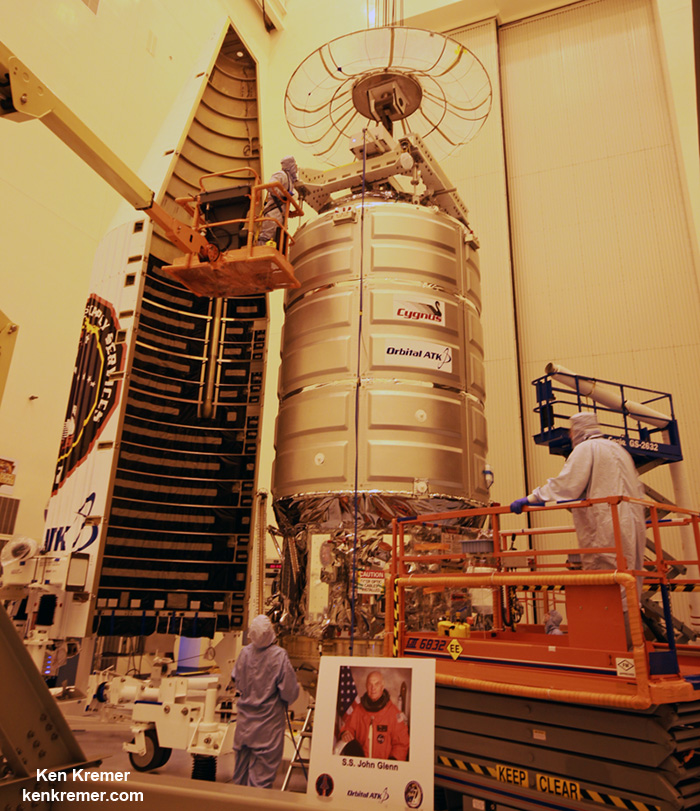
The S.S. John Glenn is scheduled to as the Orbital ATK Cygnus OA-7 spacecraft for NASA on a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket launch no earlier than March 21 from Space launch Complex-41 (SLC-41) on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.

………….
Learn more about SpaceX EchoStar 23 and CRS-10 launch to ISS, ULA SBIRS GEO 3 launch, EchoStar launch GOES-R launch, Heroes and Legends at KSCVC, OSIRIS-REx, InSight Mars lander, ULA, SpaceX and Orbital ATK missions, Juno at Jupiter, SpaceX AMOS-6, ISS, ULA Atlas and Delta rockets, Orbital ATK Cygnus, Boeing, Space Taxis, Mars rovers, Orion, SLS, Antares, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events at Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL:
Mar 13-15: “SpaceX EchoStar 23, CRS-10 launch to ISS, ULA Atlas SBIRS GEO 3 launch, EchoStar 19 comsat launch, GOES-R weather satellite launch, OSIRIS-Rex, SpaceX and Orbital ATK missions to the ISS, Juno at Jupiter, ULA Delta 4 Heavy spy satellite, SLS, Orion, Commercial crew, Curiosity explores Mars, Pluto and more,” Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, evenings