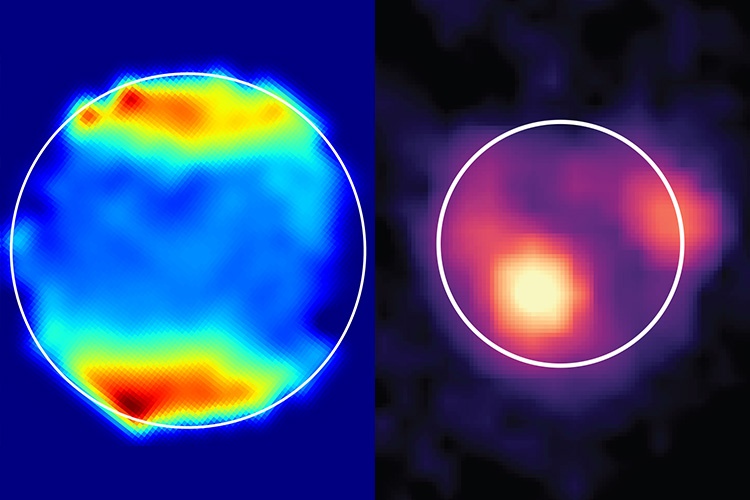
Artist’s impression of an active volcano on Venus (ESA/AOES)
Incredibly dense, visually opaque and loaded with caustic sulfuric acid, Venus’ atmosphere oppresses a scorched, rocky surface baking in planet-wide 425 ºC (800 ºF) temperatures. Although volcanoes have been mapped on our neighboring planet’s surface, some scientists believe the majority of them have remained inactive — at least since the last few hundreds of thousands of years. Now, thanks to NASA’s Pioneer Venus and ESA’s Venus Express orbiters, scientists have nearly 40 years of data on Venus’ atmosphere — and therein lies evidence of much more recent large-scale volcanic activity.
 The last six years of observations by Venus Express have shown a marked rise and fall of the levels of sulfur dioxide (SO2) in Venus’ atmosphere, similar to what was seen by NASA’s Pioneer Venus mission from 1978 to 1992.
The last six years of observations by Venus Express have shown a marked rise and fall of the levels of sulfur dioxide (SO2) in Venus’ atmosphere, similar to what was seen by NASA’s Pioneer Venus mission from 1978 to 1992.
These spikes in SO2 concentrations could be the result of volcanoes on the planet’s surface, proving that the planet is indeed volcanically active — but then again, they could also be due to variations in Venus’ complex circulation patterns which are governed by its rapid “super-rotating” atmosphere.
“If you see a sulphur dioxide increase in the upper atmosphere, you know that something has brought it up recently, because individual molecules are destroyed there by sunlight after just a couple of days,” said Dr. Emmanuel Marcq of Laboratoire Atmosphères in France, lead author of the paper, “Evidence for Secular Variations of SO2 above Venus’ Clouds Top,” published in the Dec. 2 edition of Nature Geoscience.
“A volcanic eruption could act like a piston to blast sulphur dioxide up to these levels, but peculiarities in the circulation of the planet that we don’t yet fully understand could also mix the gas to reproduce the same result,” added co-author Dr Jean-Loup Bertaux, Principal Investigator for the instrument on Venus Express.
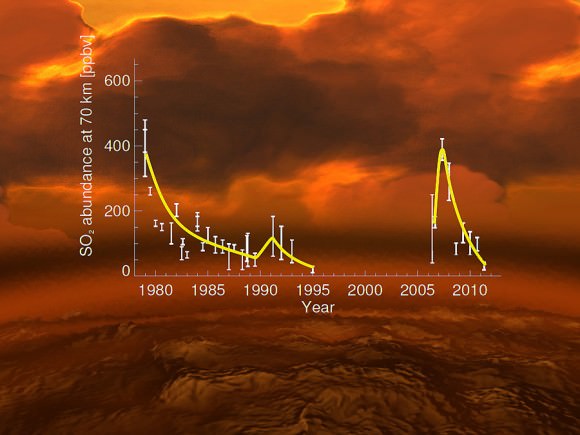
The rise and fall of sulphur dioxide in the upper atmosphere of Venus over the last 40 years, expressed in units of parts per billion by volume. Credits: Data: E. Marcq et al. (Venus Express); L. Esposito et al. (earlier data); background image: ESA/AOES
Because Venus’ dense atmosphere whips around the planet at speeds of 355 km/hour (220 mph), pinpointing an exact source for the SO2 emissions is extremely difficult. Volcanoes could be the culprit, but the SO2 could also be getting churned up from lower layers by variations in long-term circulation patterns.
Read: Venus Has a Surprisingly Chilly Layer
Venus has over a million times the concentration of sulfur dioxide than Earth, where nearly all SO2 is the result of volcanic activity. But on Venus it’s been able to build up, kept stable at lower altitudes where it’s well shielded from solar radiation.
Regardless of its source any SO2 detected in Venus’ upper atmosphere must be freshly delivered, as sunlight quickly breaks it apart. The puzzle now is to discover if it’s coming from currently-active volcanoes… or something else entirely.
“By following clues left by trace gases in the atmosphere, we are uncovering the way Venus works, which could point us to the smoking gun of active volcanism,” said Håkan Svedhem, ESA’s Project Scientist for Venus Express.
Read more on the ESA release here.