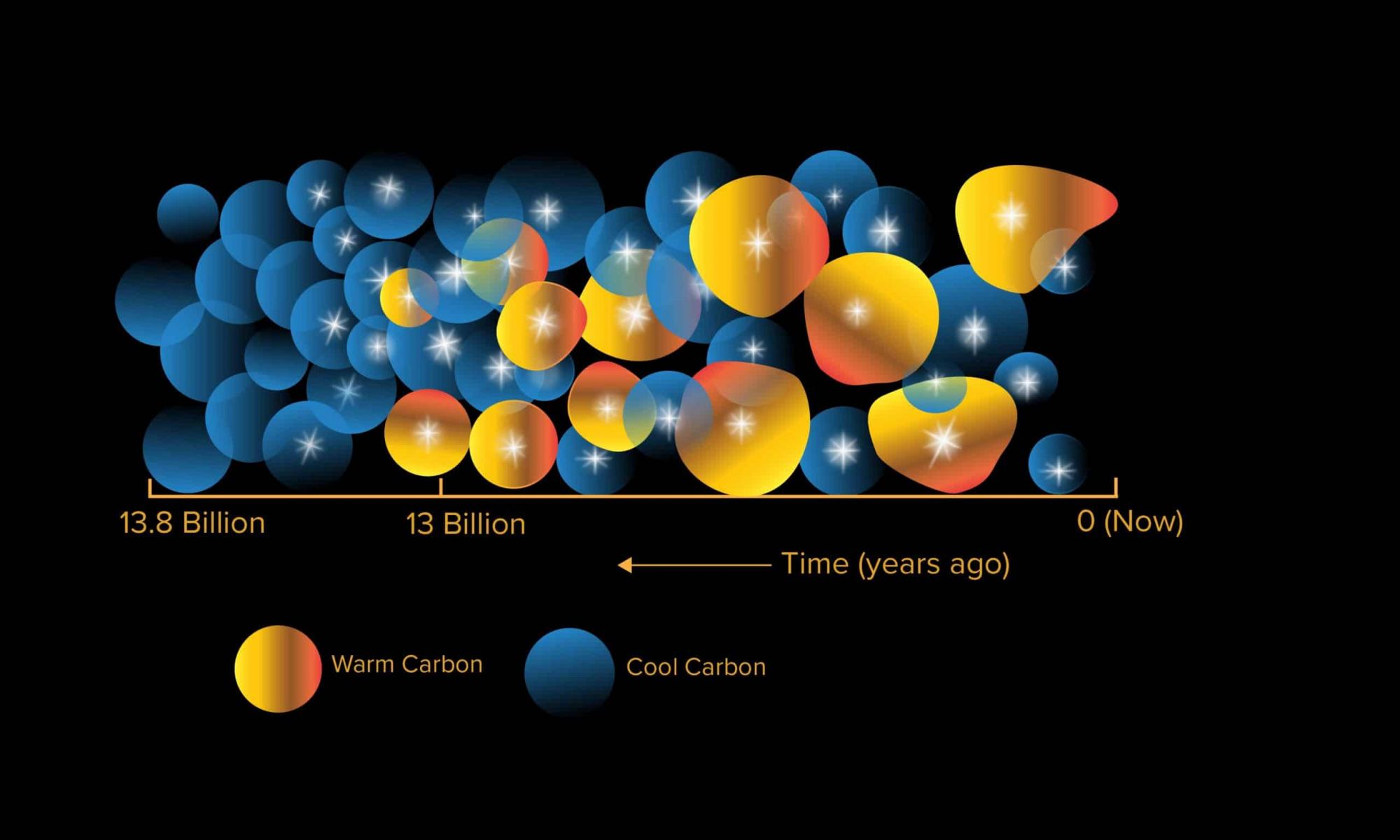
According to the most widely-accepted model of cosmology, the Universe began roughly 13.8 billion years ago with the Big Bang. As the Universe cooled, the fundamental laws of physics (the electroweak force, the strong nuclear force, and gravity) and the first hydrogen atoms formed. By 370,000 years after the Big Bang, the Universe was permeated by neutral hydrogen and very few photons (the Cosmic Dark Ages). During the “Epoch of Reionization” that followed, the first stars and galaxies formed, reoinizing the neutral hydrogen and causing the Universe to become transparent.
For astronomers, the Epoch of Reionization still holds many mysteries, like when certain heavy elements formed. This includes the element carbon, a key ingredient in the formation of planets, an important element in organic processes, and the basis for life as we know it. According to a new study by the ARC Center of Excellence for All Sky Astrophysics in 3 Dimensions (ASTRO 3D), it appears that triply-ionized carbon (C iv) existed far sooner than previously thought. Their findings could have drastic implications for our understanding of cosmic evolution.
Continue reading “Warm Carbon Increased Suddenly in the Early Universe. Made by the First Stars?”