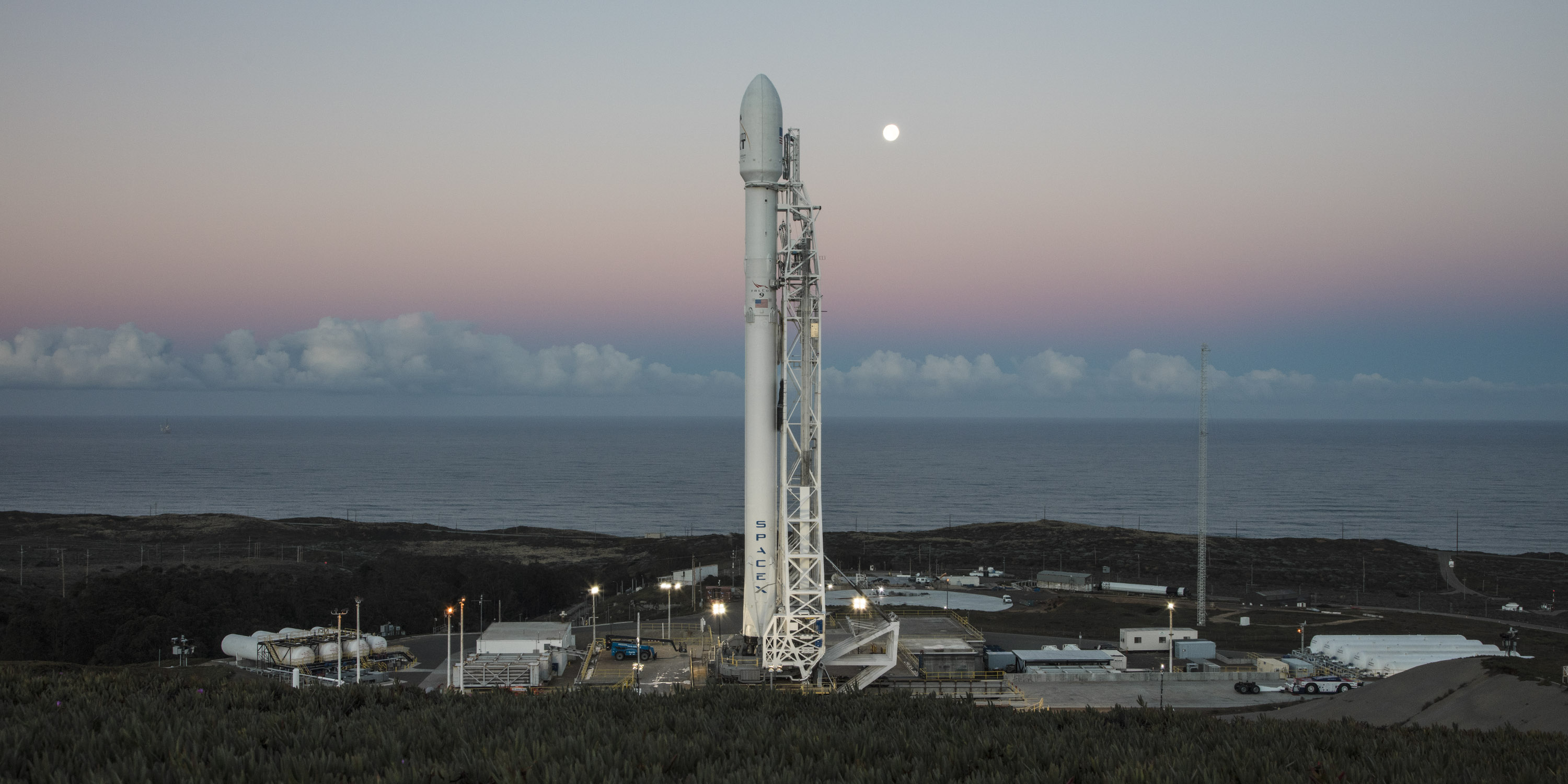
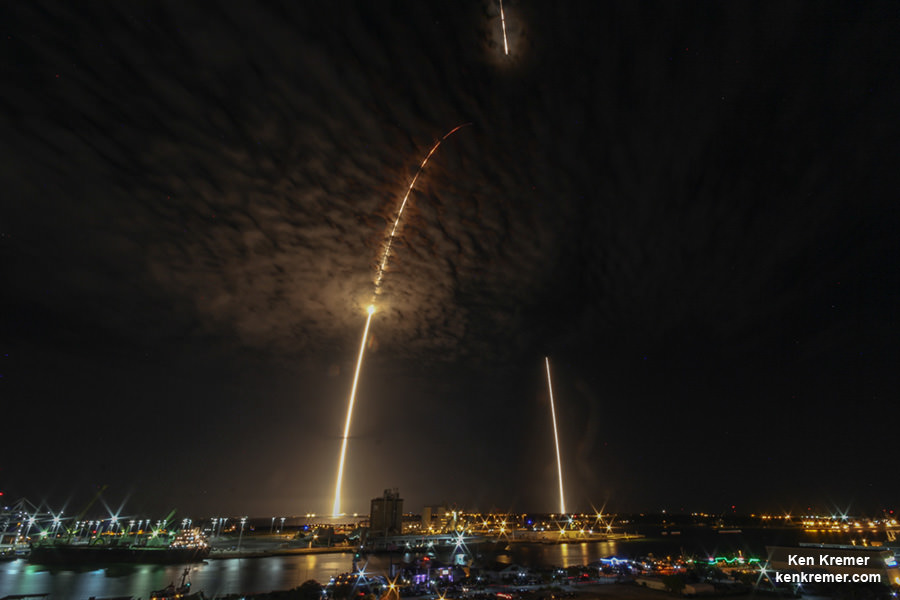
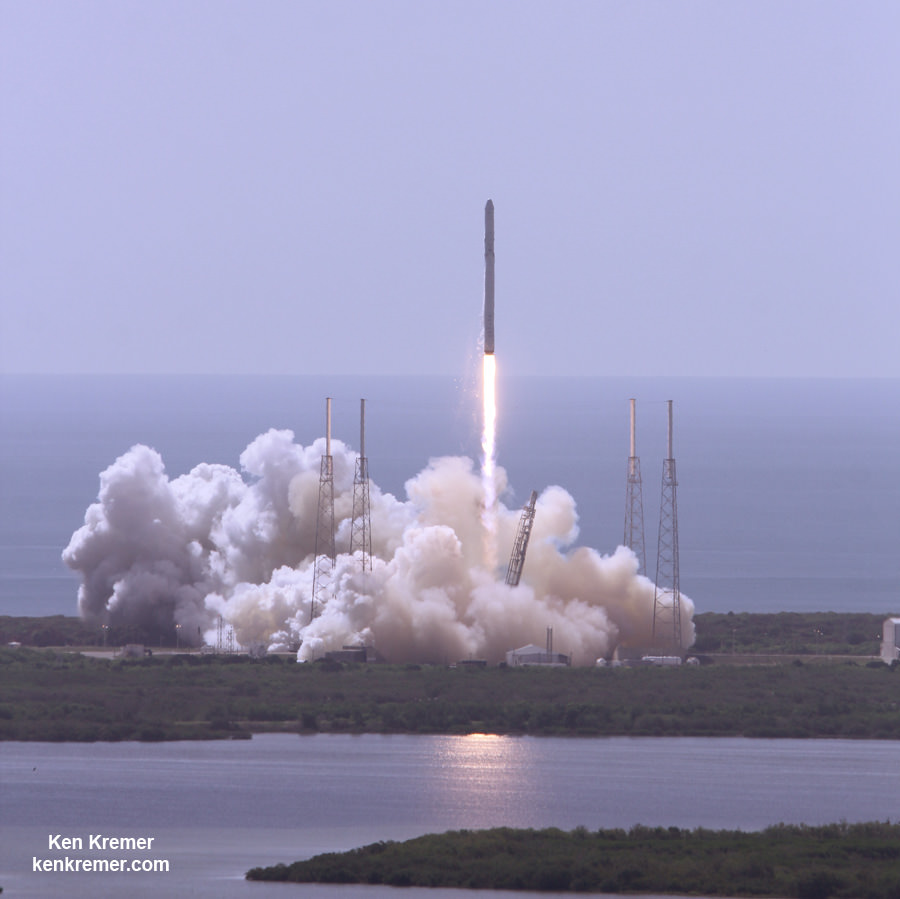
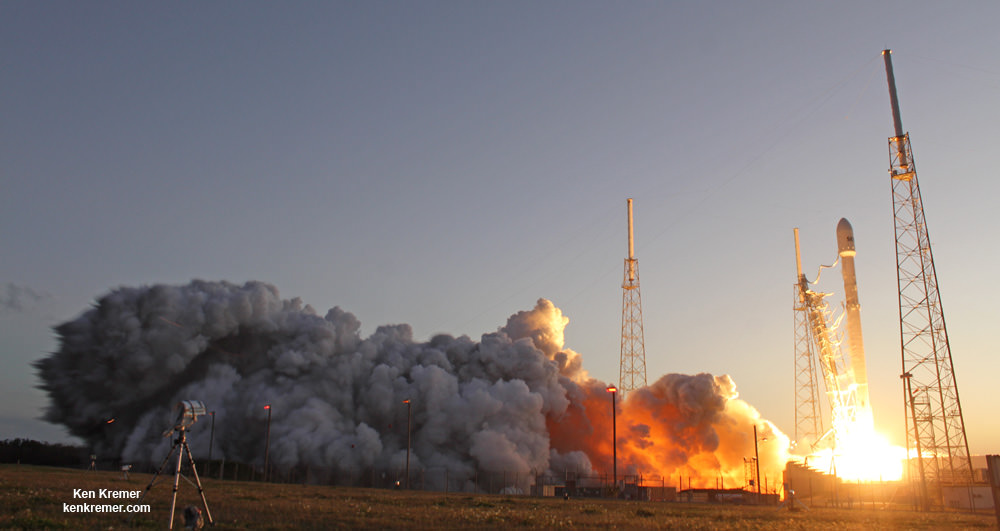
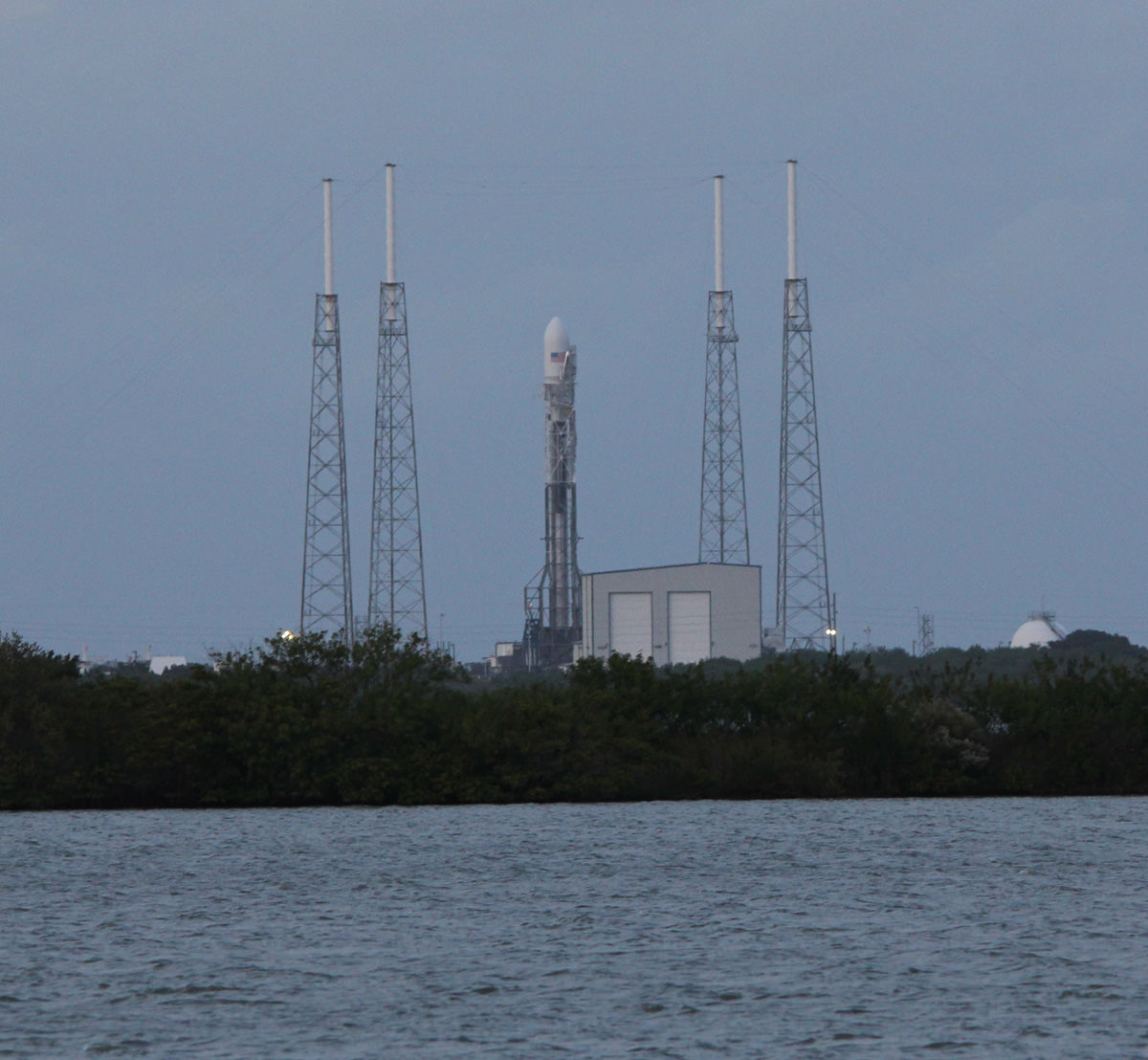
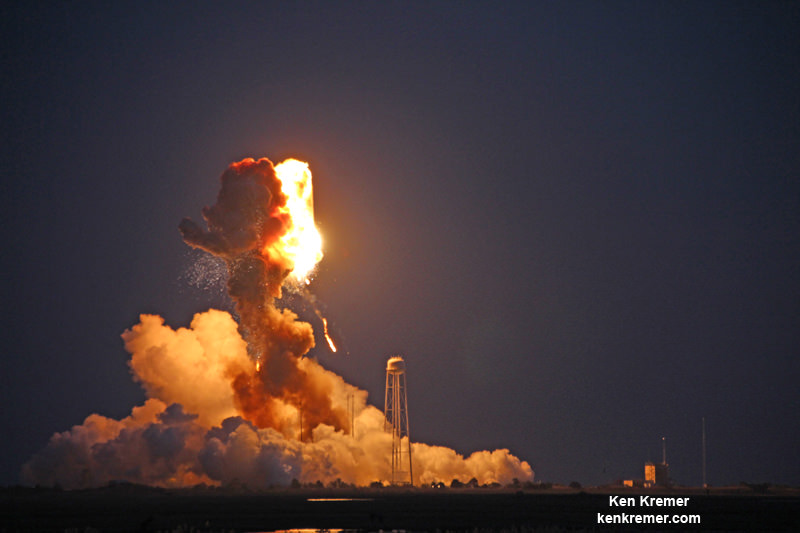
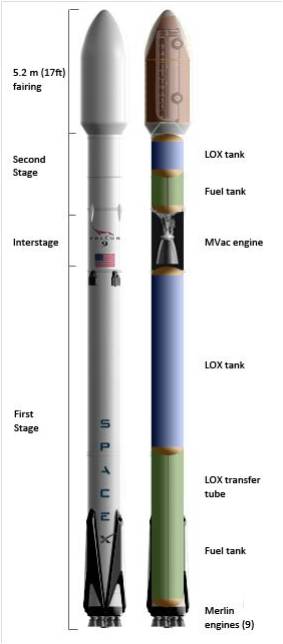
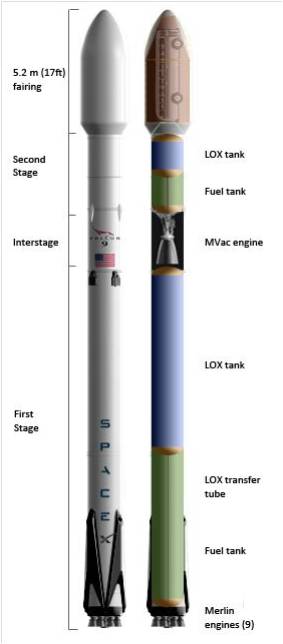
The stakes could almost not be higher for SpaceX as the firm readies their twice failed Falcon 9 rocket for a blastoff resumption on Saturday morning, Jan. 14 carrying the vanguard of the commercial Iridium NEXT satellite fleet to orbit from their California rocket base.
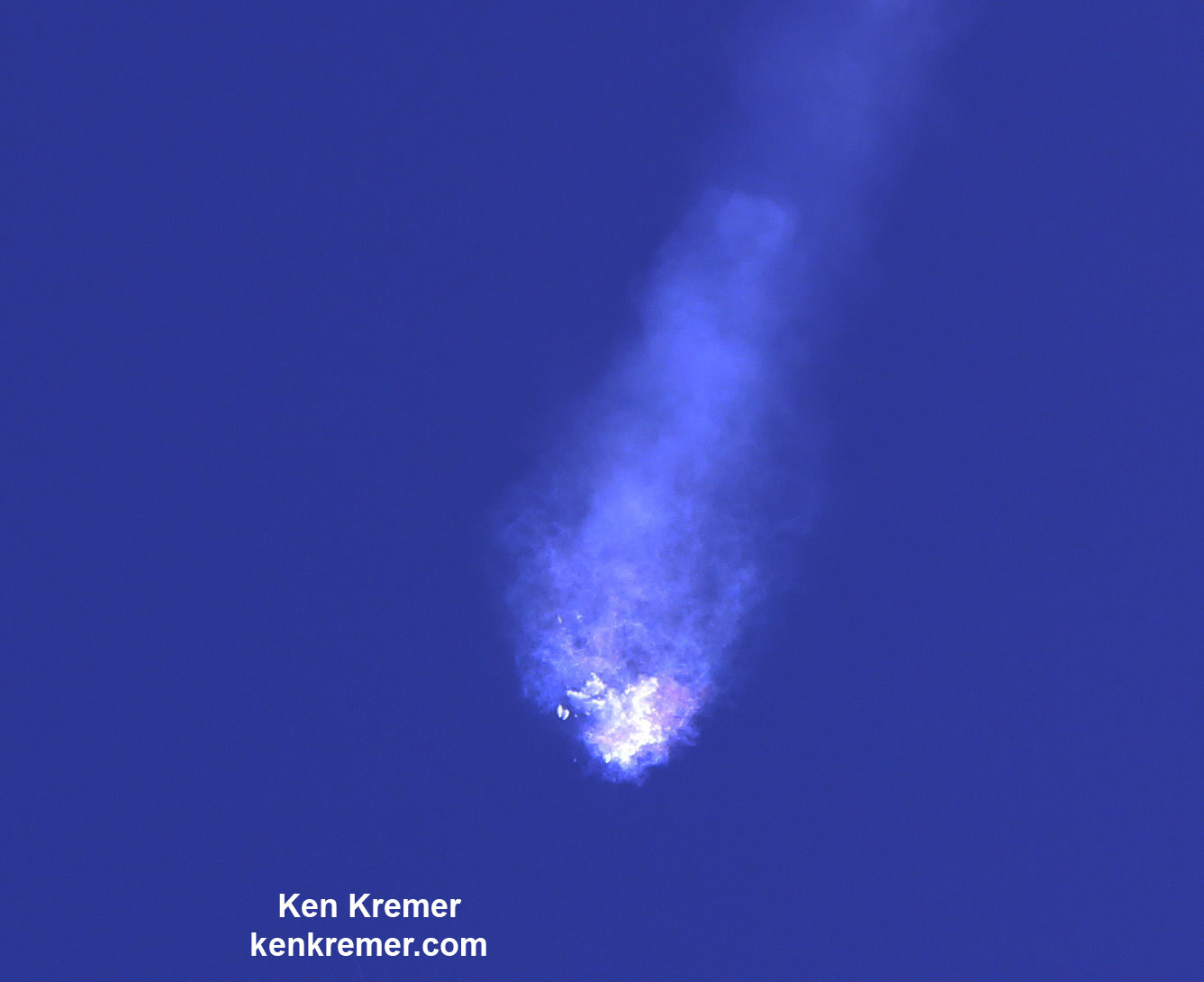
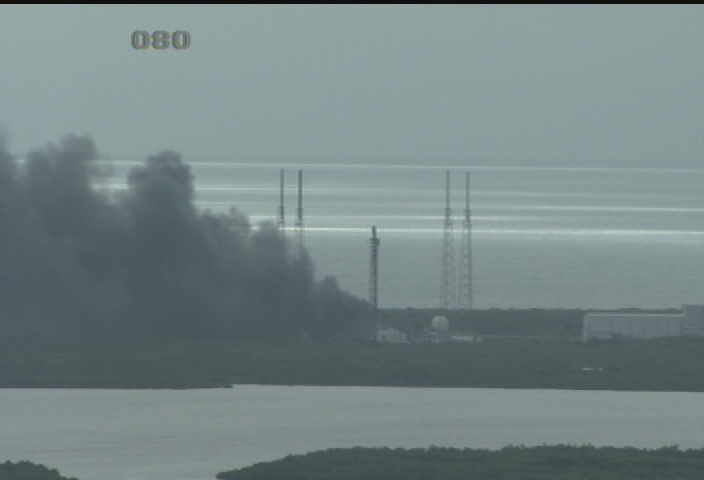
Barely four and a half months after another Falcon 9 and its $200 million Israeli commercial payload were suddenly destroyed during a prelaunch fueling test on the Florida Space Coast on Sept. 1, 2016, SpaceX says all systems are GO for the ‘Return to Flight’ launch of a new Falcon 9 on the Iridium-1 mission from the California coast tomorrow.
Another launch failure would deal a devastating blow to confidence in SpaceX’s hard won reputation – so ‘Failure is Not an Option’ as they say in the space business.
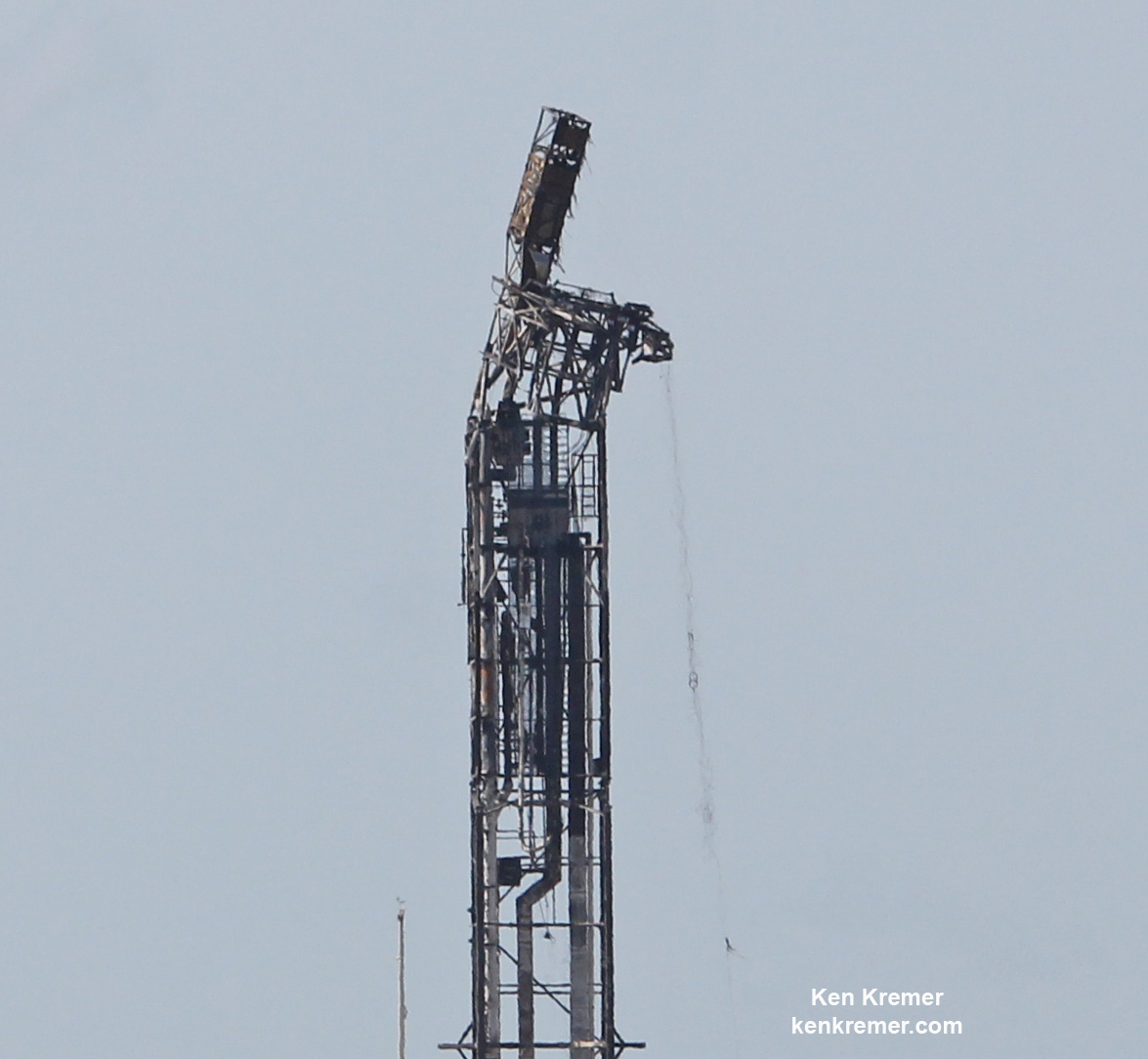
The Sept. 1, 2016 calamity was the second Falcon 9 failure within 15 months time. Both occurred inside the second stage and called into question the rockets reliability.
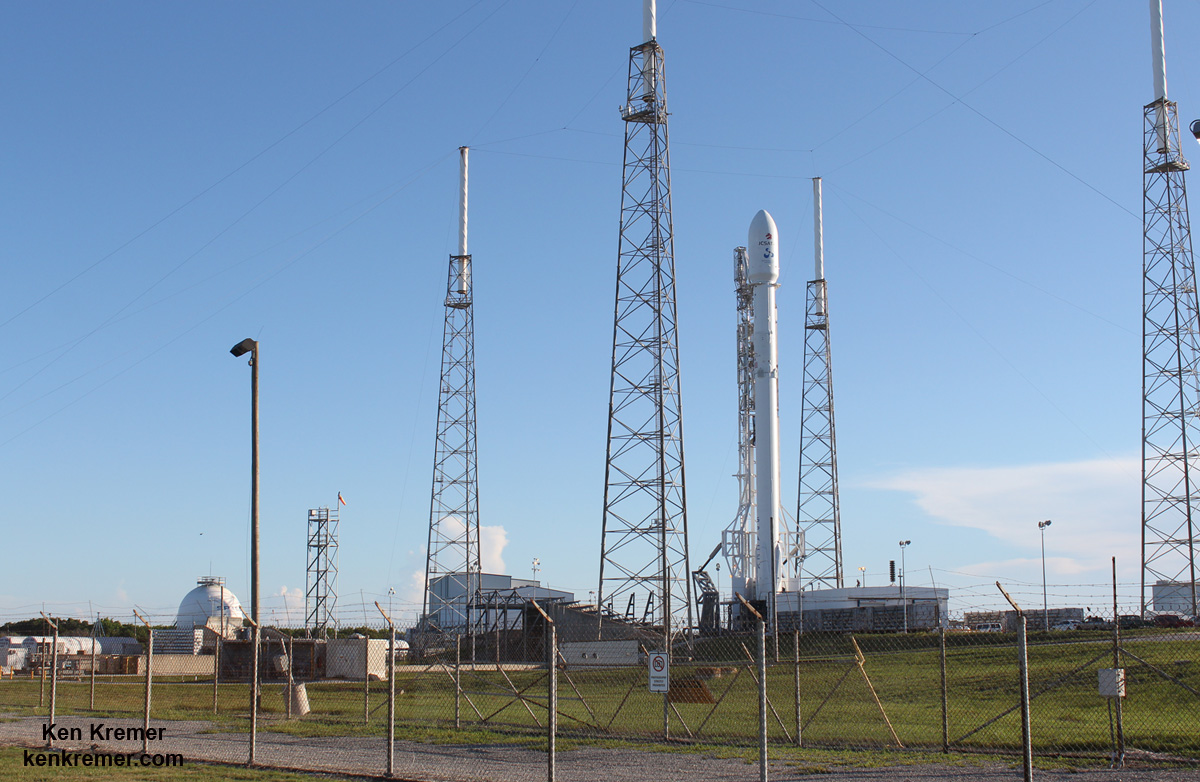
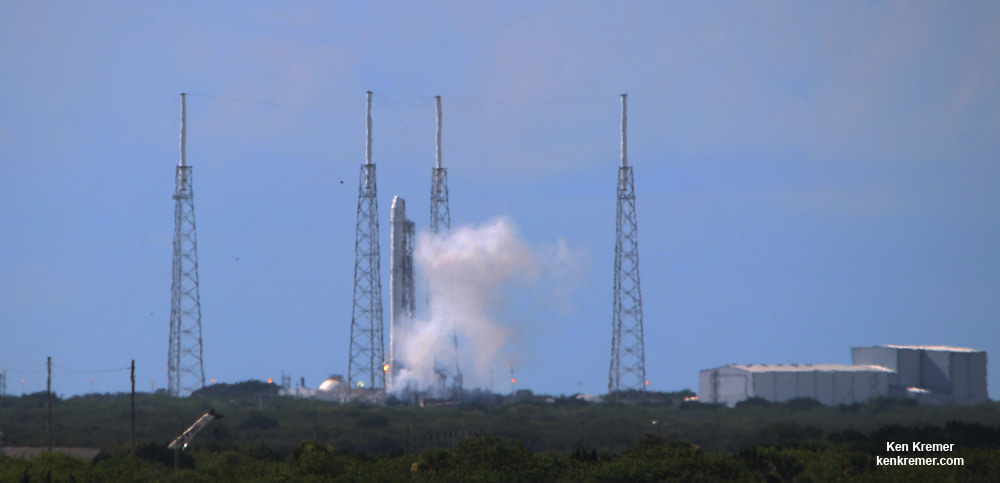
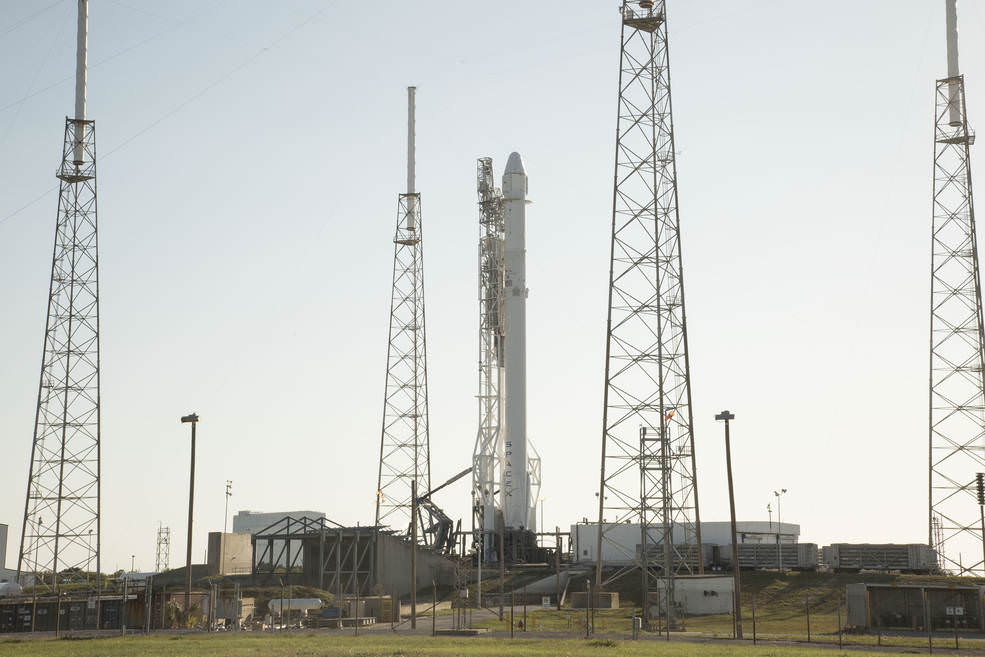
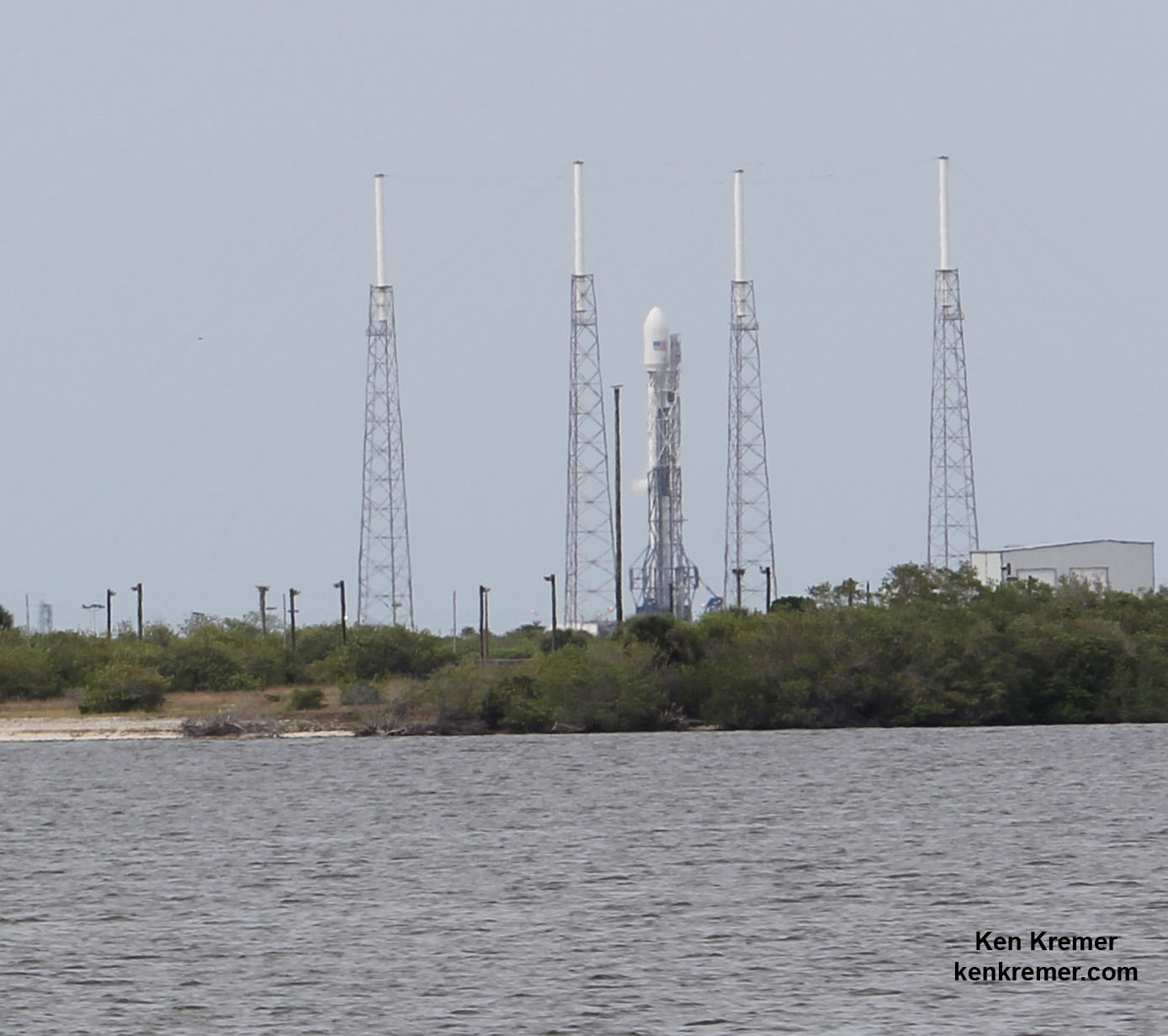
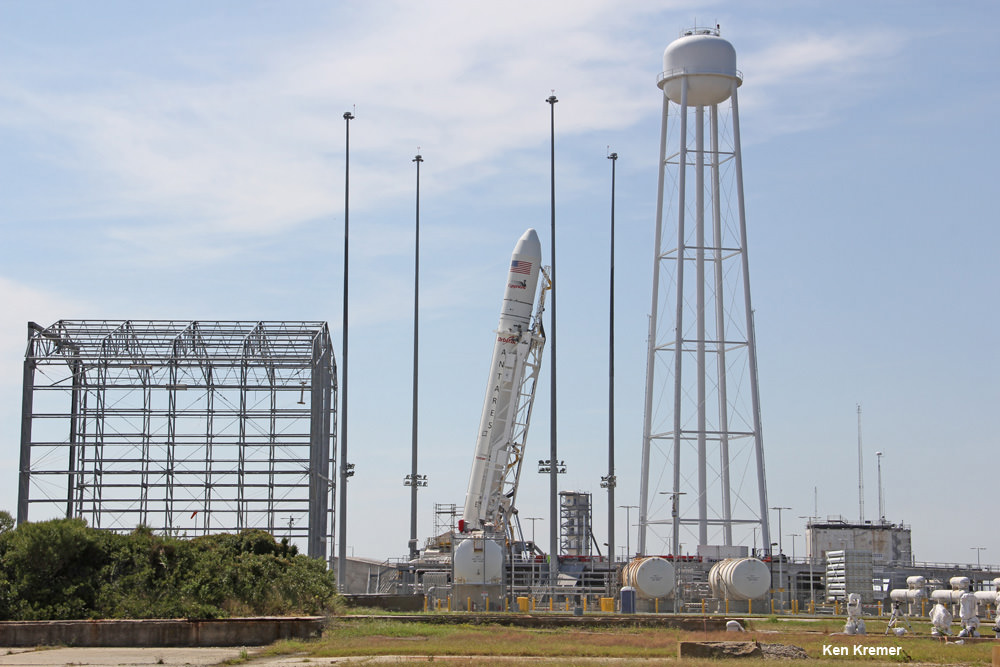
The 229-foot (70-meter) Falcon 9 rocket has been rolled out from its processing hangar to the launch pad and raised vertically.
“Beautiful picture of our ride to space tomorrow on the launch pad this morning!” tweeted Matt Desch, Iridium Communications CEO, featuring the lead photo in this story.
A license for permission to proceed with the launch originally last Sunday was only granted by the FAA last Friday, Jan. 6. But poor California weather in the form of stormy rains and high winds forced further delays to Saturday.
Today, Friday the 13th, it’s T-Minus 1 Day to the inaugural launch of the advanced Iridium NEXT voice and data relay satellites.
Liftoff of the SpaceX Falcon 9 with the payload of 10 identical next generation Iridium NEXT communications satellites is slated for 9:54:39 am PST or 5:54:39 pm UTC from Space Launch Complex 4E on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
The Iridium 1 mission only has an instantaneous launch opportunity precisely at 9:54:34 a.m. PST or 12:54:34 p.m. EST.
You can watch the launch live via a SpaceX webcast starting about 20 minutes prior to the planned liftoff time:
The launch will be broadcast at : http://www.spacex.com/webcast
Weather forecasters currently predict about a 60 percent chance of favorable conditions at launch time.
Sunday, Jan. 15 is available as a back-up launch opportunity in case of a delay for any reason including technical and weather related issues.

“The teams from Iridium, SpaceX and our partners are in the homestretch for the first launch of the Iridium NEXT satellite constellation,” said satellite owner Iridium Communications.
Meanwhile the launch teams have completed the countdown dress rehearsal’ and Launch Readiness Review in anticipation of the morning liftoff.
“Final preparations are being made for tomorrow’s inaugural launch, and with that comes a number of high-stakes verifications, involving all parties. Traditionally referred to as the ‘countdown dress rehearsal’ and ‘Launch Readiness Review’ (LRR), these milestones represent the final hurdles to clearing the path for the January 14th launch.”
“The countdown dress rehearsal and LRR include several prelaunch inspections and quality control measures. These include final clearances for the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Iridium NEXT payload, SpaceX and Iridium® ground infrastructure and associated team member responsibilities.”
Iridium says that every precaution has been taken to ensure a successful launch.
“There are so many variables that need to be considered when finalizing launch preparations, and a slight deviation or unexpected behavior by any of them can jeopardize the launch integrity,” said Iridium COO Scott Smith, in a statement.
“We’ve perfected the necessary procedures, taken every precaution we can imagine, and tomorrow, after what has felt like centuries, we’ll take the first step on a long-awaited journey to revolutionize satellite communications. The success of today’s events has brought us to an apex moment.”
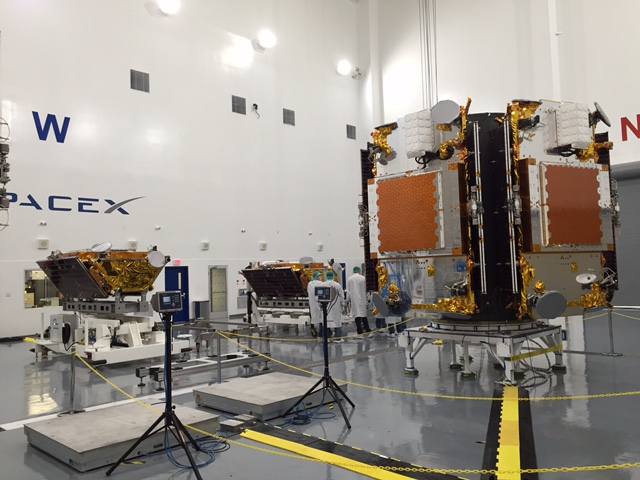

Iridium 1 is the first of seven planned Falcon 9 launches to establish the Iridium NEXT constellation which will eventually consist of 81 advanced satellites.
At least 70 will be launched by SpaceX.
The inaugural launch of the advanced Iridium NEXT satellites will start the process of replacing an aging Iridium fleet in orbit for nearly two decades.

After the Sept .1 calamity SpaceX conducted a four month long investigation seeking to determine the root cause.
And it was just last Friday, Jan. 6, that the FAA finally granted SpaceX a license to launch the ‘Return to Flight’ Falcon 9 mission – as I confirmed with the FAA.
“The FAA accepted the investigation report on the AMOS-6 mishap and has closed the investigation,” FAA spokesman Hank Price confirmed to Universe Today.
“SpaceX applied for a license to launch the Iridium NEXT satellites from Vandenberg Air Force Base. The FAA has granted a license for that purpose.”
The SpaceX investigation report into the total loss of the Falcon 9 rocket and AMOS-6 payload has not been released at this time. The FAA has oversight responsibility to encourage, facilitate, and promote U.S. commercial space transportation and ensure the protection of public safety.
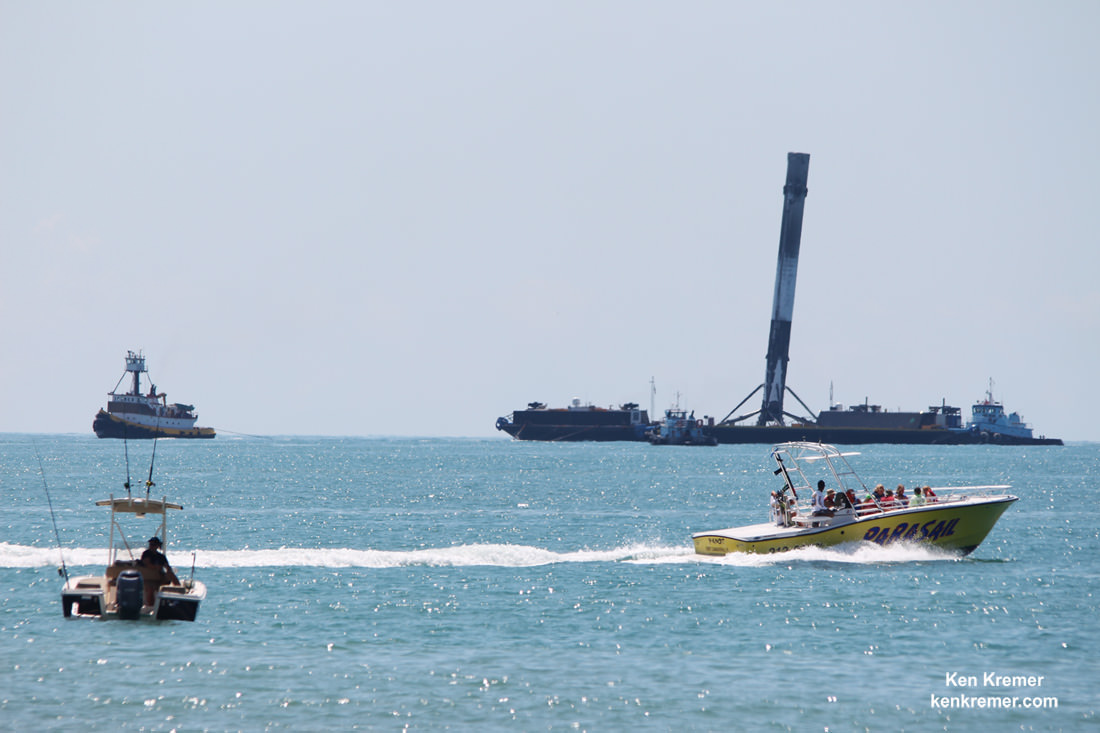

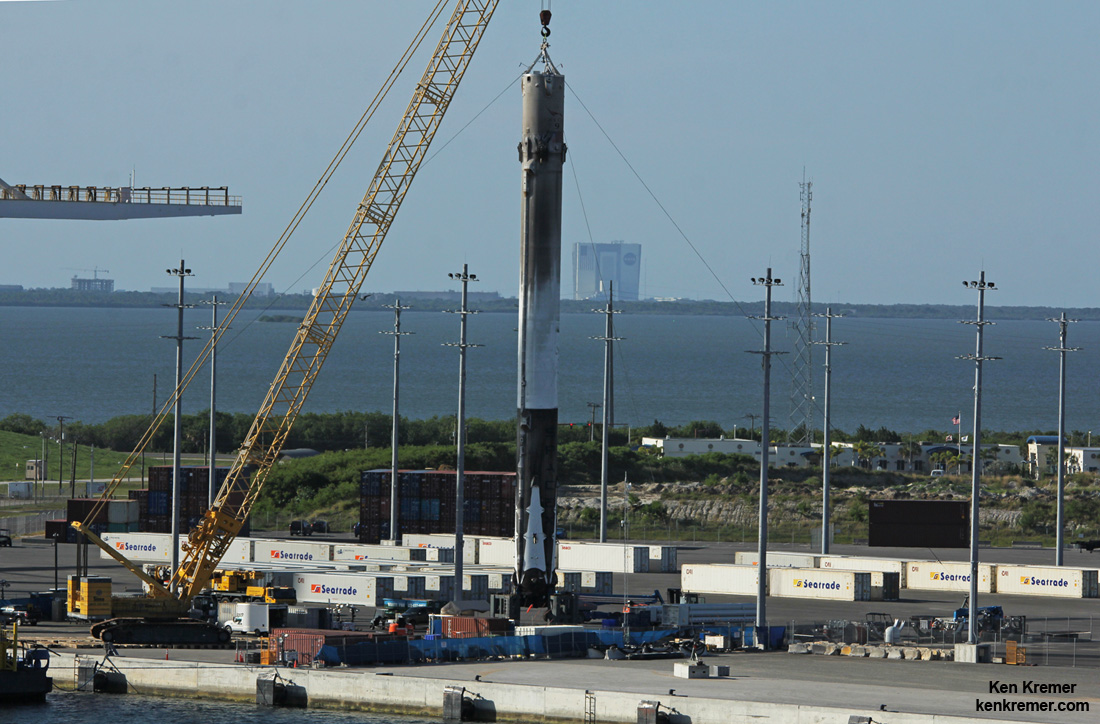
In addition to the launch, SpaceX plans to continue its secondary objective of recovering the Falcon 9 first stage via a propulsive soft landing – as done several times previously and witnessed by this author.
The Iridium-1 mission patch featured herein highlights both the launch and landing objectives.
The goal is to eventually recycle and reuse the first stage – and thereby dramatically slash launch costs per Musk’s vision.
This Falcon 9 has been outfitted with four landing legs and grid fins for a controlled landing on a tiny barge prepositioned in the Pacific Ocean several hundred miles off the west coast of California.
Watch this space for continuing updates on SpaceX.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.