Video caption: Liftoff of unmanned Russian Progress craft atop Soyuz booster on Oct. 30, 2011 from Baikonur Cosmodrome. Credit: NASA TV/Roscosmos.
Photos and rocket rollout video below
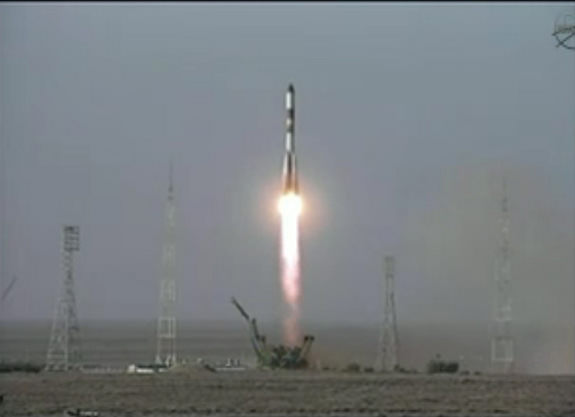
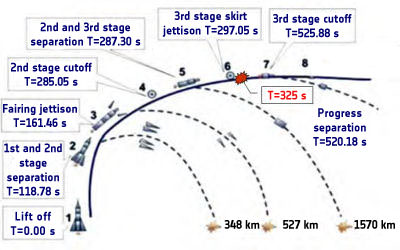
The very future of the International Space Station was on the line this morning as the Russian Progress 45 cargo ship successfully launched this morning from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan at 6:11 a.m. EDT (4:11 p.m. Baikonur time) on Oct. 30, 2011, bound for the ISS.
Today’s (Oct. 30) blastoff of the Soyuz rocket booster that is used for both the Progress cargo resupply missions and the Soyuz manned capsules was the first since the failure of the third stage of the prior Progress 44 mission on August 24 which crashed in Siberia.
[/caption]
The third stage is nearly identical for both the manned and unmanned versions of the normally highly reliable Soyuz booster rocket.
Today’s success therefore opens up the door to resumption of crewed flights to the ISS, which were grounded by Russia after the unexpected loss of the Progress 44 mission.
If this Progress flight had failed, the ISS would have had to be left in an uncrewed state for the first time since continuous manned occupation began more than 10 years ago and would have significantly increased the risk for survival of the ISS in the event of a major malfunction and no human presence on board to take swift corrective action.

Credit:RIA Novosti
NASA issued the following statement from Bill Gerstenmaier, associate administrator for Human Exploration and Operations at NASA Headquarters in Washington, about the launch of the Progress 45 spacecraft.
“We congratulate our Russian colleagues on Sunday’s successful launch of ISS Progress 45, and the spacecraft is on its way to the International Space Station. Pending the outcome of a series of flight readiness meetings in the coming weeks, this successful flight sets the stage for the next Soyuz launch, planned for mid-November. The December Soyuz mission will restore the space station crew size to six and continue normal crew rotations.”
Progress 45 is carrying nearly 3 tons of supplies to the ISS, including food, water, clothing, spare parts, fuel, oxygen and science experiments for use by the resident crews.
The resupply vehicle achieved the desired preliminary orbit after the eight and one half minute climb to space and deployed its solar arrays and communications antennae’s.
After a two day chase, Progress 45 will automatically link up with the ISS at the Pirs Docking Compartment on Nov. 2 at 7:40 a.m (EDT) and deliver 1,653 pounds of propellant, 110 pounds of oxygen and air, 926 pounds of water and 3,108 pounds of spare parts, experiment hardware and other supplies for the Expedition 29 crew.

Credit: Roscosmos
The successful launch sets the stage for the launch of the station’s next three residents on Nov. 13. NASA’s Dan Burbank and Russia’s Anton Shkaplerov and Anatoly Ivanishin will arrive at the station Nov. 16, joining NASA’s Mike Fossum, Russia’s Sergei Volkov and Japan’s Satoshi Furukawa for about six days before Fossum, Volkov and Furukawa return home.
Liftoff of Burbank’s crew was delayad from the original date on September 22 following the Progress failure in August. Because of the delayed Soyuz crew launch, the handover period from one crew to the next had to be cut short.
Since the forced retirement of the Space Shuttle, the US has absolutely no way to send human crews to orbit for several years to come at a minimum and is totally reliant on Russia.
The survival of the ISS with humans crews on board is therefore totally dependent on a fully functioning and reliable Soyuz rocket.
Video caption: Rollout of Soyuz rocket and Progress cargo craft to Baikonur launch pad.
Read Ken’s continuing features about Soyuz from South America here:
Video Duet – Soyuz Debut Blast off from the Amazon Jungle and Rockin’ Russian Rollout !
Historic 1st Launch of Legendary Soyuz from South America
Russian Soyuz Poised for 1st Blastoff from Europe’s New South American Spaceport