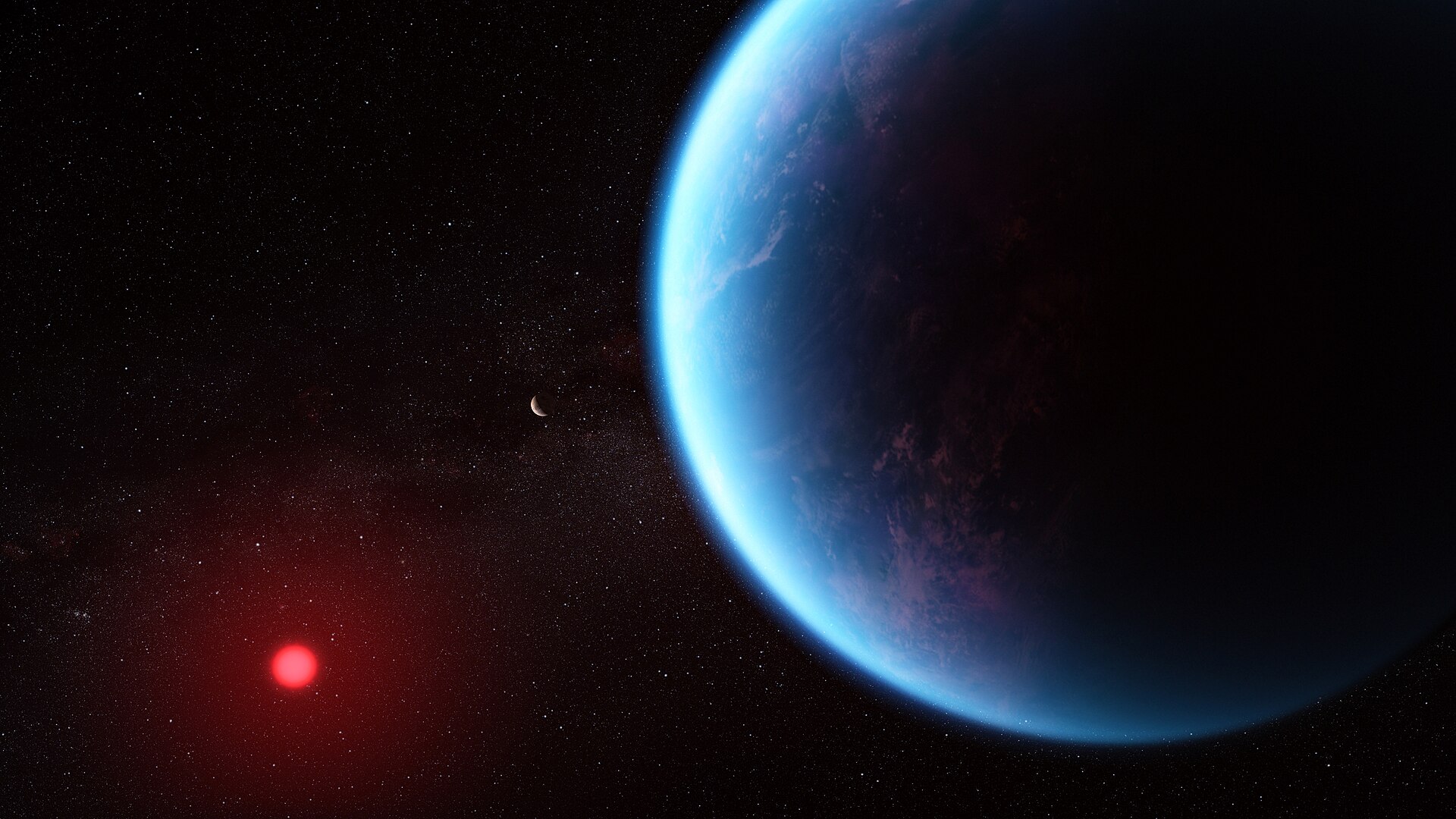
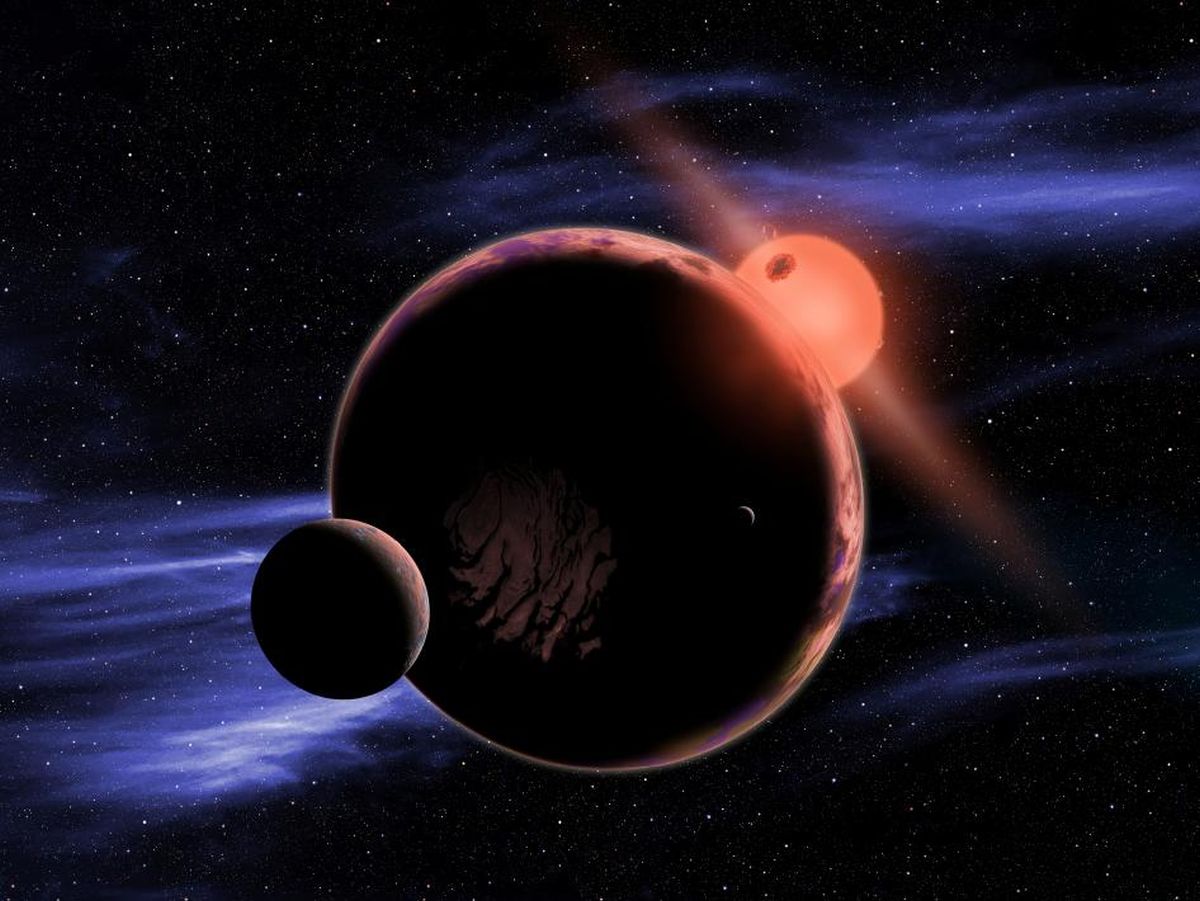
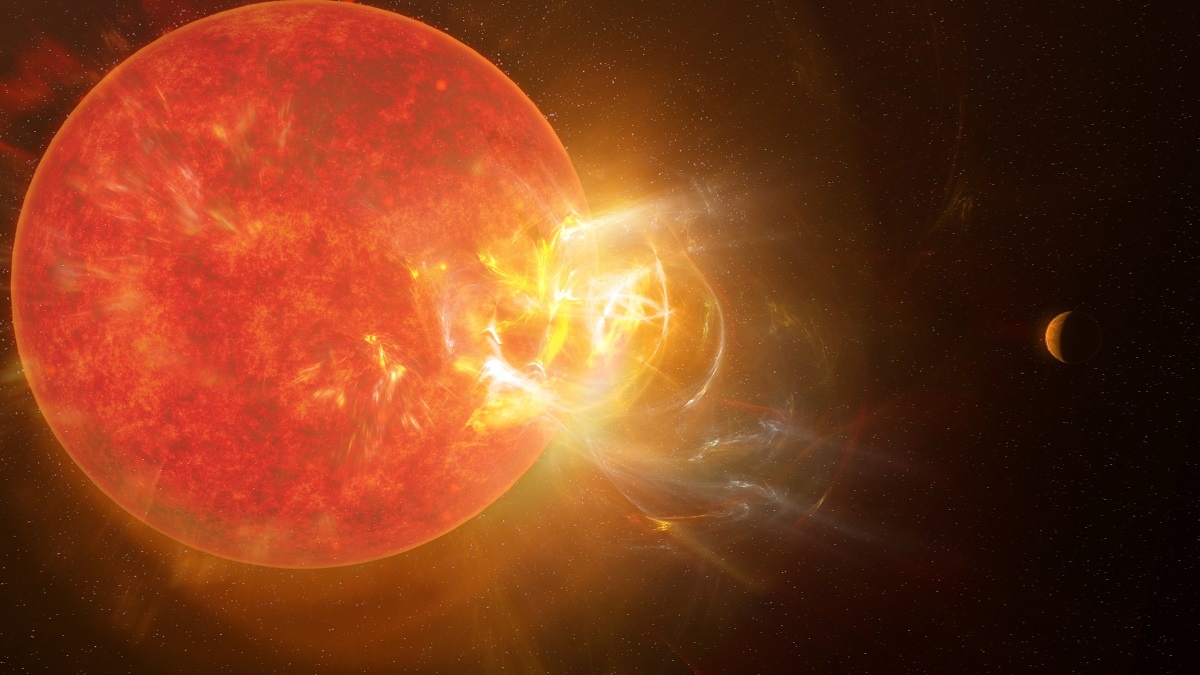
The TRAPPIST-1 system continues to fascinate astronomers, astrobiologists, and exoplanet hunters alike. In 2017, NASA announced that this red dwarf star (located 39 light-years away) was orbited by no less than seven rocky planets – three of which were within the star’s habitable zone (HZ). Since then, scientists have attempted to learn more about this system of planets to determine whether they could support life. Of particular concern is the way TRAPPIST-1 – like all M-type (red dwarf) stars – is prone to flare-ups, which could have a detrimental effect on planetary atmospheres.
Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), an international team of astrophysicists led by the University of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder) took a closer look at this volatile star. As they describe in their paper (which recently appeared online), the Webb data was used to perform a detailed spectroscopic investigation of four solar flares bursting around TRAPPIST-1. Their findings could help scientists characterize planetary environments around red dwarf stars and measure how flare activity can affect planetary habitability.
Continue reading “TRAPPIST-1 Has Flares. What Does This Mean for its Planets?”