As humanity returns to the Moon in the next few years, they’re going to need water to survive. While resupplies from Earth would work for a time, eventually the lunar base would have to become self-sustaining? So, how much water would be required to make this happen? This is what a recently submitted study hopes to address as a team of researchers from Baylor University explored water management scenarios for a self-sustaining moonbase, including the appropriate location of the base and how the water would be extracted and treated for safe consumption using appropriate personnel.
Continue reading “How Much Water Would a Self-Sustaining Moonbase Need?”Wireless Power Transmission Could Enable Exploration of the Far Side of the Moon
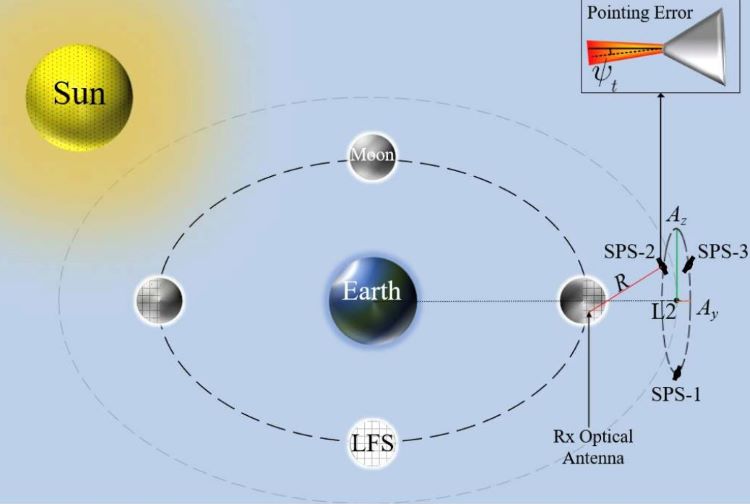
How can future lunar exploration communicate from the far side of the Moon despite never being inline with the Earth? This is what a recent study submitted to IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems hopes to address as a pair of researchers from the Polytechnique Montréal investigated the potential for a wireless power transmission method (WPT) comprised of anywhere from one to three satellites located at Earth-Moon Lagrange Point 2 (EMLP-2) and a solar-powered receiver on the far side of the Moon. This study holds the potential to help scientists and future lunar astronauts maintain constant communication between the Earth and Moon since the lunar far side of the Moon is always facing away from Earth from the Moon’s rotation being almost entirely synced with its orbit around the Earth.
Continue reading “Wireless Power Transmission Could Enable Exploration of the Far Side of the Moon”The Moon's Southern Ice is Relatively Young

Around the Moon’s southern polar region lies the South Pole-Aitken Basin, the single-largest impact basin on the lunar surface. Within this basin, there are numerous permanently shadowed regions (PSRs) that are thought to have trapped water ice over time. These deposits are crucial to future missions like the Artemis Program that will lead to the creation of permanent infrastructure. This water ice will supply crews with a steady source of water for drinking and irrigation and the means for chemically producing oxygen gas and rocket fuel.
For scientists, these PSRs are believed to have emerged when the Moon began migrating away from Earth roughly 2.5 billion years ago. Over time, these regions acted as “cold sinks” and trapped water ice that existed on the lunar surface at the time. However, according to a recent study led by the Planetary Science Institute (PSI), the Moon’s permanently shadowed areas arose less than 2.2 billion years ago and trapped ice even more recently than that. These findings could significantly impact future crewed missions as they indicate that the water ice found in lunar craters could be of more recent origin.
Continue reading “The Moon's Southern Ice is Relatively Young”
