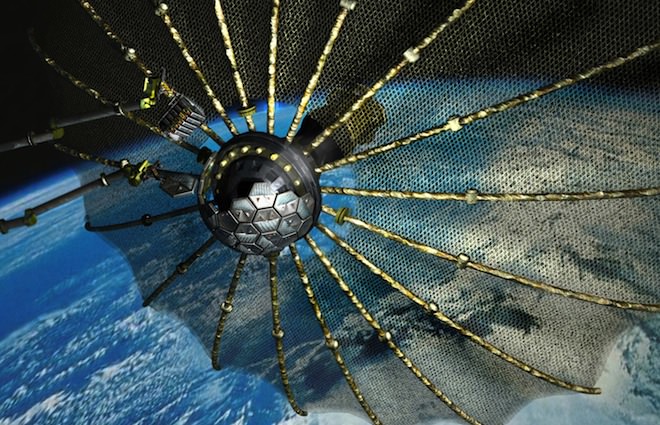
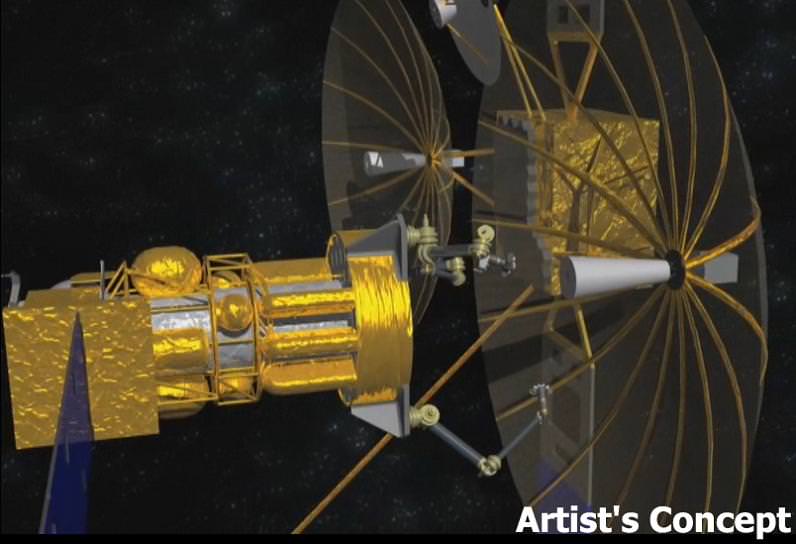
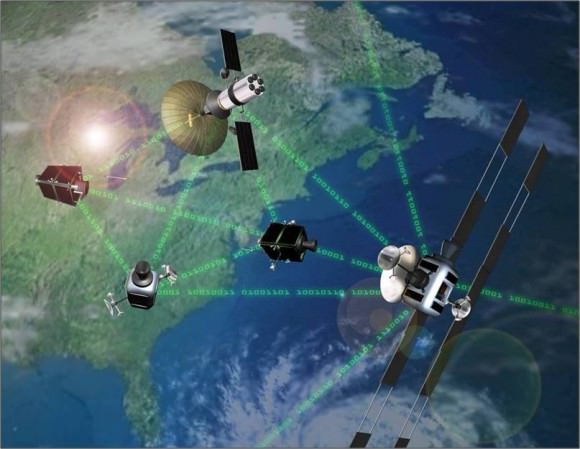
Caption: Phoenix satellite concept. Credit: DARPA
“Alien” meets “Bride of Frankenstein” and “Night of the Living Dead?” Straight from a possible sci-fi/horror movie mashup, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) wants to harvest components from dead, non-working “zombie” satellites to build new ones in space, all done remotely via a grasping, mechanical arm.
The agency would like to have the first keystone mission of what is called the Phoenix Program up and running by 2015, and they recently announced that several companies and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab have won a share of a $36 million contract award to help develop the technology to assemble new satellites from old, dead ones.
This project would harvest larger working parts, such as antennas and solar arrays from satellites that have otherwise have failed and are still in geosynchronous orbit, 35,000 kilometers (22,000 miles) above Earth. DARPA envisions robotically removing and re-using these parts from decommissioned satellites by developing a new class of very small ‘satlets,’ similar to nano satellites, which could “ride along” other commercial satellite launches, greatly reducing launch costs, DARPA says.
The satlets would attach themselves to the antenna or solar array of a non-functional satellite, remove the part and move it to a different orbit where a satellite servicing spacecraft is waiting to robotically operate on and build a new satellite while in orbit. The servicing satellite would be equipped with grasping mechanical arms for removing the satlets and components. These unique space tools are what needs to be developed for the program.
The robotic arms/grappling tools will be controlled remotely from Earth. The pieces will then be reconfigured into a new free-flying space system and operated independently to demonstrate the concept of space re-use.
DARPA is interested in building communication satellites to provide 24-hour communication capabilities for the military.
“Today, when a communication satellite fails, it usually means the expensive prospect of having to launch a brand new replacement communication satellite,” DARPA’s Phoenix Program webpage says. “The goal of the Phoenix program is to develop and demonstrate technologies to cooperatively harvest and re-use valuable components from retired, nonworking satellites in GEO and demonstrate the ability to create new space systems at greatly reduced cost.”
Among the companies that have a share in creating the components needed to make Phoenix a reality are Altius Space Machines, Space Systems/Loral; Intelsat; MacDonald, Dettwiler and Associates; Honeybee Robotics; and JPL.
Some of the technology DARPA expects to be built for the Phoenix program include:
Radiation tolerant micro-electronics and memory storage
Industrial robotics end effectors and tool changeout mechanisms and techniques
Computer-assisted medical robotics micro-surgical tele-presence, tools and imaging
Remote imaging/vision technologies
Watch DARPA’s video on the Phoenix Program:
For more information, see the DARPA Phoenix webpage.