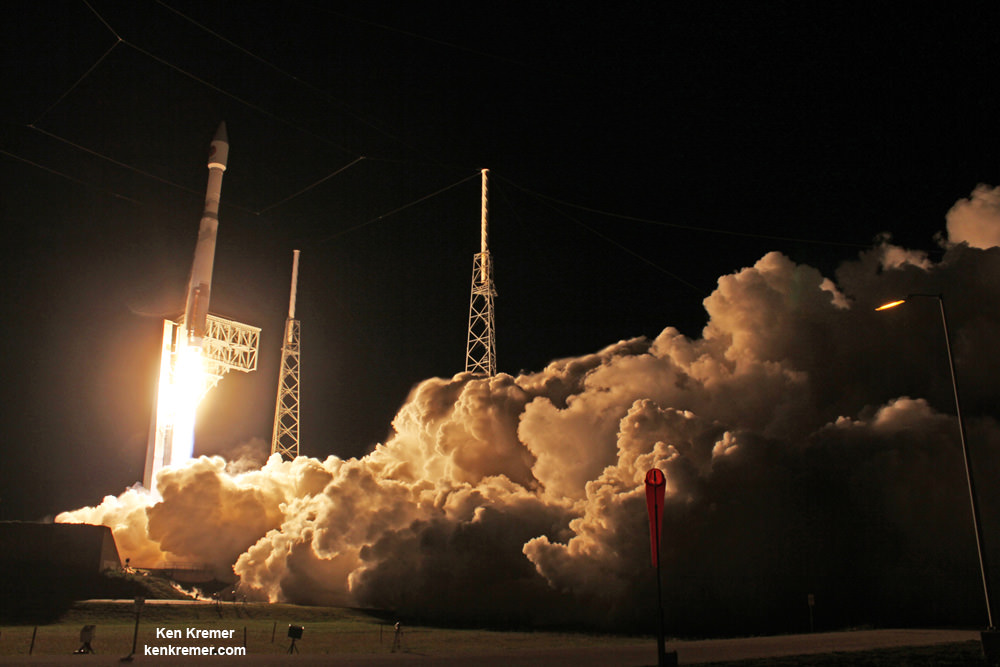
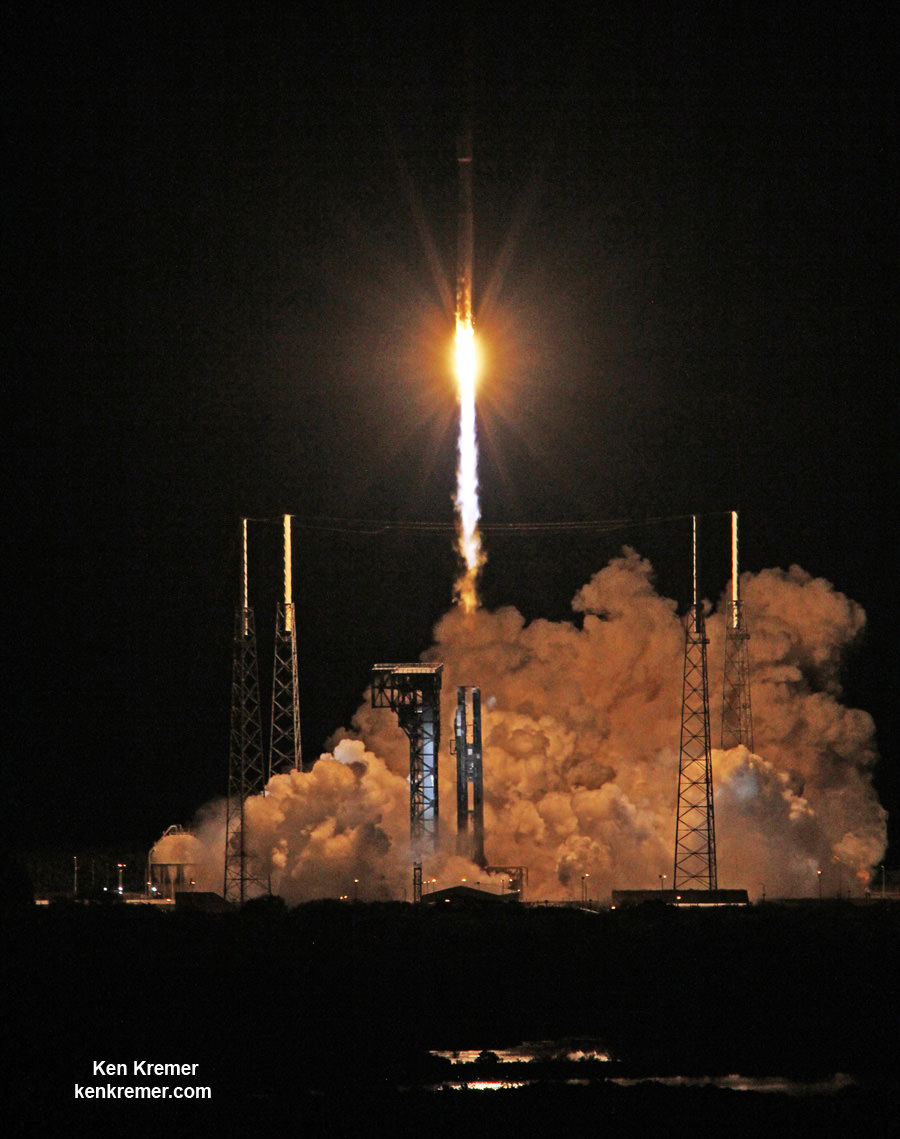
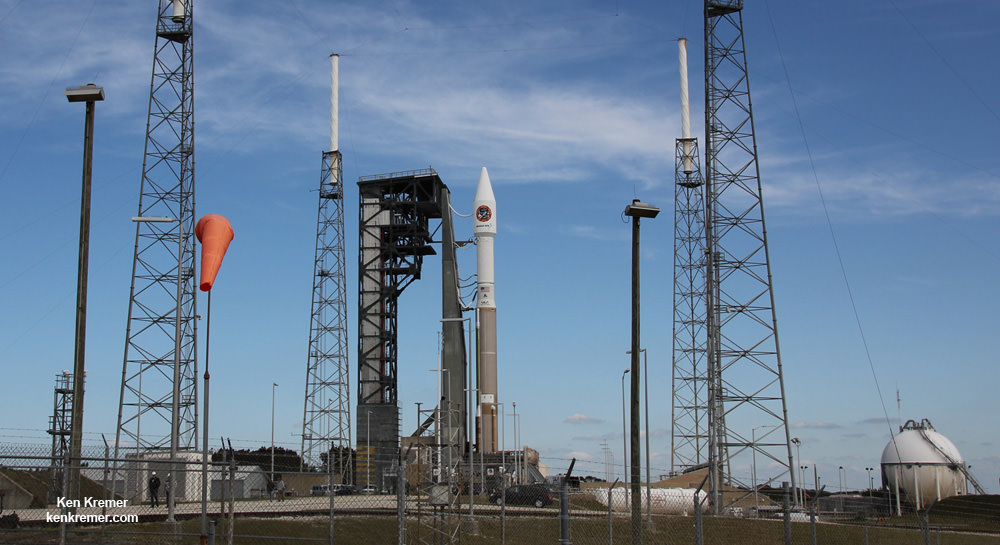
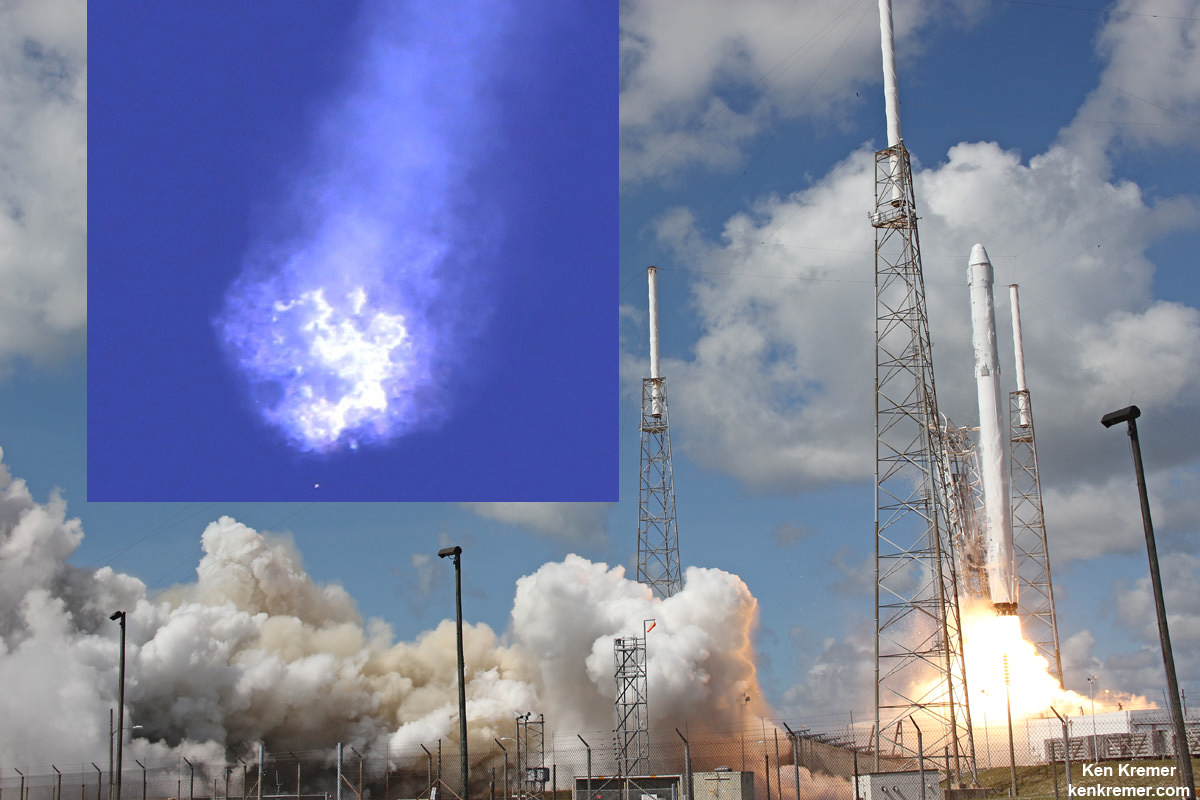
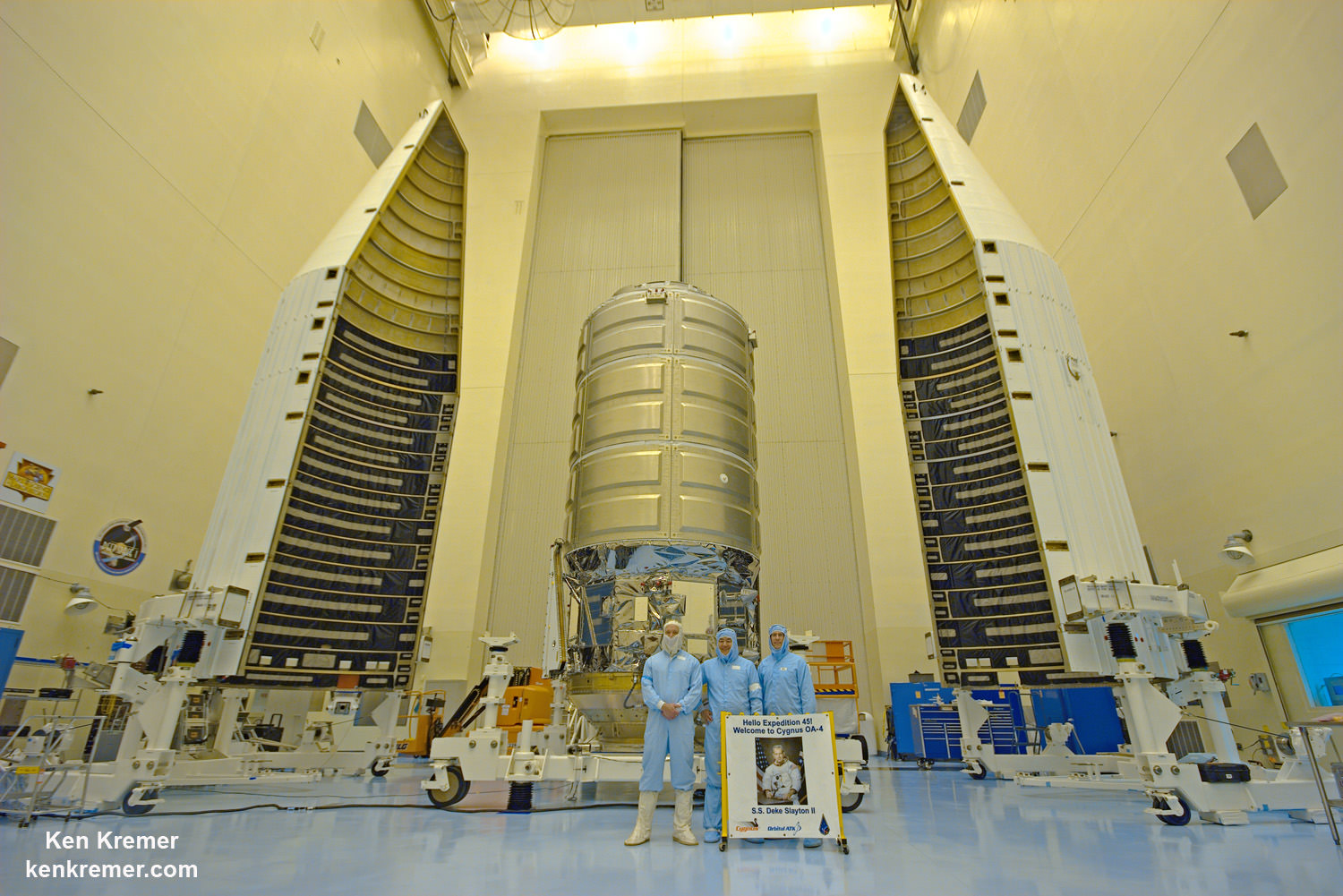
WALLOPS ISLAND, VA – The soon to be reborn Orbital ATK Antares commercial rocket sporting new first stage engines has been raised at its repaired launch pad on Virginia’s scenic eastern shore for a long awaited test firing of the powerplants. The static test firing is now slated to take place in less than 3 days on Tuesday evening, May 31.
The now revamped launch vehicle – dubbed Antares 230 – has been ‘re-engined’ and upgraded with a pair of modern and more powerful first stage engines – the Russian-built RD-181 fueled by LOX/kerosene.
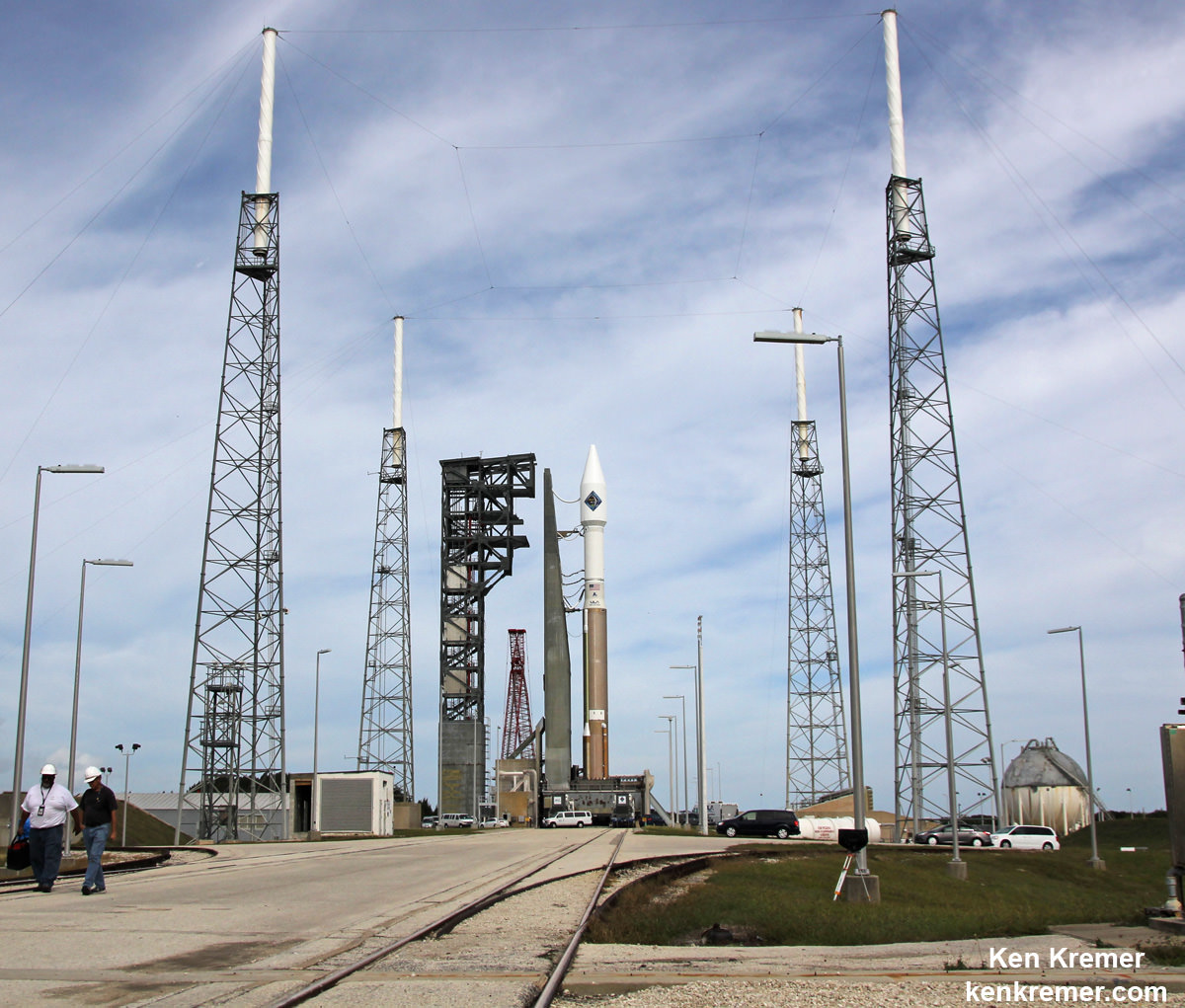
The engine test will be conducted using only the first stage of Antares at the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport’s Pad-0A at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility.
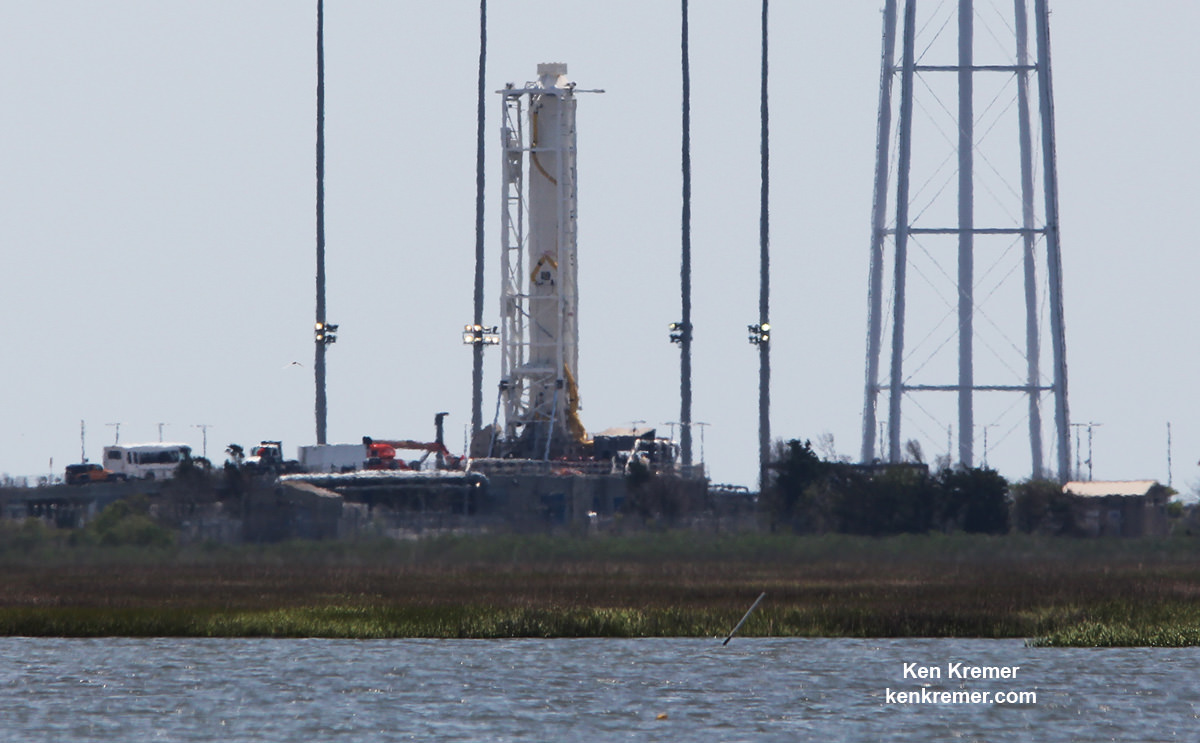
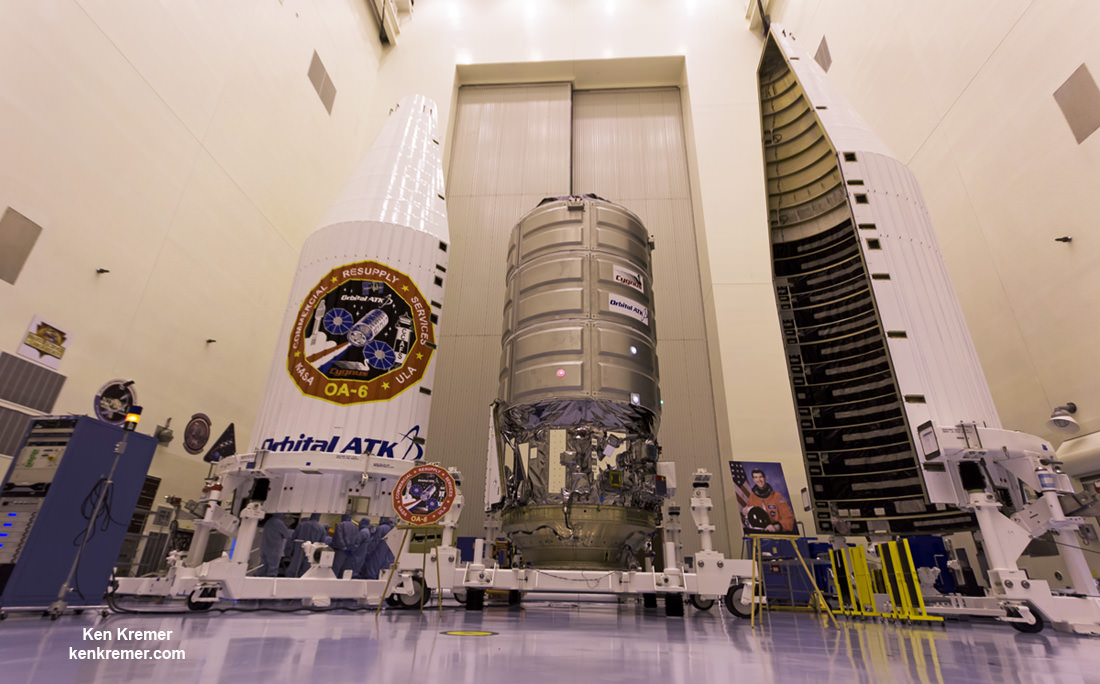
The raised rocket with the first stage capped at the top is visible right now at the Wallops pad – as seen in my new photos taken this week.
NASA announced that the static test firing is slated for no earlier than May 31 during a test window that runs from 5 p.m. to 8:15 p.m. EDT. As a contingency, the Wallops range has been reserved for backup test dates that run through June 5 just in case issues crop up.
NASA will not be carrying a live webcast of the test. Rather they will note the completion of the test on the Wallops’ Facebook and Twitter sites.
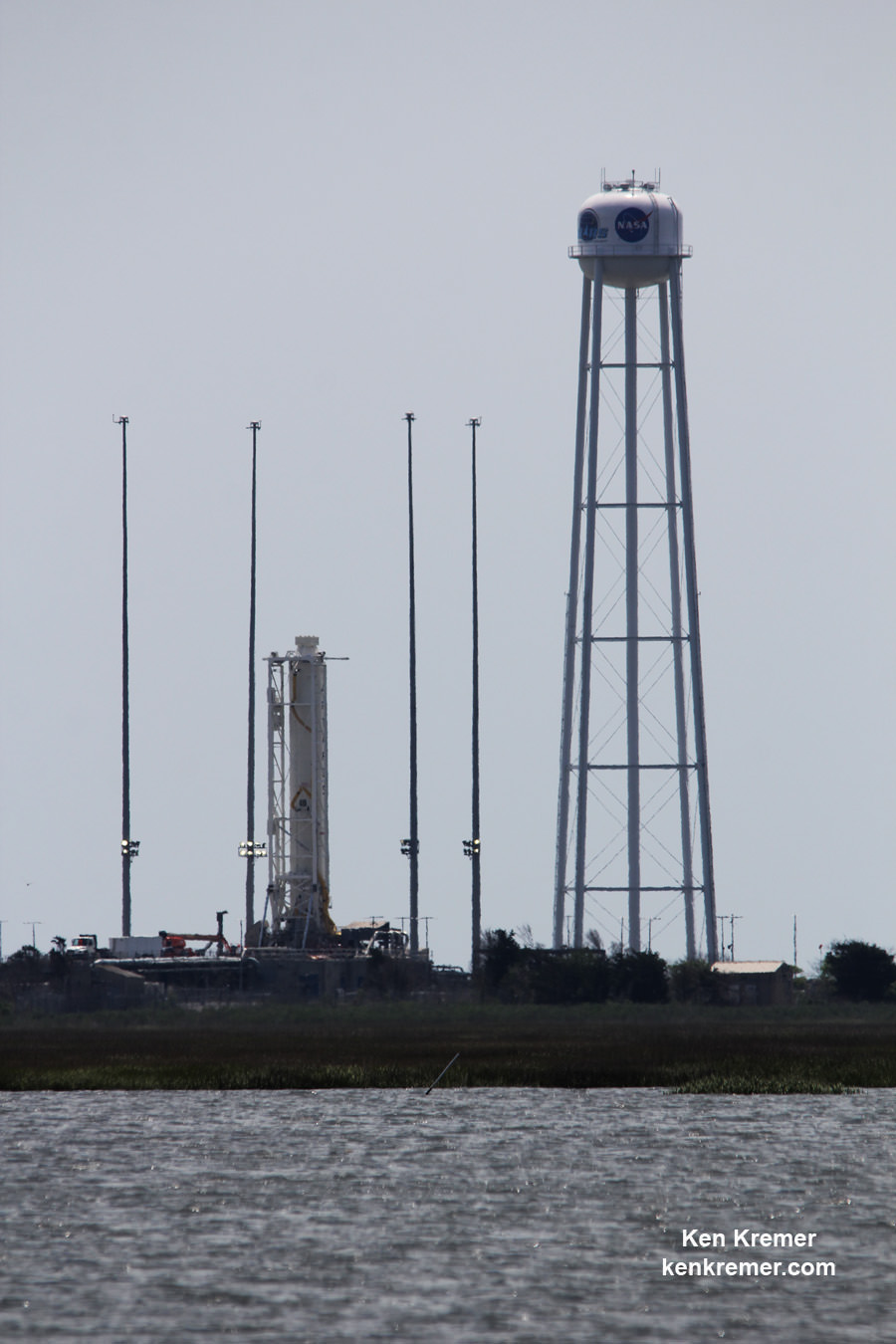

The test firing will be visible from various public viewing locations in the local Wallops area. However the NASA Wallops Visitor center will not be open.
NASA will not be carrying a live webcast of the test. Rather they will note the completion of the test on the Wallops’ Facebook and Twitter sites.
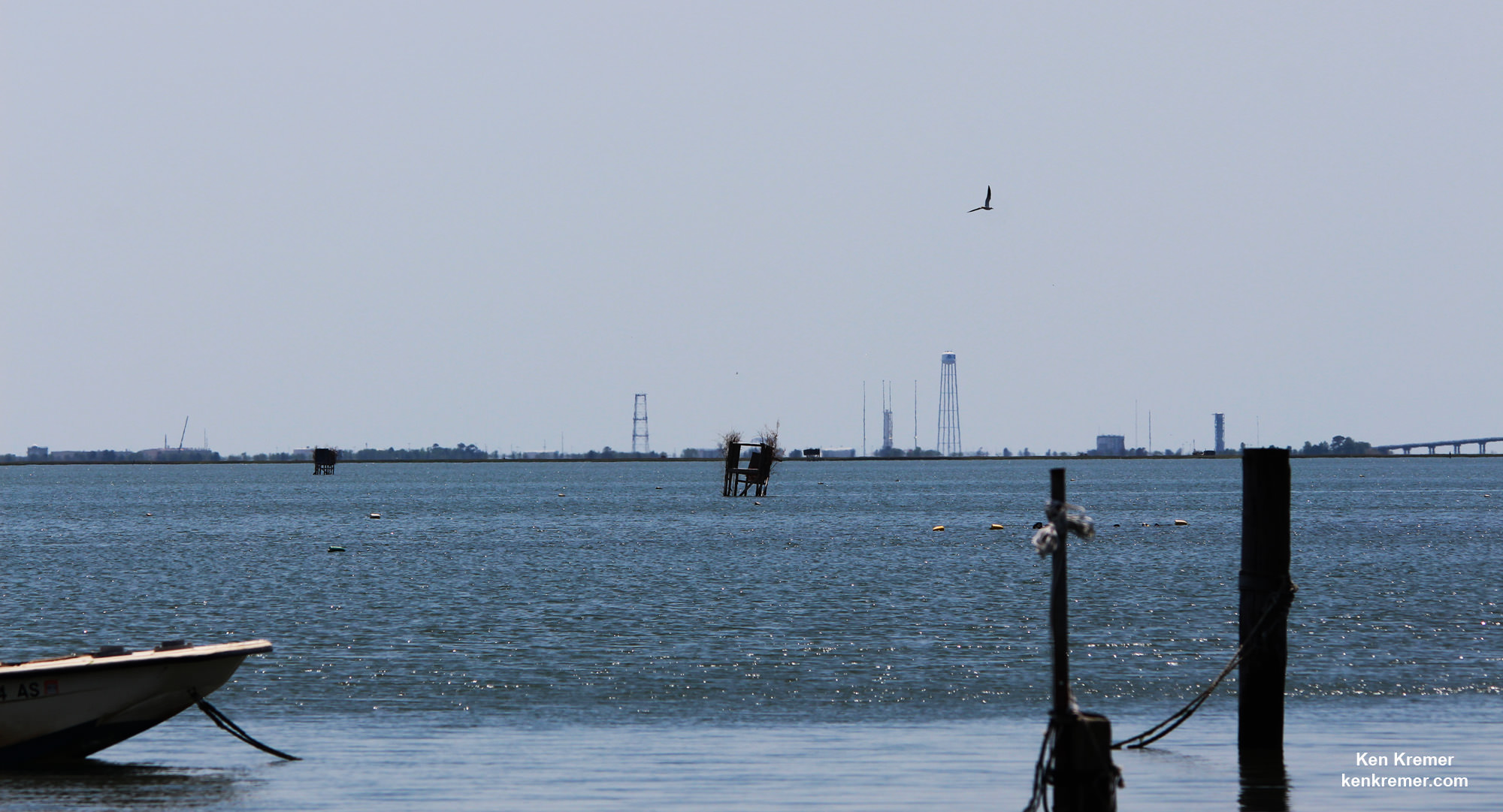

The test firing will be visible from various public viewing locations in the local Wallops area. However the NASA Wallops Visitor center will not be open.
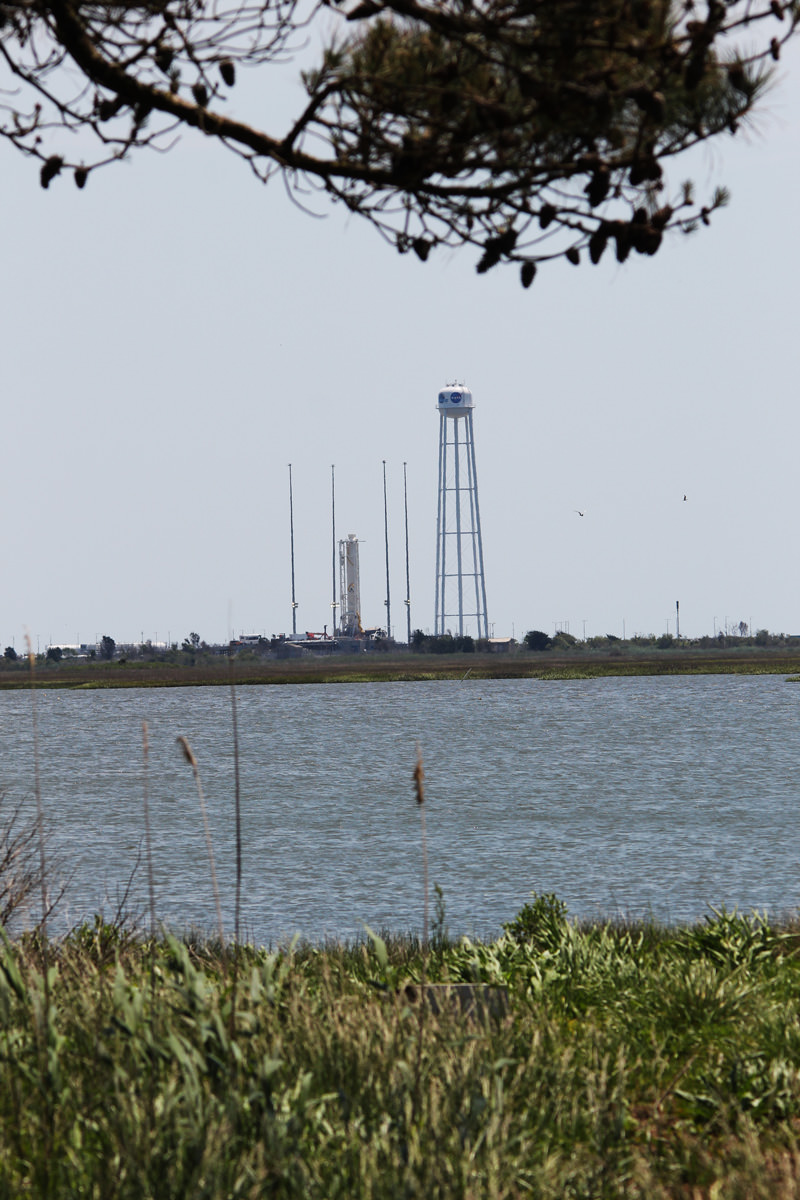

The test involves firing up Antares dual first stage RD-181 engines at full 100% power (thrust) for a scheduled duration of approximately 30 seconds. Hold down restraints will keep the rocket firmly anchored at the pad during the test.

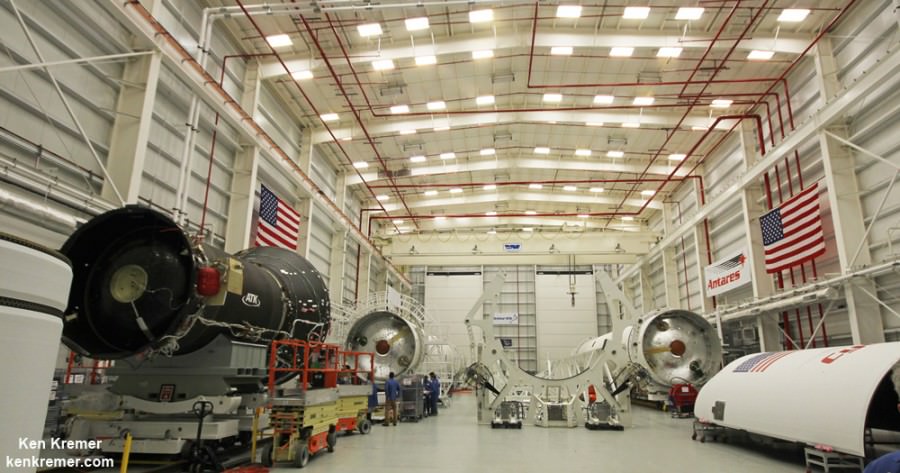
To prepare for the static hot fire test, Orbital ATK technicians rolled the vehicle on a dedicated multi-wheeled transporter erector launcher from the rockets processing hangar inside the Horizontal Integration Facility at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility to Virginia Space’s Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport Pad-0A about a mile away.
A successful outcome is absolutely crucial for permitting Antares to carry out its ‘Return to Flight’ launch dubbed OA-5 and set for sometime this summer.
“The hot fire will demonstrate the readiness of the rocket’s first stage and the launch pad fueling systems to support upcoming flights,” said NASA officials.
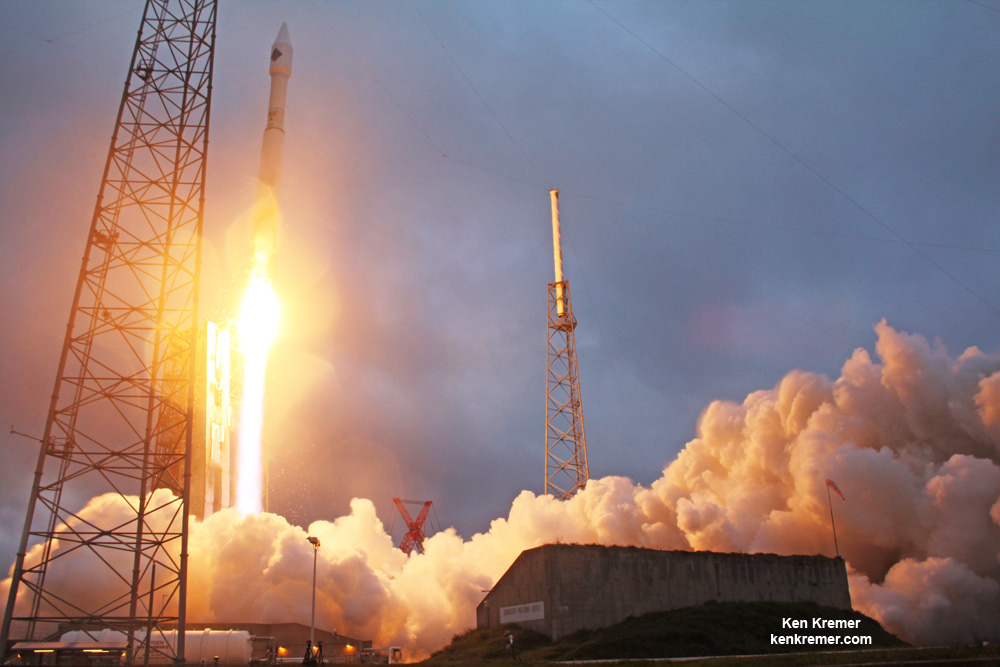
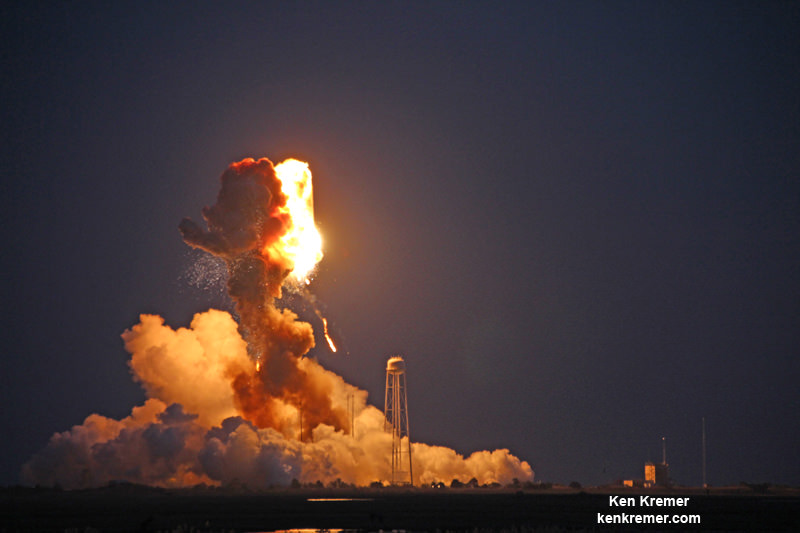
Antares launches ground to a halt following a devastating launch failure 19 months ago which destroyed the rocket and its payload of space station science and supplies for NASA in a huge fireball.
The ‘Return to Flight’ blastoff – which could come as soon as July 2016 – will be the first for the private Antares rocket since that catastrophic launch failure on Oct. 28, 2014, just seconds after liftoff from Wallops. That flight was carrying Orbital ATK’s Cygnus cargo freighter on the critical Orb-3 resupply mission for NASA and the astronauts living and working on the International Space Station (ISS).
The launch mishap was traced to a failure in the AJ26 first stage engine turbopump and caused Antares launches to immediately grind to a halt.
The RD-181 replaces the AJ26. The flight engines are built by Energomash in Russia.
“They are a good drop in replacement for the AJ26. And they offer 13% higher thrust compared to the AJ26,” said Kurt Eberly, Orbital ATK Antares deputy program manager, in an interview with Universe Today.
As a result of switching to the new RD-181 engines, the first stage also had to be modified to incorporate new thrust adapter structures, actuators, and propellant feed lines between the engines and core stage structure.
“This stage test paradigm is a design verification test,” said Eberly.
“After the 30 second test is done we will shut it down and have a pile of data to look at,” Eberly told Universe Today.
“Hopefully it will confirm all our environments and all our models and give us the confidence so we can proceed with the return to flight.”
Technicians have been processing the rocket at the pad to ready it for the test. They also conducted a wet dress rehearsal (WDR) and loaded the propellants like during an actual launch campaign.
The full up engine test follows the WDR.
“After the WDR we will do the stage test,” Eberly explained.
“It is a 30 second test. We will fire up both engines and hit all 3 power levels that we plan to use in flight.”
“We will use the thrust vector controls. So we will move the nozzles and sweep them through sinusoidal sweeps at different frequencies and excite various resonances and look for any adverse interaction between fluid modes and structural modes.”
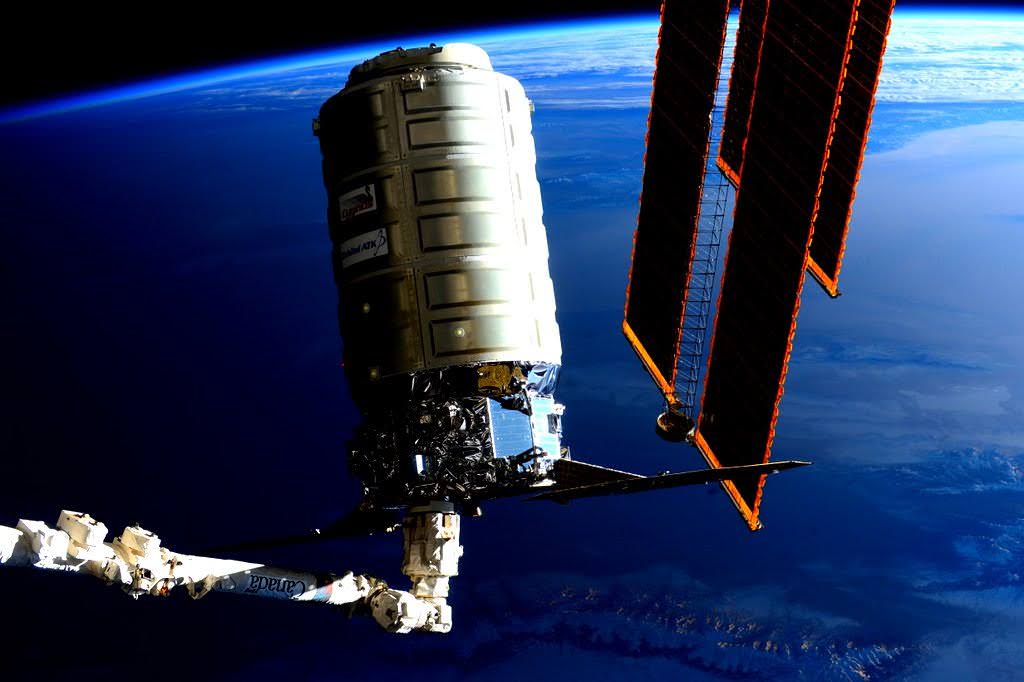
The test uses the first stage core planned to launch the OA-7 mission from Wallops late this year.
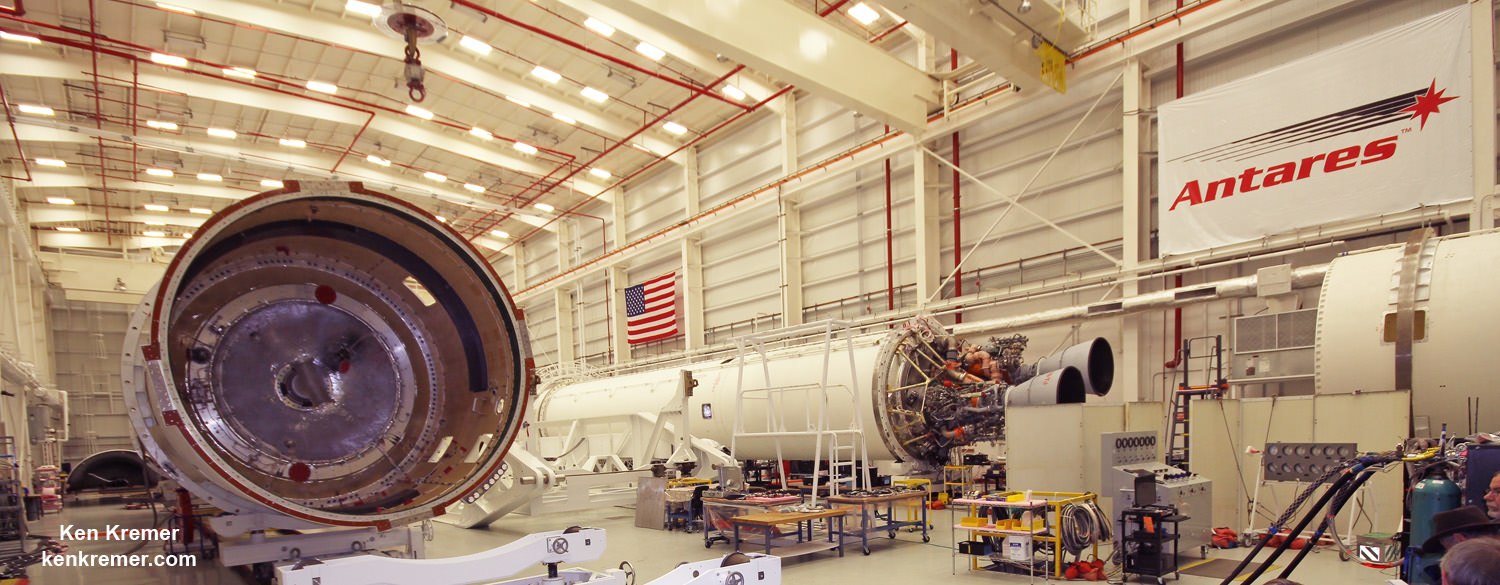

After the engine test is completed, the stage will be rolled back to the HIF and a new stage fully integrated with the Cygnus cargo freighter will be rolled out to the pad for the OA-5 ‘Return to Flight’ mission as soon as July.
“Orbital ATK is building, testing and flying the Antares rocket and Cygnus cargo spacecraft under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services contract. NASA initiatives like the cargo resupply contracts are helping develop a robust U.S. commercial space transportation industry with the goal of achieving safe, reliable and cost-effective transportation to and from the International Space Station and low-Earth orbit,” according to NASA.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.