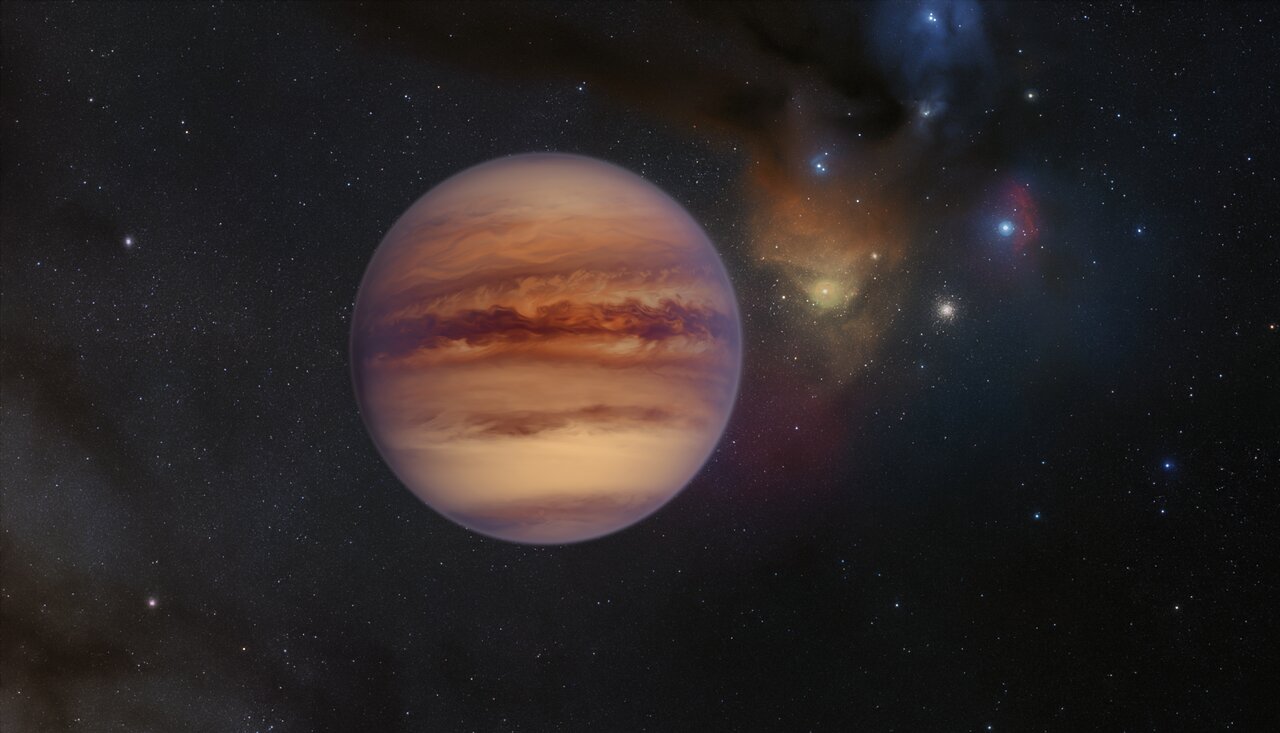
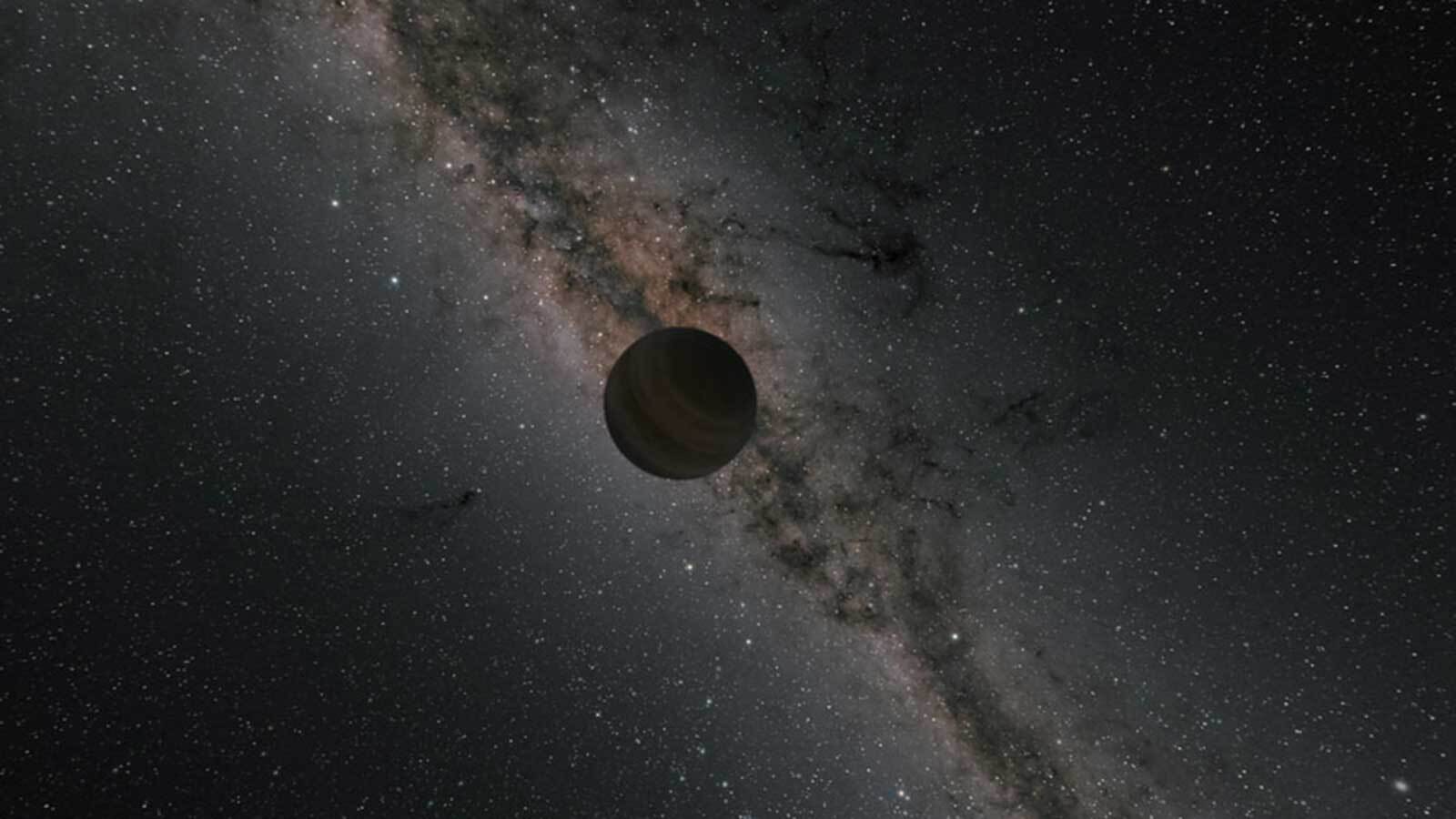
At one time, astronomers believed that the planets formed in their current orbits, which remained stable over time. But more recent observations, theory, and calculations have shown that planetary systems are subject to shake-ups and change. Periodically, planets are kicked out of their star systems to become “rogue planets,” bodies that are no longer gravitationally bound to any star and are adrift in the interstellar medium (ISM). Some of these planets may be gas giants with tightly bound icy moons orbiting them, which they could bring with them into the ISM.
Like Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, these satellites could have warm water interiors that might support life. Other research has indicated that rocky planets with plenty of water on their surfaces could also support life through a combination of geological activity and the decay of radionuclides. According to a recent paper by an international team of astronomers, there could be hundreds of rogue planets in our cosmic neighborhood. Based on their first-ever feasibility analysis, they also indicate that deep space missions could explore these unbound objects more easily than planets still bound to their stars.
Continue reading “If Rogue Planets are Everywhere, How Could We Explore Them?”