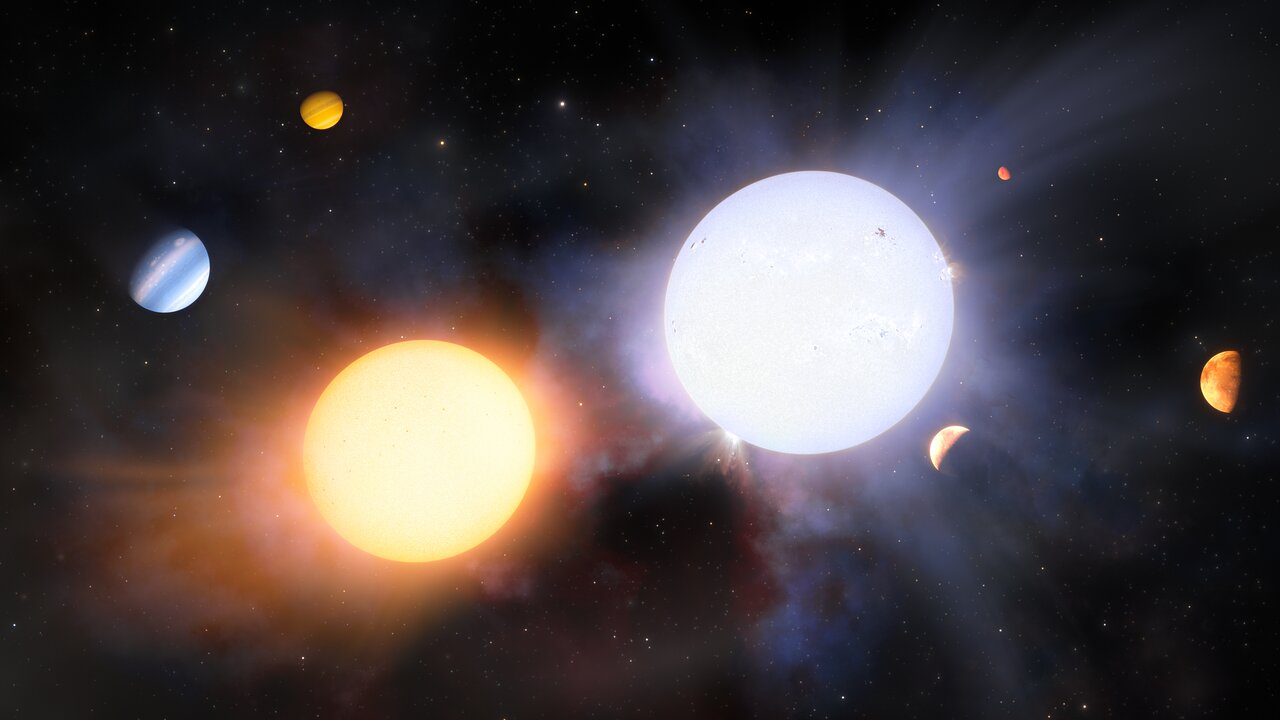
In recent years, astronomers have developed techniques to measure the metal content of stars with extreme accuracy. With that capability, astronomers have examined sibling stars to see how their metallicity differs. Some of these co-natal stars have pronounced differences in their metallicity.
New research shows that stars engulfing rocky planets are responsible.
Continue reading “Up to a Third of Stars Ate Some of their Planets”