In the late 18th century, Charles Messier was busy hunting for comets in the night sky, and noticed several “nebulous” objects. After initially mistaking them for the comets he was seeking, he began to compile a list of these objects so other astronomers would not make the same mistake. Known as the Messier Catalog, this list consists of 100 objects, consisting of distant galaxies, nebulae, and star clusters.
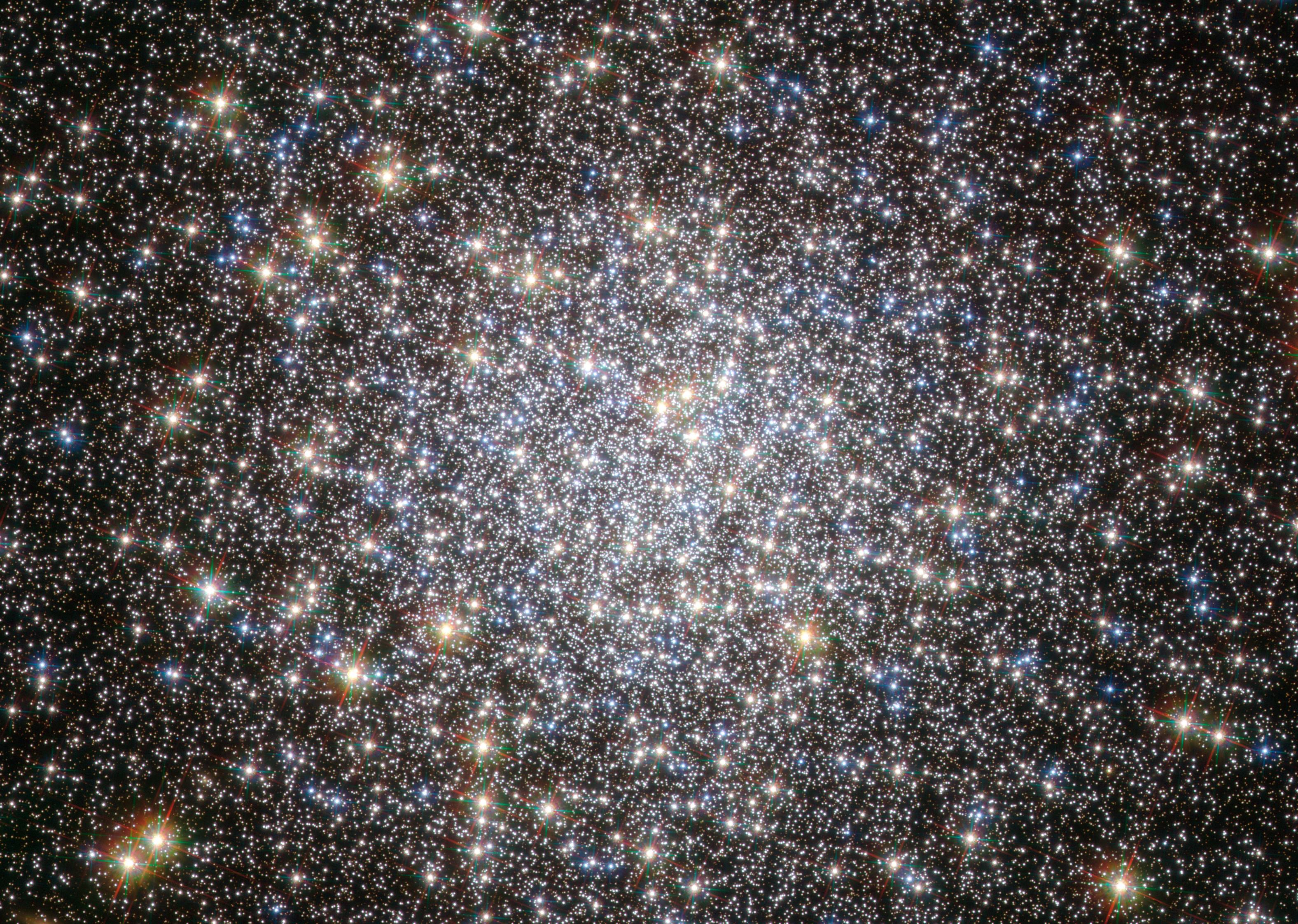
Among the many famous objects in this catalog is the M5 globular star cluster (aka. NGC 5904). Located in the galactic halo within the Serpens Constellation, this cluster of stars is almost as old as the Universe itself (13 billion years)! Though very distant from Earth and hard to spot, it is a favorite amongst amateur astronomers who swear by its beauty.