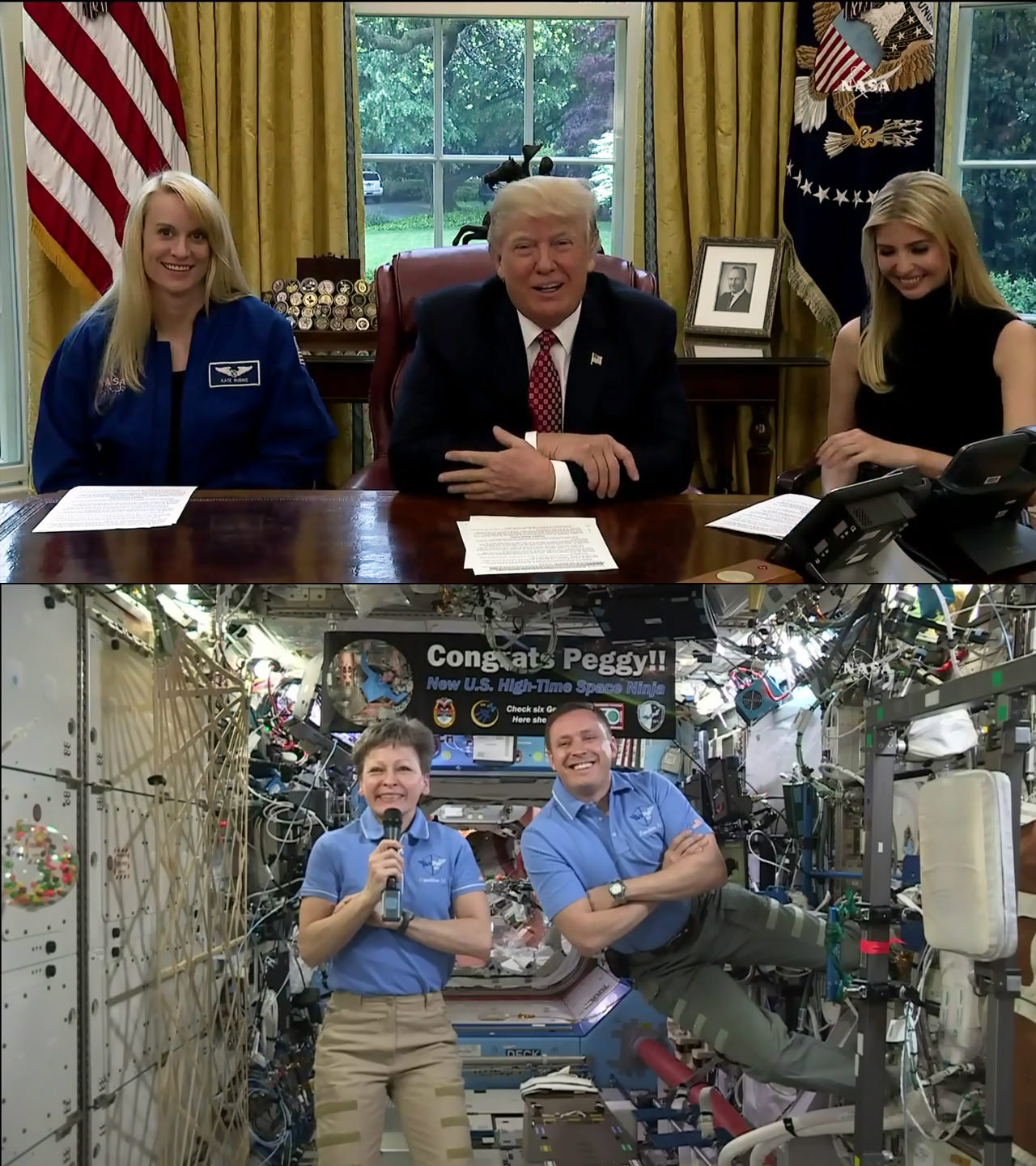
NASA’s Peggy Whitson, America’s most experienced astronaut, returned to Earth safely and smiling Sunday morning on the steppes of Kazakhstan, concluding her record-breaking stay in space aboard the International Space Station (ISS) along with Soyuz crewmates Jack Fischer of NASA and Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos.
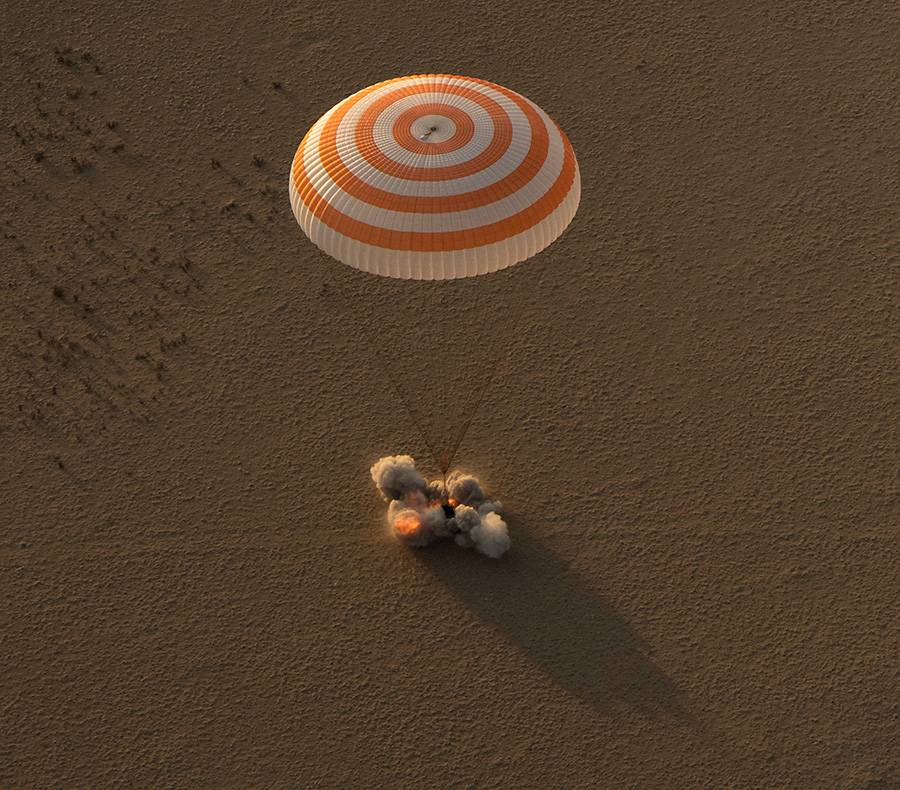
The multinational trio touched down softly on Earth inside their Soyuz MS-04 descent capsule on Saturday evening, Sept. 2 at 9:21 p.m. EDT (shortly after sunrise 7:21 a.m. Kazakhstan time, Sept. 3), some 90 miles southeast of the remote town of Dzhezkazgan in Kazakhstan.
Whitson wrapped up a 288-day extended mission in obviously good health that began in November 2016, spanning 122.2 million miles and 4,623 orbits of Earth – completing her third long-duration stay on the orbiting science outpost spanning Expeditions 50, 51 and 52.
“A flawless descent and landing,” said NASA commentator Rob Navias during the live NASA TV coverage of the return of the ISS Expedition 52 crew Saturday afternoon and evening US time.
“The crew is back on Earth safe and sound.”

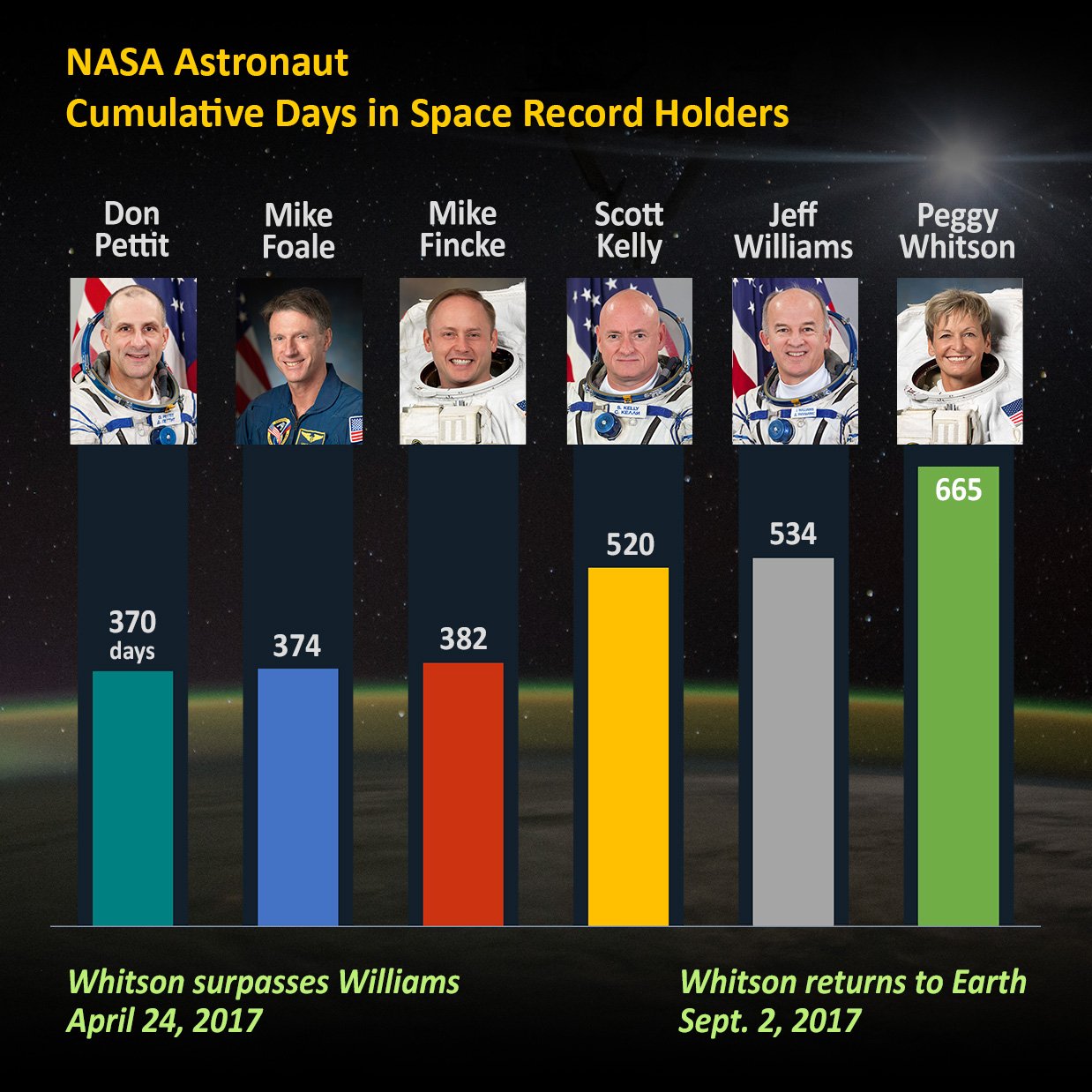
She has now accrued a total of 665 days in space – more than any American astronaut – over the course of her illustrious career during which she set multiple U.S. space records spanning a total of three spaceflights.
Whitson’s 665 total accumulated days in space places her eighth on the all-time space endurance list – just 8 days behind her Russian crewmate and Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin who now ranks 7th on the all-time list with 673 days in space on his five flights. She has exceeded the endurance record of her next closest NASA competitor by 131 days – namely NASA astronaut Jeff Williams.
The remarkable 57-year-old Ph.D biochemist by training has spent nearly 2 years of her entire life in space and she holds several other prestigious records as well – including more accumulated time in space than any other woman and the longest single spaceflight by a women – 288 days!
During this mission Whitson became the first woman to serve twice as space station commander. Indeed in 2008 Whitson became the first woman ever to command the space station during her prior stay on Expedition 16 a decade ago. Her second stint as station commander this mission began earlier this year on April 9.
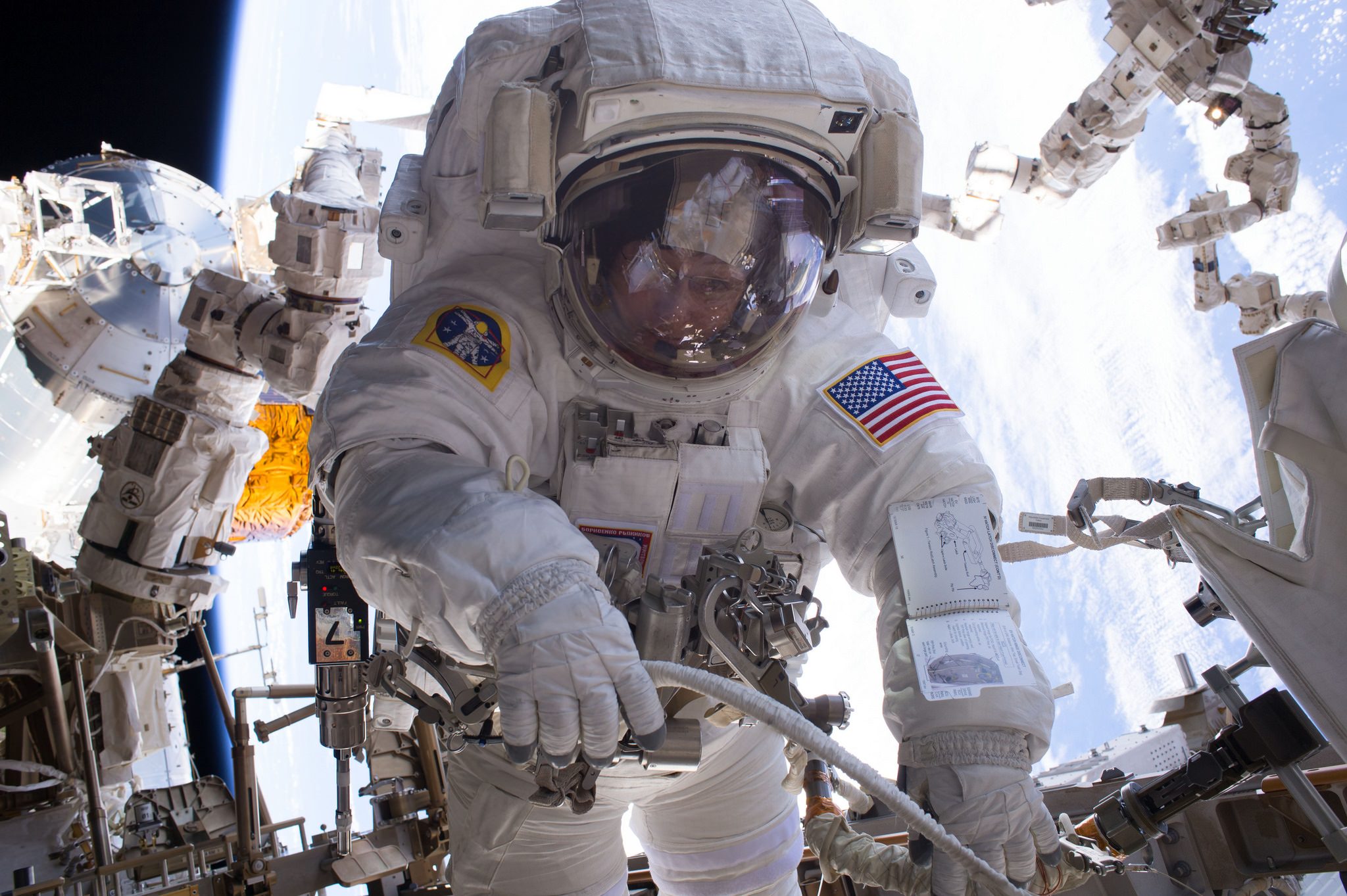
Whitson also holds the record for the most spacewalks and the most time spent spacewalking by a female astronaut. Altogether she has accumulated 60 hours and 21 minutes of EVA time over ten spacewalks -ranking her third most experienced in the world.
Notably Soyuz Commander Yurchikhin ranks fourth in spacewalking experience. Only Russia’s Anatoly Solovyev and NASA’s Michael Lopez-Alegria have more spacewalking time to their credit.
NASA’s Jack Fischer completed his rookie spaceflight accumulating 136 days in space aboard the ISS.

Whitson originally launched to the ISS on Nov 17, 2016 aboard the Russian Soyuz MS-03 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, as part of the three person Expedition 50 crew including flight engineers Oleg Novitskiy of Roscosmos and Thomas Pesquet of ESA (European Space Agency).
Her flight was unexpectedly extended in flight after the Russian government decided to cut back on the number of space station crew cosmonauts this year from three to two to save money. Thus a return seat became available on this Soyuz MS-04 return flight after NASA negotiated an extension with Rosmoscos in April enabling Whitson to remain on board the orbiting outpost an additional three months beyond her than planned June return home.
Whitson’s mission extension proved to be a boon for NASA and science research enabling the US/partner USOS crew complement to be enlarged from three to four full time astronauts much earlier than expected. This allowed NASA to about double the weekly time devoted to research aboard station – a feat not expected to happen until America’s commercial crew vehicles, namely Boeing Starliner and SpaceX Crew Dragon – finally begin inaugural launches next year from the Kennedy Space Center in mid-2018.

Descending dramatically while hanging below a single gigantic orange-and-white parachute the scorched Russian Soyuz vehicle fired its braking rockets just moments before touchdown in Kazakhstan to cushion the crew for a gentle landing under beautifully sunny skies.
A live NASA TV video feed captured the thrilling descent for over 14 minutes after the main parachute deployed all the way to the ground under clear blue sunny Sunday morning weather conditions and comfortably local Kazakh temperatures of 77 degrees F.
“Everything today went in perfect fashion from the undocking, to the deorbit burn to landing,” said Navias. “It went by the book with no issues.”
“We saw a spectacular 14 minute long live video of the Soyuz descent and landing.”

Russian search and recovery forces quickly arrived via a cluster of MI-8 helicopters after the soft landing to begin their normal procedures to extract the three Expedition 52 crew members from their cramped Soyuz descent module.
Soyuz Commander Yurchikhin in the center seat was hauled out first, followed by Fischer in the left side seat and lastly Whitson in the right seat. All 3 were placed on reclining seats sitting side by side and appeared quite well, conversing and speaking via satellite phones.
A group of Russian and US medical teams were on hand to check the astronauts and cosmonauts health and help the crewmates begin readapting to the tug of Earth’s gravity they have not experienced after many months of weightlessness in space.
Whitson’s final planned news conference from space with the media to sum up her experiences this past Wednesday had to be cancelled due to the catastrophic flooding events from Hurricane Harvey impacting Houston and elsewhere in Texas – including Mission Control which was forced to close multiple days.
The crews had bid their final farewells earlier and closed the hatches between the Soyuz and station at 2:40 p.m. EDT Saturday.
After conducting final spacecraft systems checks the trio unhooked the latches and undocked from the International Space Station at 5:58 p.m. EDT to begin their voyage home through the scorching heats of reentry in the Earth’s atmosphere that reached over 2500 degrees F (1400 degrees C) on the outside.
“While living and working aboard the world’s only orbiting laboratory, Whitson and Fischer contributed to hundreds of experiments in biology, biotechnology, physical science and Earth science, welcomed several cargo spacecraft delivering tons of supplies and research experiments, and conducted a combined six spacewalks to perform maintenance and upgrades to the station,” said NASA.
“Among their scientific exploits, Whitson and Fischer supported research into the physical changes to astronaut’s eyes caused by prolonged exposure to a microgravity environment. They also conducted a new lung tissue study that explored how stem cells work in the unique microgravity environment of the space station, which may pave the way for future stem cell research in space.”
“Additional research included an antibody investigation that could increase the effectiveness of chemotherapy drugs for cancer treatment, and the study of plant physiology and growth in space using an advanced plant habitat. NASA also attached the Cosmic Ray Energetics and Mass Investigation (ISS CREAM) on the outside of the space station in August, which is now observing cosmic rays coming from across the galaxy.”

ISS Expedition 53 began at the moment of undocking from the space station, now under the command of veteran NASA astronaut Randy Bresnik since the official change of command ceremony on Friday.
Along with his crewmates Sergey Ryazanskiy of Roscosmos and Paolo Nespoli of ESA (European Space Agency), the three-person crew will operate the station for the next 10 days until the imminent arrival of three new crew members.
The station will get back to a full complement of six crewmembers after the upcoming Sept. 12 launch and fast track 4 orbit 6 hour docking of NASA astronauts Mark Vande Hei and Joe Acaba of NASA and Alexander Misurkin of Roscosmos aboard the next Soyuz MS-06 spacecraft departing from the Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazakhstan.
Meanwhile the next launch from the Kennedy Space Center is slated for this Thursday, Sept.7 is the SpaceX Falcon 9 carrying the USAF X-37B OTV-5 military mini-shuttle to low Earth orbit -detailed here.

Watch for Ken’s continuing onsite X-37B OTV-5 and NASA mission reports direct from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
Ken Kremer