In a recent study submitted to Earth and Planetary Astrophysics, a team of researchers from Yale University investigated how to identify impact craters that may have been created by Interstellar Objects (ISOs). This study is intriguing as the examination of ISOs has gained notable interest throughout the scientific community since the discoveries and subsequent research of ‘Oumuamua and Comet 2I/Borisov in 2017 and 2019, respectively. In their paper, the Yale researchers discussed how the volume of impact melt within fixed-diameter craters could be a possible pathway for recognizing ISO craters, as higher velocity impacts produce greater volumes of impact melt.
Continue reading “Impacts From Interstellar Objects Should Leave Very Distinct Craters”An Interstellar Meteor Struck the Earth in 2014, and now Scientists Want to Search for it at the Bottom of the Ocean
Back in 2014, an object crashed into the ocean just off the coast of Papua New Guinea. Data collected at the time indicated that the meteorite just might be an interstellar object, and if that’s true, then it’s only the third such object known (after Oumuamua and Borisov), and the first known to exist on Earth. Launching an undersea expedition to find it would be a long shot, but the scientific payoff could be enormous.
Continue reading “An Interstellar Meteor Struck the Earth in 2014, and now Scientists Want to Search for it at the Bottom of the Ocean”Nancy Grace Roman Will be Launching on a Falcon Heavy Rocket
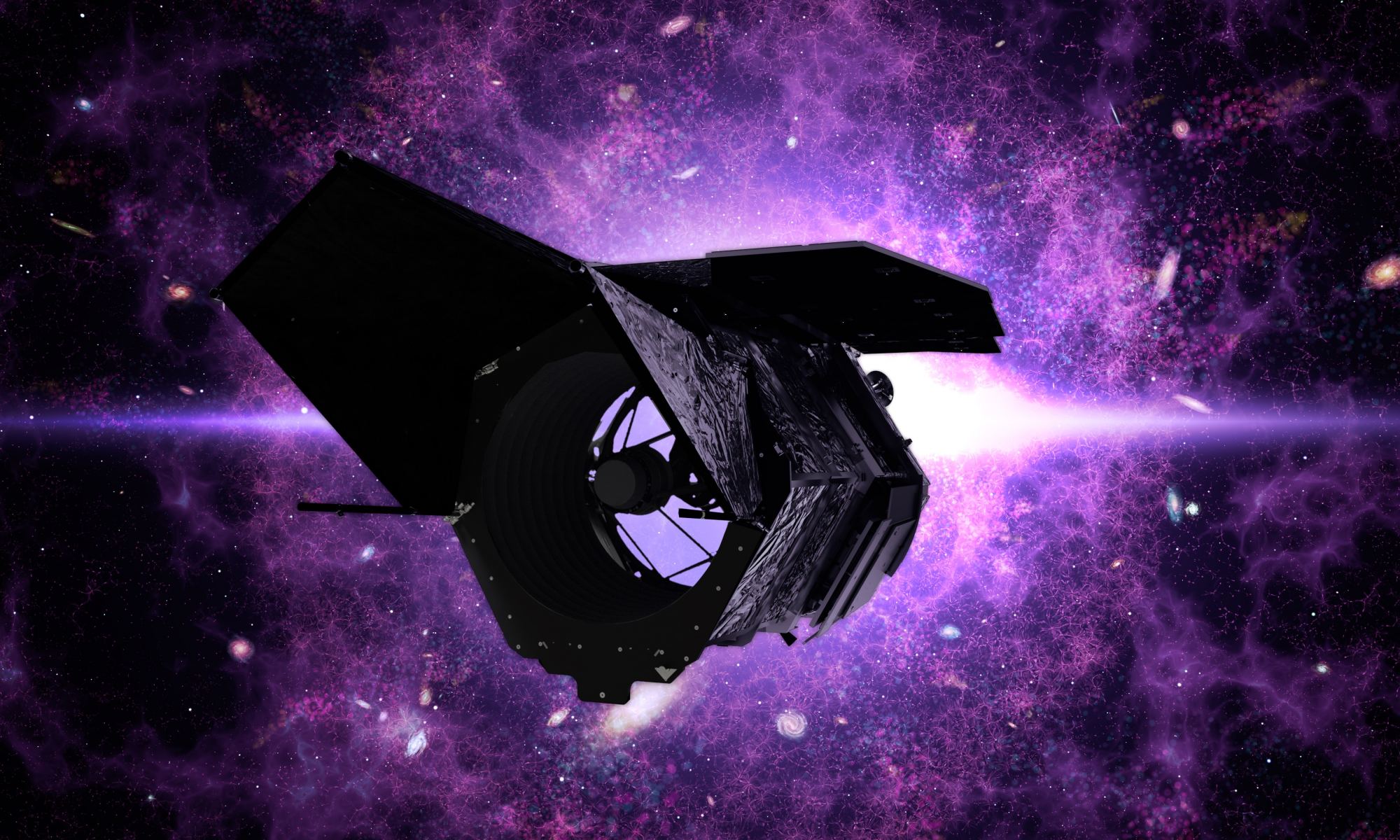

In 2026, the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (RST) – aka. the “Mother of Hubble” – will take to space and begin addressing some of the deepest mysteries of the Universe. This will include capturing the deepest field images of the cosmos, refining measurements of the Hubble Constant (aka. Hubble’s Law), and determining the role of Dark Matter and Dark Energy in the evolution of the cosmos. Alongside its next-generation partner, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), the RST will acquire infrared images with over 200 times the surveying power of its predecessor with the same rich level of detail.
On Tuesday, July 19th, NASA announced that it had awarded SpaceX with a Launch Services (NLS) II contract to provide the rocket that will deploy the RST mission to space. As specified in the NLS II, the launch will take place in October 2026 (May 2027, at the latest) and consist of a Falcon Heavy rocket transporting the RST from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center to orbit. This indefinite-delivery/indefinite-quantity contract is valued at approximately $255 million and covers the launch and other mission-related costs.
Continue reading “Nancy Grace Roman Will be Launching on a Falcon Heavy Rocket”If Launched by 2028, a Spacecraft Could Catch up With Oumuamua in 26 Years
In October 2017, the interstellar object ‘Oumuamua passed through our Solar System, leaving a lot of questions in its wake. Not only was it the first object of its kind ever to be observed, but the limited data astronomers obtained as it shot out of our Solar System left them all scratching their heads. Even today, almost five years after this interstellar visitor made its flyby, scientists are still uncertain about its true nature and origins. In the end, the only way to get some real answers from ‘Oumuamua is to catch up with it.
Interestingly enough, there are many proposals on the table for missions that could do just that. Consider Project Lyra, a proposal by the Institute for Interstellar Studies (i4is) that would rely on advanced propulsions technology to rendezvous with interstellar objects (ISOs) and study them. According to their latest study, if their mission concept launched in 2028 and performed a complex Jupiter Oberth Manoeuvre (JOM), it would be able to catch up to ‘Oumuamua in 26 years.
Continue reading “If Launched by 2028, a Spacecraft Could Catch up With Oumuamua in 26 Years”Rogue Planets Could be Habitable
The search for potentially habitable planets is focused on exoplanets—planets orbiting other stars—for good reason. The only planet we know of with life is Earth and sunlight fuels life here. But some estimates say there are many more rogue planets roaming through space, not bound to or warmed by any star.
Could some of them support life?
Continue reading “Rogue Planets Could be Habitable”Vera Rubin Observatory Should Find 5 Interstellar Objects a Year, Many of Which we Could Chase Down With Spacecraft
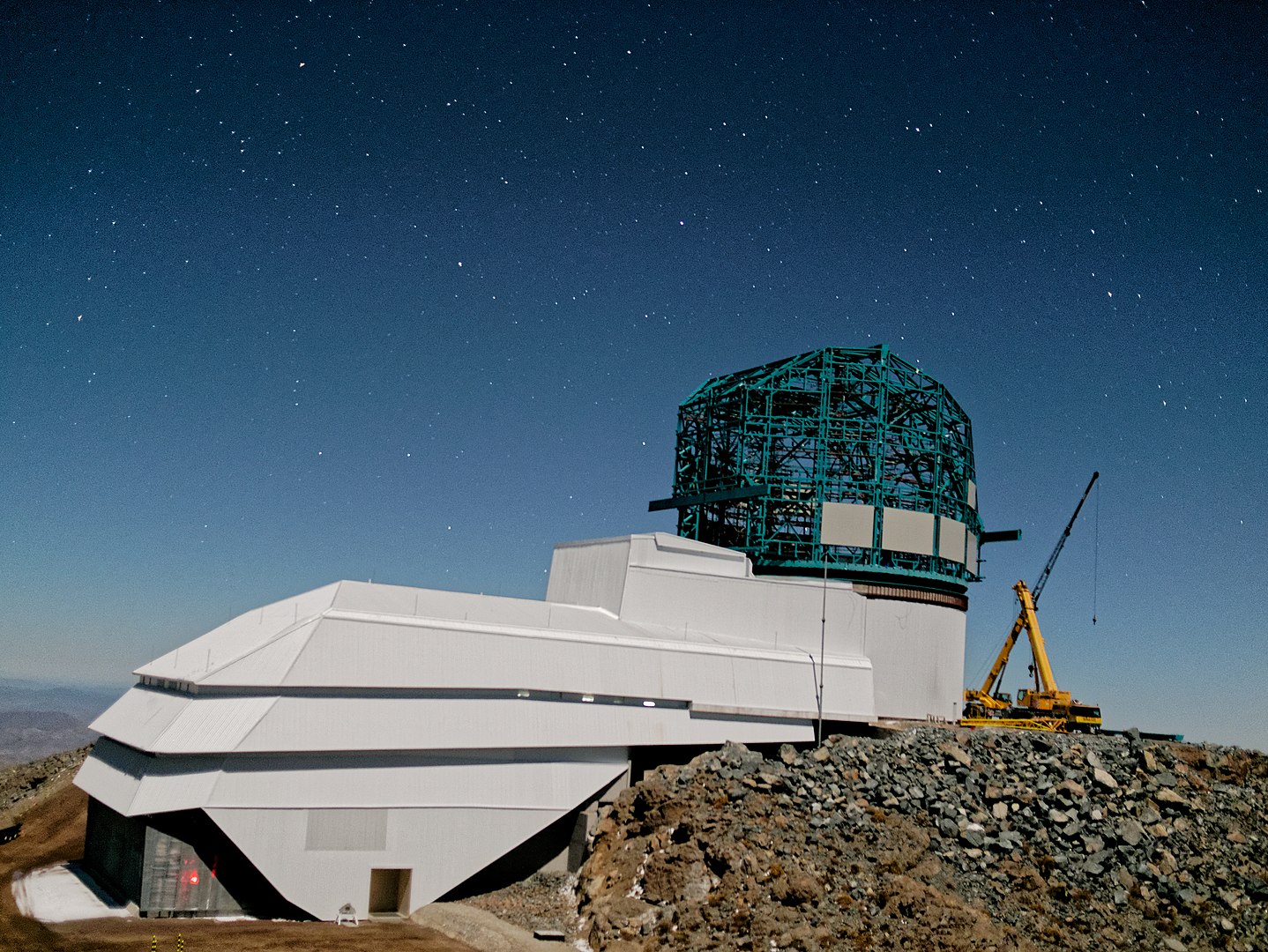

In a year (perhaps two), the Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile will become operational and commence its 10-year Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST). Using its 8.4-meter (27 foot) mirror and 3.2 gigapixel camera, this observatory is expected to collect 500 petabytes of images and data. It will also address some of the most pressing questions about the structure and evolution of the Universe and everything in it.
One of the highly-anticipated aspects of the LSST is how it will allow astronomers to locate and track interstellar objects (ISOs), which have become of particular interest since `Oumuamua flew through our system in 2017. According to a recent study by a team from the University of Chicago and the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA), the Rubin Observatory will detect around 50 objects during its 10-year mission, many of which we will be able to study up-close using rendezvous missions.
Continue reading “Vera Rubin Observatory Should Find 5 Interstellar Objects a Year, Many of Which we Could Chase Down With Spacecraft”What Happens to Interstellar Objects Captured by the Solar System?
Now that we know that interstellar objects (ISOs) visit our Solar System, scientists are keen to understand them better. How could they be captured? If they’re captured, what happens to them? How many of them might be in our Solar System?
One team of researchers is trying to find answers.
Continue reading “What Happens to Interstellar Objects Captured by the Solar System?”Galactic Panspermia. How far Could Life Spread Naturally in a Galaxy Like the Milky Way?
Can life spread throughout a galaxy like the Milky Way without technological intervention? That question is largely unanswered. A new study is taking a swing at that question by using a simulated galaxy that’s similar to the Milky Way. Then they investigated that model to see how organic compounds might move between its star systems.
Continue reading “Galactic Panspermia. How far Could Life Spread Naturally in a Galaxy Like the Milky Way?”Cosmic Rays Erode Away All But the Largest Interstellar Objects

So far we know of only two interstellar objects (ISO) to visit our Solar System. They are ‘Oumuamua and 2I/Borisov. There’s a third possible ISO named CNEOS 2014-01-08, and research suggests there should be many more.
But a new research letter shows that cosmic ray erosion limits the lifespan of icy ISOs, and though there may be many more of them, they simply don’t last as long as thought. If it’s true, then ‘Oumuamua was probably substantially larger when it started its journey, wherever that was.
Continue reading “Cosmic Rays Erode Away All But the Largest Interstellar Objects”Protoplanetary Disks Throw Out More Material Than Gets Turned Into Planets
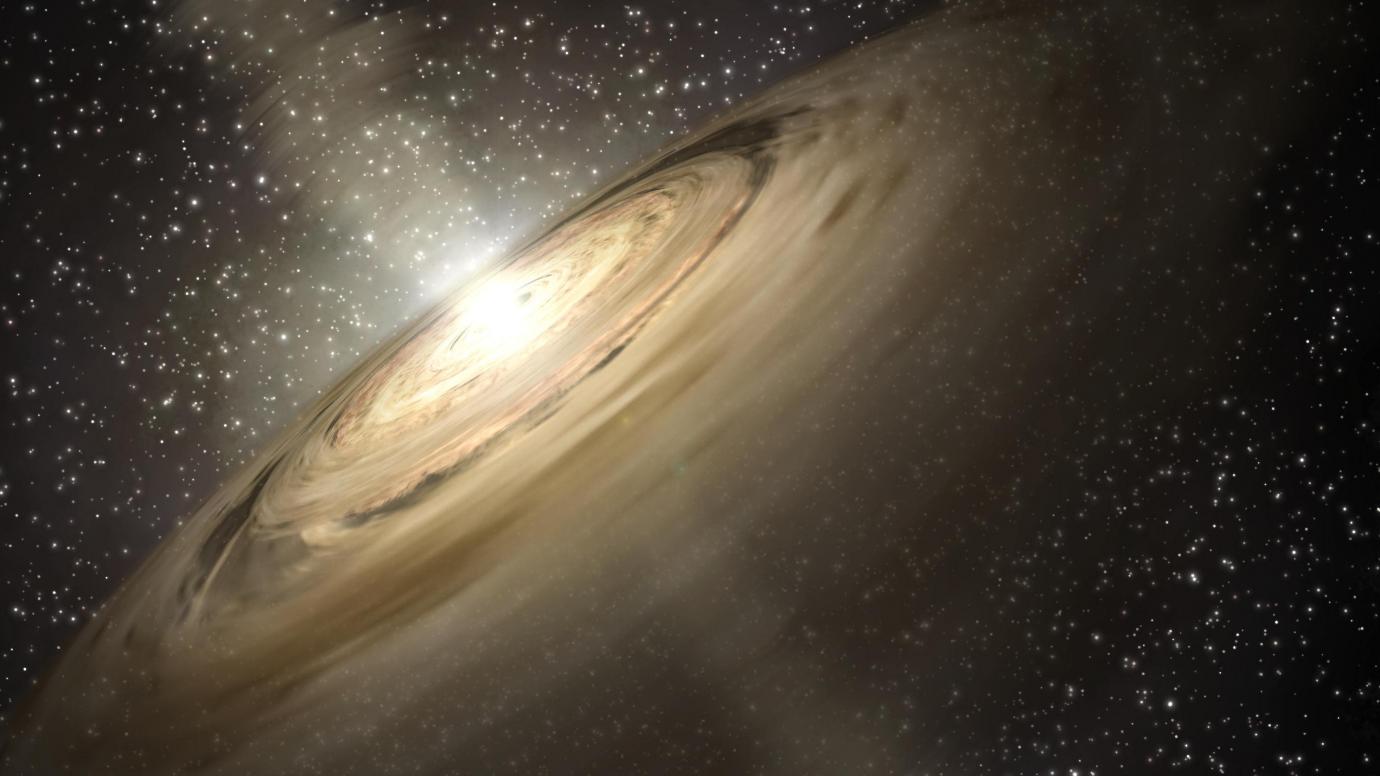

When a young solar system gets going it’s little more than a young star and a rotating disk of debris. Accepted thinking says that the swirling debris is swept up in planet formation. But a new study says that much of the matter in the disk could face a different fate.
It may not have the honour of becoming part of a nice stable planet, orbiting placidly and reliably around its host star. Instead, it’s simply discarded. It’s ejected out of the young, still-forming solar system to spend its existence as interstellar objects or as rogue planets.
Continue reading “Protoplanetary Disks Throw Out More Material Than Gets Turned Into Planets”