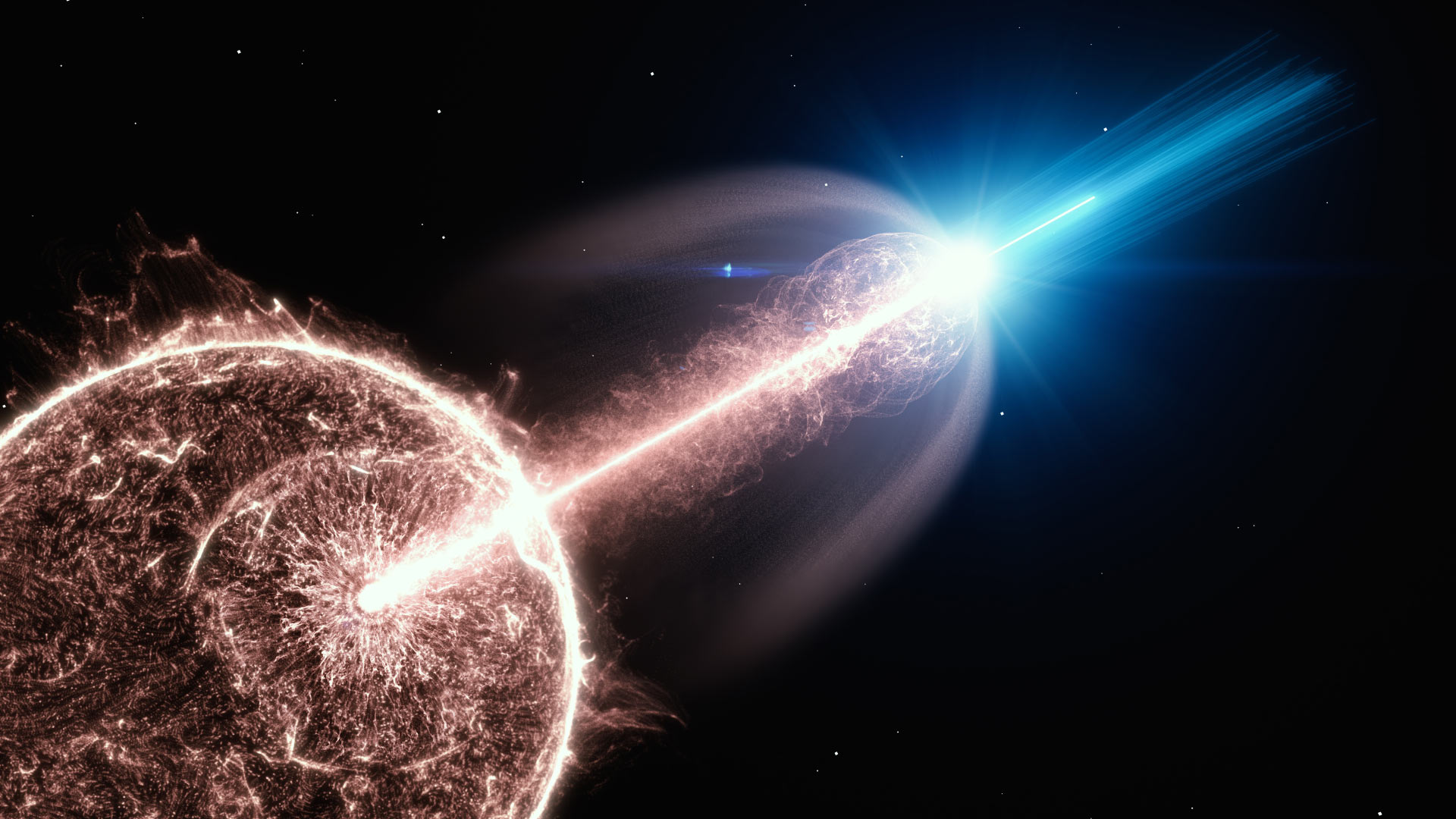
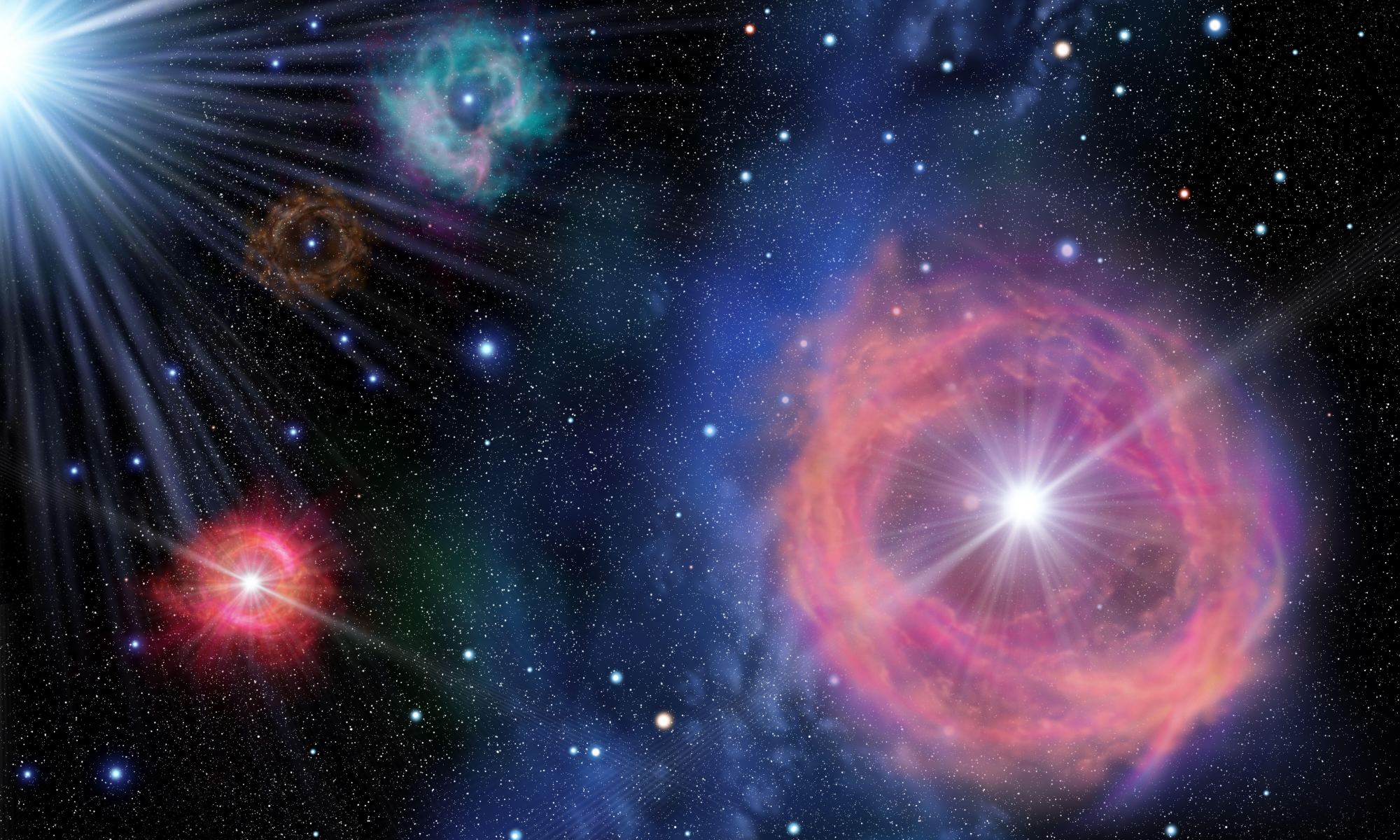
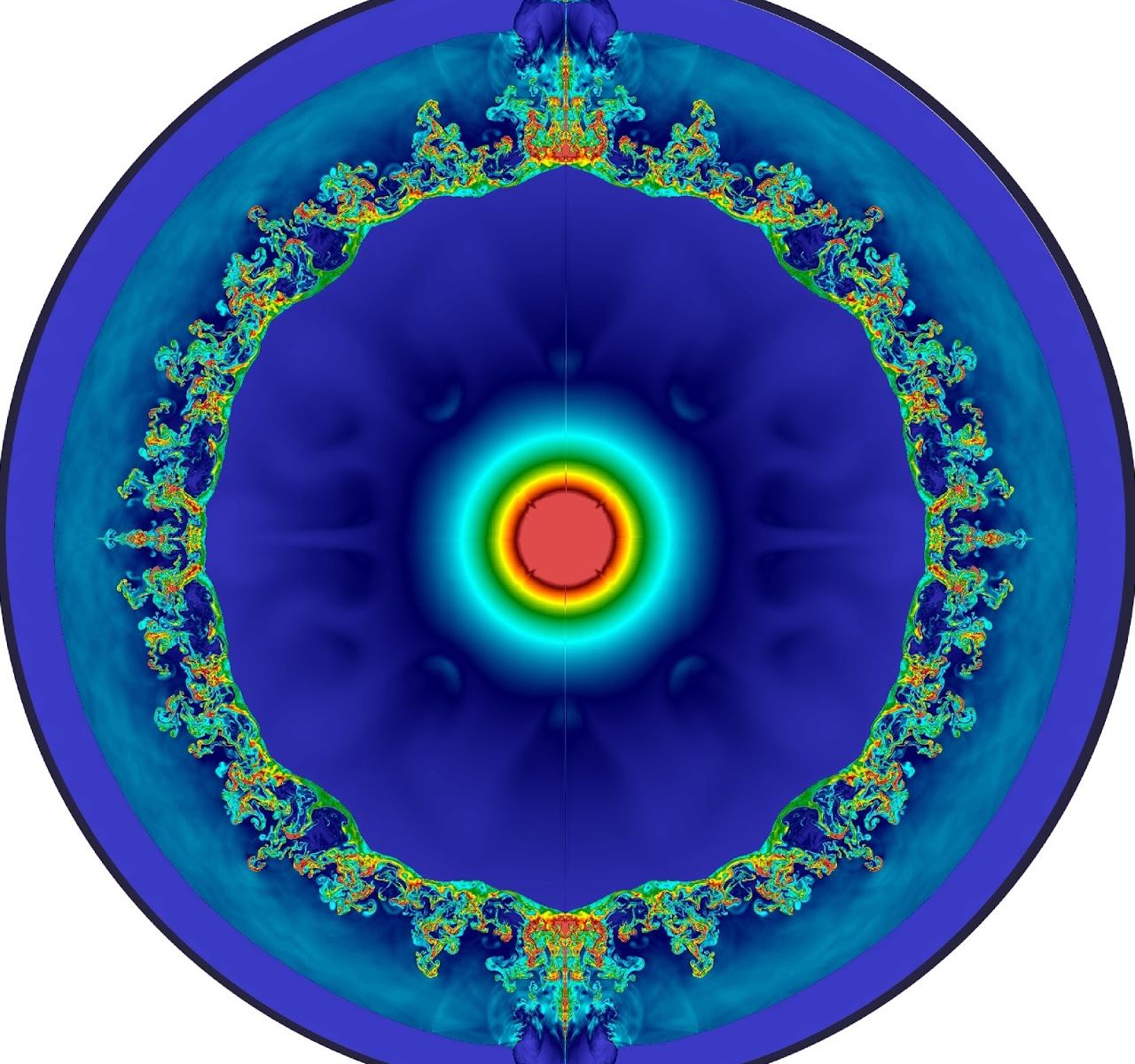
Gamma Ray Bursts (GRBs) are the most powerful astrophysical phenomena in the universe. For a span of seconds to a few minutes, they can be the most powerful high-energy event in the sky, shining across billions of light years. But recently astronomers detected a GRB that lasted more than a thousand seconds, with two blasts of gamma rays that triggered the Fermi Gamma Ray Burst Monitor. It’s such a strange cosmic event that astronomers aren’t sure what caused it, but they do have a possible idea.
Continue reading “A Gamma Ray Burst Lasted So Long it Triggered a Satellite Twice”A Gamma Ray Burst Lasted So Long it Triggered a Satellite Twice