It’s not long before a conversation about space travel is likely to turn to the impact on the human body. Our bodies have evolved to exist on Earth with a constant force of 1G acting upon them but up in orbit, all of a sudden that force is apparently lacking. The impact of this is well known; muscle loss and reduction in bone density but there are effects of spaceflight. Cosmic radiation from the Galaxy has an impact on cognition too, an effect that has recently been studied in mice!
Continue reading “What Does a Trip to Mars Do to the Brain?”Will Space Tourists Be Getting Heart Attacks in Space?
Astronauts are considered by many to be an elite bunch of people; healthy, fit and capable in many disciplines. Went they travel into space they can face health issues related to weightlessness from reduction in bone density to issues with their eyesight. These are people at the peak of physical fitness but what will happen to the rest of us when space tourism really kicks off. It is likely that anyone with underlying health issues could worsen in space. A new study suggests those with cardiovascular issues may suffer heart failure in space!
Continue reading “Will Space Tourists Be Getting Heart Attacks in Space?”A Rotating Spacecraft Would Solve So Many Problems in Spaceflight
If you watch astronauts in space then you will know how they seem to float around their spaceship. Spaceships in orbit around the Earth are in free-fall, constantly falling toward surface fo the Earth with the surface constantly falling away from it. Any occupant is also in free-fall but living like this causes muscle tone to degrade slowly. One solution is to generate artificial gravity through acceleration in particular a rotating motion. A new paper makes the case for a rotating space station and goes so far that it is achievable now.
Continue reading “A Rotating Spacecraft Would Solve So Many Problems in Spaceflight”China Has Built a Huge Space Simulation Chamber
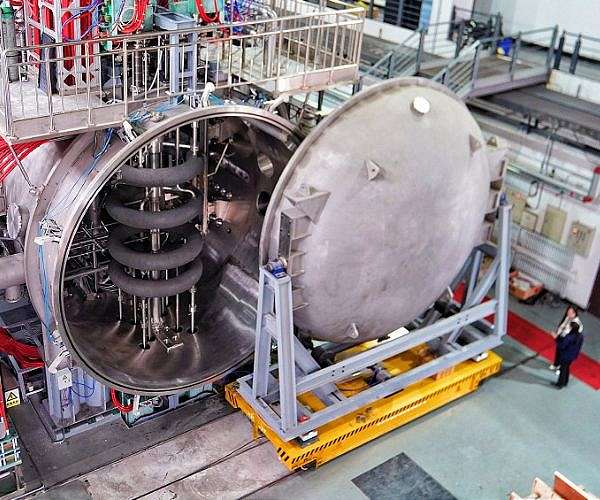
Well it certainly caught my attention when I saw the headlines “China’s first Space Environment Simulator” sounds like something right out of an adventure holiday. Whilst you can’t buy tickets to ‘have a go’ it’s actually for China to test spacecraft before launching them into the harsh environments of space. It allows researchers to simulate nine environmental factors; vacuum, high and low temperature, charged particles, electromagnetic radiation, space dust, plasma, weak magnetic field, neutral gasses and microgravity – and it even looks futuristic too!
Continue reading “China Has Built a Huge Space Simulation Chamber”Plants Growing in Space are at Risk from Bacterial Infections
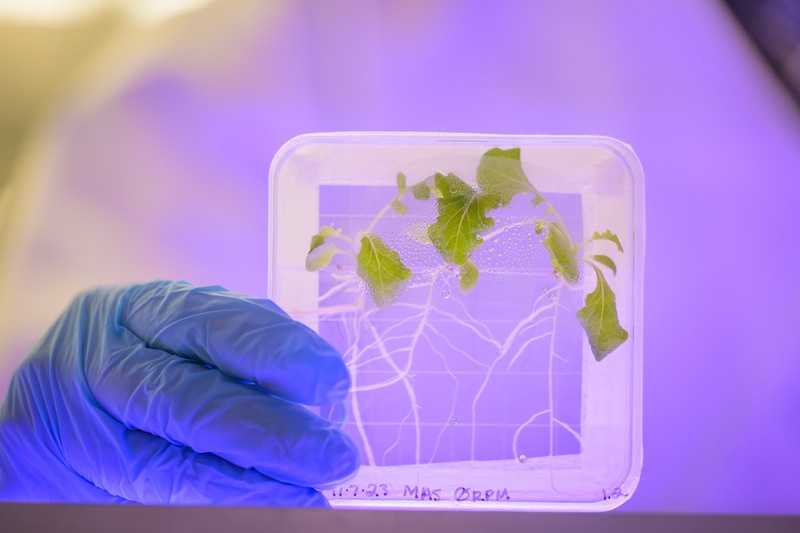

I have spent the last few years thinking, perhaps assuming that astronauts live off dried food, prepackaged and sent from Earth. There certainly is an element of that but travellers to the International Space Station have over recent years been able to feast on fresh salad grown in special units on board. Unfortunately, recent research suggests that pathogenic bacteria and fungi can contaminate the ‘greens’ even in space.
Continue reading “Plants Growing in Space are at Risk from Bacterial Infections”The International Space Station Celebrates 25 Years in Space
NASA recently celebrated the 25th anniversary of the International Space Station (ISS) with a space-to-Earth call between the 7-person Expedition 70 crew and outgoing NASA Associate Administrator, Bob Cabana, and ISS Program Manager, Joel Montalbano. On December 6, 1998, the U.S.-built Unity module and the Russian-built Zarya module were mated in the Space Shuttle Endeavour cargo bay, as Endeavour was responsible for launching Unity into orbit that same day, with Zarya having waited in orbit after being launched on November 20 from Kazakhstan.
Continue reading “The International Space Station Celebrates 25 Years in Space”Should We Send Humans to Europa?
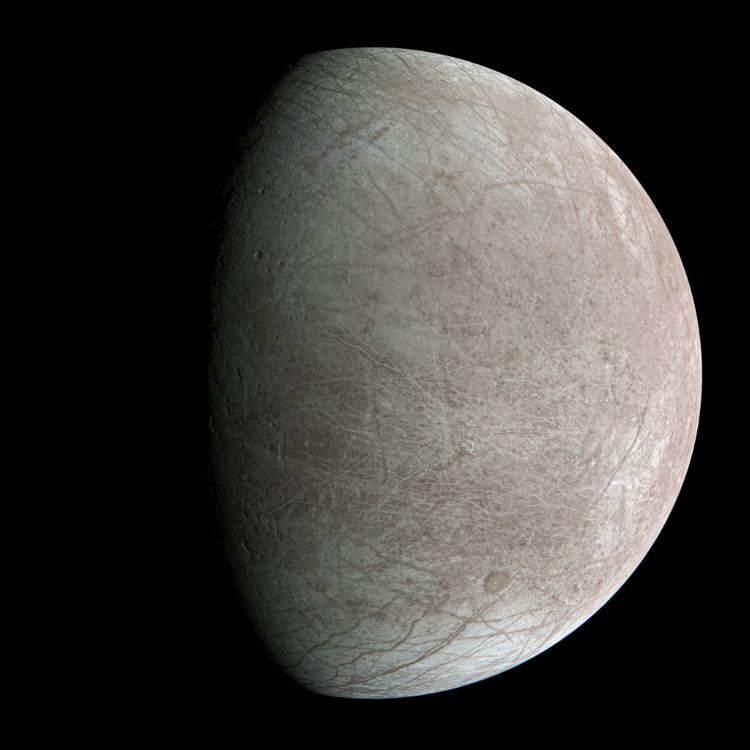

Universe Today recently examined the potential for sending humans to the planet Venus despite its extremely harsh surface conditions. But while a human mission to the clouds of Venus could be feasible given the environmental conditions are much more Earth-like, a human mission to the second planet from the Sun could be (at minimum) decades away. With NASA sending humans back to the Moon in the next few years, and hopefully to Mars, what if we could send humans to another planetary body worth exploring, though it could have its own harsh environmental conditions, as well? What about Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa? It has a massive interior liquid ocean that could harbor life, and NASA is currently scheduled to launch its Europa Clipper spacecraft to this small moon in October 2024, arriving at Jupiter in April 2030. Therefore, given the exploration potential, should we send humans to Europa?
Continue reading “Should We Send Humans to Europa?”Should We Send Humans to Venus?
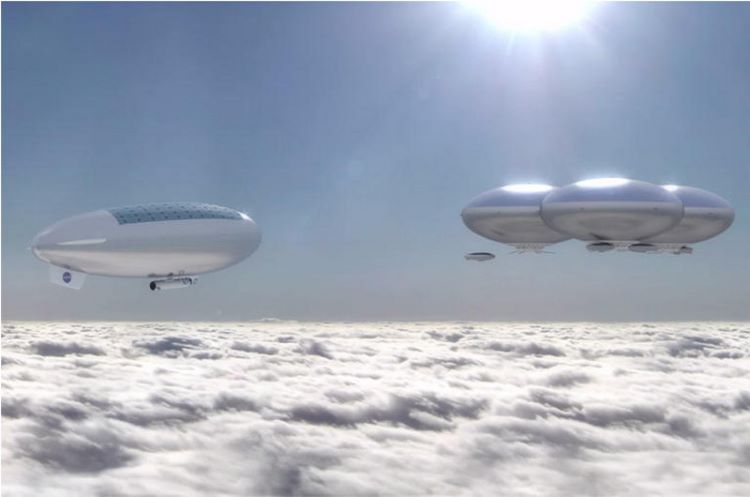

NASA is preparing to send humans back to the Moon with the Artemis missions in the next few years as part of the agency’s Moon to Mars Architecture with the long-term goal of landing humans on the Red Planet sometime in the 2030s or 2040s. But what about sending humans to other worlds of the Solar System? And, why not Venus? It’s closer to Earth than Mars by several tens of millions of kilometers, and despite its extremely harsh surface conditions, previous studies have suggested that life could exist in its clouds. In contrast, we have yet to find any signs of life anywhere on the Red Planet or in its thin atmosphere. So, should we send humans to Venus?
Continue reading “Should We Send Humans to Venus?”We Don't Know Enough About the Biomedical Challenges of Deep Space Exploration

Although humans have flown to space for decades, the missions have primarily been in low-Earth orbit, with just a handful of journeys to the Moon. Future missions with the upcoming Artemis program aim to have humans living and working on the Moon, with the hopes of one day sending humans to Mars.
However, the environments of the Moon and deep space present additional health challenges to astronauts over low-Earth orbit (LEO), such as higher radiation, long-term exposure to reduced gravity and additional acceleration and deceleration forces. A new paper looks at the future of biomedicine in space, with a sobering takeaway: We currently don’t know enough about the biomedical challenges of exploring deep space to have an adequate plan to ensure astronaut health and safety for the Artemis program.
Continue reading “We Don't Know Enough About the Biomedical Challenges of Deep Space Exploration”‘For All Mankind’ Gives Harsh Reality Check About Human Space Exploration

* Warning: Mild Spoilers Ahead *
The Apple TV+ series, For All Mankind, just wrapped up Season 3 and is a smash hit for both critics and fans, garnering Rotten Tomatoes ratings of 90% and 81%, respectively. It’s a show that (probably) came about from the Amazon hit, The Man in the High Castle, which depicted a world after the Allies lost World War II, and also garnered favorable ratings of 84% and 81%, respectively, having both fantastic characters and writing.
Continue reading “‘For All Mankind’ Gives Harsh Reality Check About Human Space Exploration”



