The study of extra-solar planets has revealed discoveries that have confounded expectations and boggled the mind! Whether it’s Super-Earths that become diamond planets, multiple rocky planets orbiting closely together, or “Hot Jupiters” with traces of gaseous metal in their atmospheres, there’s been no shortage of planets out there for which there is no comparison here in the Solar System.
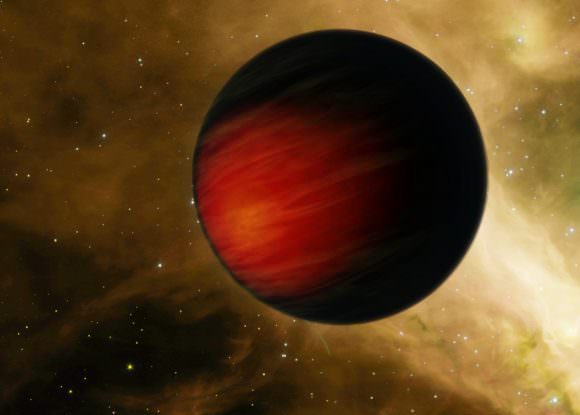
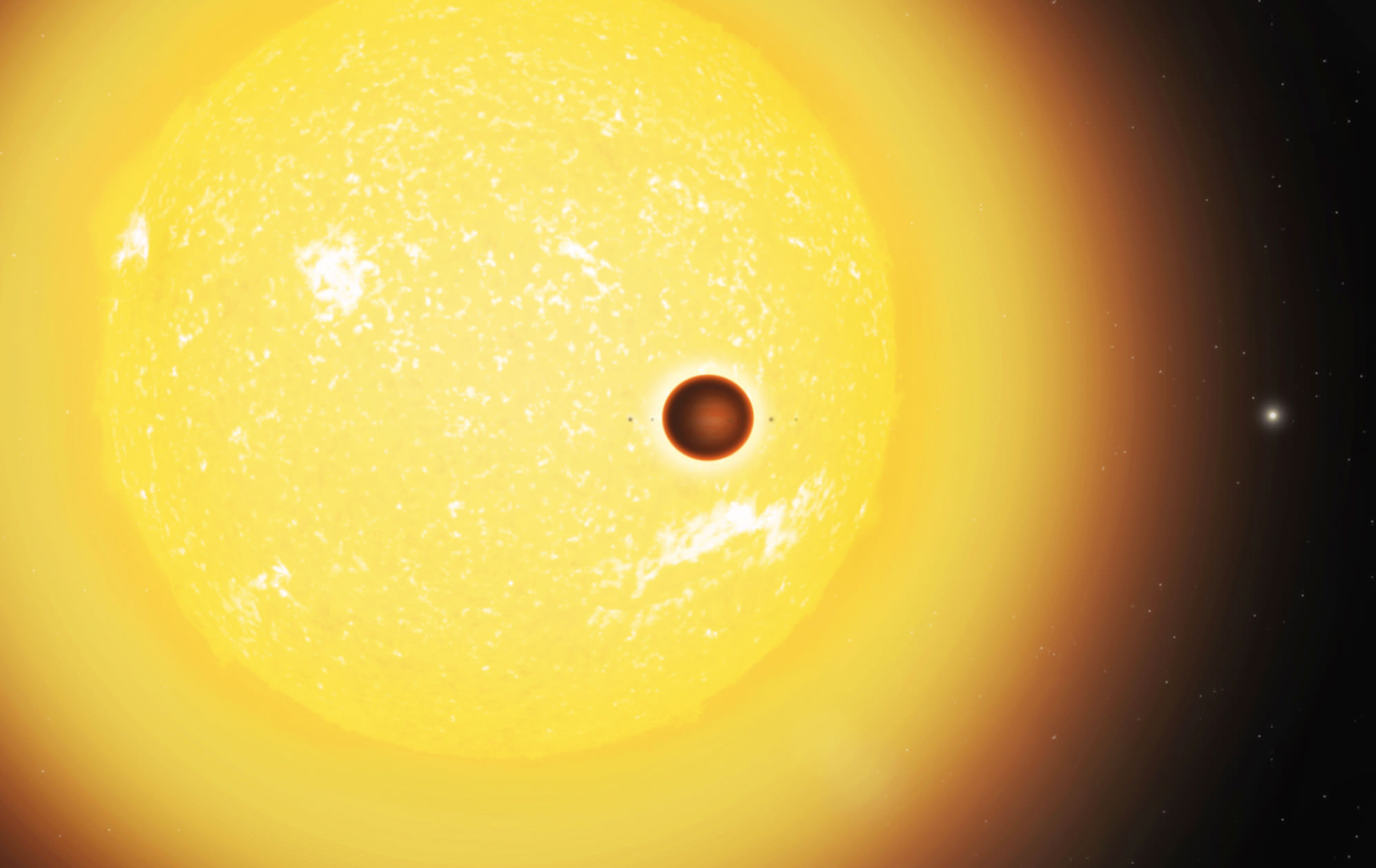
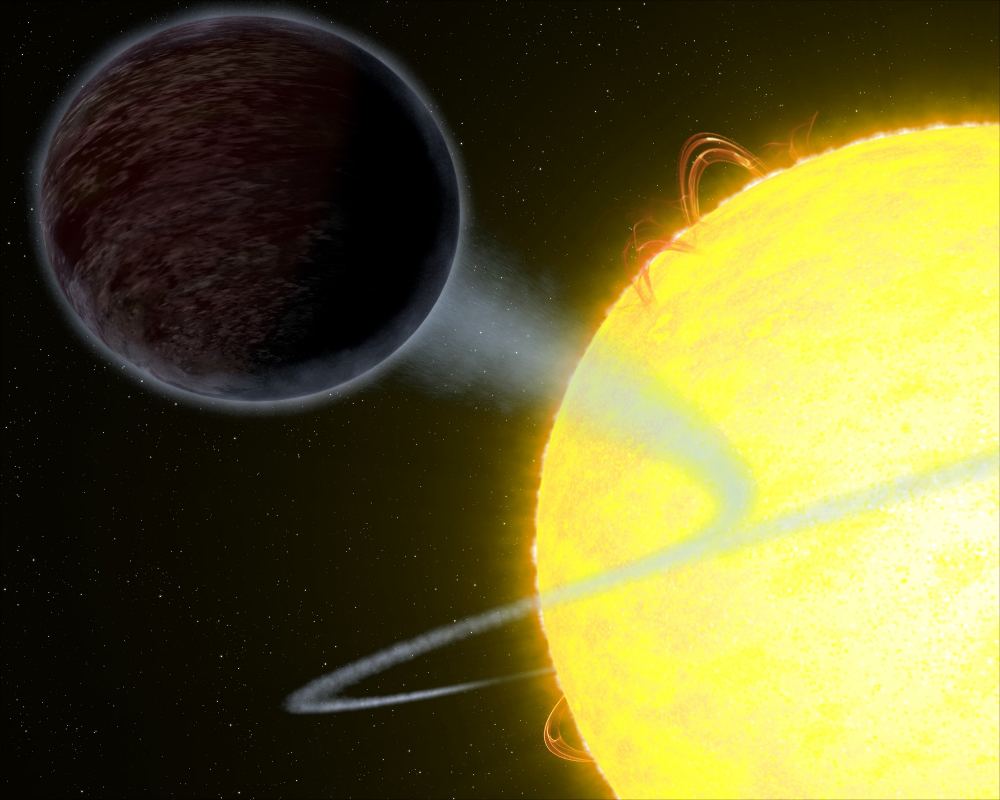
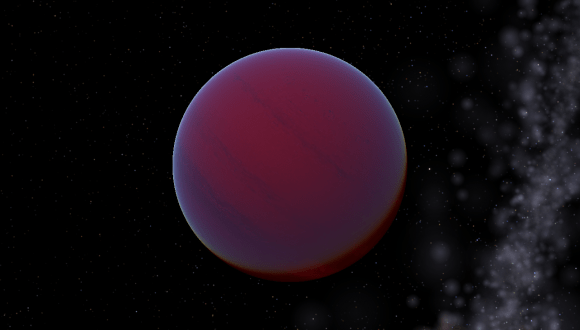
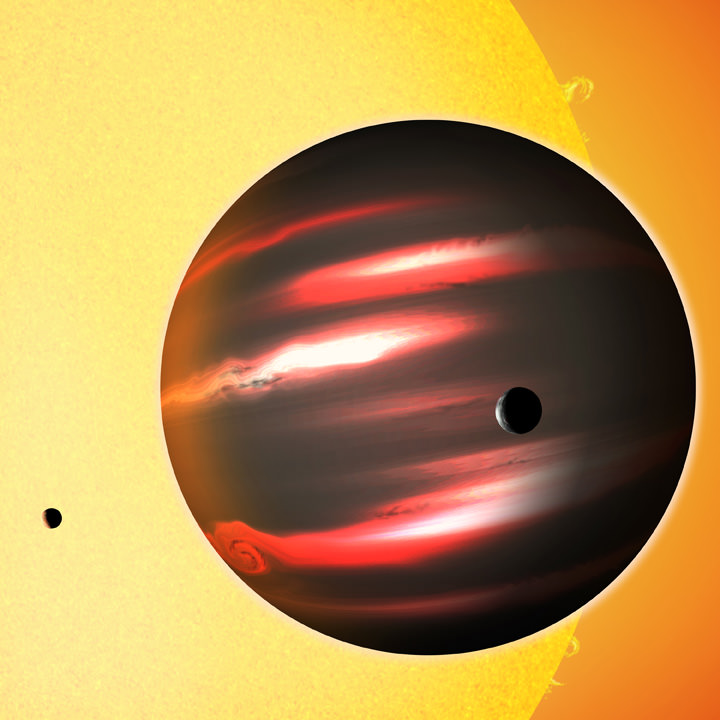
In this respect, WASP-12b is in good company. This Hot-Jupiter, located in a star system 1400 light years from Earth in the direction of the Auriga constellation, was recently studied by a team of astronomers using the Hubble Space Telescope. Due to the particular nature of its atmosphere, which absorbs the vast majority of light it receives instead of reflecting it, this planet appeared pitch black when observed by the Hubble team.
The study which details their findings, “The Very Low Albedo of WASP-12b from Spectral Eclipse Observations with Hubble“, was recently published in The Astrophysical Journal. Led by Taylor Bell, a researcher at the Institute for Research on Exoplanets (IREx) at McGill University, the team consulted data from the Hubble’s Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) to observe WASP-12b during an optical eclipse.
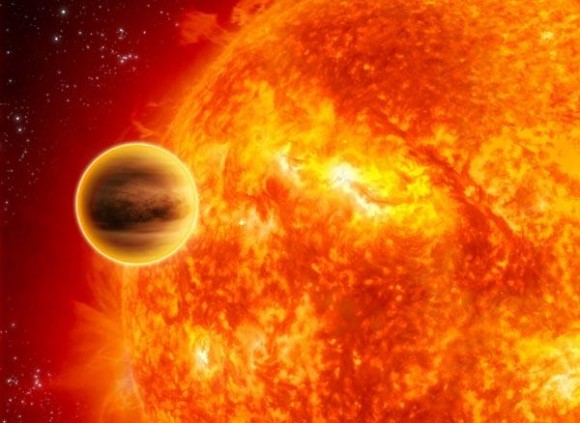

Like all Hot Jupiters, WASP-12b is similar in mass to Jupiter (1.35 to 1.43 Jupiter masses) and orbits very close to its star. At a distance of just 3.4 million km (2.115 million mi), or 0.0229 AU, it takes a little over a day to complete a single orbit. Because of its proximity, one side of the planet is constantly facing towards it’s sun – i.e. it is tidally locked with its star.
Because of its orbit, temperatures on the day side of the planet are estimated to reach as high as 2811 K (2538 °C; 4600 °F). It is because of these extreme temperatures that most molecules are unable to survive on the day side of the planet, so clouds cannot form to reflect light back into space. As a result, most incoming light penetrates deep into the planet’s atmosphere, where it is absorbed by hydrogen atoms and converted into heat energy.
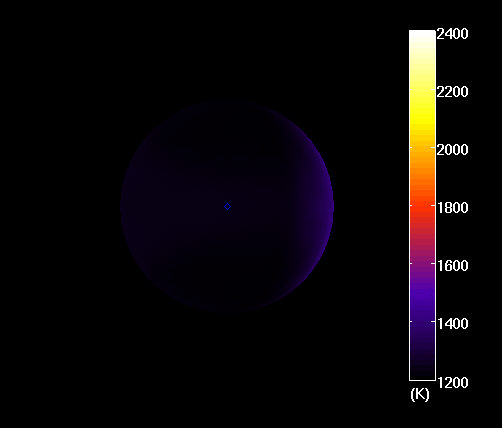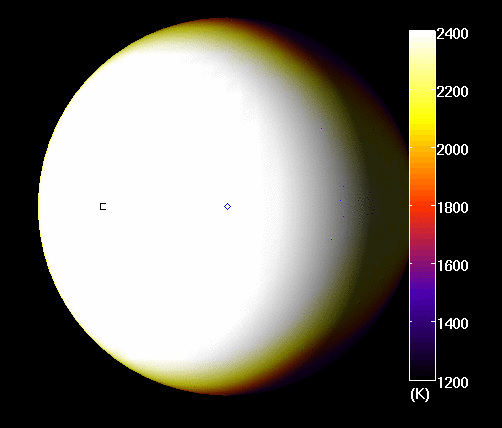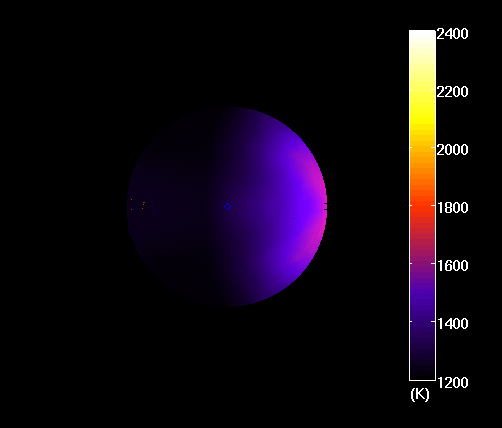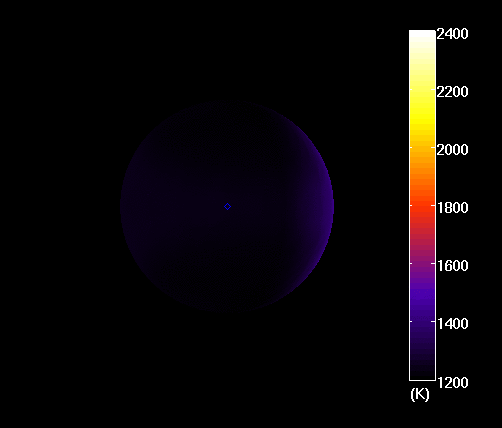
This was what Bell and his team noticed as they observed the planet passing behind its star (aka. an optical eclipse). Using the STIS, they monitored the system for any dips in starlight, which would indicate how much reflected light was being given off by the planet. However, their observations did not detect reflected light, which indicated that the sun-facing side was absorbing most of the light it was receiving.
As Bell explained in a NASA press statement, this was quite the unusual find: “We did not expect to find such a dark exoplanet,” he said. “Most hot Jupiters reflect about 40 percent of starlight.” However, observations conducted of the night side of the planet show that things are quite different there. On this side, temperatures are about 1366 K (1093 °C; 2000 °F) cooler, which allows water vapor and clouds to form.
Back in 2013, scientists working with the HST detected traces of water vapor in the atmosphere (and possible traces of clouds as well) while studying the day/night boundary. As Bell indicated, this new research just goes to show just how diverse this type of gas giant can be:
“This new Hubble research further demonstrates the vast diversity among the strange population of hot Jupiters. You can have planets like WASP-12b that are 4,600 degrees Fahrenheit and some that are 2,200 degrees Fahrenheit, and they’re both called hot Jupiters. Past observations of hot Jupiters indicate that the temperature difference between the day and night sides of the planet increases with hotter day sides. This previous research suggests that more heat is being pumped into the day side of the planet, but the processes, such as winds, that carry the heat to the night side of the planet don’t keep up the pace.”
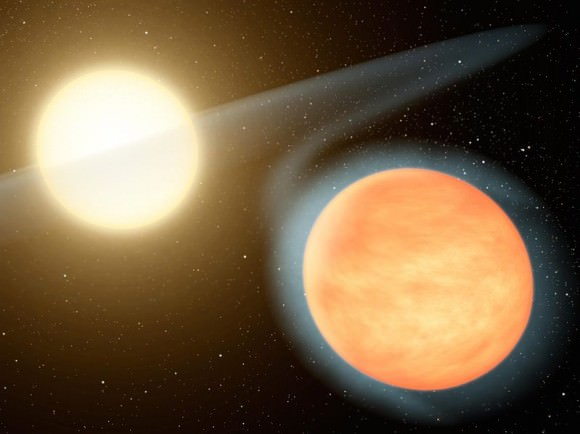
Since its discovery in 2008, several telescopes have studied WASP-12b, including Hubble, NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope, and NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory. Previous observations by Hubble’s Cosmic Origins Spectrograph (COS) also revealed that the planet may be losing size and mass due to super-heated material from its atmosphere slowly being accreted onto the star.
This is just the latest find in a slew that has confounded scientists expectations about exoplanets. The more we come to learn about the nature and diversity of these distant worlds, the more tantalizing they seem and the more appealing the prospect of exploring them directly someday becomes!
Further Reading: NASA, IREx, Astrophysical Journal Letters