A lunar moon dust sample with a strange history made its way to the auction block yesterday.
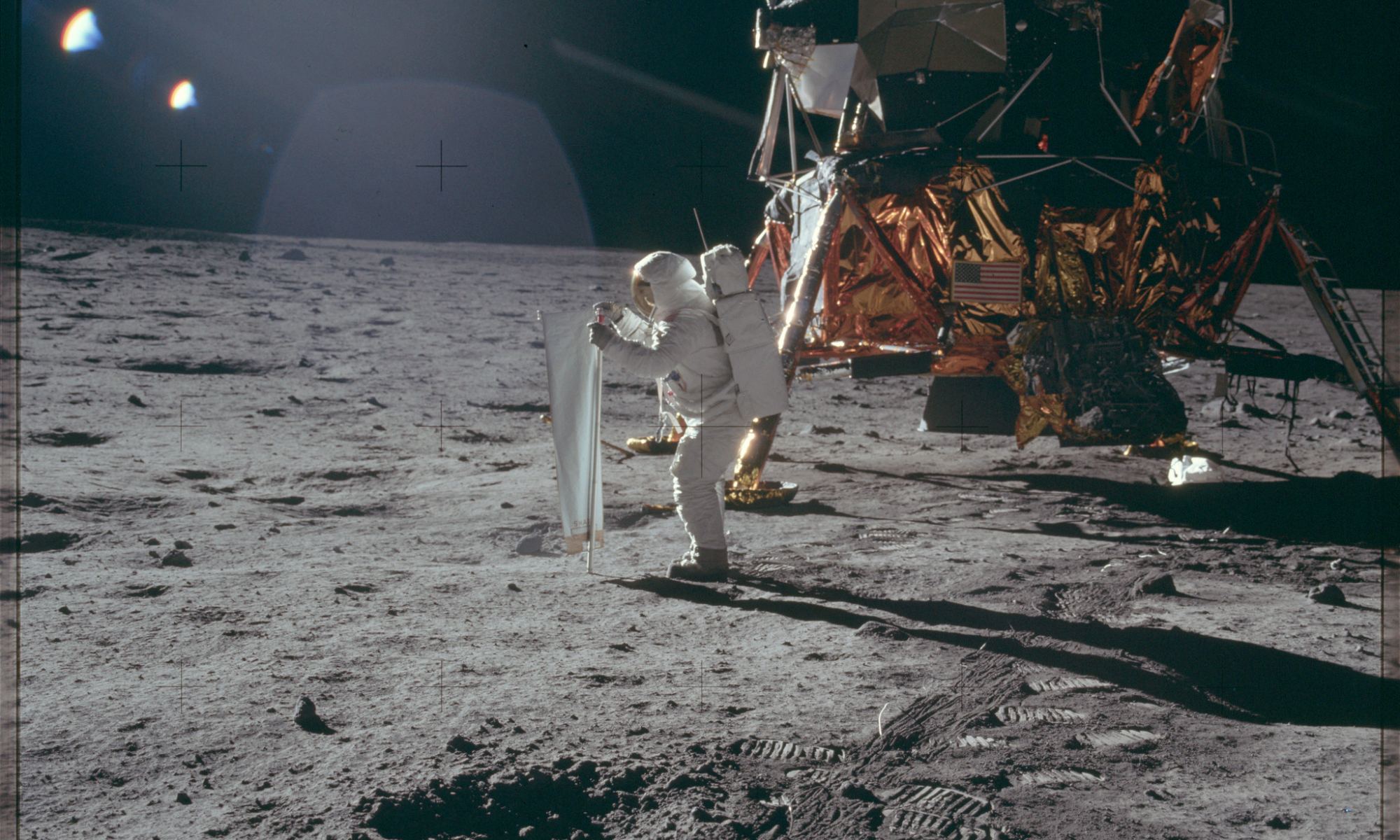
On July 20, 1969, NASA astronaut Neil Armstrong stepped off the landing pad of the Eagle lunar lander and into history. About eight minutes afterwards, Armstrong performed a crucial task, and collected a small ‘contingency sample’ of the Sea of Tranquility landing site. The sample was a small assurance that, in the event of a hasty departure—due to say, a malfunction or landing site instability—they did indeed still manage to retrieve the very first lunar material for return to Earth.
Continue reading “Apollo 11 Moon Dust Sells at Auction for a Cool Half Million”