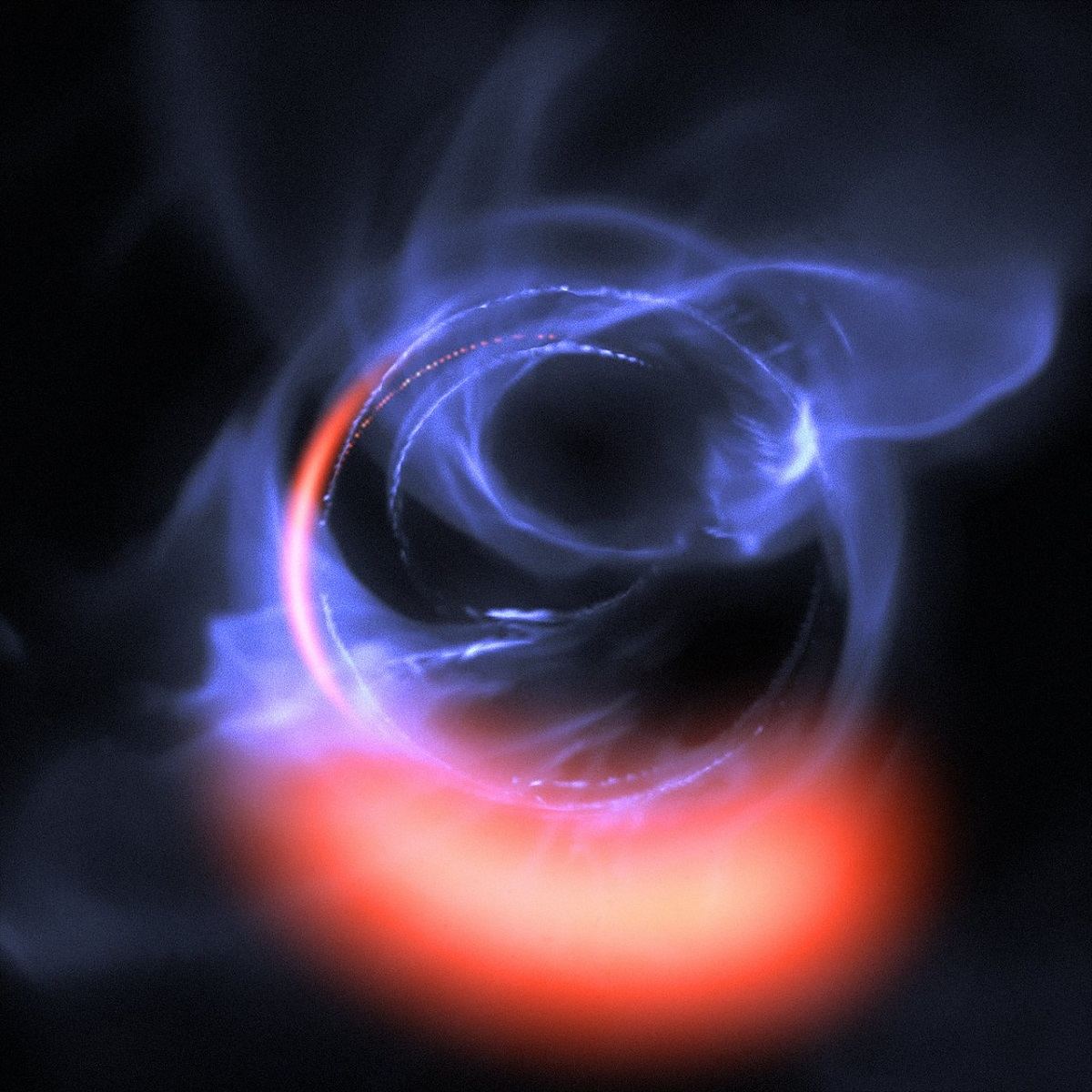
Since the 1970s, astronomers have theorized that at the center of our galaxy, about 26,000 light-years from Earth, there exists a supermassive black hole (SMBH) known as Sagittarius A*. Measuring an estimated 44 million km (27.3 million mi) in diameter and weighing in at roughly 4 million Solar masses, this black hole is believed to have had a profound influence on the formation and evolution of our galaxy.
And yet, scientists have never been able to see it directly and its existence has only been inferred from the effect it has on the stars and material surrounding it. However, new observations conducted by the GRAVITY collaboration** has managed to yield the most detailed observations to date of the matter surrounding Sagittarius A*, which is the strongest evidence yet that a black hole exists at the center of the Milky Way. Continue reading “Astronomers Get as Close as They Can to Seeing the Black Hole at the Heart of the Milky Way”