Are you hanging out at home this week, and looking to observe some naked eye planets? As we mentioned last week, while Venus is shining bright in the dusk sky, all of the other four naked eye planets of Mars, Saturn, Jupiter and Mercury are skulking in the early dawn.
Continue reading “Dawn Patrol: Following this Month’s ‘March of the Planets’”New Study Shows the Earth and Moon are not so Similar After All
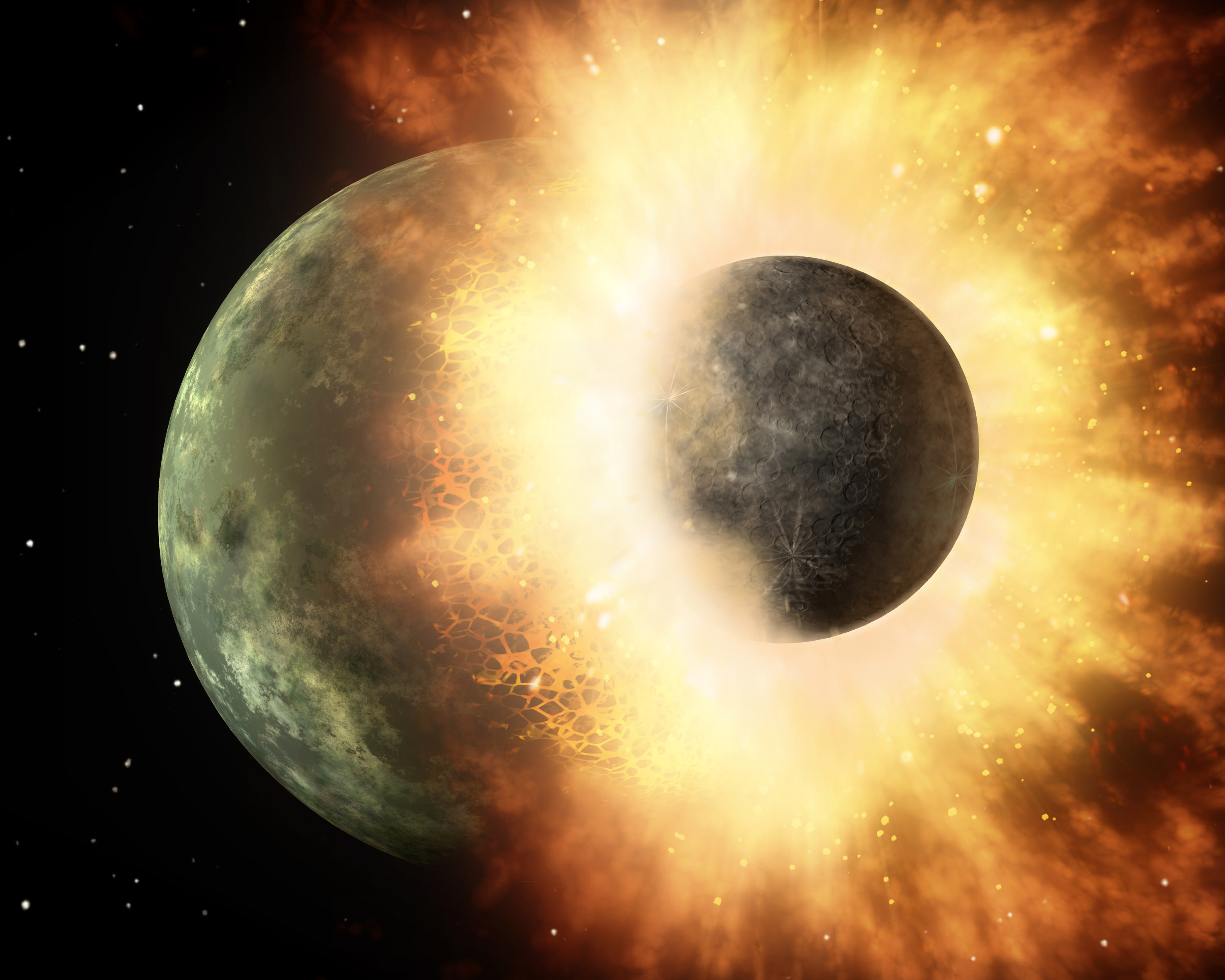

According to the most widely-accepted theory, the Moon formed roughly 4.5 billion years ago when a Mars-sized object named Theia collided with Earth (aka. the Giant Impact Hypothesis). This impact threw up considerable amounts of debris which gradually coalesced to form Earth’s only natural satellite. One of the most compelling proofs for this theory is the fact that the Earth and the Moon are remarkably similar in terms of composition.
However, previous studies involving computer simulations have shown that if the Moon were created by a giant impact, it should have retained more material from the impactor itself. But according to a new study conducted by a team from the University of New Mexico, it is possible that the Earth and the Moon are not as similar as previously thought.
Continue reading “New Study Shows the Earth and Moon are not so Similar After All”As Temperatures Increase, Forests are Having More Trouble Soaking up Carbon

On Earth, one of the most important factors regulating our climate is the carbon cycle. This refers to the processes by which carbon compounds are sequestered by biological (photosynthesis) and geological processes and released through volcanic activity and organic processes (decay and respiration). For billions of years, this cycle has kept temperatures relatively stable on Earth and allowed for life to flourish.
For the past few centuries, human activity has tipped the scales to the point that some refer to the current geological epoch as the Anthropocene. According to a new study by an international team of researchers, human activity is also leading to a situation where tropical rainforests (a major sequester of carbon dioxide) are not only losing their ability to soak up carbon but could actually be adding to the problem in the coming years.
Continue reading “As Temperatures Increase, Forests are Having More Trouble Soaking up Carbon”A Star Has Been Found That Pulsates, But Only on One Side
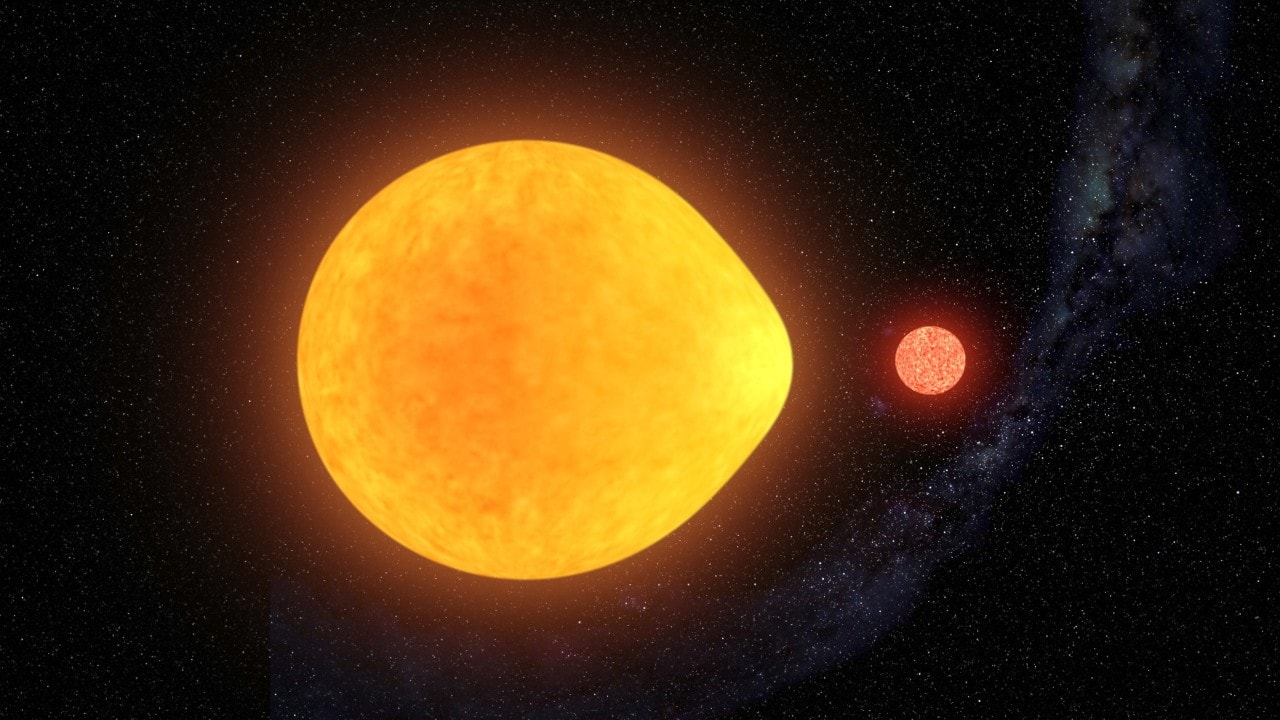
In the 17th century, astronomers witnessed many stellar events that proved that the starry sky was not “fixed and eternal.” This included stars whose brightness varied over time – aka. “variable stars.” By the 20th century, many variable stars had been cataloged and astronomers have discerned subclasses of them as well – notably, stars that swell and shrink, known as pulsating variables.
In all cases, these variable stars were found to have rhythmic pulsations that were visible from all sides. But a recent discovery by an international team has confirmed that there are variable stars that can pulse from only one side. This pulsating star, part of a system known as HD 74423, is located about 1,500 light-years from Earth and is the first of its kind to be found.
Read moreAstronomers Spot Rare Brown Dwarf Pair

Sometimes, the strangest stellar finds are right in our own cosmic neighborhood. Astronomers recently made an interesting discovery while putting a new set of telescopes through their paces: an eclipsing pair of sub-stellar brown dwarfs.
Continue reading “Astronomers Spot Rare Brown Dwarf Pair”Gas and Dust Stop Planets From Eating Their Moons
Beyond Earth’s only satellite (the Moon), the Solar System is packed full of moons. In fact, Jupiter alone has 79 known natural satellites while Saturn has the most know moons of any astronomical body – a robust 82. For the longest time, astronomers have theorized that moons form from circumplanetary disks around a parent planet and that the moons and planet form alongside each other.
However, scientists have conducted multiple numerical simulations that have shown this theory to be flawed. What’s more, the results of these simulations are inconsistent with what we see throughout the Solar System. Thankfully, a team of Japanese researchers recently conducted a series of simulations that yielded a better model of how disks of gas and dust can form the kinds of moon systems that we see today.
Continue reading “Gas and Dust Stop Planets From Eating Their Moons”Is the “D-star Hexaquark” the Dark Matter Particle?
Since the 1960s, astronomers have theorized that all the visible matter in the Universe (aka. baryonic or “luminous matter) constitutes just a small fraction of what’s actually there. In order for the predominant and time-tested theory of gravity to work (as defined by General Relativity), scientists have had to postulate that roughly 85% of the mass in the Universe consists of “Dark Matter”.
Despite many decades of study, scientists have yet to find any direct evidence of Dark Matter and the constituent particle and its origins remain a mystery. However, a team of physicists from the University of York in the UK has proposed a new candidate particle that was just recently discovered. Known as the d-star hexaquark, this particle could have formed the “Dark Matter” in the Universe during the Big Bang.
Continue reading “Is the “D-star Hexaquark” the Dark Matter Particle?”Following the Inner Worlds: Mercury and Venus in 2020
Where have all the planets gone in early 2020? While most of the naked eye planets are hiding in the early dawn sky, one world dominates the evening: brilliant Venus.
Continue reading “Following the Inner Worlds: Mercury and Venus in 2020”Seti@home is on Pause. Unfortunately, it’s not Because They’ve Discovered Aliens
In May of 1999, the Berkeley SETI Research Center launched a citizen-science program that would make the Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence (SETI) open to the public. The brainchild of computer scientist David Gedye, this program would rely on large numbers of internet-connected computers to sort through the volumes of data collected by institutions participating in SETI efforts.
The program was appropriately named SETI@home and would rely on the computers of volunteers to process radio signals for signs of transmissions. And after twenty years, the program recently announced that it has gone into hibernation. The reason, they claim, is that the program’s network has become too big for its own britches and the scientists behind it need time to process and share all the results they’ve obtained so far.
Continue reading “Seti@home is on Pause. Unfortunately, it’s not Because They’ve Discovered Aliens”SpaceX Launches its Last Dragon 1 Mission to the ISS
On Friday, March 6th, as part of the company’s 20th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-20) mission, SpaceX launched a Dragon 1 capsule destined for the International Space Station (ISS). The mission involved the transport of supplies, as well as materials related to the more than 250 science investigations taking place aboard the ISS. More than that, it represented a milestone for the aerospace manufacturer.
Continue reading “SpaceX Launches its Last Dragon 1 Mission to the ISS”





