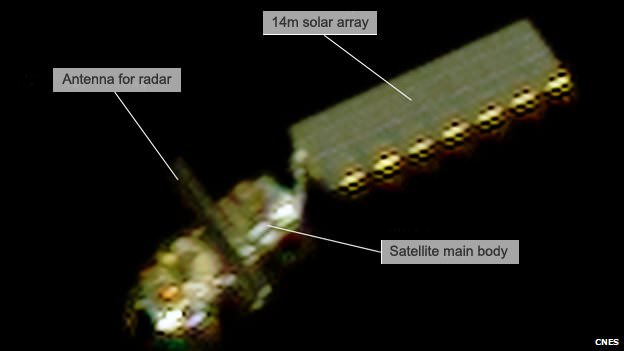
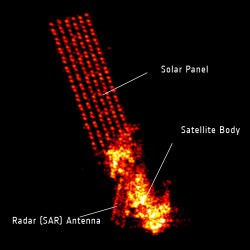
[/caption]
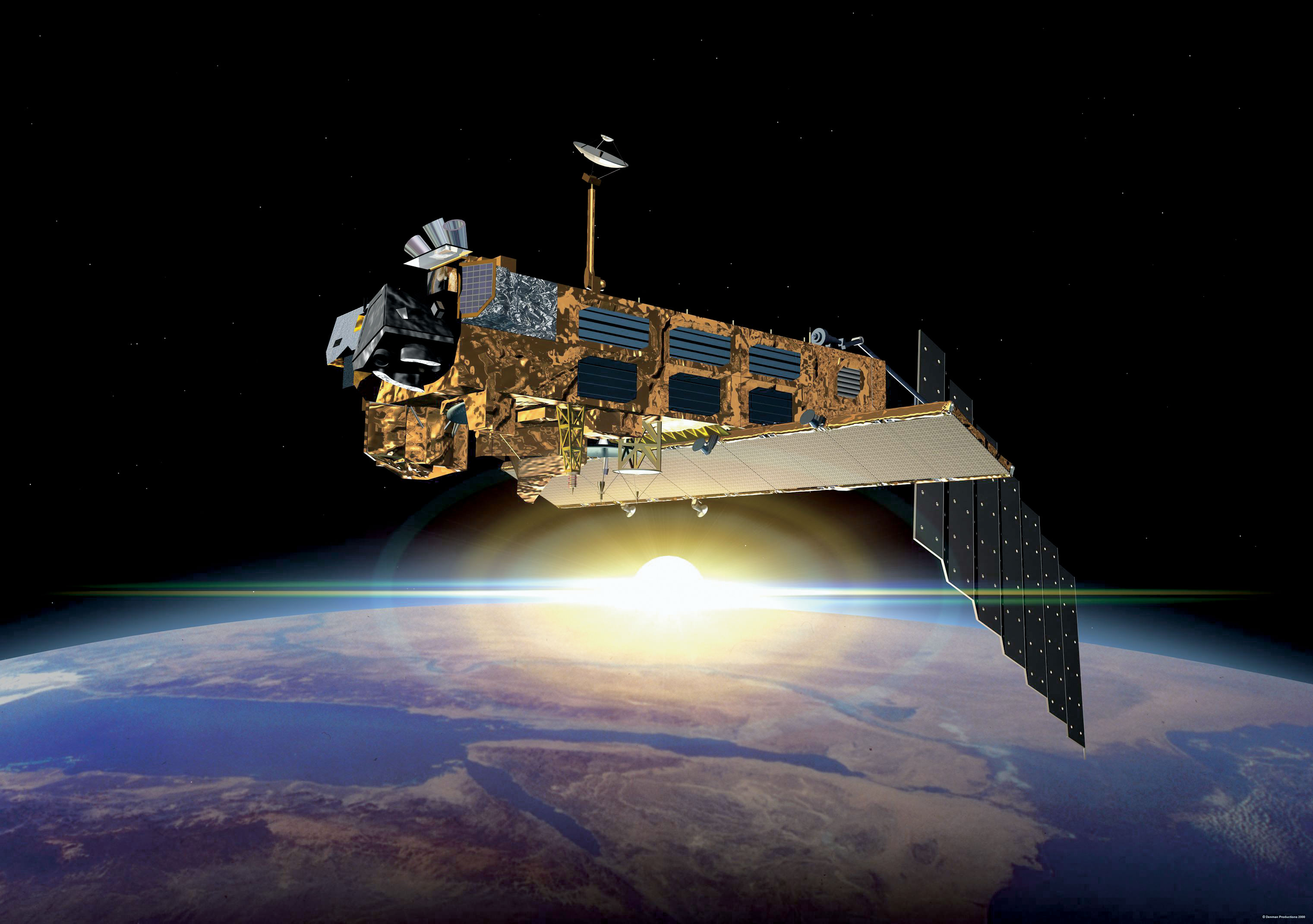
Well, it’s official. After ten years of groundbreaking observation of our planet, ESA has declared the end of the Envisat mission after losing contact with the satellite on April 8, 2012. All attempts to re-establish communication with Envisat have so far been unsuccessful, and although recovery teams will continue to determine the cause of signal loss and try to regain a signal over the next several weeks, the mission — and the satellite — have been retired.
Having performed twice as long as originally planned, the hardworking Envisat has definitely earned its rest.
On April 8, the European Space Agency lost communication with the Earth-observation satellite, preventing reception of data as it passed over the Kiruna station in Sweden. Although later confirmed that the satellite is still in orbit, the recovery team has not been able to re-establish contact.
It’s thought that a loss of a power regulator could be blocking telemetry and telecommands from reaching Envisat, or else the satellite may have experienced a short-circuit and attempted to go into “safe mode” but experienced difficulties during the transition, leaving it in an unknown state.
Read: Is This the Last Image From Envisat?
ESA states that the chances of ever regaining communication with Envisat are extremely low.
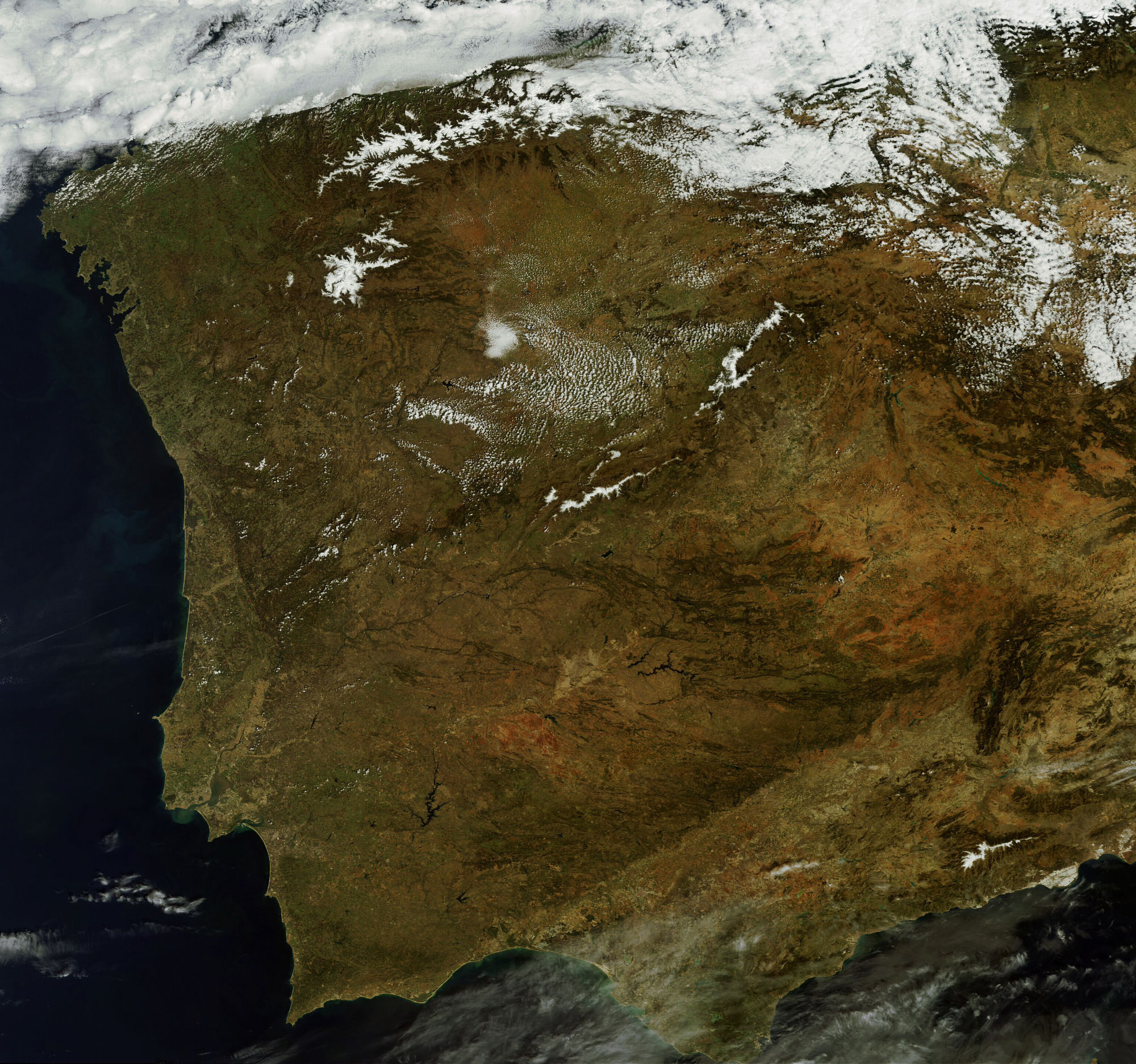
While we had reported before on the last image received before falling silent, the image below is actually the final image from Envisat, an X-band image of the Canary Islands.
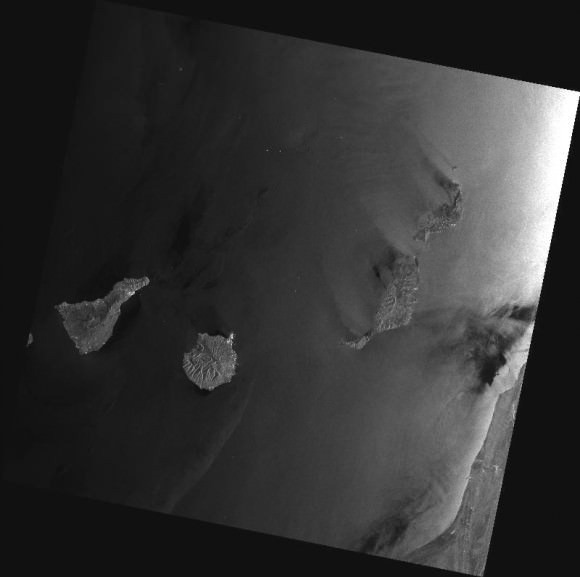
During its lifetime, Envisat completed 50,000 orbits of Earth and returned over a thousand terabytes of data, containing invaluable measurements of our planet’s surface and atmosphere that were used in more than 2500 science publications.
The video below gives a fitting eulogy for a satellite that’s definitely overachieved and over-performed, giving us a decade of crucial observations of our world from orbit.
Read more on the ESA news release here.