A quarter of a century has passed since NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft snapped the iconic image of Earth known as the “Pale Blue Dot” that shows all of humanity as merely a tiny point of light.
The outward bound Voyager 1 space probe took the ‘pale blue dot’ image of Earth 25 years ago on Valentine’s Day, on Feb. 14, 1990 when it looked back from its unique perch beyond the orbit of Neptune to capture the first ever “portrait” of the solar system from its outer realms.
Voyager 1 was 4 billion miles from Earth, 40 astronomical units (AU) from the sun and about 32 degrees above the ecliptic at that moment.
The idea for the images came from the world famous astronomer Carl Sagan, who was a member of the Voyager imaging team at the time.
He head the idea of pointing the spacecraft back toward its home for a last look as a way to inspire humanity. And to do so before the imaging system was shut down permanently thereafter to repurpose the computer controlling it, save on energy consumption and extend the probes lifetime, because it was so far away from any celestial objects.
Sagan later published a well known and regarded book in 1994 titled “Pale Blue Dot,” that refers to the image of Earth in Voyagers series.
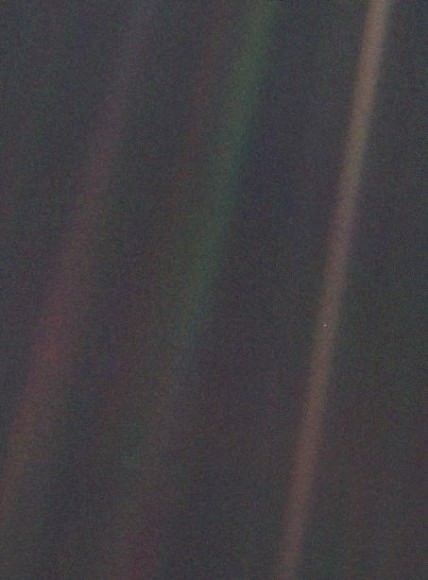

“Twenty-five years ago, Voyager 1 looked back toward Earth and saw a ‘pale blue dot,’ ” an image that continues to inspire wonderment about the spot we call home,” said Ed Stone, project scientist for the Voyager mission, based at the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, in a statement.
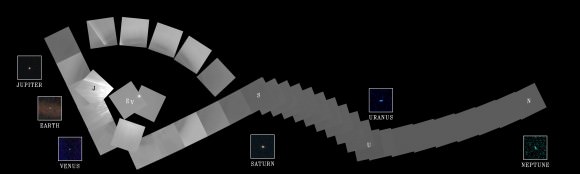
Six of the Solar System’s nine known planets at the time were imaged, including Venus, Earth, Jupiter, and Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. The other three didn’t make it in. Mercury was too close to the sun, Mars had too little sunlight and little Pluto was too dim.
Voyager snapped a series of images with its wide angle and narrow angle cameras. Altogether 60 images from the wide angle camera were compiled into the first “solar system mosaic.”
Voyager 1 was launched in 1977 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida as part of a twin probe series with Voyager 2. They successfully conducted up close flyby observations of the gas giant outer planets including Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune in the 1970s and 1980s.
Both probes still operate today as part of the Voyager Interstellar Mission.
“After taking these images in 1990, we began our interstellar mission. We had no idea how long the spacecraft would last,” Stone said.
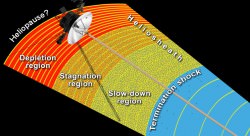
Hurtling along at a distance of 130 astronomical units from the sun, Voyager 1 is the farthest human-made object from Earth.
Voyager 1 still operates today as the first human made instrument to reach interstellar space and continues to forge new frontiers outwards to the unexplored cosmos where no human or robotic emissary as gone before.
Here’s what Sagan wrote in his “Pale Blue Dot” book:
“That’s here. That’s home. That’s us. On it everyone you love, everyone you know, everyone you ever heard of, every human being who ever was, lived out their lives. … There is perhaps no better demonstration of the folly of human conceits than this distant image of our tiny world.”
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.