A spacecraft that can provide the propulsion necessary to reach other planets while also being reproducible, relatively light, and inexpensive would be a great boon to larger missions in the inner solar system. Micocosm, Inc., based in Hawthorne, California, proposed just such a system via a NASA Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) grant. Its Hummingbird spacecraft would have provided a platform to visit nearby planets and asteroids and a payload to do some basic scouting of them.
Continue reading “A Cheap Satellite with Large Fuel Tank Could Scout For Interplanetary Missions”A 3U CubeSat Could Collect Data During an Asteroid Flyby

One of the great things about CubeSat designs is that they constrain the engineers who design them. Constraints are a great way to develop novel solutions to problems that might otherwise be ignored without them. As CubeSats become increasingly popular, more and more researchers are looking at how to get them to do more with less. A paper from 2020 contributes to that by designing a 3U CubeSat mission that weighs less than 4 kilograms to perform a fly-by of a Near Earth Asteroid (NEA) using entirely off-the-shelf parts.
Continue reading “A 3U CubeSat Could Collect Data During an Asteroid Flyby”A CubeSat Mission to Phobos Could Map Staging Bases for a Mars Landing
The moons of Mars are garnering increased attention, not only because they could provide a view of the solar system’s past but also because they could provide invaluable staging areas for any future human settlement on Mars itself. However, missions specifically designed to visit Phobos, the bigger of the two moons, have met with varying stages of failure. So why not make an inexpensive mission to do so – one that could launch multiple copies of itself if necessary? That’s the idea behind a CubeSat-based mission to Phobos, known as Perseus, which was initially described back in 2020.
Continue reading “A CubeSat Mission to Phobos Could Map Staging Bases for a Mars Landing”SpIRIT CubeSat Demonstrates a Operational Gamma and X-Ray Detector
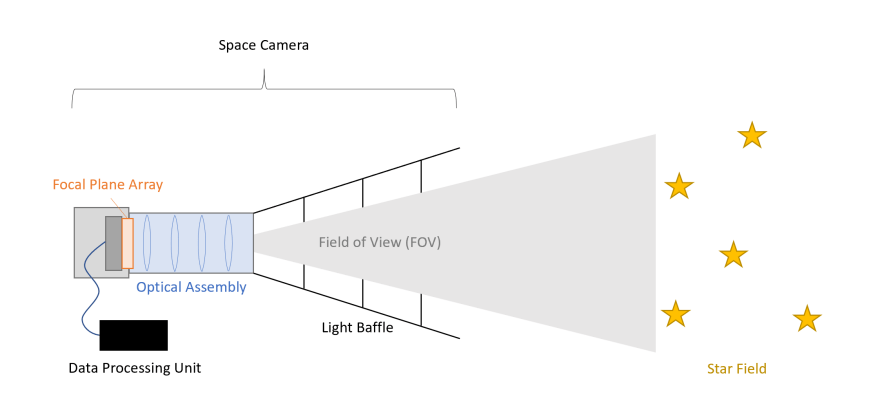
CubeSats are becoming more and more capable, and it seems like every month, another CubeSat is launched doing something new and novel. So far, technology demonstration has been one of the primary goals of those missions, though the industry is moving into playing an active role in scientific discovery. However, there are still some hurdles to jump before CubeSats have as many scientific tools at their disposal as larger satellites. That is where the Space Industry Responsive Intelligent Thermal (SpIRIT) CubeSat, the first from the Univeristy of Melbourne’s Space Lab, hopes to make an impact. Late in 2023, it launched with a few novel systems to operate new scientific equipment, and its leaders published a paper a few months ago detailing the progress of its mission so far.
Continue reading “SpIRIT CubeSat Demonstrates a Operational Gamma and X-Ray Detector”What Did We Learn From Manufacturing the ACS3 Solar Sail Mission?
We recently reported on the successful deployment of the solar sail of the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System (ACS3) technology demonstration mission. That huge achievement advances one of the most important technologies available to CubeSats – a different form of propulsion. But getting there wasn’t easy, and back in May, a team of engineers from NASA’s Langley Research Center who worked on ACS3 published a paper detailing the trials and tribulations they went through to prepare the mission for prime time. Let’s take a look at what they learned.
Continue reading “What Did We Learn From Manufacturing the ACS3 Solar Sail Mission?”A Pair of CubeSats Using Ground Penetrating Radar Could Map The Interior of Near Earth Asteroids

Characterizing near-Earths asteroids (NEAs) is critical if we hope to eventually stop one from hitting us. But so far, missions to do so have been expensive, which is never good for space exploration. So a team led by Patrick Bambach of the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research in Germany developed a mission concept that utilizes a relatively inexpensive 6U CubeSat (or, more accurately, two of them) to characterize the interior of NEAs that would cost only a fraction of the price of previous missions.
Continue reading “A Pair of CubeSats Using Ground Penetrating Radar Could Map The Interior of Near Earth Asteroids”Swarms of Orbiting Sensors Could Map An Asteroid’s Surface
It seems like every month, a new story appears announcing the discovery of thousands of new asteroids. Tracking these small body objects from ground and even space-based telescopes helps follow their overall trajectory. But understanding what they’re made of is much more difficult using such “remote sensing” techniques. To do so, plenty of projects get more up close and personal with the asteroid itself, including one from Dr. Sigrid Elschot and her colleagues from Stanford, which was supported by NASA’s Institute for Advanced Concepts back in 2018. It uses an advanced suite of plasma sensors to detect an asteroid’s surface composition by utilizing a unique phenomenon – meteoroid impacts.
Continue reading “Swarms of Orbiting Sensors Could Map An Asteroid’s Surface”ESA’s Tiny Pinhole Thruster is Ready for Production.
Rocket propulsion technology has progressed leaps and bounds since the first weaponised rockets of the Chinese and Mongolian empires. They were nothing more than rocket powered arrows and spears but they set the foundations for our exploration of space. Liquid propellant, ion engines and solar sails have all hit the headlines as we strive for more efficient methods of travel but a team has taken the next leap with a palm sized thruster system that could boost future tiny space craft across the gulf of space.
Continue reading “ESA’s Tiny Pinhole Thruster is Ready for Production. “Lost In Space? Just Use Relativity
One of the hardest things for many people to conceptualize when talking about how fast something is going is that they must ask, “Compared to what?” All motion only makes sense from a frame of reference, and many spacecraft traveling in the depths of the void lack any regular reference from which to understand how fast they’re going. There have been several different techniques to try to solve this problem, but one of the ones that have been in development the longest is StarNAV – a way to navigate in space using only the stars.
Continue reading “Lost In Space? Just Use Relativity”A Tiny Telescope is Revealing “Hot Jupiter” Secrets

A recent study presented this week at the 2023 meeting of the American Geophysical Union discusses observations of “hot Jupiters” from the NASA-funded CubeSat mission known as the Colorado Ultraviolet Transit Experiment (CUTE). Unlike most exoplanet-hunting telescopes, whose sizes are comparable to a small school bus, CUTE measures 36 centimeters (14 inches) in length, equivalent to the size of a cereal box. These findings come after members of the team, which consists of undergraduate and graduate students, published an overview paper about CUTE in The Astronomical Journal in January 2023 and results from CUTE observing WASP-189b in The Astrophysical Journal Letters in August 2023.
Continue reading “A Tiny Telescope is Revealing “Hot Jupiter” Secrets”