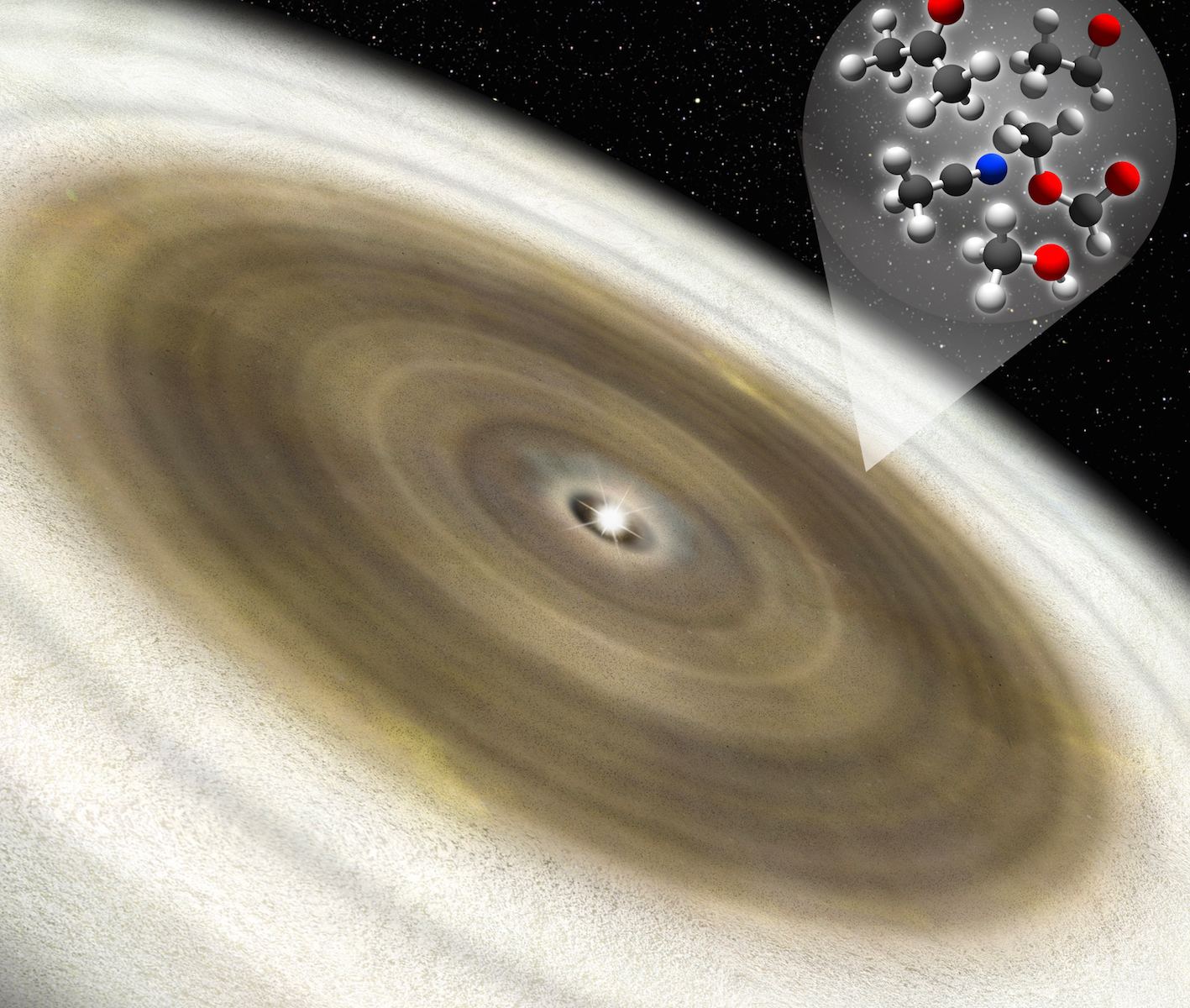
According to widely-accepted theories, the Solar System formed roughly 4.6 billion years ago from a massive cloud of dust and gas (aka. Nebular Theory). This process began when the nebula experienced a gravitational collapse in the center that became our Sun. The remaining dust and gas formed a protoplanetary disk that (over time) accreted to form the planets.
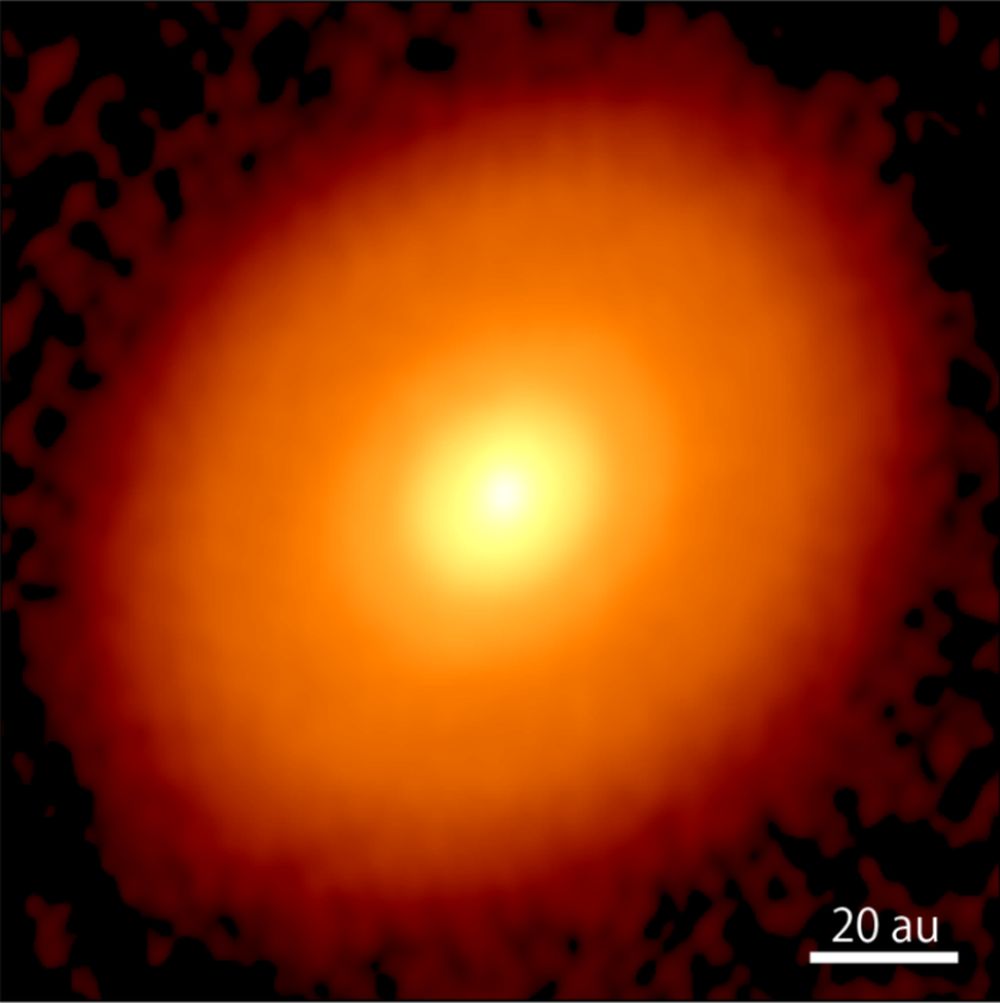
However, scientists remain unsure about when organic molecules first appeared in our Solar System. Luckily, a new study by an international team of astronomers may be able to help answer that question. Using the Atacama Large Millimeter-submillimeter Array (ALMA), the team detected complex organic molecules around the young star V883 Ori, which could someday lead to the emergence of life in that system.
Continue reading “A Star’s Outburst is Releasing Organic Molecules Trapped in the ice Around it”