On January 21st, 2024, a meter-sized asteroid (2024 BX1) entered Earth’s atmosphere and exploded over Berlin at 12:33 am UTC (07:45 pm EST; 04:33 pm PST). Before it reached Earth, 2024 BX1 was a Near-Earth Asteroid (NEA) with an orbit that suggests it was part of the Apollo group. The fragments have since been located by a team of scientists from the Freie Universität Berlin, the Museum für Naturkunde (MfN), the German Aerospace Center (DLR), the Technische Universität Berlin, and the SETI Institute and identified as a rare type of asteroid known as “aubrites.”
Continue reading “Fragments From That Asteroid That Exploded Above Berlin Have Been Recovered and They're Really Special”NASA Discovers 72 New Asteroids Near Earth
Of the more than 600,000 known asteroids in our Solar System, almost 10 000 are known as Near-Earth Objects (NEOs). These are asteroids or comets whose orbits bring them close to Earth’s, and which could potentially collide with us at some point in the future. As such, monitoring these objects is a vital part of NASA’s ongoing efforts in space. One such mission is NASA’s Near-Earth Object Wide-field Survey Explorer (NEOWISE), which has been active since December 2013.
And now, after two years of study, the information gathered by the mission is being released to the public. This included, most recently, NEOWISE’s second year of survey data, which accounted for 72 previously unknown objects that orbit near to our planet. Of these, eight were classified as potentially hazardous asteroids (PHAs), based on their size and how closely their orbits approach Earth.
Continue reading “NASA Discovers 72 New Asteroids Near Earth”
The Next Generation of Exploration: The NEOCam Mission
In February of 2014, NASA put out the call for submissions for the thirteenth mission of their Discovery Program. In keeping with the program’s goal of mounting low-cost, highly focused missions to explore the Solar System, the latest program is focused on missions that look beyond Mars to new research goals. On September 30th, 2015, five semifinalists were announced, which included proposals for sending probes back to Venus, to sending orbiters to study asteroids and Near-Earth Objects.
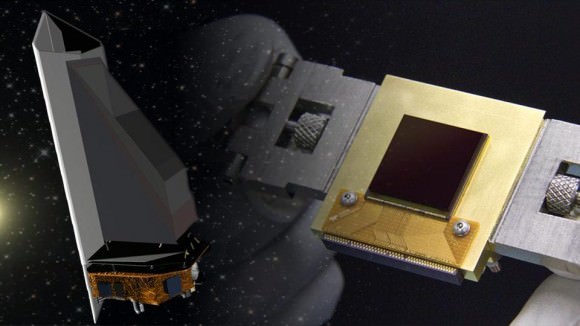
Among the proposed NEO missions is the Near Earth Object Camera, or NEOCam. Consisting of a space-based infrared telescope designed to survey the Solar System for potentially hazardous asteroids, the NEOCam would be responsible for discovering and characterizing ten times more near-Earth objects than all NEOs that have discovered to date.
If deployed, NEOCam will begin discovering approximately one million asteroids in the Main Belt and thousands of comets in the course of its 4 year mission. However, the primary scientific goal of NEOCam is to discover and characterize over two-thirds of the asteroids that are larger that 140 meters, since it is possible some of these might pose a threat to Earth someday.

The technical term is Potentially Hazardous Objects (PHO), and it applies to near-Earth asteroids/comets that have an orbit that will allow them to make close approaches to Earth. And measuring more than 140 meters in diameter, they are of sufficient size that they could cause significant regional damage if they struck Earth.
In fact, a study conducted in 2010 through the Imperial College of London and Purdue University found that an asteroid measuring 50-meters across with a density of 2.6 grams per cubic centimeter and a speed of 12.7 kps could generate 2.9 Megatons of airburst energy once it passed through our atmosphere. To put that in perspective, that’s the equivalent of about nine W87 thermonuclear warheads!
By comparison, the meteor that appeared over the small Russian community of Chelyabinsk in 2013 measured only 20 meters across. Nevertheless, the explosive airbust caused by it entering our atmosphere generated only 500 kilotons of energy, creating a zone of destruction tens of kilometers wide and injuring 1,491 people. One can imagine without much effort how much worse it would have been had the explosion been six times as big!
What’s more, as of August 1st, 2015, NASA has listed a total of 1,605 potentially hazardous asteroids and 85 near-Earth comets. Among these, there are 154 PHAs believed to be larger than one kilometer in diameter. This represents a tenfold increase in discoveries since the end of the 1990s, which is due to several astronomical surveys being performed (as well as improvements in detection methods) over the past two and a half decades.
As a result, monitoring and characterizing which of these objects is likely to pose a threat to Earth in the future has been a scientific priority in recent years. It is also why the U.S. Congress passed the “George E. Brown, Jr. Near-Earth Object Survey Act” in 2005. Also known as the “NASA Authorization Act of 2005”, this Act of Congress mandated that NASA identify 90% of all NEOs that could pose a threat to Earth.
If deployed, NEOCam will monitor NEOs from the Earth–Sun L1 Lagrange point, allowing it to look close to the Sun and see objects inside Earth’s orbit. To this, NEOCam will rely on a single scientific instrument: a 50 cm diameter telescope that operates at two heat-sensing infrared wavelengths, to detect the even the dark asteroids that are hardest to find.
By using two heat-sensitive infrared imaging channels, NEOCam can also make accurate measurements of NEO and gain valuable information about their sizes, composition, shapes, rotational states, and orbits. As Dr. Amy Mainzer, the Principal Investigator of the NEOCam mission, explained:
“Everyone wants to know about asteroids hitting the Earth; NEOCam is designed to tackle this issue. We expect that NEOCam will discover about ten times more asteroids than are currently known, plus millions of asteroids in the main belt between Mars and Jupiter. By conducting a comprehensive asteroid survey, NEOCam will address three needs: planetary defense, understanding the origins and evolution of our solar system, and finding new destinations for future exploration.”
Dr. Mainzer is no stranger to infrared imaging for the sake of space exploration. In addition to being the Principal Investigator on this mission and a member of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, she is also the Deputy Project Scientist for the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) and the Principal Investigator for the NEOWISE project to study minor planets.
She has also appeared many times on the History Channel series The Universe, the documentary featurette “Stellar Cartography: On Earth”, and serves as the science consultant and host for the live-action PBS Kids series Ready Jet Go!, which will be debuting in the winter of 2016. Under her direction, the NEOCam mission will also study the origin and ultimate fate of our solar system’s asteroids, and finding the most suitable NEO targets for future exploration by robots and humans.
Proposals for NEOCam have been submitted a total of three times to the NASA Discovery Program – in 2006, 2010, and 2015, respectively. In 2010, NEOCam was selected to receive technology development funding to design and test new detectors optimized for asteroid and comet detection and discovery. However, the mission was ultimately overruled in favor of the Mars InSight Lander, which is scheduled for launch in 2016.
As one of the semifinalists for Discovery Mission 13, the NEOCam mission has received $3 million for year-long studies to lay out detailed mission plans and reduce risks. In September of 2016, one or two finalist will be selected to receive the program’s budget of $450 million (minus the cost of a launch vehicle and mission operations), and will launch in 2020 at the earliest.
In related news, NASA has confirmed that the asteroid known as 86666 (2000 FL10) will be passing Earth tomorrow. No need to worry, though. At its closest approach, the asteroid will still be at a distance of 892,577 km (554,000 mi) from Earth. Still, every passing rock underlines the need for knowing more about NEOs and where they might be headed one day!
Newly Released Security Cam Video Shows Chelyabinsk Meteorite Impact in Lake Chebarkul
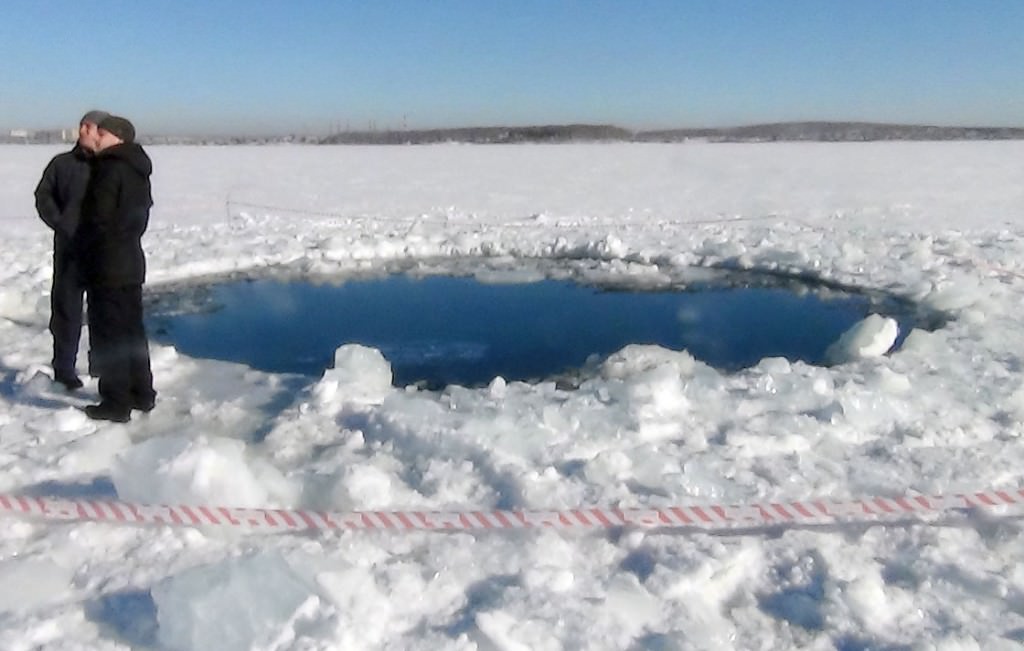

Security camera video showing the impact of the largest piece of the Chelyabinsk meteorite striking Lake Chebarkul during the Feb. 15, 2013 Russian fireball. Credit: Nikolaj Mel’nikov.
When I first watched this video of the half-ton Chelyabinsk meteorite crashing into Lake Chebarkul last Feb. 15 I didn’t see anything. But once you pay close attention, what you’ll see is nothing short of amazing. You’ll recall that a 20-foot (6 meter) hole appeared in the ice immediately after the fall. While no one witnessed the impact, a security camera caught the critical moment from the other side of the lake.
The video recently appeared in an online presentation by Peter Jenniskens, noted meteorite expert and senior research scientist at the SETI Institute. It was released as part of a paper and Powerpoint on the Chelyabinsk airburst. You can listen to Jenniskens’ presentation HERE.

When you watch the video, focus your attention just to the left of what looks like an ice fishing shack at top center and use the handy frame grab above. In the slowed-down portion of the footage you’ll see a cloud of ice and snow blow up and quickly drift to the right of the shack seconds after impact. While blurry and small, it’s amazing good fortune we have a document of this fall.
Video of the recovery of the largest piece of the Chelyabinsk meteorite
Divers ultimately fished the 1/2 ton Chelyabinsk meteorite – the largest found so far – from the lake on Oct. 16. It measured 5 feet long (1.5 meter) and broke into three pieces as scientists hoisted it into a scale to weigh it.
As a return favor, the little piece of heaven broke the scale.
Weekly Space Hangout, Feb. 15, 2013: Space Rocks Edition
We interrupt your regular Weekly Space Hangout with this extra special edition to cover to the two asteroid-related events: the Russian meteor explosion and the close pass of Asteroid 2012 DA14.
Joining us for the space round table:
Dr. Ian O’Neill, Dr. Pamela Gay, Dr. Thad Szabo, Dr. Nicole Gugliucci, Nancy Atkinson, and Scott Lewis
Host: Fraser Cain
We record the Weekly Space Hangout every Friday at 12 pm Pacific / 3 pm Eastern. You can watch us live on Google+, Cosmoquest or listen after as part of the Astronomy Cast podcast feed (audio only).

