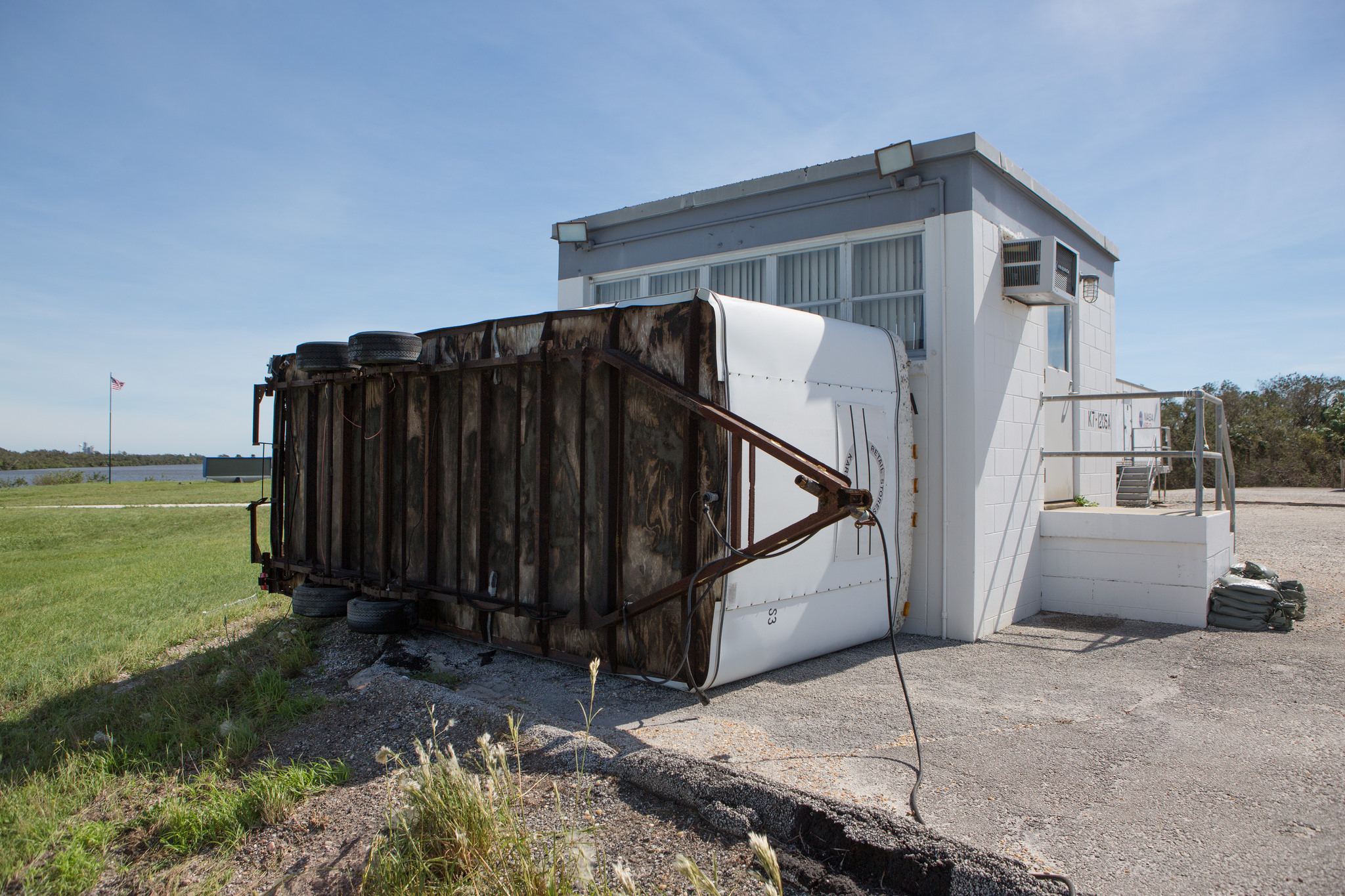
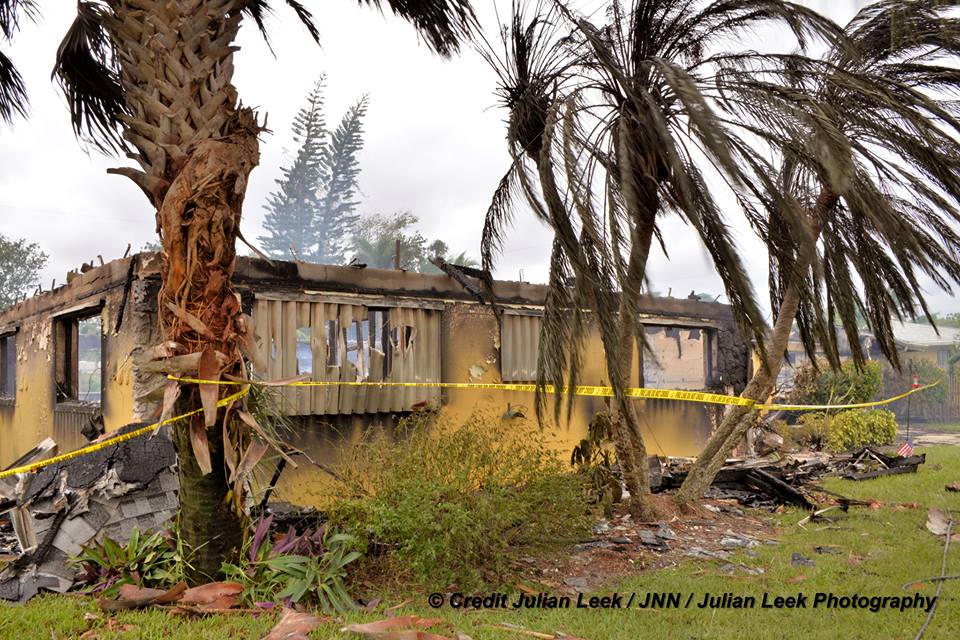
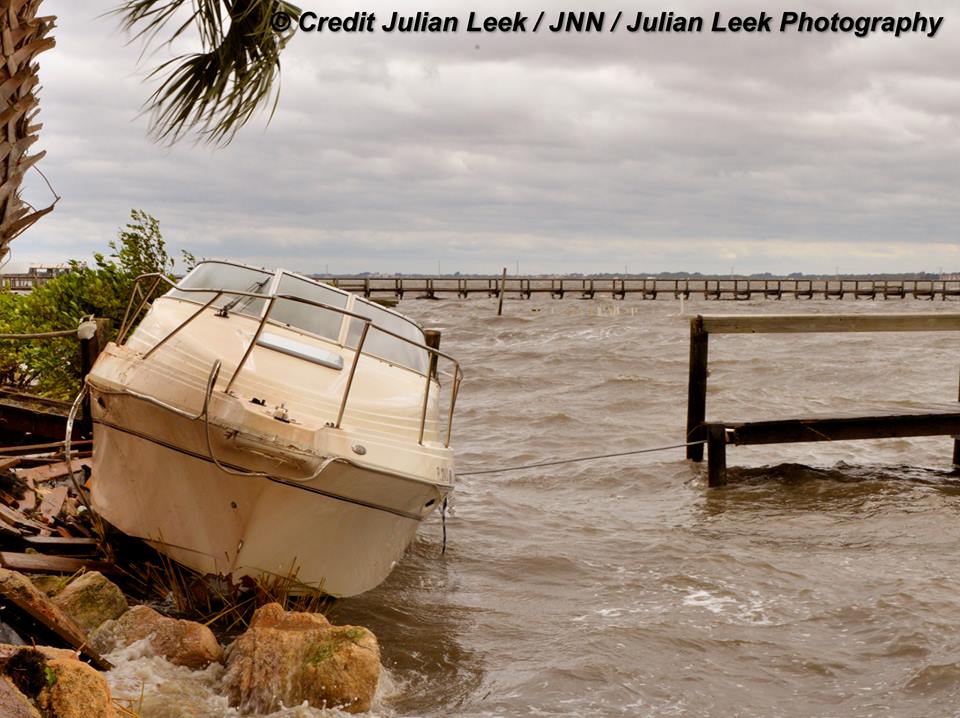
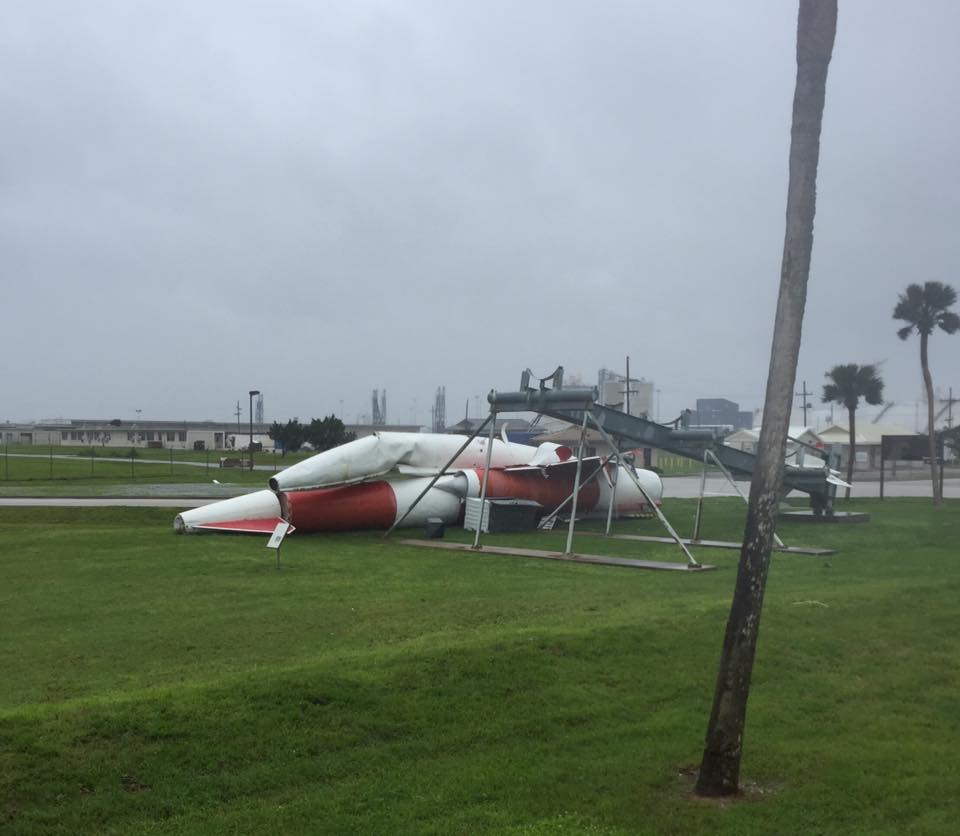
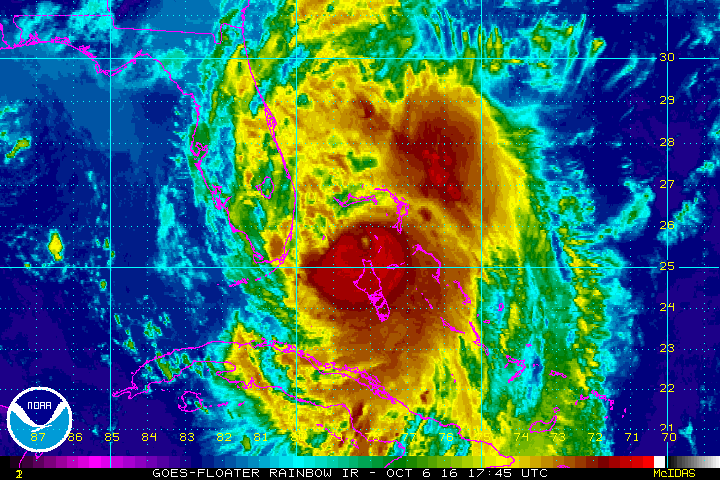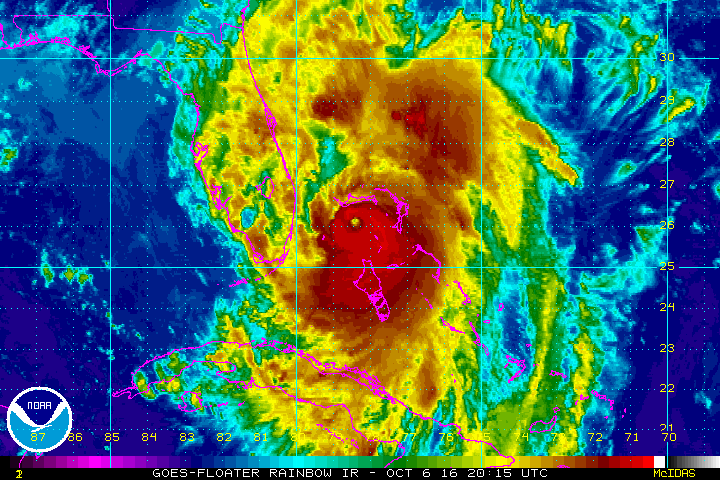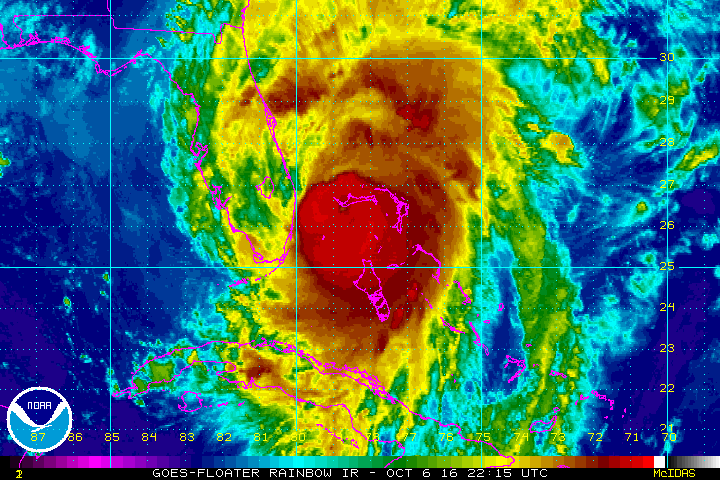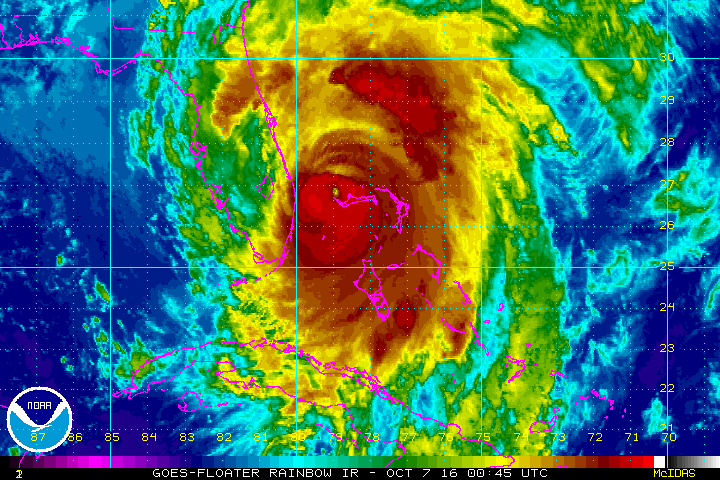
TITUSVILLE/CAPE CANAVERAL, FL – NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, the KSC Visitor Complex and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station have reopened as of today (Sept. 16) and yesterday, respectively, in the aftermath of Cat 1 hurricane force winds from Hurricane Irma that lashed the Florida Space Coast on Saturday, Sunday and Monday (Sept. 9/10/11) – forcing launch delays and leaving damaged and destroyed homes, buildings, infrastructure and launch viewing locations in its wake – see photos.
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station military forces partially reopened certain critical runways hours after Irma swept by the space coast to assist in emergency recovery operations.
“Kennedy Space Center will resume normal operations Saturday, Sept. 16,” NASA announced. “The “All Clear” has been given to reopen.”
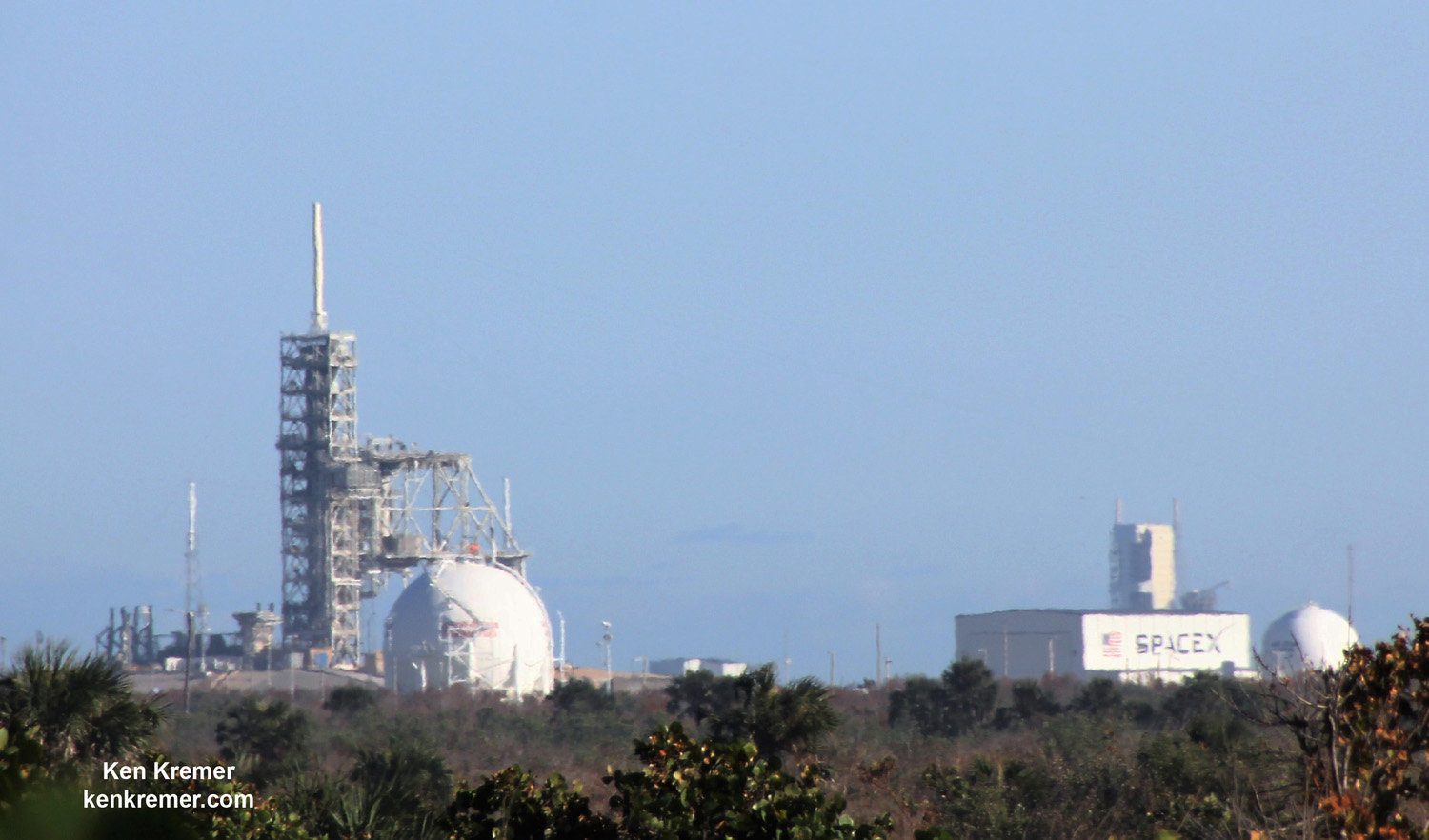
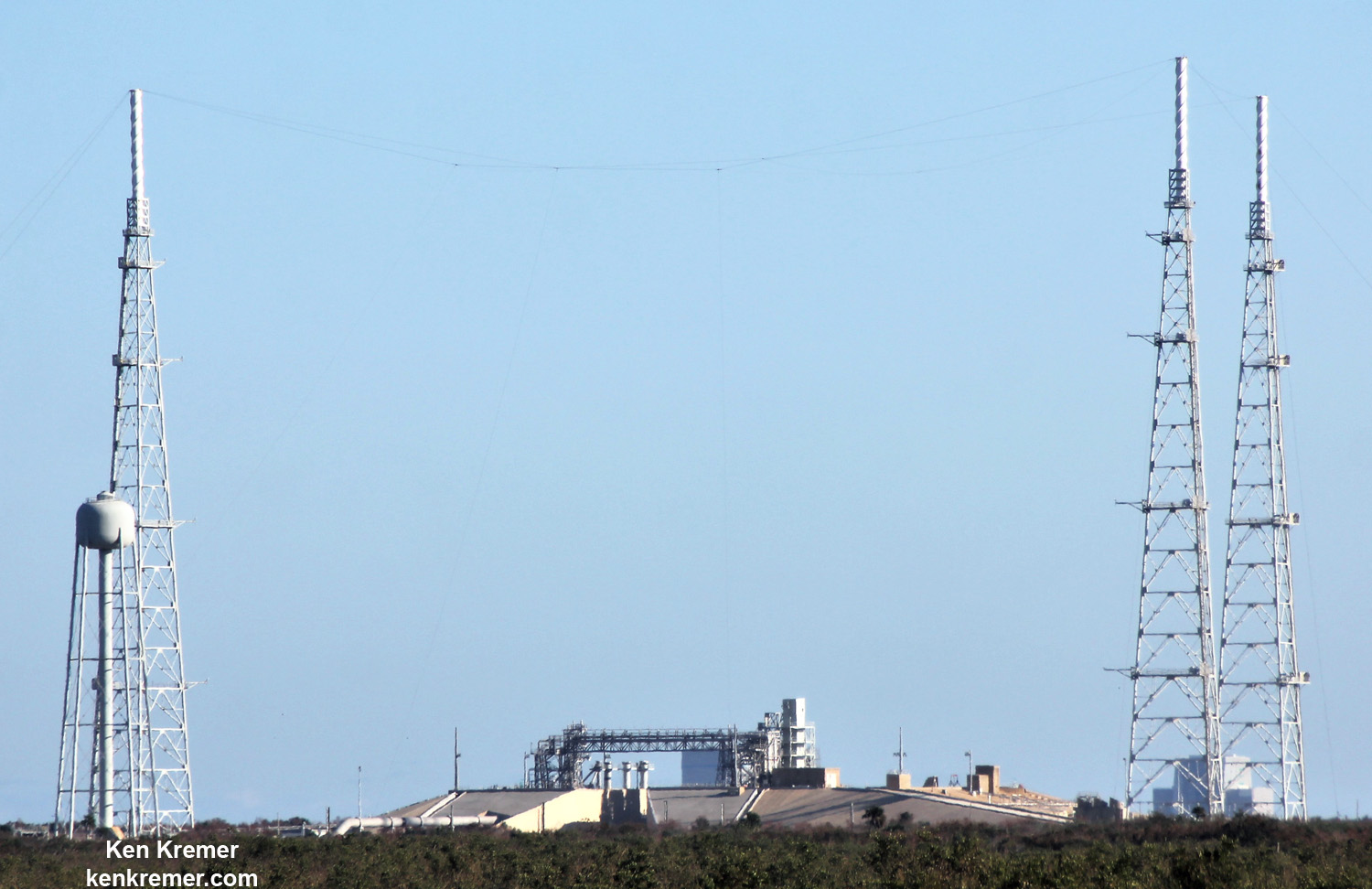
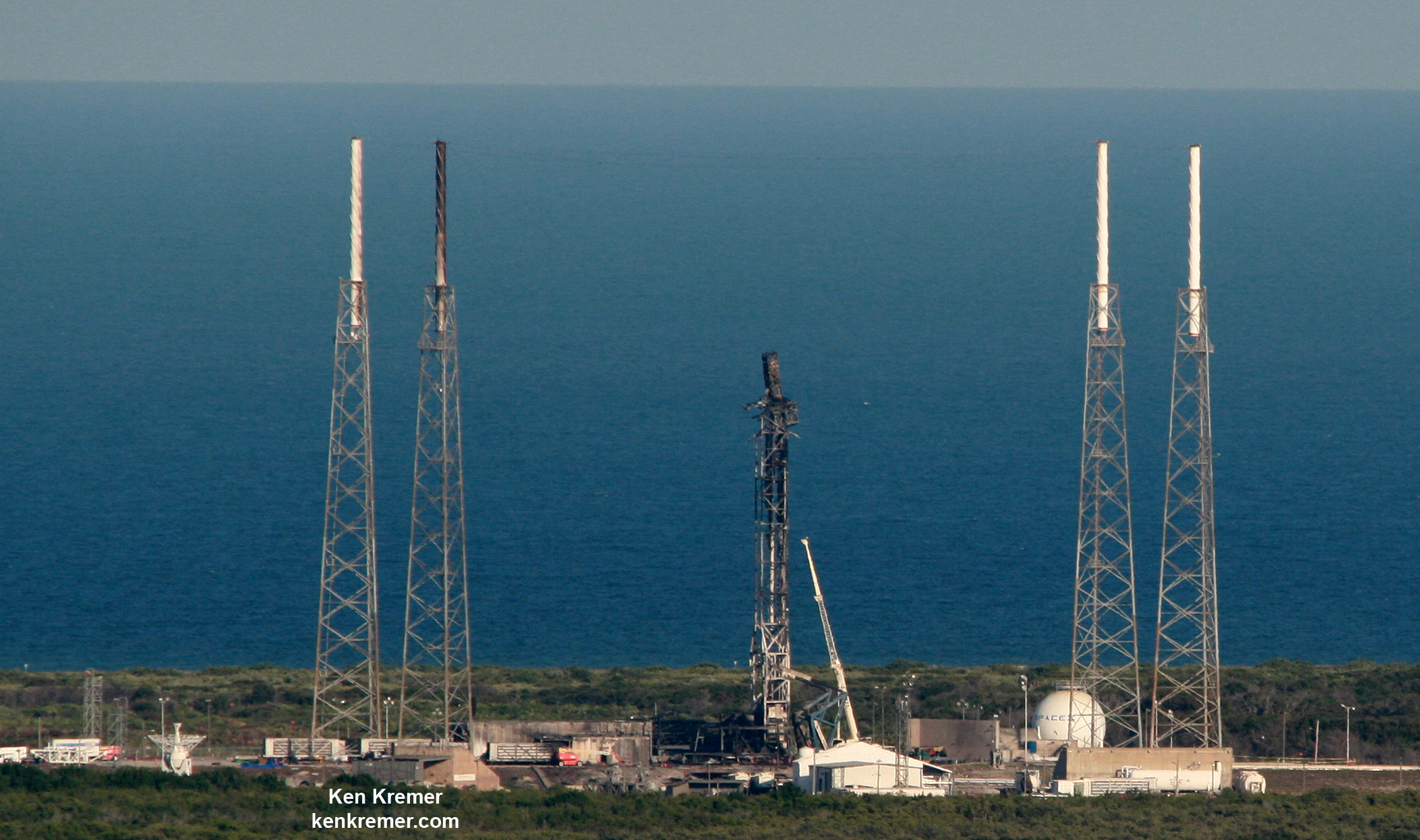
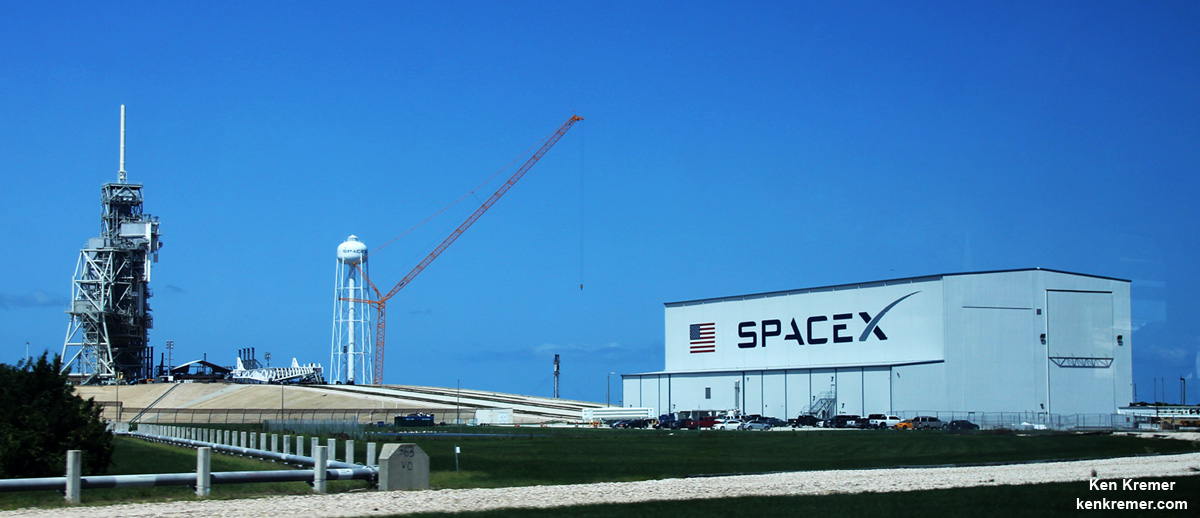
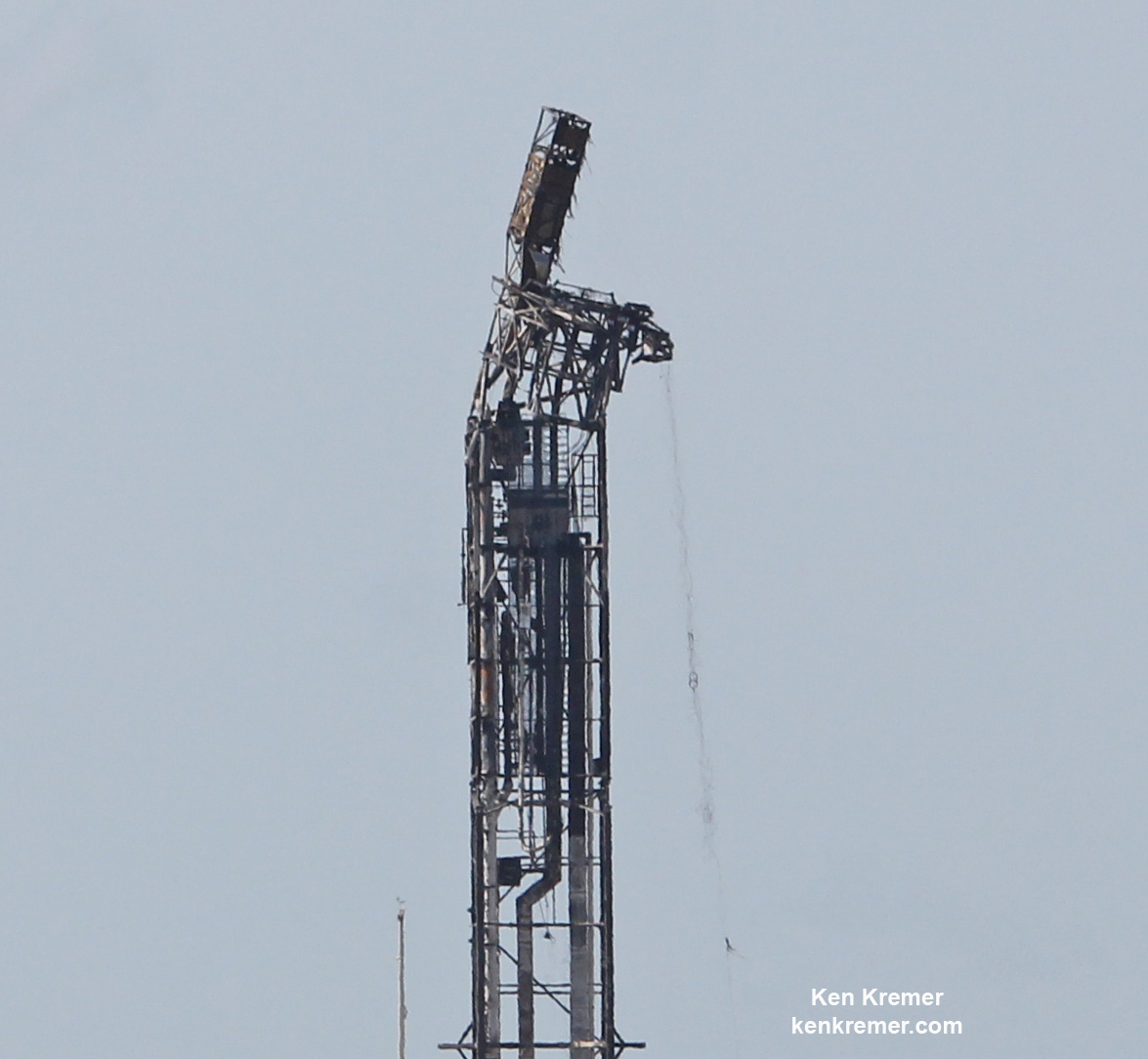
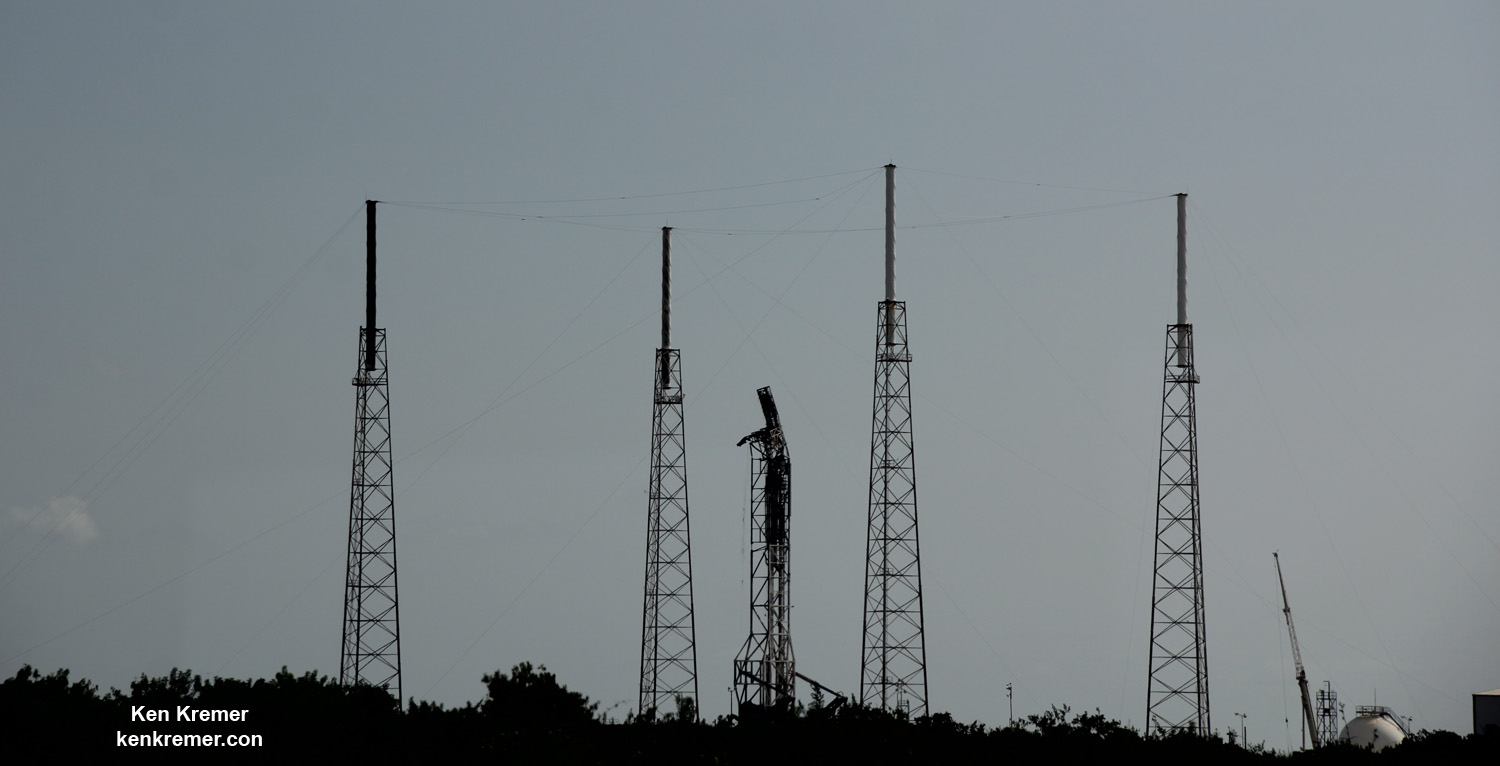
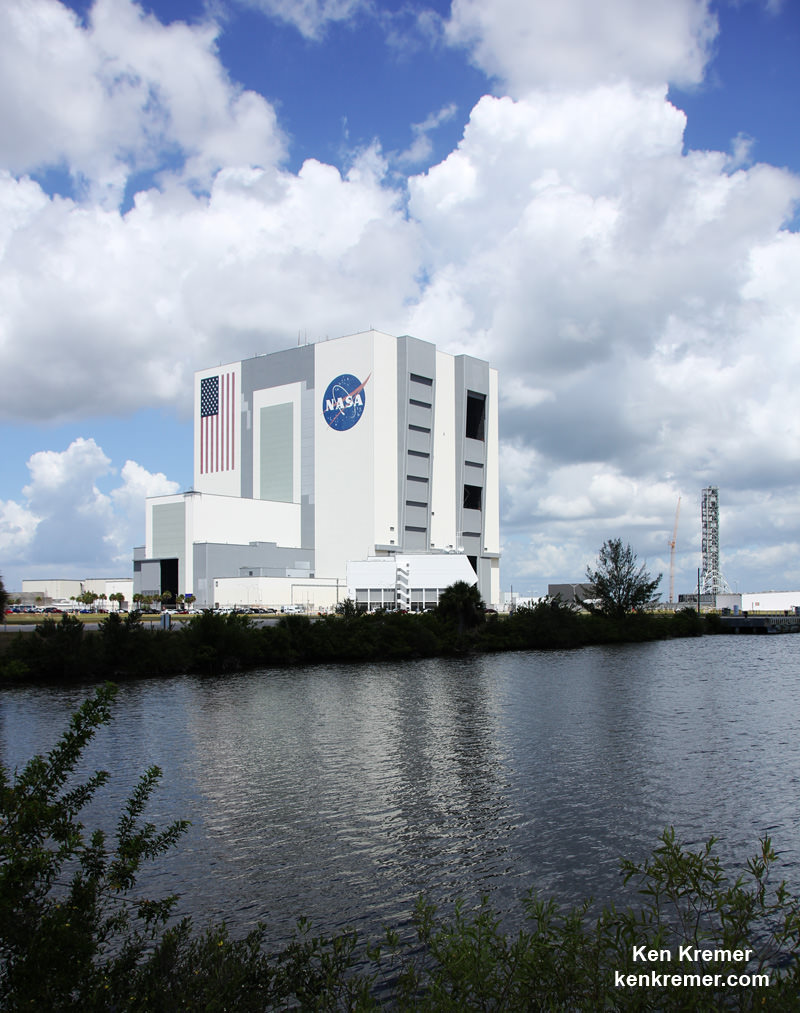
NASA’s world famous Vehicle Assembly Building and the Space Coast launch pads are still standing – as seen in photos from myself and more from NASA.
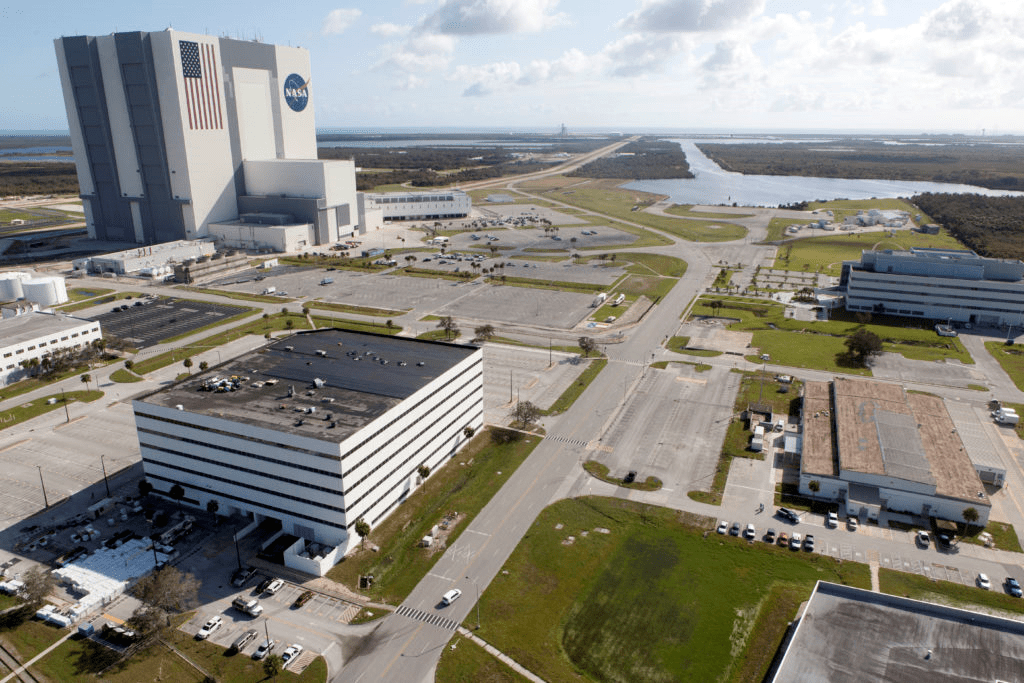

“As you’ve all seen by now, the Center will be open for normal operations at midnight tonight, and we’ll be ready to get back into the full swing of things Monday morning,” KSC Center Director Bob Cabana said in a message to employees.
Hurricane Irma knocked out water and power to KSC, the Cape, the visitor complex and the barrier islands including Merritt Island which is home to America’s premier Spaceport.
Wind speeds at KSC “varied from 67-94 mph (59-82 knots) at the 54-foot level to 90-116 mph (79-101 knots) at the 458-foot level during the storm.”
As a direct result of Irma, the next Space Coast launches of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V and SpaceX Falcon 9 has been postponed into October.
“The storm did delay the next launches,” said Brig. Gen. Wayne R. Monteith, Commander, 45th Space Wing, at a media briefing.
“We think the next launch will be approximately the first week of October.”
However although there was damage to a numerous buildings, both the spacecraft and rockets are safe and sound.
“The spacecraft we have on station right now are healthy and are being monitored.”
“The seven rocket boosters [Atlas, Falcon, Delta IV Heavy] we have on the Cape rode out the storm just fine,” Montieth elaborated.
The base and the visitor complex both lacked potable water service used for drinking, food preparation and cleaning.
Multiple water pipes in the nearby community of Cocoa were severed. KSC, the Cape and the Visitor Center as well as the surrounding community were under a boil water restriction for several days.
“Full water service is now available and the center has received an all clear following several days of closure related to Hurricane Irma,” noted KSC officials.

Indeed over 87% of customers lost power in Brevard County – home to the Florida Space Coast. Over 2/3 of customers lost power throughout Florida- impacting over 16 million people.
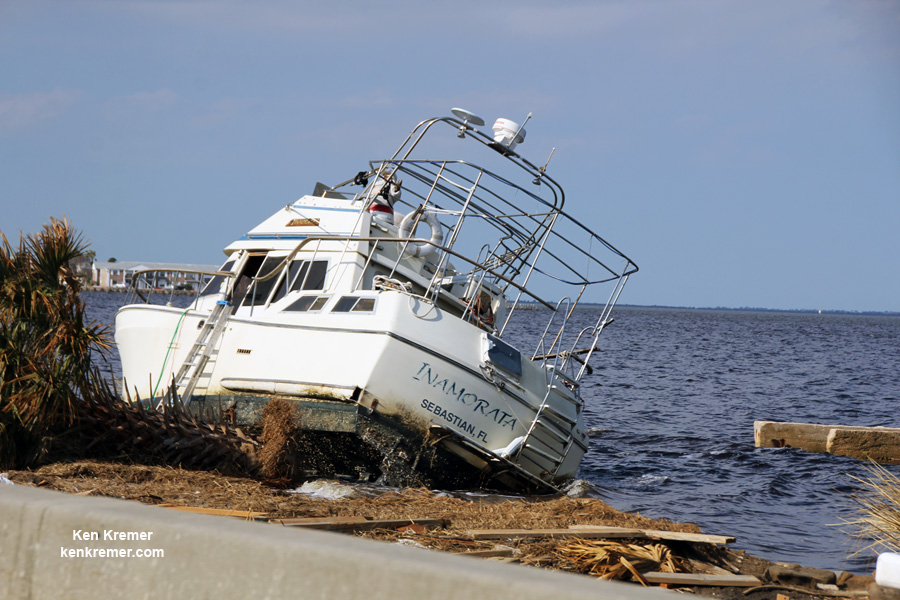
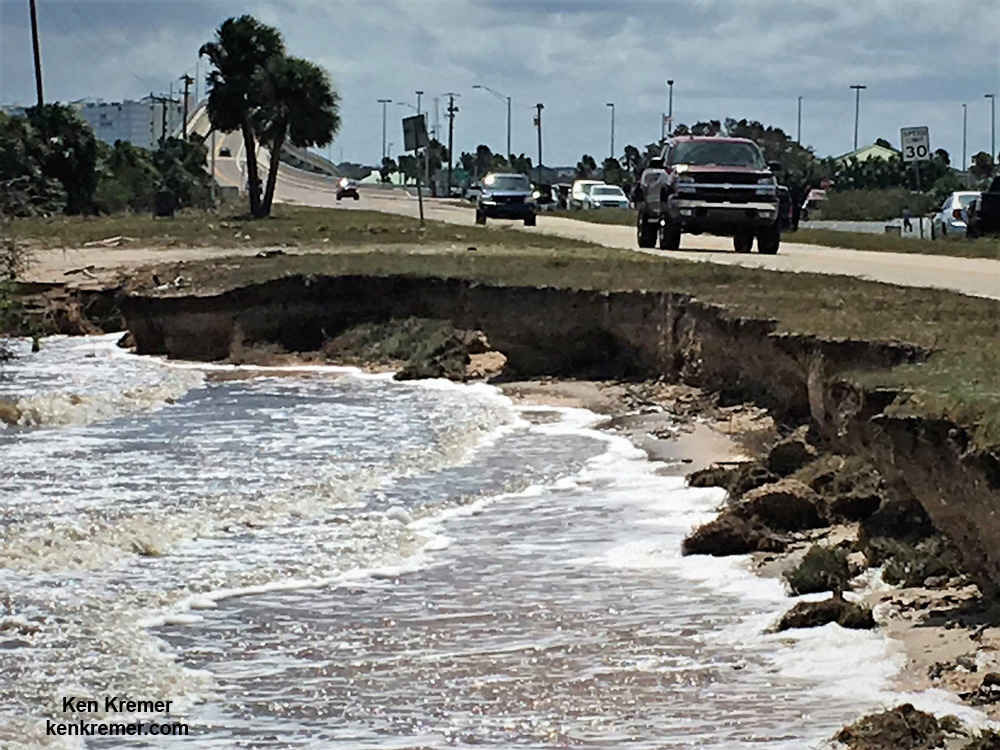
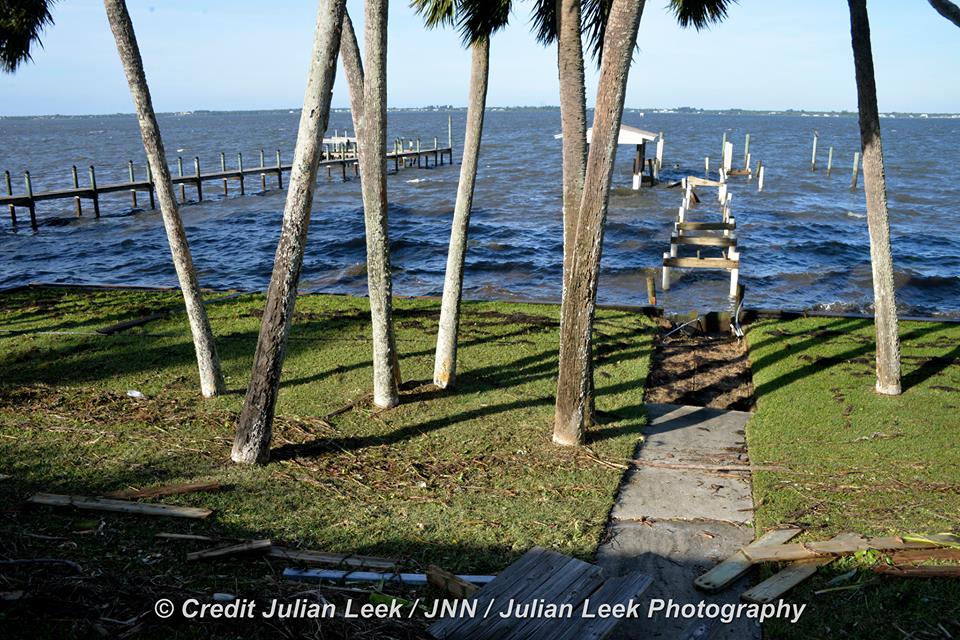
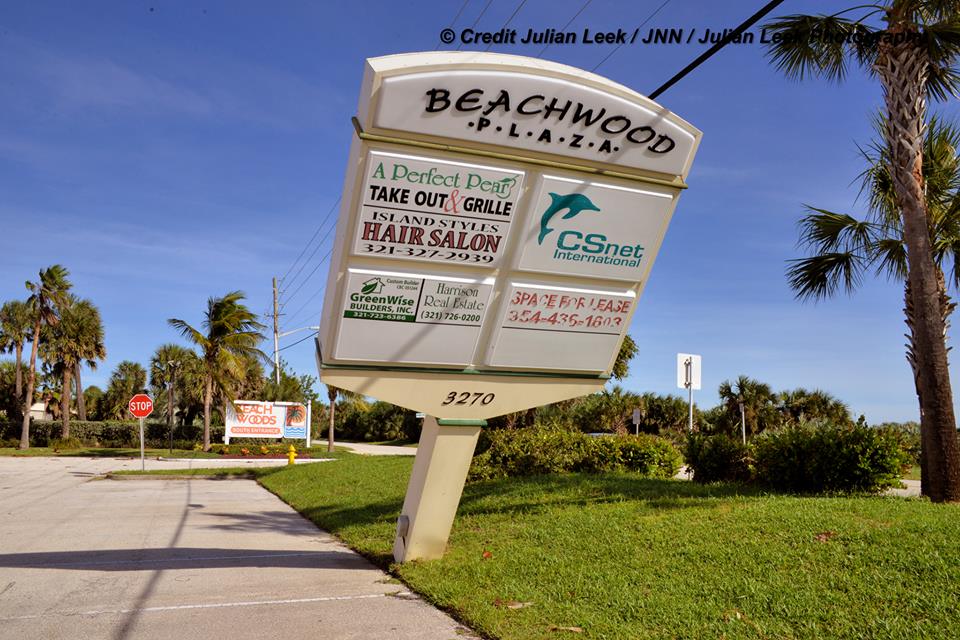
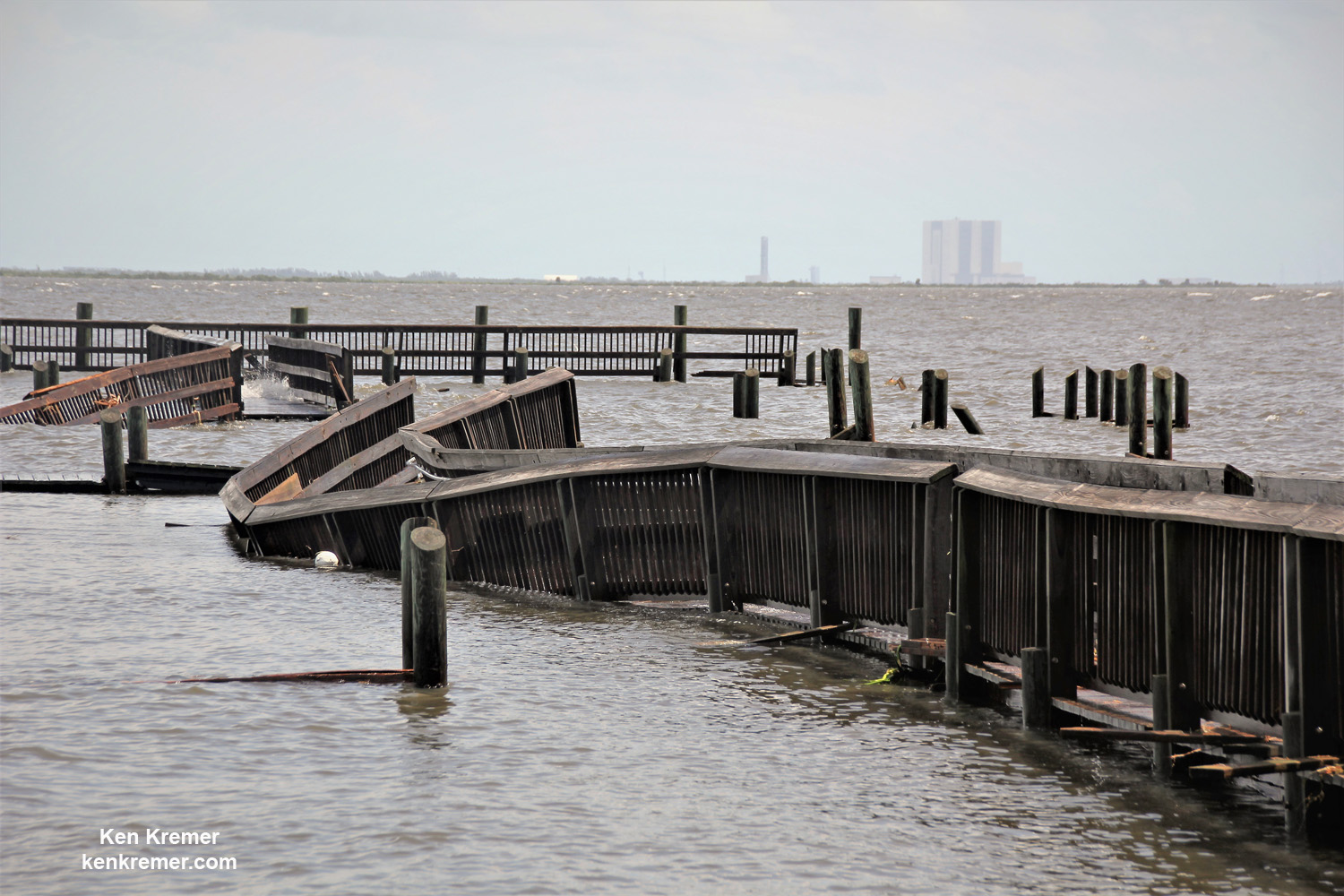
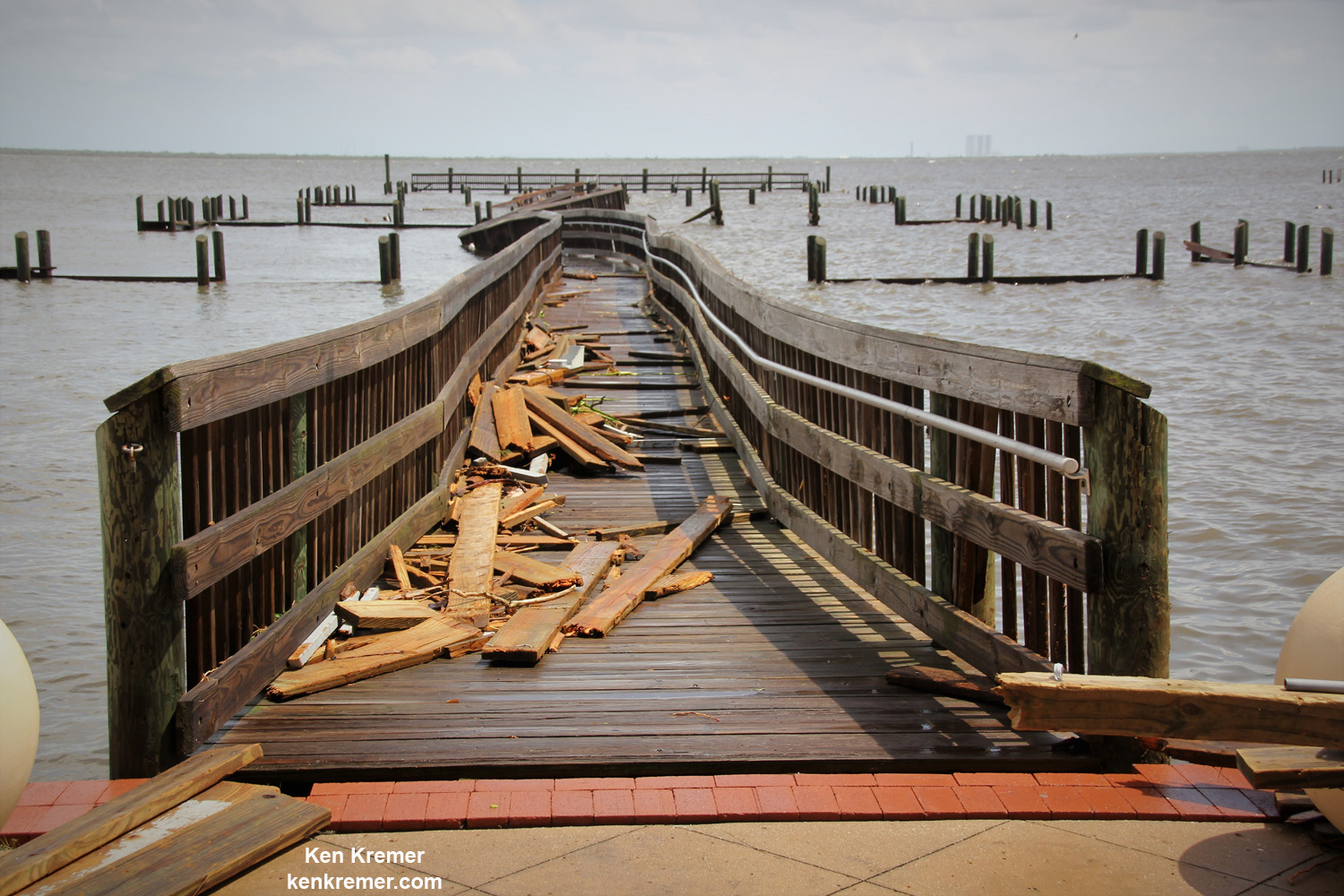
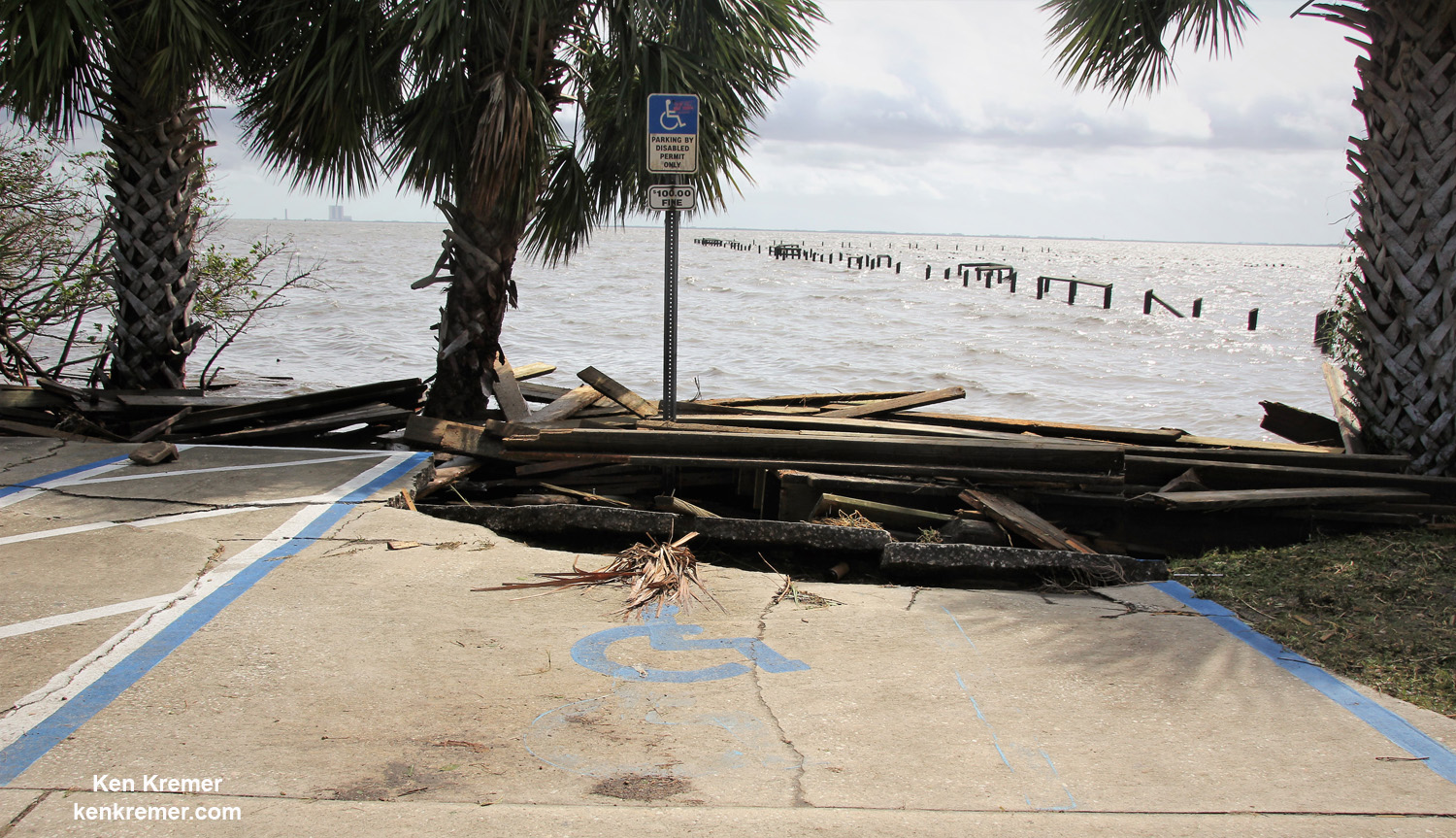
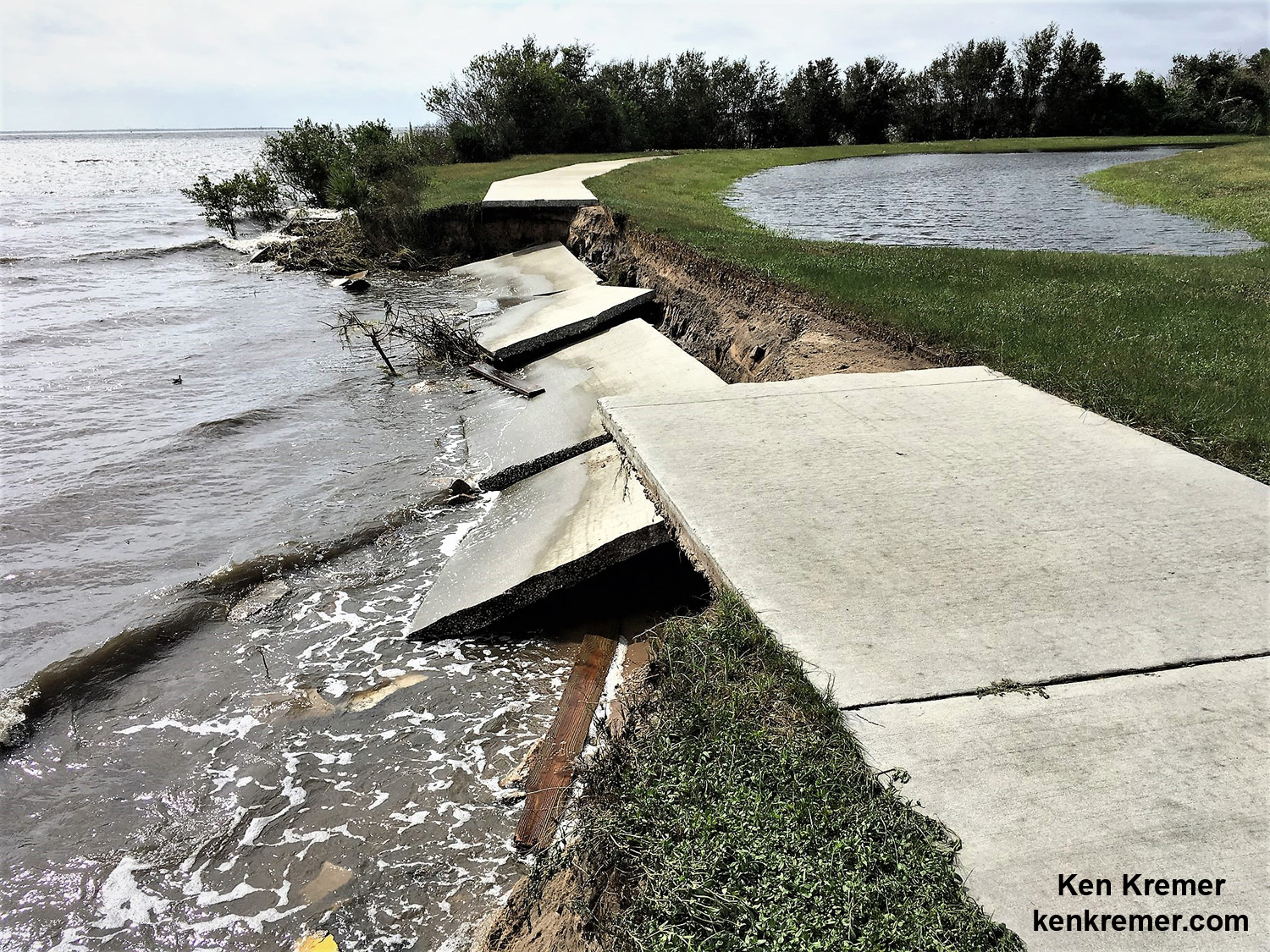
A number of popular public launch viewing locations were also severely damaged or destroyed as I witnessed personally driving in Titusville around just hours after Irma fled north.
See my photos from Rotary River Front Park, Space View Park and others along Rt. 1 in Titusville – which had offered unimpeded, spectacular and beautiful views across the Indian Rover lagoon to the KSC and Cape Canaveral launch pads.

Piers, docks, walkways, parking areas, piping and more were ripped up, smashed, sunken and devastated with piles of metal, bricks, wood, trees, bushes, trash and more scattered about in sad and unrecognizable heaps.

From a distance of several miles, the iconic VAB and the launch pads themselves did not seem to suffer obvious destruction – see my photos herein.
As of today over 500,000 customers across Florida remain without power, including tens of thousands in central Florida.
Numerous traffic lights in Titusville, Cape Canaveral, Cocoa Beach and Melbourne and other Brevard County and central Florida cities and communities are still not functioning today – creating all sorts of road traffic hazards!

Damage assessment teams from NASA, ULA, SpaceX, the USAF and contractors are now carefully scrutinizing every aspect of the Space Coast launch pads and facilities to ensure successful liftoffs whenever they resume in a few weeks.
Virtually all traffic lights were not operating and businesses and gas stations were closed in the hours before and after Irma pummeled communities across the space coast and central Florida. There were very long lines at the first gas stations that did reopen on Monday and Tuesday.

KSC was closed and evacuated of all personnel during the storm, except for only a small ‘Ride-out’ team of roughly 130 or so KSC personnel based inside the Emergency Operations Center (EOC) inside the Launch Control Center. They remained on site to monitor spaceport facilities.
“I want to take this opportunity to thank—and commend—the Ride-out and Damage Assessment and Recovery Teams for the outstanding job they did watching over the Center in our absence and getting it ready for our return in the aftermath of Hurricane Irma,” Cabana added. “I also want to thank all of you for the outstanding job that you did in getting the Center ready for the hurricane. As a result of your efforts, the Center was well prepared for the storm.”
The Damage Assessment and Recovery Teams explained that “the industrial and Launch Complex 39 areas have been inspected and are safe for personnel to return to work. This includes the KSC Child Development Center and all administrative work areas.”

“All facility systems including communication, power, and air conditioning are functional.”
Montieth confirmed damage to many buildings.
“In an initial assessment of the Cape facilities, about 40 % of buildings we inspected so far have received some damage. So 107 of 216 buildings at the Cape inspected have already been identified with damage.

“Lots of roof and siding damage, Montieth explained on Sept. 13. “We haven’t inspected the beaches yet.
“We have water issues at the Cape. We need water for the chillers to cool the operational buildings.”
Luckily the damage from Irma was less than feared.
“Under Hurricane Matthew there was about $50 million worth of damage between us and our launch partners. We think it will be less this time for Irma but we have a lot more work to do,” noted Montieth.
“The storm wasn’t as bad as expected. You hope for the best and prepare for the worst and that’s what we did. We had a ride-out team on base in a secure facility. Irma traveling over land helped us out. But we still got hit here by over 90 MPH winds gusts and over 58 mph winds – which are hurricane category 1 winds.”
“We also got hit by what we believe are 3 probable small tornadoes that hit the base. That claim is up to the NWS.”
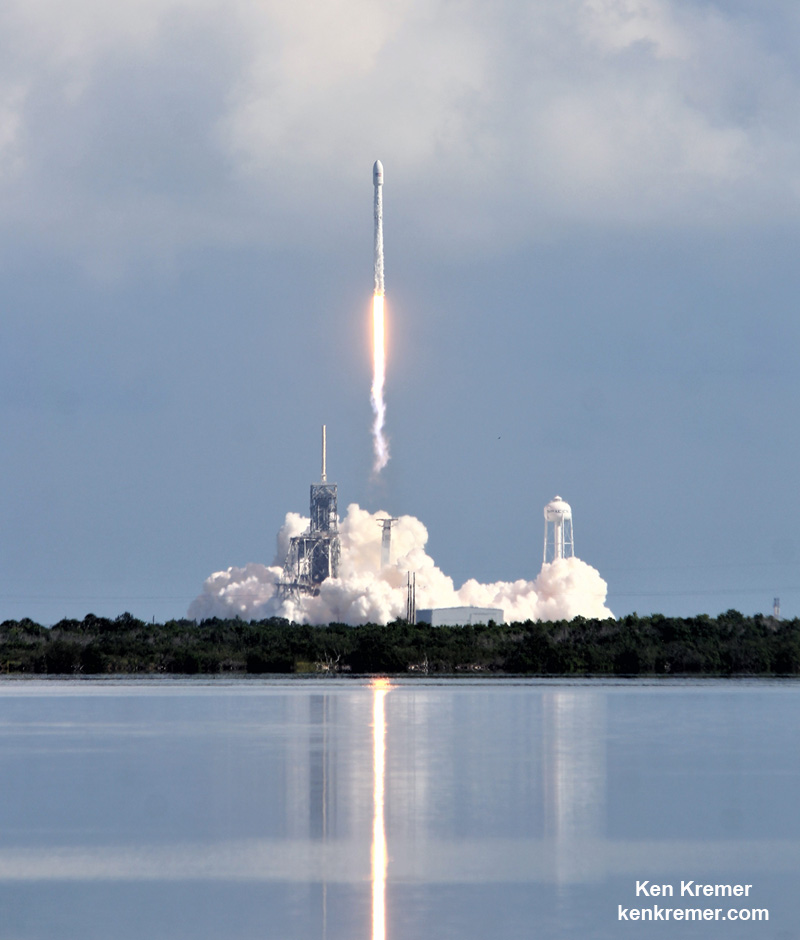
He noted that the X-37B was launched successfully last Friday by SpaceX and that ongoing hurricane preparations and evacuations went to full swing right afterward the morning blastoff.

Watch for Ken’s continuing onsite X-37B OTV-5 and NASA mission reports direct from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.